tensorflow 笔记 16:tf.pad
函数:
tf.compat.v1.padtf.pad
函数表达式如下:
tf.pad(
tensor,
paddings,
mode='CONSTANT',
name=None,
constant_values=0
)
函数用途:对各个维度进行填充,padding
输入:
- tensor :是要填充的张量; shape 维度为 : (N1,N2,N3,...);
- padings:填充方式,也是一个张量,shape : (n,2), n :表示需要的pad的tensor的维度个数;
- mode:有三种取值:分别是"CONSTANT" ,"REFLECT", "SYMMETRIC",对padding 的维度也有限制,如下padded;
- mode="CONSTANT" 是直接填充 constant_values;
- mode = "REFLECT" 是轴对称填充(对称轴为边界列),此时constant_values 无效,用tensor 中的值填充;
- mode = "SYMMETRIC" 是轴对称填充(对称轴为边界线),此时 constant_values 无效,用tensor 中的值填充;
- constant_values:要填充的 value 值,默认为0;
padding shape举个例子:
要求:pad 维度为(n,2) n:为tensor 的维度个数;
第一组:
input tensor,shape【3,4,5】三维 tensor
padding shape:【3,2】
第二组:
input tensor,shape【3,4,5,6】四维 tensor
padding shape:【4,2】
padding 的每一维度,都有两个数,第一个表示前面添加几维度,第二个表示 后面添加几维度;
padded 填充之后的每一维度:
The padded size of each dimension D of the output is:
paddings[D, 0] + tensor.dim_size(D) + paddings[D, 1]
if mode == "REFLECT" or mode == "SYMMETRIC":
paddings[D, 0] + paddings[D, 1] <= tensor.dim_size(D) - 1
举个例子-》填充后的tensor shape:
tensor shape : (3,5,4)
padding = [[1,1],[2,2],[1,0]]
padded shape: (3+1+1,5+2+2,4+1+0)= (5,9,5)
REFLECT:的填充方式使用的是一种通过对称轴进行对称复制的方式进行填充(复制时不包括对称轴,边界的那一列是对称轴),通过使用tensor边缘作为对称;
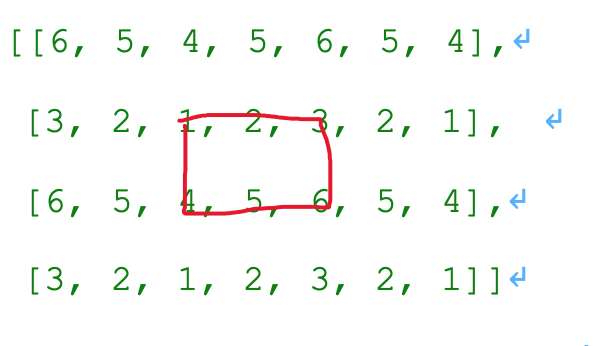
SYMMETRIC:的填充方式于REFLECT填充方式类似,也是按照对称轴就是复制的,只是它包括对称轴(边界外的线是对称轴)。

举例一:(来自官方):
t = tf.constant([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]) #shape(2,3)
paddings = tf.constant([[1, 1,], [2, 2]]) # shape(2,2),第一维度,前面补一维度,后面补一维度;第二维度,前面补两维度,后面补两维度;
# 'constant_values' is 0.
# rank of 't' is 2.
tf.pad(t, paddings, "CONSTANT") # [[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
# [0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 0],
# [0, 0, 4, 5, 6, 0, 0],
# [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]] tf.pad(t, paddings, "REFLECT") # [[6, 5, 4, 5, 6, 5, 4],
# [3, 2, 1, 2, 3, 2, 1], # 黄色为对称轴
# [6, 5, 4, 5, 6, 5, 4],
# [3, 2, 1, 2, 3, 2, 1]] tf.pad(t, paddings, "SYMMETRIC") # [[2, 1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 2],
# [2, 1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 2], #
# [5, 4, 4, 5, 6, 6, 5],
# [5, 4, 4, 5, 6, 6, 5]]
举例二:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np m1 = tf.random_normal([1,2,3,4],mean=0.0,stddev=1.0,dtype=tf.float32) m2 = tf.pad(m1,[[2,0],[0,0],[0,0],[0,0]],constant_values = 1) m2_s = tf.shape(m2) # shape(3,2,3,4) with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run(m1))
print(sess.run(m2))
print(sess.run(m2_s))
output:
# m1
[[[[-1.8582115 -1.170714 -0.4478178 2.0172668 ]
[-0.74805504 -0.08016825 -0.7742696 -0.02516617]
[-0.8256318 0.591446 -0.00889379 1.7998788 ]] [[ 0.00565176 -0.31549874 1.5197186 0.07842494]
[ 0.00609808 1.9219669 -0.42632174 1.5106113 ]
[ 0.67241013 -0.38563538 -0.976289 0.2032768 ]]]] #m2
[[[[ 1. 1. 1. 1. ]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. ]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. ]] [[ 1. 1. 1. 1. ]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. ]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. ]]] [[[ 1. 1. 1. 1. ]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. ]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. ]] [[ 1. 1. 1. 1. ]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. ]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. ]]] [[[-1.2366703 -1.0050759 -0.3843815 1.0201392 ]
[-1.3438475 0.8829414 -1.3399163 1.078826 ]
[-0.09356844 0.35896888 1.5112561 0.28352356]] [[ 0.45909956 -0.23824279 -0.31440428 1.1913226 ]
[-0.40780786 0.58995795 -0.9147027 0.05860058]
[-0.0659609 1.4536899 -0.12121342 -0.9752257 ]]]] #output shape
[3 2 3 4]
最新文章
- .NET 基础 一步步 一幕幕 [.NET 系列预热]
- python--爬虫入门(八)体验HTMLParser解析网页,网页抓取解析整合练习
- IPC机制--Binder
- 洛谷 P1209 修理牛棚== Codevs 2079 修理牛棚
- PC远程调试设备(转)
- Unity LayerMask
- ActiveMq主从机制
- IntelliJ IDEA安装scala插件并创建scala示例
- tomcat关闭时Log4j2报错 Log4j Log4j2-TF-4-Scheduled-1 memory leak
- Flask 学习目录
- HTML head标签内部常用设置
- MySQL中interactive_timeout和wait_timeout的区别【转】
- ( linker command failed with exit code 1) 错误解决方案 项目使用的是pod
- wechat-注意事项
- 区别JS中类的静态方法,静态变量,实例方法,实例变量
- 浅谈JavaScript预编译原理
- .net core webapi 使用过滤器。
- SSM项目引入文件失败
- HDU 6148 Valley Numer (数位DP)
- mac下安装ionic