吴丽丽-201871010123《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第七周学习总结
吴丽丽-201871010123《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第七周学习总结
| 项目 | 内容 |
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 |
http://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ |
| 这个作业的要求在哪里 | https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p/11654436.html |
| 作业的学习目标 |
(1) 掌握四种访问权限修饰符的使用特点; (2) 掌握Object类的用途及常用API; (3) 掌握ArrayList类的定义方法及用法; (4)掌握枚举类定义方法及用途; (5)结合本章实验内容,理解继承与多态性两个面向对象程序设计特征,并体会其优点。 |
实验内容和步骤
实验1:在“System.out.println(...);”语句处按注释要求设计代码替换...,观察代码录入中IDE提示,以验证四种权限修饰符的用法。
package project;
class Parent {
private String p1 = "这是Parent的私有属性";
public String p2 = "这是Parent的公有属性";
protected String p3 = "这是Parent受保护的属性";
String p4 = "这是Parent的默认属性";
private void pMethod1() {
System.out.println("我是Parent用private修饰符修饰的方法");
}
public void pMethod2() {
System.out.println("我是Parent用public修饰符修饰的方法");
}
protected void pMethod3() {
System.out.println("我是Parent用protected修饰符修饰的方法");
}
void pMethod4() {
System.out.println("我是Parent无修饰符修饰的方法");
}
}
class Son extends Parent{
private String s1 = "这是Son的私有属性";
public String s2 = "这是Son的公有属性";
protected String s3 = "这是Son受保护的属性";
String s4 = "这是Son的默认属性";
public void sMethod1() {
System.out.println(p2);//分别尝试显示Parent类的p1、p2、p3、p4值
System.out.println("我是Son用public修饰符修饰的方法");
}
private void sMethod2() {
System.out.println("我是Son用private修饰符修饰的方法");
}
protected void sMethod() {
System.out.println("我是Son用protected修饰符修饰的方法");
}
void sMethod4() {
System.out.println("我是Son无修饰符修饰的方法");
}
}
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent parent=new Parent();
Son son=new Son();
System.out.println(parent.p2);
System.out.println(parent.p3);
System.out.println(parent.p4);//分别尝试用parent调用Paren类的方法、用son调用Son类的方法
System.out.println(son.p2);
System.out.println(son.p3);
System.out.println(son.p4);
System.out.println(son.s2);
System.out.println(son.s3);
System.out.println(son.s4);
parent.pMethod2();
son.pMethod2();
son.sMethod1();
}
}
该代码是将子类父类以及主函数放在同一个包的同一个文件中,其除了parent类的private不可调用外,其他三个类都可以。子类除了不可以调用父类的私有域外,同样可以调用父类的其他域和方法。
程序结果运行如下:
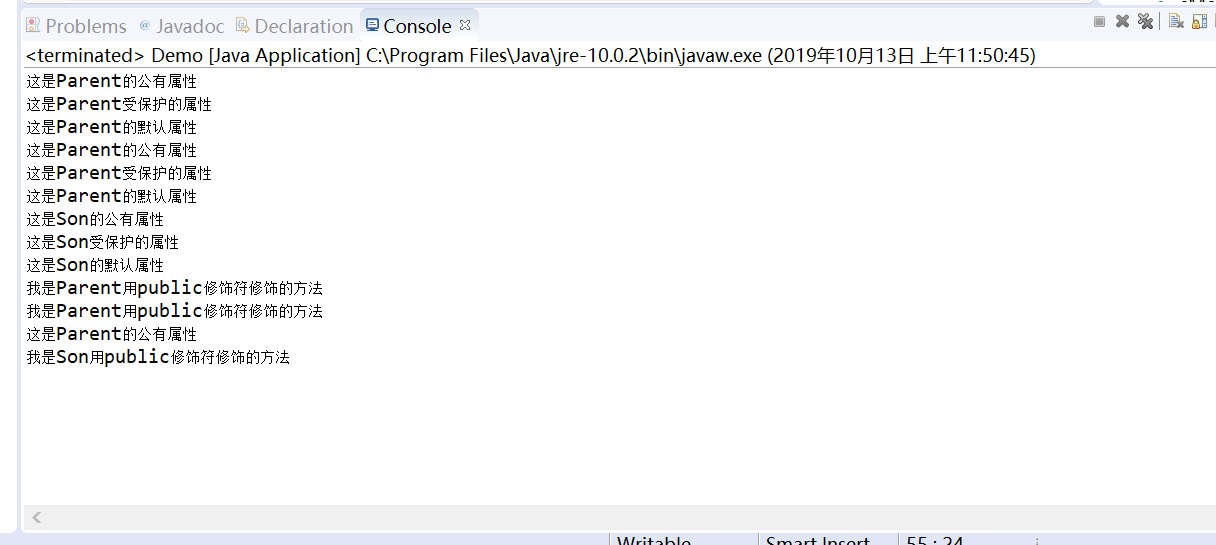
以下是将parent类重新放入一个新的文件中:
parent类代码如下:
package project;
public class Parent {
private String p1 = "这是Parent的私有属性";
public String p2 = "这是Parent的公有属性";
protected String p3 = "这是Parent受保护的属性";
String p4 = "这是Parent的默认属性";
private void pMethod1() {
System.out.println("我是Parent用private修饰符修饰的方法");
}
public void pMethod2() {
System.out.println("我是Parent用public修饰符修饰的方法");
}
protected void pMethod3() {
System.out.println("我是Parent用protected修饰符修饰的方法");
}
void pMethod4() {
System.out.println("我是Parent无修饰符修饰的方法");
}
}
son类代码如下:
package project;
class Son extends Parent{
private String s1 = "这是Son的私有属性";
public String s2 = "这是Son的公有属性";
protected String s3 = "这是Son受保护的属性";
String s4 = "这是Son的默认属性";
public void sMethod1() {
System.out.println(p2);//分别尝试显示Parent类的p1、p2、p3、p4值
System.out.println("我是Son用public修饰符修饰的方法");
}
private void sMethod2() {
System.out.println("我是Son用private修饰符修饰的方法");
}
protected void sMethod3() {
System.out.println("我是Son用protected修饰符修饰的方法");
}
void sMethod4() {
System.out.println("我是Son无修饰符修饰的方法");
}
}
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent parent=new Parent();
Son son=new Son();
System.out.println(parent.p2);
System.out.println(parent.p3);
System.out.println(parent.p4);
System.out.println(son.s2);
System.out.println(son.s3);
parent.pMethod3();
son.sMethod1();
son.pMethod3();
}
}
程序运行结果如下:
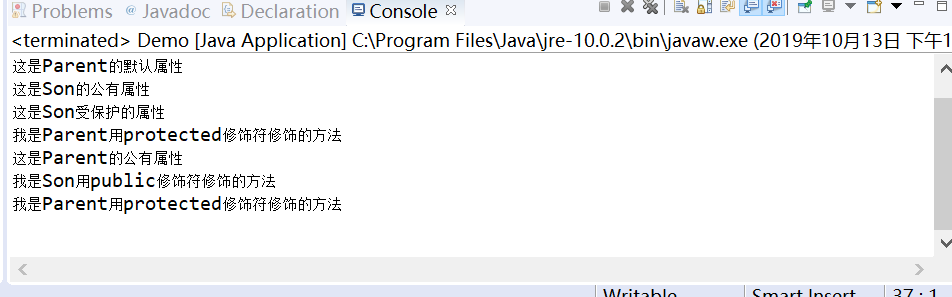
下面是将parent类放入以自己名字命名的包里面
以下是Demo.java文件里的相关代码:
package project;
import wll.Parent;
class Son extends Parent{
private String s1 = "这是Son的私有属性";
public String s2 = "这是Son的公有属性";
protected String s3 = "这是Son受保护的属性";
String s4 = "这是Son的默认属性";
public void sMethod1() {
System.out.println(p2);//分别尝试显示Parent类的p1、p2、p3、p4值
System.out.println("我是Son用public修饰符修饰的方法");
}
private void sMethod2() {
System.out.println("我是Son用private修饰符修饰的方法");
}
protected void sMethod3() {
System.out.println("我是Son用protected修饰符修饰的方法");
}
void sMethod4() {
System.out.println("我是Son无修饰符修饰的方法");
}
}
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent parent=new Parent();
Son son=new Son();
System.out.println(parent.p2);
System.out.println(son.s2);
System.out.println(son.s3);
son.sMethod1();
}
}
以下是parent类的代码:
package wll;
public class Parent {
private String p1 = "这是Parent的私有属性";
public String p2 = "这是Parent的公有属性";
protected String p3 = "这是Parent受保护的属性";
String p4 = "这是Parent的默认属性";
private void pMethod1() {
System.out.println("我是Parent用private修饰符修饰的方法");
}
public void pMethod2() {
System.out.println("我是Parent用public修饰符修饰的方法");
}
protected void pMethod3() {
System.out.println("我是Parent用protected修饰符修饰的方法");
}
void pMethod4() {
System.out.println("我是Parent无修饰符修饰的方法");
}
}
以下是放入不同包里的运行结果:
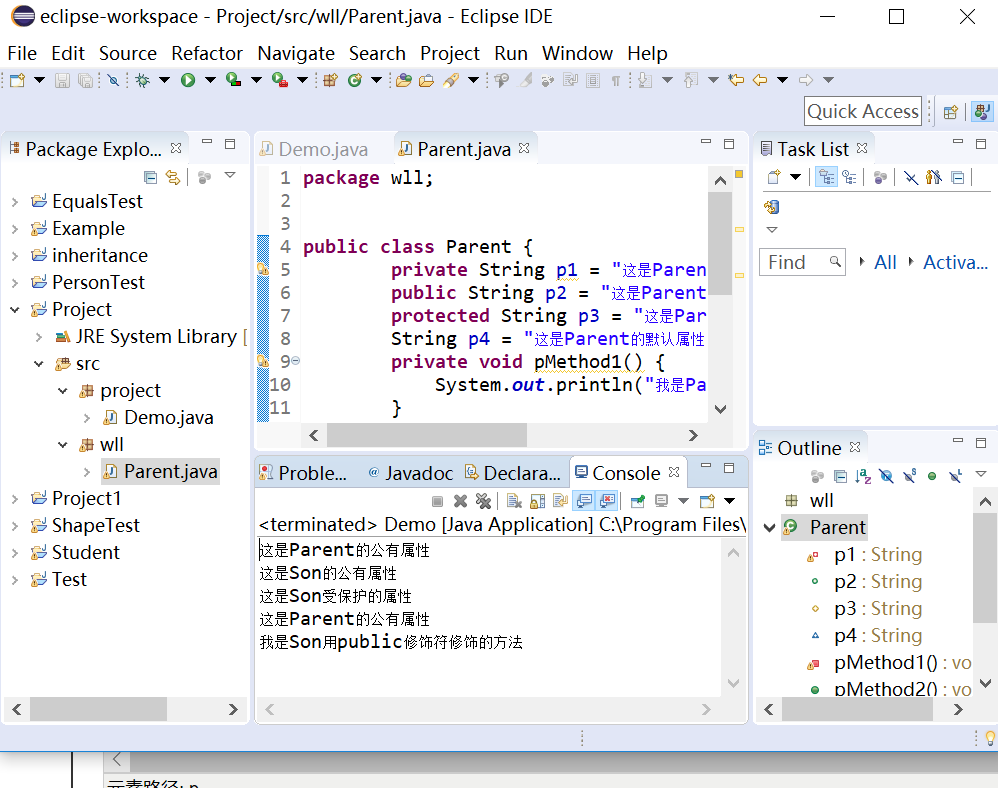
这个实验主要是让我们了解关于四种访问权限的修饰符:
| 位置 | private | 默认 | protected | public |
| 同一个类 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 同一个包里的类 | 否 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
|
不同包内的子类 |
否 | 否 | 是 | 是 |
| 不同包并且不是子类 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 是 |
实验2:导入第5章以下示例程序,测试并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
a)运行教材程序5-8、5-9、5-10,结合程序运行结果理解程序(教材174页-177页);
b) 删除程序中Employee类、Manager类中的equals()、hasCode()、toString()方法,背录删除方法,在代码录入中理解类中重写Object父类方法的技术要点。
Employee类代码如下:
package equals; import java.time.*;
import java.util.Objects; public class Employee
{
private String name; //实例域定义
private double salary;
private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)//构造器定义
{
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day);
} public String getName()
{
return name;
} public double getSalary()
{
return salary;
} public LocalDate getHireDay()
{
return hireDay;
} public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise = salary * byPercent / ;
salary += raise;
} public boolean equals(Object otherObject)
{
// 快速检查对象是否相同
//这里获得一个对象参数,第一个if语句判断两个引用是否是同一个,如果是那么这两个对象肯定相等
if (this == otherObject) return true; // 如果显式参数为空,则必须返回false
if (otherObject == null) return false; // getClass()方法是得到对象的类,如果两个对象的类不一样,那么就不相等
if (getClass() != otherObject.getClass()) return false; //现在我们知道另一个对象是非空雇员
//在以上判断完成,再将得到的参数对象强制转换为该对象,考虑到父类引用子类的对象的出现,然后再判断对象的属性是否相同 var other = (Employee) otherObject; //测试字段是否具有相同的值
return Objects.equals(name, other.name)
&& salary == other.salary && Objects.equals(hireDay, other.hireDay);
} public int hashCode()
// 哈希散列
{
return Objects.hash(name, salary, hireDay);
}
// toString()方法,可自动生成
public String toString() {
return getClass().getName() + "[name=" + name + ",salary=" + salary + ",hireDay="
+ hireDay + "]";
}
}
EqualsTest类代码如下:
package equals; /**
* This program demonstrates the equals method.
* @version 1.12 2012-01-26
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class EqualsTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
var alice1 = new Employee("Alice Adams", , , , ); //创建对象,并初始化
var alice2 = alice1;
var alice3 = new Employee("Alice Adams", , , , );
var bob = new Employee("Bob Brandson", , , , ); System.out.println("alice1 == alice2: " + (alice1 == alice2)); System.out.println("alice1 == alice3: " + (alice1 == alice3)); System.out.println("alice1.equals(alice3): " + alice1.equals(alice3)); System.out.println("alice1.equals(bob): " + alice1.equals(bob)); System.out.println("bob.toString(): " + bob); var carl = new Manager("Carl Cracker", , , , );
var boss = new Manager("Carl Cracker", , , , );
boss.setBonus();
System.out.println("boss.toString(): " + boss);
System.out.println("carl.equals(boss): " + carl.equals(boss));
System.out.println("alice1.hashCode(): " + alice1.hashCode());
System.out.println("alice3.hashCode(): " + alice3.hashCode());
System.out.println("bob.hashCode(): " + bob.hashCode());
System.out.println("carl.hashCode(): " + carl.hashCode());
}
}
Manager类代码如下:
package equals; public class Manager extends Employee
{
private double bonus; public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
{
super(name, salary, year, month, day);
bonus = ;
} public double getSalary()
{
double baseSalary = super.getSalary();
return baseSalary + bonus;
} public void setBonus(double bonus)
{
this.bonus = bonus;
} public boolean equals(Object otherObject)
{
if (!super.equals(otherObject)) return false;
var other = (Manager) otherObject;
//检查这个和其他属于同一个类
return bonus == other.bonus;
} public int hashCode()
{
return java.util.Objects.hash(super.hashCode(), bonus);
} public String toString()
{
return super.toString() + "[bonus=" + bonus + "]";
}
}
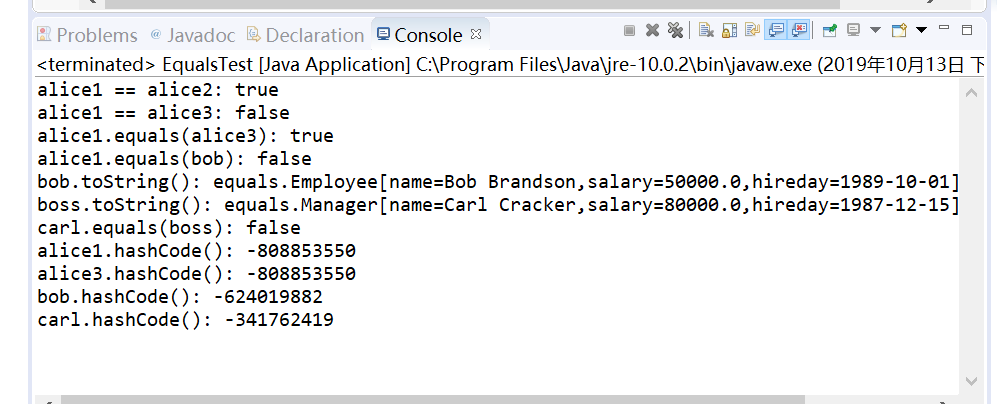
其运行结果如下:

删除程序中Employee类、Manager类中的equals()、hasCode()、toString()方法,背录删除方法后代码如下:
Override后Manager类代码如下:
package equals; public class Manager extends Employee
{
private double bonus;
public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) {
super(name, salary, year, month, day);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
bonus = ;
}
public void setBonus(double bonus) {
this.bonus = bonus;
}
@Override
public double getSalary() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
double baseSalary= super.getSalary();
return baseSalary+bonus;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object otherObject) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(!super.equals(otherObject)) return false;
Manager other=(Manager)otherObject;
return bonus==other.bonus;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return super.hashCode()+*new Double(bonus).hashCode();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return super.toString()+"[bonus="+bonus+"]";
} }
Override后Employee代码如下:
package equals; import java.time.*;
import java.util.Objects; public class Employee
{
private String name; //实例域定义
private double salary;
private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)//构造器定义
{
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
} public double getSalary() {
return salary;
} public LocalDate getHireDay() {
return hireDay;
}
public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise=salary*byPercent/;
salary+=raise;
} @Override
public boolean equals(Object otherObject) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(this==otherObject) return true;
if(this==null) return false;
if(getClass() != otherObject.getClass()) return false;
Employee other=(Employee)otherObject;
return Objects.equals(name,other.name)&&salary == other.salary&&Objects.equals(hireDay,other.hireDay);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return Objects.hash(name,salary,hireDay);
} @Override
public String toString() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return getClass().getName()+"[name="+name+",salary="+salary+",hireday="+hireDay+"]";
} }
其运行结果如下:
测试程序2:
a) 在elipse IDE中调试运行程序5-11(教材182页),结合程序运行结果理解程序;
b) 掌握ArrayList类的定义及用法;
c) 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释;
e)设计适当的代码,测试ArrayList类的set()、get()、remove()、size()等方法的用法。
程序代码如下:
package arrayList; import java.util.*; /**
* This program demonstrates the ArrayList class.
* @version 1.11 2012-01-26
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ArrayListTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// fill the staff array list with three Employee objects
ArrayList<Employee> staff = new ArrayList<Employee>(); //声明和构造一个保存Employee对象的数组列表 staff.add(new Employee("Carl Cracker", , , , ));//使用add方法将元素添加到数组列表中
staff.add(new Employee("Harry Hacker", , , , ));
staff.add(new Employee("Tony Tester", , , , )); // raise everyone's salary by 5%
for (Employee e : staff)
e.raiseSalary(); // print out information about all Employee objects
for (Employee e : staff)
System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary() + ",hireDay="
+ e.getHireDay());
}
}
Employee类代码如下:
package arrayList; import java.time.*; public class Employee
{
private String name;
private double salary;
private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
{
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day);
} public String getName()
{
return name;
} public double getSalary()
{
return salary;
} public LocalDate getHireDay()
{
return hireDay;
} public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise = salary * byPercent / ;
salary += raise;
}
}
运行结果如下:
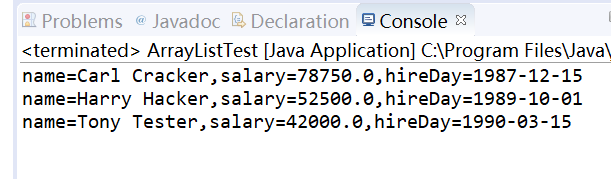
在程序中添加remove(),get(),size()方法后代码如下:
package arrayList;
import java.util.*;
/**
* This program demonstrates the ArrayList class.
* @version 1.11 2012-01-26
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ArrayListTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// fill the staff array list with three Employee objects
ArrayList<Employee> staff = new ArrayList<Employee>(); //声明和构造一个保存Employee对象的数组列表
staff.add(new Employee("Carl Cracker", , , , ));//使用add方法将元素添加到数组列表中
staff.add(new Employee("Harry Hacker", , , , ));
staff.add(new Employee("Tony Tester", , , , ));
staff.remove(); //从数组列表中删除元素
int n = staff.size();
System.out.println(n);
System.out.println(staff.get()!=staff.get());
// raise everyone's salary by 5%
for (Employee e : staff)
e.raiseSalary();
// print out information about all Employee objects
for (Employee e : staff)
System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary() + ",hireDay="
+ e.getHireDay());
}
}
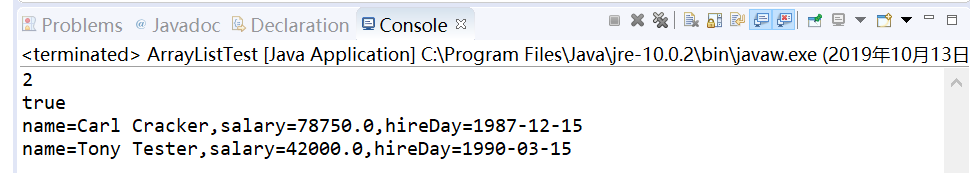
测试程序3:
a) 编辑、编译、调试运行程序5-12(教材189页),结合运行结果理解程序;
b)掌握枚举类的定义及用法;
c)在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释;
d)删除程序中Size枚举类,背录删除代码,在代码录入中掌握枚举类的定义要求。
程序代码如下:
package enums; import java.util.*; /**
* This program demonstrates enumerated types.
* @version 1.0 2004-05-24
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class EnumTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
var in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a size: (SMALL, MEDIUM, LARGE, EXTRA_LARGE) ");
String input = in.next().toUpperCase();
Size size = Enum.valueOf(Size.class, input); //静态方法valueOf
System.out.println("size=" + size);
System.out.println("abbreviation=" + size.getAbbreviation());
if (size == Size.EXTRA_LARGE)
System.out.println("Good job--you paid attention to the _.");
}
}
//在枚举类型中添加一些构造器、方法和域
enum Size
{
SMALL("S"), MEDIUM("M"), LARGE("L"), EXTRA_LARGE("XL"); //实例名 private Size(String abbreviation) { this.abbreviation = abbreviation; }
public String getAbbreviation() { return abbreviation; } private String abbreviation;
}
程序运行结果如下:
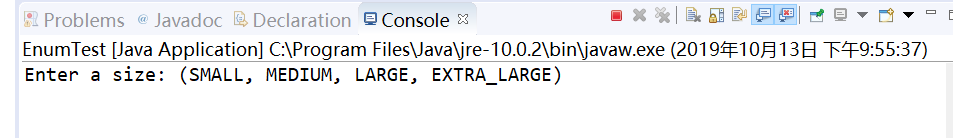
删除程序中Size枚举类override后代码如下:
package enums; import java.util.*; /**
* This program demonstrates enumerated types.
* @version 1.0 2004-05-24
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class EnumTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
var in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a size: (SMALL, MEDIUM, LARGE, EXTRA_LARGE) ");
String input = in.next().toUpperCase();
Size size = Enum.valueOf(Size.class, input); //静态方法valueOf
System.out.println("size=" + size);
System.out.println("abbreviation=" + size.getAbbreviation());
if (size == Size.EXTRA_LARGE)
System.out.println("Good job--you paid attention to the _.");
}
}
//在枚举类型中添加一些构造器、方法和域
enum Size
{
SMALL("S"), MEDIUM("M"), LARGE("L"), EXTRA_LARGE("XL"); //实例名 private Size(String abbreviation) { this.abbreviation = abbreviation; }
@Override
public String toString() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return super.toString();
} public String getAbbreviation() {
return abbreviation;
}
public void setAbbreviation(String abbreviation) {
this.abbreviation = abbreviation;
} private String abbreviation;
}
测试程序4:录入以下代码,结合程序运行结果了解方法的可变参数用法
代码如下:
public class TestVarArgus {
public static void dealArray(int... intArray){
for (int i : intArray)
System.out.print(i +" ");
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
dealArray();
dealArray();
dealArray(, , );
}
}
程序运行结果如下:
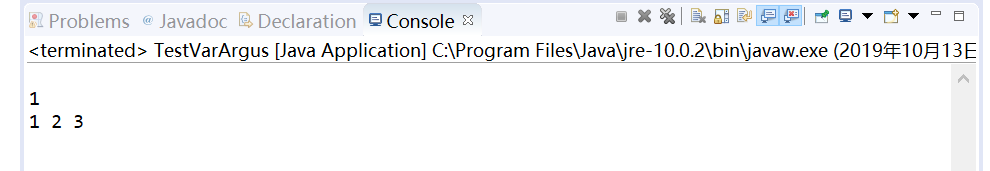
实验3:编程练习:参照输出样例补全程序,使程序输出结果与输出样例一致。
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Son son = new Son();
son.method();
}
}
class Parent {
Parent() {
System.out.println("Parent's Constructor without parameter");
}
Parent(boolean b) {
System.out.println("Parent's Constructor with a boolean parameter");
}
public void method() {
System.out.println("Parent's method()");
}
}
class Son extends Parent {
//补全本类定义
}
要求输出样式如下:
Parent's Constructor with a boolean parameter
Son's Constructor without parameter
Son's method()
Parent's method()
补全代码后如下:
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Son son = new Son();
son.method();
}
}
class Parent {
Parent() {
System.out.println("Parent's Constructor without parameter");
}
Parent(boolean b) {
System.out.println("Parent's Constructor with a boolean parameter");
}
public void method() {
System.out.println("Parent's method()");
}
}
class Son extends Parent {
Son(){
super(false);
System.out.println("Son's Constructor without parameter");
public void method(){
System.out.println("Son's method()");
super.method();
}
}
程序运行结果如下:

第二部分:实验总结
在本次实验中我掌握了四种访问权限修饰符的用法及其特点,Object类的用途及常用的API,并且了解了有关ArrayList类的定义及用法,知道了枚举类定义的方法,但是对枚举类的方法和用途还不太清楚,还有点模糊,对ArrayList的方法还不够熟练,在本次实验3中补全定义,感觉自己做得不太好,对继承之间的关系有点混乱,之后自己会通过问老师或者助教来将相关知识点弄懂掌握,同时也会通过线上的学习将知识点再次巩固。
最新文章
- UDP
- python基础-函数式编程
- 数据结构图文解析之:哈夫曼树与哈夫曼编码详解及C++模板实现
- CentOS - FTP server
- Paths_Quartz2D
- 18 TaskScheduler任务调度器抽象基类——Live555源码阅读(一)任务调度相关类
- sass初步认识3
- EditPlus添加到右键菜单
- Qt 延时
- linux gcc++漏洞:普通用户获得root权限
- c语言分析函数调用关系图(call graph)的几种方法
- 并发编程(一): POSIX 使用互斥量和条件变量实现生产者/消费者问题
- Android群英传帝落篇——程序人生,路漫漫其修远兮,吾将上下而求索!
- Eclipse中导入项目后js报错解决方法
- docker info 警告"WARNING: No swap limit support"
- ActiveMQ入门案例-生产者代码实现
- SpringBoot邮件发送
- paste
- spring boot 之 spring task(定时任务)
- Tarjan学习笔记