OpenCV+TensorFlow图片手写数字识别(附源码)
2024-09-01 01:06:00
初次接触TensorFlow,而手写数字训练识别是其最基本的入门教程,网上关于训练的教程很多,但是模型的测试大多都是官方提供的一些素材,能不能自己随便写一串数字让机器识别出来呢?纸上得来终觉浅,带着这个疑问昨晚研究了下,利用这篇文章来记录下自己的一些心得!
以下这个图片是我随机写的一串数字,我的目标是利用训练好的模型来识别出图片里面的手写数字,开始实战!
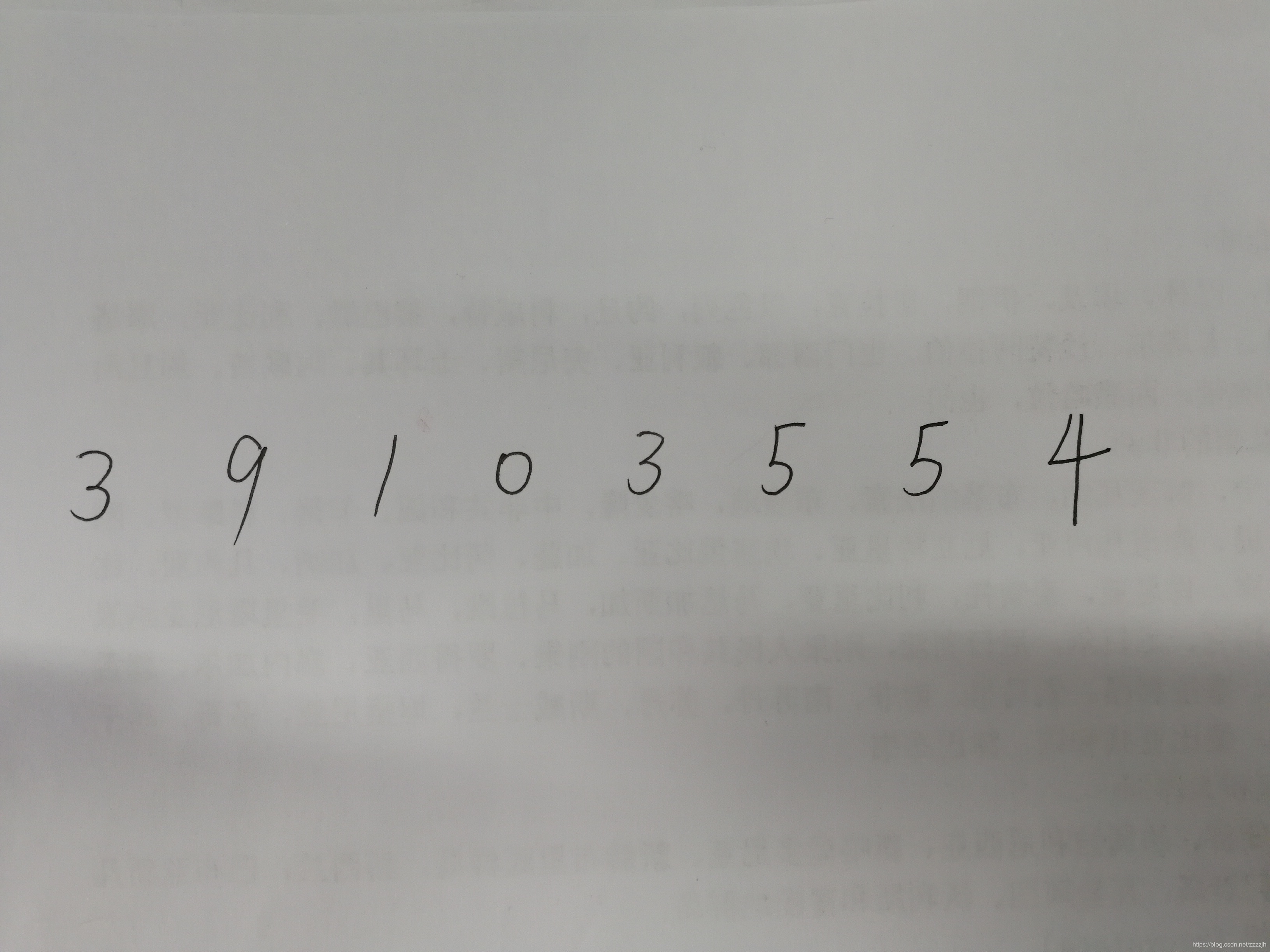
2层卷积神经网络的训练:
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
# 保存模型需要的库
from tensorflow.python.framework.graph_util import convert_variables_to_constants
from tensorflow.python.framework import graph_util
# 导入其他库
import tensorflow as tf
import cv2
import numpy as np
# 获取MINIST数据
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data", one_hot=True)
# 创建会话
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
# 占位符
x = tf.placeholder("float", shape=[None, 784], name="Mul")
y_ = tf.placeholder("float", shape=[None, 10], name="y_")
# 变量
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10]), name='x')
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]), 'y_')
# 权重
def weight_variable(shape):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial)
# 偏差
def bias_variable(shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial)
# 卷积
def conv2d(x, W):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
# 最大池化
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME') # 相关变量的创建
W_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32])
b_conv1 = bias_variable([32])
x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1])
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1)
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1)
W_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64])
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64])
# 激活函数
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)
W_fc1 = weight_variable([7 * 7 * 64, 1024])
b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024])
W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024, 10])
b_fc2 = bias_variable([10])
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1)
keep_prob = tf.placeholder("float", name='rob')
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob)
# 用于训练用的softmax函数
y_conv = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, W_fc2) + b_fc2, name='res')
# 用于训练作完后,作测试用的softmax函数
y_conv2 = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1, W_fc2) + b_fc2, name="final_result")
# 交叉熵的计算,返回包含了损失值的Tensor。
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y_conv))
# 优化器,负责最小化交叉熵
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy) correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
# 计算准确率
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
# 初始化所以变量
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# 保存输入输出,可以为之后用
tf.add_to_collection('res', y_conv)
tf.add_to_collection('output', y_conv2)
tf.add_to_collection('x', x)
# 训练开始
for i in range(10000):
batch = mnist.train.next_batch(50)
if i % 100 == 0:
train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={
x: batch[0], y_: batch[1], keep_prob: 1.0})
print("step %d, training accuracy %g" % (i, train_accuracy))
# run()可以看做输入相关值给到函数中的占位符,然后计算的出结果,这里将batch[0],给xbatch[1]给y_
train_step.run(feed_dict={x: batch[0], y_: batch[1], keep_prob: 0.5})
# 将当前图设置为默认图
graph_def = tf.get_default_graph().as_graph_def()
# 将上面的变量转化成常量,保存模型为pb模型时需要,注意这里的final_result和前面的y_con2是同名,只有这样才会保存它,否则会报错,
# 如果需要保存其他tensor只需要让tensor的名字和这里保持一直即可
output_graph_def = tf.graph_util.convert_variables_to_constants(sess,graph_def, ['final_result'])
# 用saver 保存模型
saver = tf.train.Saver()
saver.save(sess, "model_data/model")
网络训练成功后在model_data文件夹里有如下四个文件:
网络模型的验证可大致从以下三个部分来进行:
接下来就是要利用上面的图片来测试我们的模型。实际上图像的预处理部分很关键,也就是如何准确的提取出上面图像中的数字的区域,并且进行阈值分割,传统的单一阈值分割很难达到要求,因此本次分割采用基于改进的Niblack的分割方法,大家有兴趣可以查阅相关的资料。
分割完了之后要标记连通区域,去除那些小点区域。找到其外接矩形,可认为这个矩形区域就是我们感兴趣的区域。
降采样为28*28的大小来进行识别。
代码部分如下所示:
"""
基于TensorFlow的手写数字识别
Author_Zjh
2018/12/3
"""
import numpy as np
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import imutils
import matplotlib.patches as mpatches
from skimage import data,segmentation,measure,morphology,color
import tensorflow as tf
class Number_recognition():
""" 模型恢复初始化"""
def __init__(self,img):
self.sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph('model_data/model.meta')
saver.restore(self.sess, 'model_data/model') #模型恢复
# graph = tf.get_default_graph()
# 获取输入tensor,,获取输出tensor
self.input_x = self.sess.graph.get_tensor_by_name("Mul:0")
self.y_conv2 = self.sess.graph.get_tensor_by_name("final_result:0")
self.Preprocessing(img)#图像预处理
def recognition(self,im):
im = cv2.resize(im, (28, 28), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
x_img = np.reshape(im, [-1, 784])
output = self.sess.run(self.y_conv2, feed_dict={self.input_x: x_img})
print('您输入的数字是 %d' % (np.argmax(output)))
return np.argmax(output)#返回识别的结果 def Preprocessing(self,image):
if image.shape[0]>800:
image = imutils.resize(image, height=800) #如果图像太大局部阈值分割速度会稍慢些,因此图像太大时进行降采样 img = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # convert to gray picture
m1, n1 = img.shape
k = int(m1 / 19) + 1
l = int(n1 / 19) + 1
img = cv2.GaussianBlur(img, (3, 3), 0) # 高斯滤波
imm = img.copy()
# 基于Niblack的局部阈值分割法,对于提取文本类图像分割效果比较好
for x in range(k):
for y in range(l):
s = imm[19 * x:19 * (x + 1), 19 * y:19 * (y + 1)]
me = s.mean() # 均值
var = np.std(s) # 方差
t = me * (1 - 0.2 * ((125 - var) / 125))
ret, imm[19 * x:19 * (x + 1), 19 * y:19 * (y + 1)] = cv2.threshold(
imm[19 * x:19 * (x + 1), 19 * y:19 * (y + 1)], t, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
label_image = measure.label(imm) # 连通区域标记
for region in measure.regionprops(label_image): # 循环得到每一个连通区域属性集
# 忽略小区域
if region.area < 100:
continue
minr, minc, maxr, maxc = region.bbox# 得到外包矩形参数
cv2.rectangle(image, (minc, minr), (maxc, maxr), (0, 255, 0), 2)#绘制连通区域
im2 = imm[minr - 5:maxr + 5, minc - 5:maxc + 5] #获得感兴趣区域,也即每个数字的区域
number = self.recognition(im2)#进行识别
cv2.putText(image, str(number), (minc, minr - 10), 0, 2, (0, 0, 255), 2)#将识别结果写在原图上
cv2.imshow("Nizi", imm)
cv2.imshow("Annie", image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
if __name__=='__main__':
img = cv2.imread("num.jpg")
x=Number_recognition(img)
分割结果如下所示:

识别结果如下所示:

发现9和4识别错误,其余的均识别正确,有可能是数据量和网络迭代次数较少的原因!
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「zzzzjh」的原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/zzzzjh/article/details/84783277
关注【OpenCV与AI深度学习】
长按或者扫描下面二维码即可关注

最新文章
- windows bat批处理语法简析
- strcpy 库函数 拷贝函数
- Windows7下安装搭建Ngnix教程
- sharedPreference的奇怪bug
- DOM中的node与element的区别
- 原码、反码、补码的正(nao)确(can)打开方式
- webpack 1.x 配合npm scripts管理多站点
- 你应该知道的 volatile 关键字
- 浅析PHP中的闭包和匿名函数
- HTTP进阶学习笔记
- Spark操作:Aggregate和AggregateByKey
- 深度学习(Deep Learning)算法简介
- 【C/C++】嵌入式程序员应该知道的0X10个C语言问题
- Restframework 渲染器 render 组件实例-4
- (第二章)改善JavaScript,编写高质量代码。
- php的数组汉字符串常用函数
- 判断ios当前的sdk版本的方法
- 软件设计模式(Design pattern)(待续)
- 海报工厂之(一)android 如何给图片添加水印和文字
- 排排看(p20)