webbench源码学习笔记
学习内容
一共五百多行代码,其中包含了linux编程常用的API。可以通过学习源码,把不熟悉的API练习练习。
1 如何使用webbench
(1)查看参数帮助

(2)运行方法
即以上模拟30个客户端在30秒期间并发请求百度,结果如下:
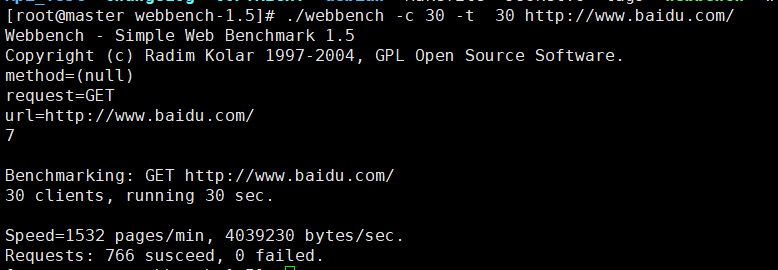
每分钟平均有1532次请求连接,服务器每秒传输字节为4039230,在30秒期间请求连接成功为766次,失败0次。
2 源码常用函数练习
(1) 选项参数
int getopt_long(int argc, char * const argv[],const char *optstring, const struct option *longopts,int *longindex);
函数中的argc和argv通常直接从main()的两个参数传递而来。optsting是选项参数组成的字符串:
option结构数组,option结构称为长选项表,其声明如下:
struct option
{
const char *name;
int has_arg;
int *flag;
int val;
};
结构中的元素解释如下:
const char *name:选项名,前面没有短横线。譬如"help"、"verbose"之类。
int has_arg:描述长选项是否有选项参数,如果有,是哪种类型的参数,其值见下表: 符号常量 数值
含义
no_argument 0 选项没有参数
required_argument 1 选项需要参数
optional_argument 2 选项参数是可选的
int *flag:
如果该指针为NULL,那么getopt_long返回val字段的值;
如果该指针不为NULL,那么会使得它所指向的结构填入val字段的值,同时getopt_long返回0 int val:
如果flag是NULL,那么val通常是个字符常量,如果短选项和长选项一致,那么该字符就应该与optstring中
字符串optstring可以下列元素:
1.单个字符,表示选项,
2.单个字符后接一个冒号:表示该选项后必须跟一个参数。参数紧跟在选项后或者以空格隔开。该参数的指针赋给optarg。
3 单个字符后跟两个冒号,表示该选项后可以有参数也可以没有参数。如果有参数,参数必须紧跟在选项后不能以空格隔开。该参数的指针赋给optarg。(这个特性是GNU的扩张)。
optstring是一个字符串,表示可以接受的参数。例如,"a:b:cd",表示可以接受的参数是a,b,c,d,其中,a和b参数后面跟有更多的参数值。(例如:-a host --b name)
最后一个参数:longindex参数一般赋为NULL即可;如果没有设置为NULL,那么它就指向一个变量,这个变量会被赋值为寻找到的长选项在longopts中的索引值,这可以用于错误诊断。
函数使用方法:
1 #include <getopt.h>
2
3 #include <stdio.h>
4
5 #include <stdlib.h>
6
7
8
9 static const char *program =NULL;
10
11
12
13 static const struct option long_opts[] = {
14
15 {"help", no_argument, NULL, 'h'},
16
17 {"version", no_argument, NULL, 'v'},
18
19 {"author", required_argument, NULL, 'a'},
20
21 {"date", no_argument, NULL, 'd'},
22
23 {"time", no_argument, NULL, 't'},
24
25 {0, 0, 0}
26
27 };
28
29 void usage()
30
31 {
32
33 printf("argument: \n");
34
35 printf("\t --version,-v \n"
36
37 "\t --author, -a\n"
38
39 "\t --date, -d\n"
40
41 "\t --time, -t\n"
42
43 "\t --help, -h\n"
44
45 );
46
47 }
48
49
50
51 int main(int argc,char* argv[])
52
53 {
54
55 char *str;
56
57 int long_index,c,ret;
58
59 program = argv[0];
60
61 while((c=getopt_long(argc, argv, "hva:dt", long_opts, &long_index))!=EOF){
62
63 switch(c){
64
65 case 'h':
66
67 usage();
68
69 exit(0);
70
71 case 'v':
72
73 printf("version 1.2.0\n");
74
75 break;
76
77 case 'a':
78
79 str=optarg;
80
81 printf("author is %s\n",str);
82
83 break;
84
85 case 'd':
86
87 printf("date is 2016.10.20\n");
88
89 break;
90
91 case 't':
92
93 printf("time is 12:30:45\n");
94
95 break;
96
97 default:
98
99 printf("ERR: please try: %s -h\n", program);
100
101 exit(0);
102
103 }
104
105 }
106
107 return 0;
108
109 }
(2)字符串相关API strlen()//字符串长度 bzero()//清空 strstr()//子串查找 strncpy()//复制 strcat()//拼接 1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <string.h>
3 #include <errno.h>
4
5 int main(void)
6 {
7 char string[20];
8 char *str1="nihao";
9 strncpy(string,str1,3);
10 string[3]='\0';//字符串末尾0
11 printf("%s\n",string);
12 //strcat(str1,str2)
13 char destnination[25];
14 char *blank="",*c="python",*borland="boland";
15 strcpy(destnination,borland);
16 strcat(destnination,blank);
17 strcat(destnination,c);
18 printf("%s\n",destnination);
19
20 //strncat(str1,str2,n)
21 char url[100]="http://www.baidu.com";
22 char path[20]="/cpp/string";
23 strncat(url,path,100);//100超过了path的长度
24 printf("%s\n",url);
25
26
27 //strlen(str)
28 char str[5]="abcd";
29 printf("strlen(str)=%d,sizeof(str)=%d",strlen(str),sizeof(str));//4 5
30
31 //strcmp 相等饭回0 str1大于str2 饭回正数
32 char *a="aBcDeE";
33 char *b="AbCdEf";
34 printf("strcmp(a,b):%d\n",strcmp(a,b));
35
36
37 //strchr(str,c) 在str字符串中查找首次出现字符c的位置
38 char *s3="";
39 char *p5;
40 p5=strchr(s3,'');
41
42 printf("%ld\n",s3);
43
44 //strpbrk(str1,str2) 依次检验字符串str1的字符 当被检验字符在字符串str2中也包含的时候则停止检验 返回这个字符的位置
45 char *s1="see you again";
46 char *s2 = "you";
47 char *p=strpbrk(s1,s2);
48 if(p)
49 {
50 printf("the result is:%s\n",p);
51 }else
52 {
53 printf("sorry\n");
54 }
55
56 //atoi(str) 字符串转换为int整数
57 //strstr 检索子串在字符串首次出现的位置
58 char *str5="hellodfdflhellop";
59 char *substr="hello";
60 char *s=strstr(str5,substr);
61 printf("%s\n",s);
62
63 //strerror 返回指向错误信息字符串的指针
64 char *buffer2=NULL;
65 buffer2=strerror(errno);
66 printf("Error:%s\n",buffer2);
67
68 //bzero(void *s,int n)
69 struct
70 {
71 int a;
72 char s[5];
73 float f;
74 }tt;
75 char ss[20];
76 bzero(&tt,sizeof(tt));
77 bzero(ss,20);//等价于memset(s,0,20)
78 return 0;
79
80
81
82
83 }
(3)信号相关API
案例https://www.cnblogs.com/yxk529188712/p/4983565.html
(4)IO相关
fwrite()
fread()
read()
(5)管道
int pipe(int fd[2]) 成功返回0,失败返回-1
管道和有名管道是进程间通信机制之一
管道是半双工,所以双方通信需要建立两个通道
FILE * fdopen(int fildes,const char * mode);
fdopen取一个现存的文件描述符(我 们可能从 o p e n , d u p , d u p 2 , f c n t l或p i p e函数得到此文件描述符) ,并使一个标准的I / O流与该描述符相结合。此函数常用于由创建管道和网络通信通道函数获得的描述符。因为这些特殊类型的文件不能用标准I/O fopen函数打开,首先必须先调用设备专用函数以获得一个文件描述符,然后用f d o p e n使一个标准I / O流与该描述符相结合。
fdopen()会将参数fildes 的文件描述符,转换为对应的文件指针后返回。参数mode 字符串 则代表着文件指针的流形态,此形态必须和原先文件描述词读写模式相同。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
char buf[];
int fds[],fds2[]; //fds[0]用于读 fds[1]用于写
pipe(fds);
pipe(fds2);
if(fork()>)//父亲进程
{
close(fds[]);//读的时候应先关闭写
close(fds2[]); //写的时候先关闭读
while(memset(buf,,),read(fds[],buf,)>)//从管道读
{
write(,buf,strlen(buf)); //read是一个阻塞函数,会一直停在这里
}
close(fds[]); //要使用close关闭管道 管道也会堵塞 printf("father speaking:\n");
FILE *fs=fdopen(fds2[],"w");//管道与文件指针建立连接 可以不实用文件指针直接对管道操作
if(fs==NULL) //while(memset(buf,0,1024),read(0,buf,1024)>0)
{ //{ write(fds[1],buf,strlen(buf));}
perror("father died!\n");
}
while(memset(buf,,),fgets(buf,,stdin)!=NULL)//输入buf中
{
fprintf(fs,"father message:%s",buf);//写入文件
fflush(fs);
}
close(fds2[]);
wait(NULL);
}
else
{
close(fds[]);
close(fds2[]);//关闭写
FILE *fd=fdopen(fds[],"w");//管道当作一个文件
if(fd==NULL)
{
perror("fdopen wrong\n");
}
while(memset(buf,,),fgets(buf,,stdin)!=NULL)
{
fprintf(fd,"child message:%s",buf);
fflush(fd);
}
close(fds[]); while(memset(buf,,),read(fds2[],buf,)>)
{
write(,buf,strlen(buf));
}
close(fds2[]);
exit();
}
return ;
}
2 执行流程
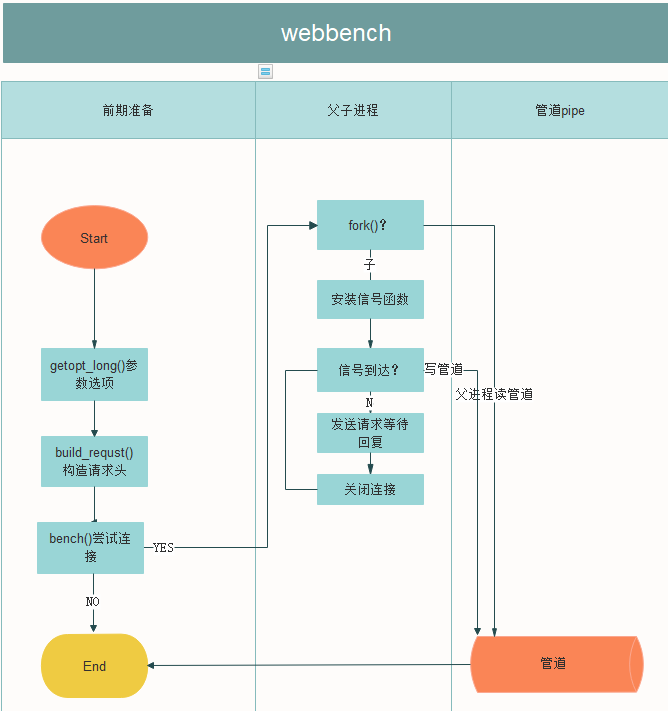
3 源码注释
/*
* (C) Radim Kolar 1997-2004
* This is free software, see GNU Public License version 2 for
* details.
*
* Simple forking WWW Server benchmark:
*
* Usage:
* webbench --help
*
* Return codes:
* 0 - sucess
* 1 - benchmark failed (server is not on-line)
* 2 - bad param
* 3 - internal error, fork failed
*
*/ #include "socket.c"
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/param.h>
#include <rpc/types.h>
#include <getopt.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <signal.h> /* values */
volatile int timerexpired=0;
int speed=0;
int failed=0;
int bytes=0; /* globals */
int http10=1; /* 0 - http/0.9, 1 - http/1.0, 2 - http/1.1 */
/* Allow: GET, HEAD, OPTIONS, TRACE */
#define METHOD_GET 0
#define METHOD_HEAD 1
#define METHOD_OPTIONS 2
#define METHOD_TRACE 3
#define PROGRAM_VERSION "1.5"
int method=METHOD_GET;
int clients=1;
int force=0;
int force_reload=0;
int proxyport=80;
char *proxyhost=NULL;
int benchtime=30; /* internal */
int mypipe[2];
char host[MAXHOSTNAMELEN];
#define REQUEST_SIZE 2048
char request[REQUEST_SIZE]; static const struct option long_options[]=
{
{"force",no_argument,&force,1},
{"reload",no_argument,&force_reload,1},
{"time",required_argument,NULL,'t'},
{"help",no_argument,NULL,'?'},
{"http09",no_argument,NULL,''},
{"http10",no_argument,NULL,''},
{"http11",no_argument,NULL,''},
{"get",no_argument,&method,METHOD_GET},
{"head",no_argument,&method,METHOD_HEAD},
{"options",no_argument,&method,METHOD_OPTIONS},
{"trace",no_argument,&method,METHOD_TRACE},
{"version",no_argument,NULL,'V'},
{"proxy",required_argument,NULL,'p'},
{"clients",required_argument,NULL,'c'},
{NULL,0,NULL,0}
}; /* prototypes */
static void benchcore(const char* host,const int port, const char *request);
static int bench(void);
static void build_request(const char *url); static void alarm_handler(int signal)
{
timerexpired=1;
} static void usage(void)
{
fprintf(stderr,
"webbench [option]... URL\n"
" -f|--force Don't wait for reply from server.\n"
" -r|--reload Send reload request - Pragma: no-cache.\n"
" -t|--time <sec> Run benchmark for <sec> seconds. Default 30.\n"
" -p|--proxy <server:port> Use proxy server for request.\n"
" -c|--clients <n> Run <n> HTTP clients at once. Default one.\n"
" -9|--http09 Use HTTP/0.9 style requests.\n"
" -1|--http10 Use HTTP/1.0 protocol.\n"
" -2|--http11 Use HTTP/1.1 protocol.\n"
" --get Use GET request method.\n"
" --head Use HEAD request method.\n"
" --options Use OPTIONS request method.\n"
" --trace Use TRACE request method.\n"
" -?|-h|--help This information.\n"
" -V|--version Display program version.\n"
);
} int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int opt=0;
int options_index=0;
char *tmp=NULL; if(argc==1)
{
usage();
return 2;
}
//getopt_long 参数处理 根据不同的选项对应不同的操作
while((opt=getopt_long(argc,argv,"912Vfrt:p:c:?h",long_options,&options_index))!=EOF )
{
switch(opt)
{
case 0 : break;
case 'f': force=1;break;
case 'r': force_reload=1;break;
case '': http10=0;break;
case '': http10=1;break;
case '': http10=2;break;
case 'V': printf(PROGRAM_VERSION"\n");exit(0);
case 't': benchtime=atoi(optarg);break;
case 'p':
/* proxy server parsing server:port */
tmp=strrchr(optarg,':');
proxyhost=optarg;
if(tmp==NULL)
{
break;
}
if(tmp==optarg)
{
fprintf(stderr,"Error in option --proxy %s: Missing hostname.\n",optarg);
return 2;
}
if(tmp==optarg+strlen(optarg)-1)
{
fprintf(stderr,"Error in option --proxy %s Port number is missing.\n",optarg);
return 2;
}
*tmp='\0';
proxyport=atoi(tmp+1);break;
case ':':
case 'h':
case '?': usage();return 2;break;
case 'c': clients=atoi(optarg);break;
}
} if(optind==argc) {
fprintf(stderr,"webbench: Missing URL!\n");
usage();
return 2;
}
//默认clients用户为1
if(clients==0)
clients=1;
//默认压测30s
if(benchtime==0)
benchtime=30; /* Copyright */
fprintf(stderr,"Webbench - Simple Web Benchmark "PROGRAM_VERSION"\n"
"Copyright (c) Radim Kolar 1997-2004, GPL Open Source Software.\n"
);
//构造请求
build_request(argv[optind]); // print request info ,do it in function build_request
/*printf("Benchmarking: "); switch(method)
{
case METHOD_GET:
default:
printf("GET");break;
case METHOD_OPTIONS:
printf("OPTIONS");break;
case METHOD_HEAD:
printf("HEAD");break;
case METHOD_TRACE:
printf("TRACE");break;
} printf(" %s",argv[optind]); switch(http10)
{
case 0: printf(" (using HTTP/0.9)");break;
case 2: printf(" (using HTTP/1.1)");break;
} printf("\n");
*/ printf("Runing info: "); if(clients==1)
printf("1 client");
else
printf("%d clients",clients); printf(", running %d sec", benchtime); if(force)
printf(", early socket close");
if(proxyhost!=NULL)
printf(", via proxy server %s:%d",proxyhost,proxyport);
if(force_reload)
printf(", forcing reload"); printf(".\n"); return bench();
} //构造请求
void build_request(const char *url)
{
char tmp[10];
int i; //bzero(host,MAXHOSTNAMELEN);
//bzero(request,REQUEST_SIZE);
memset(host,0,MAXHOSTNAMELEN);
memset(request,0,REQUEST_SIZE); if(force_reload && proxyhost!=NULL && http10<1)
http10=1;
if(method==METHOD_HEAD && http10<1)
http10=1;
if(method==METHOD_OPTIONS && http10<2)
http10=2;
if(method==METHOD_TRACE && http10<2)
http10=2;
//不同的构造头方法
/*
http头部格式
请求方法 空格 URL 空格 协议版本 \r\n
头部字段名 值 \r\n
\r\n
*/
switch(method)
{
default:
case METHOD_GET: strcpy(request,"GET");break;
case METHOD_HEAD: strcpy(request,"HEAD");break;
case METHOD_OPTIONS: strcpy(request,"OPTIONS");break;
case METHOD_TRACE: strcpy(request,"TRACE");break;
} strcat(request," "); if(NULL==strstr(url,"://"))
{
fprintf(stderr, "\n%s: is not a valid URL.\n",url);
exit(2);
}
//url限制大小为1500
if(strlen(url)>1500)
{
fprintf(stderr,"URL is too long.\n");
exit(2);
}
if (0!=strncasecmp("http://",url,7))
{
fprintf(stderr,"\nOnly HTTP protocol is directly supported, set --proxy for others.\n");
exit(2);
} /* protocol/host delimiter */
i=strstr(url,"://")-url+3; if(strchr(url+i,'/')==NULL) {
fprintf(stderr,"\nInvalid URL syntax - hostname don't ends with '/'.\n");
exit(2);
} if(proxyhost==NULL)
{
/* get port from hostname */
if(index(url+i,':')!=NULL && index(url+i,':')<index(url+i,'/'))
{
strncpy(host,url+i,strchr(url+i,':')-url-i);
//bzero(tmp,10);
memset(tmp,0,10);
strncpy(tmp,index(url+i,':')+1,strchr(url+i,'/')-index(url+i,':')-1);
/* printf("tmp=%s\n",tmp); */
proxyport=atoi(tmp);
if(proxyport==0) proxyport=80;
}
else
{
strncpy(host,url+i,strcspn(url+i,"/"));
}
// printf("Host=%s\n",host);
strcat(request+strlen(request),url+i+strcspn(url+i,"/"));
}
else
{
// printf("ProxyHost=%s\nProxyPort=%d\n",proxyhost,proxyport);
strcat(request,url);
} if(http10==1)
strcat(request," HTTP/1.0");
else if (http10==2)
strcat(request," HTTP/1.1"); strcat(request,"\r\n");
//到这里头部构造完成 if(http10>0)
strcat(request,"User-Agent: WebBench "PROGRAM_VERSION"\r\n");
if(proxyhost==NULL && http10>0)
{
strcat(request,"Host: ");
strcat(request,host);
strcat(request,"\r\n");
} if(force_reload && proxyhost!=NULL)
{
strcat(request,"Pragma: no-cache\r\n");
} if(http10>1)
strcat(request,"Connection: close\r\n"); /* add empty line at end */
if(http10>0)
strcat(request,"\r\n"); printf("\nRequest:\n%s\n",request);
} /* vraci system rc error kod */
static int bench(void)
{
int i,j,k;
pid_t pid=0;
FILE *f; /* check avaibility of target server */
i=Socket(proxyhost==NULL?host:proxyhost,proxyport);
if(i<0) {
fprintf(stderr,"\nConnect to server failed. Aborting benchmark.\n");
return 1;
}
close(i); /* 创建管道 */
if(pipe(mypipe))
{
perror("pipe failed.");
return 3;
} /* not needed, since we have alarm() in childrens */
/* wait 4 next system clock tick */
/*
cas=time(NULL);
while(time(NULL)==cas)
sched_yield();
*/ /* fork childs */
//多少个用户多少个进程 fork一次返回两个
for(i=0;i<clients;i++)
{
pid=fork();
if(pid <= (pid_t) 0)
{
/* child process or error*/
sleep(1); /* make childs faster */
break;
}
} if( pid < (pid_t) 0)
{
fprintf(stderr,"problems forking worker no. %d\n",i);
perror("fork failed.");
return 3;
}
//如果是子进程 if(pid == (pid_t) 0)
{
/* I am a child */
if(proxyhost==NULL)
benchcore(host,proxyport,request);
else
benchcore(proxyhost,proxyport,request); /* write results to pipe */
//构造完请求得到结果写入管道
f=fdopen(mypipe[1],"w");
if(f==NULL)
{
perror("open pipe for writing failed.");
return 3;
}
/* fprintf(stderr,"Child - %d %d\n",speed,failed); */
fprintf(f,"%d %d %d\n",speed,failed,bytes);
fclose(f); return 0;
}
else
{
//父进程从管道读数据
f=fdopen(mypipe[0],"r");
if(f==NULL)
{
perror("open pipe for reading failed.");
return 3;
} setvbuf(f,NULL,_IONBF,0);//不使用缓冲。每个 I/O 操作都被即时写入。buffer 和 size 参数被忽略 speed=0;
failed=0;
bytes=0; while(1)
{
pid=fscanf(f,"%d %d %d",&i,&j,&k);
if(pid<2)
{
fprintf(stderr,"Some of our childrens died.\n");
break;
} speed+=i;
failed+=j;
bytes+=k; /* fprintf(stderr,"*Knock* %d %d read=%d\n",speed,failed,pid); */
if(--clients==0)
break;
} fclose(f); printf("\nSpeed=%d pages/min, %d bytes/sec.\nRequests: %d susceed, %d failed.\n",
(int)((speed+failed)/(benchtime/60.0f)),
(int)(bytes/(float)benchtime),
speed,
failed);
} return i;
} void benchcore(const char *host,const int port,const char *req)
{
int rlen;
char buf[1500];
int s,i;
struct sigaction sa; /* setup alarm signal handler */
sa.sa_handler=alarm_handler;
sa.sa_flags=0;
if(sigaction(SIGALRM,&sa,NULL))
exit(3); alarm(benchtime); // after benchtime,then exit rlen=strlen(req);
nexttry:while(1)
{
if(timerexpired)
{
if(failed>0)
{
/* fprintf(stderr,"Correcting failed by signal\n"); */
failed--;
}
return;
} s=Socket(host,port); //尝试连接
//失败次数统计
if(s<0)
{
failed++;
continue;
} if(rlen!=write(s,req,rlen))
{
failed++;
close(s);
continue;
}
if(http10==0)
if(shutdown(s,1))
{
failed++;
close(s);
continue;
}
if(force==0)
{
/* read all available data from socket */
while(1)
{
if(timerexpired) break;
i=read(s,buf,1500);
/* fprintf(stderr,"%d\n",i); */
if(i<0)
{
failed++;
close(s);
goto nexttry;
}
else
if(i==0)
break;
else
bytes+=i;//read返回的是字节数 所以在此可以统计字节数
}
}
if(close(s))
{
failed++;
continue;
}
speed++;
}
}
最新文章
- union all 与order by的连用
- nginx: [warn] conflicting server name "locahost" on 0.0.0.0:80, ignored
- mac下SVN上传.a静态库文件
- ubuntu qt :-1: error cannot find lgl
- J2EE的十三种技术(规范)
- c#语句 (随堂练习)
- AABB包围盒、OBB包围盒、包围球的比較
- [转] Makefile的条件执行
- Maven 打包可运行 jar
- HTTP的报文格式解析
- mac nodejs安装
- 搭建ntp时间服务器 ntp - (Network Time Protocol)
- Github 上 Star 最多的个人 Spring Boot 开源学习项目
- 2018-2019-2 网络对抗技术 20165318 Exp2 后门原理与实践
- RESTful Loads
- C#日志记录设计与实现(BenXHLog)
- 记录结果再利用的"动态规划"
- 关于QueryCache的一次打脸
- iOS - 系统权限(关键时刻很有用的)
- 弹出层小插件之(二) layer&layui