C++20 以 Bazel & Clang 开始
C++20 如何以 Bazel & Clang 进行构建呢?
本文将介绍:
- Bazel 构建系统的安装
- LLVM 编译系统的安装
- Clang is an "LLVM native" C/C++/Objective-C compiler
- Bazel Clang 工具链的配置
- C++20 库与应用的构建
本文示例可见: https://github.com/ikuokuo/start-cpp20
本文是于 Ubuntu 20 上进行的实践,Windows 可以用 WSL 准备环境。
安装 Bazel,以二进制方式
Bazelisk 是安装 Bazel 的推荐方式,我们安装它的二进制发布即可:
cd ~
wget https://github.com/bazelbuild/bazelisk/releases/download/v1.12.0/bazelisk-linux-amd64 -O bazelisk-1.12.0-linux-amd64
chmod a+x bazelisk-*
sudo ln -s $(pwd)/bazelisk-1.12.0-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/bazel
touch WORKSPACE
# 国内下载 Bazel 可能遇到如下问题,配置 .bazeliskrc 解决
# could not resolve the version 'latest' to an actual version number
# https://github.com/bazelbuild/bazelisk/issues/220
cat <<-EOF > .bazeliskrc
BAZELISK_BASE_URL=https://github.com/bazelbuild/bazel/releases/download
USE_BAZEL_VERSION=5.2.0
EOF
bazel version
更多方式,可见官方文档。进一步,推荐安装 buildtools,下载后软链一下:
sudo ln -s $(pwd)/buildifier-5.1.0-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/buildifier
sudo ln -s $(pwd)/buildozer-5.1.0-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/buildozer
Bazel 如何构建 C++ 项目,可见我的 Start Bazel 笔记。
安装 LLVM,以源码方式
Clang 有关 std::fromat 文本格式化的特性,默认未开启:
The paper is implemented but still marked as an incomplete feature (the feature-test macro is not set and the libary is only available when built with LIBCXX_ENABLE_INCOMPLETE_FEATURES). Not yet implemented LWG-issues will cause API and ABI breakage.
C++20 特性,编译器支持情况:
因此,这里以源码方式安装 LLVM,需要构建 Clang & libc++:
git clone -b llvmorg-14.0.6 --depth 1 https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project.git
cd llvm-project
mkdir _build
cd _build
# llvm install path, such as /usr/local/llvm
LLVM_PREFIX=$HOME/Apps/llvm-14.0.6
cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release \
-DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=$LLVM_PREFIX \
-DLLVM_ENABLE_PROJECTS=clang \
-DLLVM_ENABLE_RUNTIMES="libcxx;libcxxabi" \
-DLIBCXX_ENABLE_INCOMPLETE_FEATURES=ON \
../llvm
make -j`nproc`
make install
sudo ln -s $LLVM_PREFIX /usr/local/llvm
cat <<-EOF >> ~/.bashrc
# llvm
export LLVM_HOME=/usr/local/llvm
export PATH=\$LLVM_HOME/bin:\$PATH
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=\$LLVM_HOME/lib/x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu:\$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
EOF
llvm-config --version
clang --version
LLVM_PREFIX 安装路径自己决定。最后,编译测试:
cat <<-EOF > hello.cc
#include <format>
#include <iostream>
int main() {
std::string message = std::format("The answer is {}.", 42);
std::cout << message << std::endl;
}
EOF
clang++ -std=c++20 -stdlib=libc++ hello.cc -o hello
./hello
安装 LLVM,以二进制方式
可省略该节。本文实践未用此方式,因为想开启更多 C++20 特性。这里仅作记录,有需要可参考。
方式 1. 安装二进制发布:
cd ~
wget https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project/releases/download/llvmorg-13.0.0/clang+llvm-13.0.0-x86_64-linux-gnu-ubuntu-20.04.tar.xz
tar -xf clang+llvm-*.tar.xz
sudo ln -s $(pwd)/clang+llvm-13.0.0-x86_64-linux-gnu-ubuntu-20.04 /usr/local/llvm
cat <<-EOF >> ~/.bashrc
# llvm
export LLVM_HOME=/usr/local/llvm
export PATH=\$LLVM_HOME/bin:\$PATH
EOF
llvm-config --version
clang --version
方式 2. 用 apt 进行安装: https://apt.llvm.org/
方式 3. 用已配好的工具链: LLVM toolchain for Bazel
配置 Clang 工具链
本文依照 Bazel Tutorial: Configure C++ Toolchains 步骤配置的 Clang 工具链,最后项目根目录会多如下文件:
WORKSPACE 表示 Bazel 工作区,内容空。
.bazelrc 允许 --config=clang_config 启用 Clang 工具链:
# Use our custom-configured c++ toolchain.
build:clang_config --crosstool_top=//toolchain:clang_suite
# Use --cpu as a differentiator.
build:clang_config --cpu=linux_x86_64
# Use the default Bazel C++ toolchain to build the tools used during the build.
build:clang_config --host_crosstool_top=@bazel_tools//tools/cpp:toolchain
toolchain/BUILD 配置 Clang 工具链信息:
load(":cc_toolchain_config.bzl", "cc_toolchain_config")
package(default_visibility = ["//visibility:public"])
#filegroup(name = "clang_suite")
cc_toolchain_suite(
name = "clang_suite",
toolchains = {
"linux_x86_64": ":linux_x86_64_toolchain",
},
)
filegroup(name = "empty")
cc_toolchain(
name = "linux_x86_64_toolchain",
toolchain_identifier = "linux_x86_64-toolchain",
toolchain_config = ":linux_x86_64_toolchain_config",
all_files = ":empty",
compiler_files = ":empty",
dwp_files = ":empty",
linker_files = ":empty",
objcopy_files = ":empty",
strip_files = ":empty",
supports_param_files = 0,
)
#filegroup(name = "linux_x86_64_toolchain_config")
cc_toolchain_config(name = "linux_x86_64_toolchain_config")
toolchain/cc_toolchain_config.bzl 配置 Clang 工具链规则:
# C++ Toolchain Configuration
# https://bazel.build/docs/cc-toolchain-config-reference
# https://github.com/bazelbuild/bazel/blob/master/tools/build_defs/cc/action_names.bzl
load("@bazel_tools//tools/build_defs/cc:action_names.bzl", "ACTION_NAMES")
load(
"@bazel_tools//tools/cpp:cc_toolchain_config_lib.bzl",
"feature",
"flag_group",
"flag_set",
"tool_path",
)
all_compile_actions = [
ACTION_NAMES.c_compile,
ACTION_NAMES.cpp_compile,
ACTION_NAMES.linkstamp_compile,
ACTION_NAMES.assemble,
ACTION_NAMES.preprocess_assemble,
ACTION_NAMES.cpp_header_parsing,
ACTION_NAMES.cpp_module_compile,
ACTION_NAMES.cpp_module_codegen,
]
all_link_actions = [
ACTION_NAMES.cpp_link_executable,
ACTION_NAMES.cpp_link_dynamic_library,
ACTION_NAMES.cpp_link_nodeps_dynamic_library,
]
def _impl(ctx):
llvm_version = "14.0.6"
llvm_prefix = "/home/john/Apps/llvm-{}".format(llvm_version)
llvm_bindir = llvm_prefix + "/bin"
tool_paths = [
tool_path(
name = "gcc",
path = llvm_bindir + "/clang",
),
tool_path(
name = "ld",
path = llvm_bindir + "/ld.lld",
),
tool_path(
name = "ar",
path = llvm_bindir + "/llvm-ar",
),
tool_path(
name = "cpp",
path = llvm_bindir + "/clang-cpp",
),
tool_path(
name = "gcov",
path = llvm_bindir + "/llvm-cov",
),
tool_path(
name = "nm",
path = llvm_bindir + "/llvm-nm",
),
tool_path(
name = "objdump",
path = llvm_bindir + "/llvm-objdump",
),
tool_path(
name = "strip",
path = llvm_bindir + "/llvm-strip",
),
]
features = [
feature(
name = "default_compiler_flags",
enabled = True,
flag_sets = [
flag_set(
actions = all_compile_actions,
flag_groups = ([
flag_group(
flags = [
"-O2", "-DNDEBUG",
"-Wall", "-Wextra", "-Wpedantic", "-fPIC",
"-std=c++20", "-stdlib=libc++",
],
),
]),
),
],
),
feature(
name = "default_linker_flags",
enabled = True,
flag_sets = [
flag_set(
actions = all_link_actions,
flag_groups = ([
flag_group(
flags = [
"-lc++", "-lc++abi",
"-lm", "-ldl", "-lpthread",
],
),
]),
),
],
),
]
return cc_common.create_cc_toolchain_config_info(
ctx = ctx,
features = features,
cxx_builtin_include_directories = [
llvm_prefix + "/lib/clang/{}/include".format(llvm_version),
llvm_prefix + "/include/x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu/c++/v1",
llvm_prefix + "/include/c++/v1",
"/usr/local/include",
"/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu",
"/usr/include",
],
toolchain_identifier = "local",
host_system_name = "local",
target_system_name = "local",
target_cpu = "linux_x86_64",
target_libc = "unknown",
compiler = "clang",
abi_version = "unknown",
abi_libc_version = "unknown",
tool_paths = tool_paths,
)
cc_toolchain_config = rule(
implementation = _impl,
attrs = {},
provides = [CcToolchainConfigInfo],
)
llvm_prefix 给到自己的 LLVM 安装路径。
构建 C++20 库与应用
本文示例的 code/00/ 路径下准备了 C++20 的库与应用:
code/00/
├── BUILD
├── greet
│ ├── BUILD
│ ├── greet.cc
│ └── greet.h
└── main.cc
编写 binary
main.cc:
#include <format>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <string_view>
#include "greet/greet.h"
template <typename... Args>
std::string dyna_print(std::string_view rt_fmt_str, Args&&... args) {
return std::vformat(rt_fmt_str, std::make_format_args(args...));
}
int main() {
std::cout << greet::hello("world") << std::endl;
std::string fmt;
for (int i{}; i != 3; ++i) {
fmt += "{} "; // constructs the formatting string
std::cout << fmt << " : ";
std::cout << dyna_print(fmt, "alpha", 'Z', 3.14, "unused");
std::cout << '\n';
}
}
BUILD:
load("@rules_cc//cc:defs.bzl", "cc_binary")
cc_binary(
name = "main",
srcs = ["main.cc"],
deps = [
"//code/00/greet:greet",
],
)
编写 library
greet.h:
#pragma once
#include <string>
#include <string_view>
namespace greet {
std::string hello(std::string_view who);
} // namespace greet
greet.cc:
#include "greet.h"
#include <format>
#include <utility>
namespace greet {
std::string hello(std::string_view who) {
return std::format("Hello {}!", std::move(who));
}
} // namespace greet
BUILD:
load("@rules_cc//cc:defs.bzl", "cc_library")
package(default_visibility = ["//visibility:public"])
cc_library(
name = "greet",
srcs = [
"greet.cc",
],
hdrs = [
"greet.h",
],
)
Bazel 构建
bazel build --config=clang_config //code/00:main
运行测试
$ bazel-bin/code/00/main
Hello world!
{} : alpha
{} {} : alpha Z
{} {} {} : alpha Z 3.14
查看依赖
sudo apt update && sudo apt install graphviz xdot -y
# view
xdot <(bazel query --notool_deps --noimplicit_deps "deps(//code/00:main)" --output graph)
# to svg
dot -Tsvg <(bazel query --notool_deps --noimplicit_deps "deps(//code/00:main)" --output graph) -o 00_main.svg
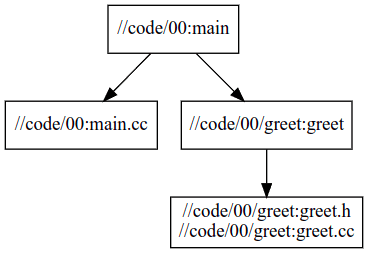
更多参考
- Bazel Tutorial
- Bazel Issue
- Project Example
GoCoding 个人实践的经验分享,可关注公众号!
最新文章
- [LeetCode] Top K Frequent Elements 前K个高频元素
- 报表移动端app如何实现页面自适应?
- 源码编译Nodejs 4.6 on CentOS6
- 知方可补不足~sqlserver中对xml类型字段的操作
- VS2015 Xamarin for iOS
- HTML--8Window.document对象
- Data Base MongoDB 插入时间不正确的问题
- hadoop 2.0--YARN
- class$1,class$2,class$innerclass中的$的含义
- post请求和get请求的区别
- Strategic Game(匈牙利算法,最小点覆盖数)
- 求助(VC++) 隐藏Console窗体无效
- Spring (3.2.4) 常用jar 包解析
- js封装成插件-------Canvas统计图插件编写
- GitLab简单使用
- CAP带你轻松玩转Asp.Net Core消息队列
- Centos 7(linux)系统下如何给jar应用程序创建桌面快捷方式
- 并发控制--Concurrency control--乐观、悲观及方法
- 51Nod1675 序列变换 数论 莫比乌斯反演
- iOS开发-UIButton浅谈