TCP-IP Architecture and IP Packet
2024-10-16 01:21:09
Why Internet working?
- To build a “network of networks” or internet.
- operating over multiple, coexisting(共存的), different networks
- providing ubiquitous(无处不在的) connectivity through IP packet transfer .
- achieving huge economies of scale.
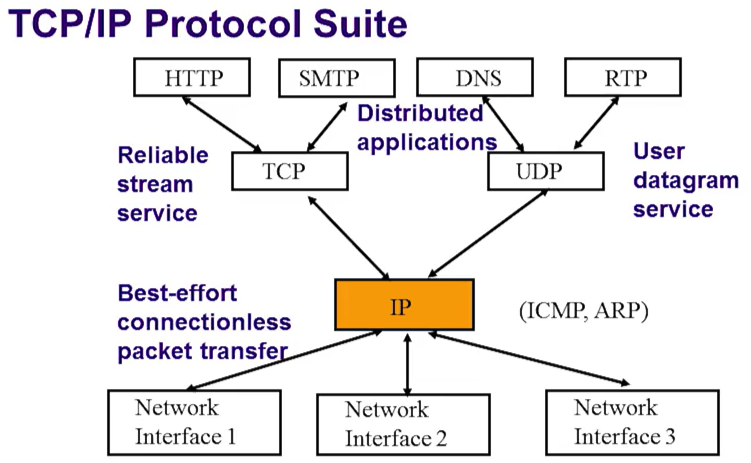
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
Encapsulation(封装)
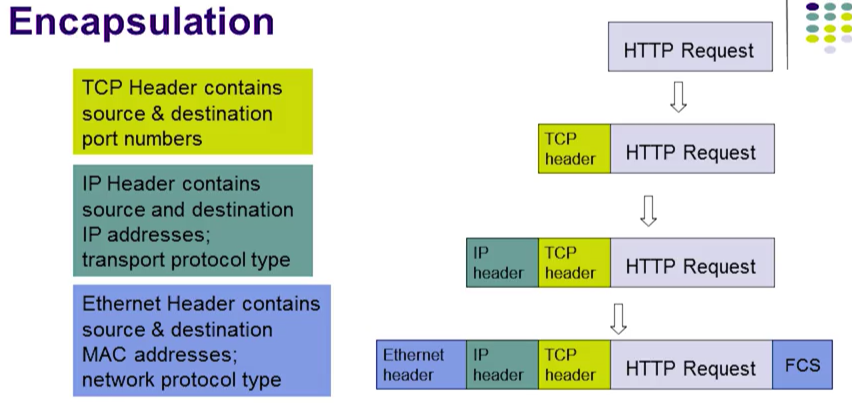
- Base:HTTP Request ->TCP header->IP header->Ethernet header
Internet Addresses
- Each host has globally unique logical IP address
- Separate address for each physical connection to a network
- Routing decision is done based on destination IP address
- IP address has two parts:
- netid(网络标识符) and hostid
- netid unique, facilitates routing
- Dotted Decimal(十进制) Notation(记号):
int1.int2.int3.int4
(intj = jth octet)
128.100.10.13
Internet Protocol
- Provides best effort, connectionless packet delivery
- motivated by need to keep routers simple and by adaptibility to failure of network elements
- packets may be lost, out of order, or even duplicated(复制)
- higher layer protocols must deal with these, if necessary
- IP also includes:
- Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
- Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP)
IP Packet Header
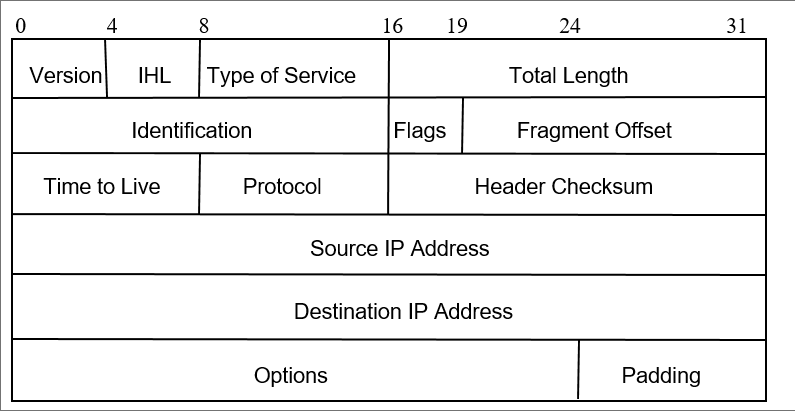
- Minimum 20 bytes
- Up to 40 bytes in options fields
- Version: current IP version is 4.
- Internet header length (IHL): length of the header in 32-bit words.
- Type of service (TOS): traditionally priority of packet at each router. Recent Differentiated Services redefines TOS field to include other services besides best effort.
- Total length: number of bytes of the IP packet including header and data
- Identification, Flags, and Fragment Offset: for fragmentation and reassembly.
- Time to live (TTL): number of hops packet is allowed to traverse(穿过) in network.
- Each router along the path to the destination decrements this value by one.
- If the value reaches zero before the packet reaches the destination, the router discards the packet and sends an error message back to the source.
- Protocol: specifies upper-layer protocol that is to receive IP data at the destination. Examples include TCP (protocol = 6), UDP (protocol = 17), and ICMP (protocol = 1).
- Header checksum(校验和): verifies the integrity of the IP header.
- Source IP address and destination IP address: contain the addresses of the source and destination hosts.
- Options: Variable length field, allows packet to request special features such as security level, route to be taken by the packet, and timestamp at each router. Detailed descriptions of these options can be found in [RFC 791].
- Padding: This field is used to make the header a multiple of 32-bit words.
IP Header Processing
- Compute header checksum(校验和) for correctness and check that fields in header (e.g. version and total length) contain valid values
- Consult routing table to determine next hop
- Change fields that require updating (TTL, header checksum)
最新文章
- Mellanox 8亿美元收购EZchip
- python 下 tinker、matplotlib 混合编程示例一个
- KnockoutJS 3.X API 第四章 数据绑定(3) 控制流if绑定和ifnot绑定
- 剑指Offer 二叉树的镜像
- Go文件操作
- 无法产生coredump的问题
- Load a script file in sencha, supports both asynchronous and synchronous approaches
- 写两个线程,一个对n每次加一,一个对n每次减一
- USB学习小记-HID类键盘的报告描述符的理解
- offset获取位置
- Django之Apps源码学习
- 【基于url权限管理 shiro(一)】--基础
- Java中的过滤器,拦截器,监听器---------简单易懂的介绍
- Angular 序列化和反序列化和遍历
- chapter15中使用generator来实现异步化操作的同步化表达的例子
- sklearn:Python语言开发的通用机器学习库
- java指针与引用(转载)
- 微信小程序两种滑动方式
- 智课雅思词汇---二十三、动词性后缀-ate-fy-ish-ize
- python抓取新浪首页的小例子
热门文章
- node.js学习网址
- Linux 更新python至2.7后ImportError: No module named _ssl
- JS判断数字类型
- Grunt usemin前端自动化打包流程
- Android蓝牙自动配对Demo,亲测好使!!!
- 转:hive-列转行和行转列
- RocketMQ读书笔记5——消息队列的核心机制
- python3 报错:UnicodeDecodeError: 'utf-8' codec can't decode byte 0xd6 in position 201: invalid continuation byte
- git revert .vs. git reset .vs. git rebase
- JavaScript返回上一页