codeforces 920 EFG 题解合集 ( Educational Codeforces Round 37 )
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You are given an undirected graph consisting of n vertices and 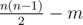 edges. Instead of giving you the edges that exist in the graph, we give you m unordered pairs (x, y) such that there is no edge between x and y, and if some pair of vertices is not listed in the input, then there is an edge between these vertices.
edges. Instead of giving you the edges that exist in the graph, we give you m unordered pairs (x, y) such that there is no edge between x and y, and if some pair of vertices is not listed in the input, then there is an edge between these vertices.
You have to find the number of connected components in the graph and the size of each component. A connected component is a set of vertices X such that for every two vertices from this set there exists at least one path in the graph connecting these vertices, but adding any other vertex to X violates this rule.
The first line contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n ≤ 200000, 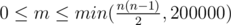 ).
).
Then m lines follow, each containing a pair of integers x and y (1 ≤ x, y ≤ n, x ≠ y) denoting that there is no edge between x and y. Each pair is listed at most once; (x, y) and (y, x) are considered the same (so they are never listed in the same test). If some pair of vertices is not listed in the input, then there existsan edge between those vertices.
Firstly print k — the number of connected components in this graph.
Then print k integers — the sizes of components. You should output these integers in non-descending order.
5 5
1 2
3 4
3 2
4 2
2 5
2
1 4
题意:一个无向图,给出没有连边的点对(没有给出的点对都有直接连边),求联通块个数和每个联通块的大小。
题解:首先是存边的问题,不可能把所有边都记录下来吧。那么久只能记录不连通关系了,用邻接表记录的话,询问两个点之间是否有连边不大方便。
可以给每个点开一个set,set里面存不连通关系,询问两个点之间是否有连边就在set里面查找有没有对应元素就行了。
也可以给每个点开一个map,当做邻接矩阵用。我采用的是这种。
思路:维护一个集合(set),存储当前不确定在哪个联通块中的点,初始时所有点都在里面。
然后在其中依次取点,dfs遍历它的联通块,统计一下,把遍历到的点都扔出这个集合,因为它们的连通关系已经确定,不用再对其进行dfs。
注意:dfs一个点x的时候,要寻找x的出边,这样很慢,应该在set中依次查找,判断set中的点与x是否有直接连边。
遍历set的时候不要for(set<int>iterator::it=s.begin();it!=s.end();it++) ,由于有删除操作,还是递归删除,所以it指向的元素可能在下一层递归中被删掉,然后……就RE了。可以用lower_bound()或upper_bound()查找下一个元素,具体见代码。
/*
Welcome Hacking
Wish You High Rating
*/
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<ctime>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<string>
#include<map>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
int read(){
int xx=,ff=;char ch=getchar();
while(ch>''||ch<''){if(ch=='-')ff=-;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>=''&&ch<=''){xx=(xx<<)+(xx<<)+ch-'';ch=getchar();}
return xx*ff;
}
const int maxn=;
int N,M,t1,t2,temp[maxn],ans;
set<int>s;
map<int,bool>e[maxn];
void dfs(int x){
int prev=;
while(){
int t=*s.lower_bound(prev);
if(t==(<<))
break;
prev=t+;
if(!e[x][t]){
temp[ans]++;
s.erase(t);
dfs(t);
}
}
}
int main(){
//freopen("in","r",stdin);
N=read(),M=read();
for(int i=;i<=N;i++)
s.insert(i);
s.insert(<<);
for(int i=;i<=M;i++){
t1=read(),t2=read();
e[t1][t2]=e[t2][t1]=;
}
int prev=;
while(){
int t=*s.lower_bound(prev);
if(t==(<<))
break;
prev=t+;
s.erase(t);
temp[++ans]=;
dfs(t);
}
sort(temp+,temp++ans);
printf("%d\n",ans);
for(int i=;i<=ans;i++)
printf("%d ",temp[i]);
puts("");
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Let D(x) be the number of positive divisors of a positive integer x. For example, D(2) = 2 (2 is divisible by 1 and 2), D(6) = 4 (6 is divisible by 1, 2, 3 and 6).
You are given an array a of n integers. You have to process two types of queries:
- REPLACE l r — for every
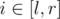 replace ai with D(ai);
replace ai with D(ai); - SUM l r — calculate
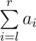 .
.
Print the answer for each SUM query.
The first line contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 3·105) — the number of elements in the array and the number of queries to process, respectively.
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 106) — the elements of the array.
Then m lines follow, each containing 3 integers ti, li, ri denoting i-th query. If ti = 1, then i-th query is REPLACE li ri, otherwise it's SUM li ri (1 ≤ ti ≤ 2, 1 ≤ li ≤ ri ≤ n).
There is at least one SUM query.
For each SUM query print the answer to it.
7 6
6 4 1 10 3 2 4
2 1 7
2 4 5
1 3 5
2 4 4
1 5 7
2 1 7
30
13
4
22
大意:对于一个给定序列,有两种操作:
1:给定区间[L,R],将其中的每个元素x变为D(x)
D(x)是x的因子数。
2:给定区间[L,R],求和。
题解:
线段树套路题。
注意到在x属于1e6以内时,D(x)最大是240.
x,D(x),D(D(x))……的衰减速度非常快。
打表可知,对于一个数1e6以内的x,最多进行第一个操作6次,就会变成2(除了1 , D(1)=1)
先把序列中的所有1都换成2,同时记录一下,方便统计回来。
维护一个线段树记录区间内1操作数的次数的最小值和区间和
对于每个1操作,暴力修改到线段树底层,直到1操作次数最小值大于等于6.
这样修改的复杂度最差O(N*logN) (最多修改6次,6是常数)
查询的复杂度为O(1)
UOJ round 和 hdu 上都有类似的题。
/*
Welcome Hacking
Wish You High Rating
*/
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<ctime>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
inline int read(){
int xx=,ff=;char ch=getchar();
while(ch>''||ch<''){if(ch=='-')ff=-;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>=''&&ch<=''){xx=(xx<<)+(xx<<)+ch-'';ch=getchar();}
return xx*ff;
}
inline int mymin(int xx,int yy)
{if(xx<yy)return xx;return yy;}
const int maxn=,limit=;
int N,M,D[limit+],tot=,sum[maxn],a[maxn];
struct Segment_Tree{
long long sum;
}T[maxn*];
int x,y,opt;
void build(int L,int R,int root){
if(L==R){
T[root].sum=a[L];
return;
}
int mid=(L+R)>>;
build(L,mid,root*);
build(mid+,R,root*+);
T[root].sum=T[root*].sum+T[root*+].sum;
}
void upd(int L,int R,int root){
if(T[root].sum==(R-L+)*)
return;
if(x>R||y<L)
return;
if(L==R){
T[root].sum=D[T[root].sum];
return;
}
int mid=(L+R)>>;
upd(L,mid,root*);
upd(mid+,R,root*+);
T[root].sum=T[root*].sum+T[root*+].sum;
}
long long query(int L,int R,int root){
if(x>R||y<L)
return ;
if(x<=L&&y>=R)
return T[root].sum;
int mid=(L+R)>>;
return query(L,mid,root*)+query(mid+,R,root*+);
}
int main(){
//freopen("in","r",stdin);
for(int i=;i<=limit;i++)
for(int j=i;j<=limit;j+=i)
D[j]++;
N=read(),M=read();
for(int i=;i<=N;i++){
a[i]=read();
sum[i]=sum[i-];
if(a[i]==)
a[i]=,sum[i]++;
}
build(,N,);
while(M--){
opt=read();
if(opt==){
x=read(),y=read();
upd(,N,);
}
else{
x=read(),y=read();
printf("%I64d\n",query(,N,)-(sum[y]-sum[x-]));
}
}
return ;
}
5 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Let's denote as L(x, p) an infinite sequence of integers y such that gcd(p, y) = 1 and y > x (where gcd is the greatest common divisor of two integer numbers), sorted in ascending order. The elements of L(x, p)are 1-indexed; for example, 9, 13 and 15 are the first, the second and the third elements of L(7, 22), respectively.
You have to process t queries. Each query is denoted by three integers x, p and k, and the answer to this query is k-th element of L(x, p).
The first line contains one integer t (1 ≤ t ≤ 30000) — the number of queries to process.
Then t lines follow. i-th line contains three integers x, p and k for i-th query (1 ≤ x, p, k ≤ 106).
Print t integers, where i-th integer is the answer to i-th query.
3
7 22 1
7 22 2
7 22 3
9
13
15
5
42 42 42
43 43 43
44 44 44
45 45 45
46 46 46
187
87
139
128
141
大意:t个询问,给出x,p,k求与p互质的大于x的第k个数。
5 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Let's denote as L(x, p) an infinite sequence of integers y such that gcd(p, y) = 1 and y > x (where gcd is the greatest common divisor of two integer numbers), sorted in ascending order. The elements of L(x, p)are 1-indexed; for example, 9, 13 and 15 are the first, the second and the third elements of L(7, 22), respectively.
You have to process t queries. Each query is denoted by three integers x, p and k, and the answer to this query is k-th element of L(x, p).
The first line contains one integer t (1 ≤ t ≤ 30000) — the number of queries to process.
Then t lines follow. i-th line contains three integers x, p and k for i-th query (1 ≤ x, p, k ≤ 106).
Print t integers, where i-th integer is the answer to i-th query.
3
7 22 1
7 22 2
7 22 3
9
13
15
5
42 42 42
43 43 43
44 44 44
45 45 45
46 46 46
187
87
139
128
141
题解:二分加容斥。
每个数的因子可以用筛法筛出来。
然后就是二分查找ans,容斥原理计算ans内有多少个与p互质的数。
至于大于x嘛,只需用容斥算出小于等于x的与p互质的数有多少个,加进k里面就行了。
/*
Welcome Hacking
Wish You High Rating
*/
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<ctime>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int read(){
int xx=,ff=;char ch=getchar();
while(ch>''||ch<''){if(ch=='-')ff=-;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>=''&&ch<=''){xx=(xx<<)+(xx<<)+ch-'';ch=getchar();}
return xx*ff;
}
const int limit=;
vector<int>V[limit+];
void get_fac(){
for(int i=;i<=limit;i++)
if(!V[i].size())
for(int j=i;j<=limit;j+=i)
V[j].push_back(i);
}
int x,p,k,delta;
int L,R,mid;
int calc(int num,int rb){
int siz=V[num].size();
int re=;
for(int i=;i<(<<siz);i++){
int s=,tim=;
for(int j=;j<siz;j++)
if((i>>j)&)
s*=V[num][j],tim++;
if(tim&)
re+=rb/s;
else
re-=rb/s;
}
return rb-re;
}
int main(){
//freopen("in","r",stdin);
get_fac();
for(int T=read();T;T--){
x=read(),p=read(),k=read();
delta=calc(p,x);
L=x,R=int(1e8);
while(L+<R){
mid=(L+R)/;
if(calc(p,mid)-delta>=k)
R=mid;
else
L=mid;
}
printf("%d\n",R);
}
return ;
}
最新文章
- 使用T-SQL找出执行时间过长的作业
- iOS-----正则表达式
- Spring整合Ehcache管理缓存(转)
- Intent意图
- Dedecms 首页调用副栏目内容方法
- eclipse workspace出错而导致启动不了
- Oracle主键自增的实现
- Cygwin的包管理器:apt-cyg
- ViewPager中使用自定义的ListView实例
- c++中基本的语法问题
- 操作hadoop的经验积累
- SQL Server 创建表分区
- 元素NULL判断
- PyCharm安装Pygame方法
- 音频降噪算法 附完整C代码
- laravel的firstOrCreate的作用:先查找表,如果有就输出数据,如果没有就插入数据
- C++复习:多态
- 代码UITableView点击cell跳转
- Mysql在linux下载、安装详情,附带mysql安装包路径
- 如何将Ubuntu左边的面板放到底部