Struts—自定义一个简单的mystruct
传统mvc开发总结:
1. 跳转代码写死,不灵活
2. 每次都去写servlet,web.xml中配置servlet!
(配置目的: 请求, Servlet处理类)
一个简单的struct案例,描述如下
登陆、注册
登陆成功 首页
登入失败 登入页
注册成功 登陆页
整理如下
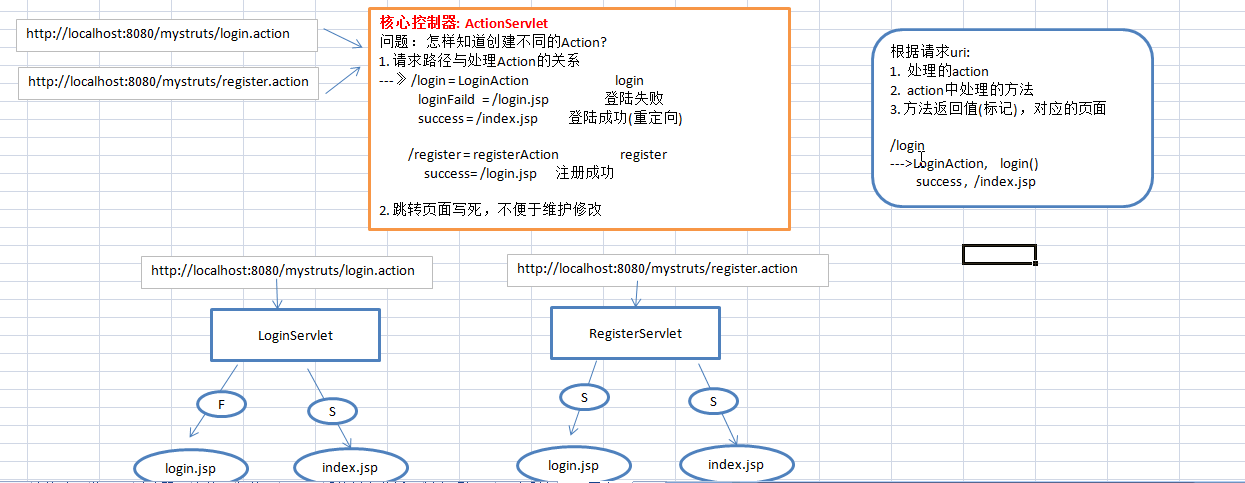
项目列表如下

代码实现
前台页面登入页:
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/login.action" name="frmLogin" method="post">
用户名: <input type="text" name="name"> <br/>
密码: <input type="text" name="pwd"> <br/>
<input type="submit" value="登陆"> <br/>
</form>
注册页:
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/register.action" name="frmRegister" method="post">
用户名: <input type="text" name="name"> <br/>
密码: <input type="text" name="pwd"> <br/>
<input type="submit" value="注册"> <br/>
</form>
首页
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<title>index</title>
</head> <body>
欢迎你的到来,${sessionScope.userInfo.name }
</body>
</html>
后台处理代码
1、假设有一个用户类
package com.gqx.entity;
public class User {
private String name;
private String pwd;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPwd() {
return pwd;
}
public void setPwd(String pwd) {
this.pwd = pwd;
}
}
2、还有一个UserDao类,处理用户的登入问题与注册问题,然后则是还有一个业务逻辑层service
package com.gqx.dao; import com.gqx.entity.User;
public class UserDao { // 模拟登陆
public User login(User user){
if ("gqxing".equals(user.getName()) && "888".equals(user.getPwd()) ){
// 登陆成功
return user;
}
// 登陆失败
return null;
} // 模拟注册
public void register(User user) {
System.out.println("注册成功:用户," + user.getName());
}
}
service
package com.gqx.service; import com.gqx.dao.UserDao;
import com.gqx.entity.User; public class UserService {
private UserDao dao=new UserDao();
// 模拟登陆
public User login(User user){
return dao.login(user); } // 模拟注册
public void register(User user) {
dao.register(user);
}
}
3、mystruct.xml文件,对整个页面跳转的逻辑的配置,每一action对应的result表示要跳转的页面的信息和处理他的相关类
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<mystruct>
<package>
<!-- 配置请求路径,与处理action类的关系 -->
<!--
1. 请求路径与处理Action的关系
/login = LoginAction login
success = /index.jsp 登陆成功(重定向)
loginFaild = /login.jsp 登陆失败
-->
<action name="login" class="com.gqx.framework.action.LoginAction" method="login" >
<result name="loginSuccess" type="redirect">/index.jsp</result>
<result name="loginFailed">/login.jsp</result> <!-- 默认是转发 -->
</action> <action name="register" class="com.gqx.framework.action.RegisterAction" method="register">
<result name="registerSuccess">/login.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</mystruct>
4、写两个类分别用来处理登入和注册响应这两个事件(注册事件和登入事件)。注意这不和servlet相同,这里返回的是一种状态(对应着前面的struct配置的xml文件中要跳转的页面)。
LoginAction类
package com.gqx.framework.action; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import com.gqx.entity.User;
import com.gqx.service.UserService;
/**
* Action表示动作类
* 1. 一个servlet对应一个action
* 2. action中负责处理具体的请求
*/
public class LoginAction { /**
* 处理登陆请求
*/
public Object login(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
Object uri = null; // 1. 获取请求数据,封装
String name = request.getParameter("name");
String pwd = request.getParameter("pwd");
User user = new User();
user.setName(name);
user.setPwd(pwd); // 2. 调用Service
UserService userService = new UserService();
User userInfo = userService.login(user);
// 3. 跳转
if (userInfo == null) {
// 登陆失败
uri="loginFailed"; //login.jsp
} else {
// 登陆成功
request.getSession().setAttribute("userInfo", userInfo);
// 首页
uri ="loginSuccess"; //index.jsp
}
return uri;
}
}
RegisterAction类
package com.gqx.framework.action; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import com.gqx.entity.User;
import com.gqx.service.UserService; public class RegisterAction {
/*
* 处理注册事件
*/
public Object register(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 1. 获取请求数据,封装
String name = request.getParameter("name");
String pwd = request.getParameter("pwd");
User user = new User();
user.setName(name);
user.setPwd(pwd); // 2. 调用Service
UserService userService = new UserService();
userService.register(user);
return "registerSuccess"; //login.jsp }
}
5、为了能更好的解析mystruct.xml文件,这里写了几个javabean去封装这个xml文件的信息
首先是对result(<result name="loginSuccess" type="redirect">/index.jsp</result>)的信息封装类
package com.gqx.framework.bean;
/**
* 封装结果视图
* <result name="loginSuccess" type="redirect">/index.jsp</result>
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class Result {
private String name; //封装结果的标记
private String type; //封装跳转类型,默认为“redirect”—重定向
private String page; //封装跳转的页面
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getPage() {
return page;
}
public void setPage(String page) {
this.page = page;
}
}
然后是action节点的封装
package com.gqx.framework.bean; import java.util.Map; /**
* 封装action节点
* <action name="login" class="com.gqx.framework.action.LoginAction" method="login" >
<result name="loginSuccess" type="redirect">/index.jsp</result>
<result name="loginFailed">/login.jsp</result> <!-- 默认是转发 -->
* </action>
*/
public class ActionMapping { private String name; //封装路径名称
private String className; //封装action的类全名
private String method; //封装处理方法
private Map<String, Result> result; //封装视图集合
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getClassName() {
return className;
}
public void setClassName(String className) {
this.className = className;
}
public String getMethod() {
return method;
}
public void setMethod(String method) {
this.method = method;
}
public Map<String, Result> getResult() {
return result;
}
public void setResult(Map<String, Result> result) {
this.result = result;
} }
最后一个则是对整个action的管理,即管理着mystruct的类,在这里去解析xml文件(这里用到了dom4j的jar包)同时将解析的信息封装到action中去,在这里的构造方法中传入了init()函数(该函数用于封装action信息),然后通过本类去操控需求
package com.gqx.framework.bean; import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map; import javax.management.RuntimeErrorException; import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader; /**
* 加载配置文件,封装整个mystruct.xml
* @author Administrator
*
*/ public class ActionMappingManager {
//保存action的集合(根据action的name去拿result)
Map<String , ActionMapping> allAction; //由于init方法无法被外界被调用(private修饰),这里要写一个无参的构造方法去调用
public ActionMappingManager() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
allAction=new HashMap<String, ActionMapping>();
//初始化
this.init();
} /**
* 根据请求路径名称,返回action映射对象
* 即有action的name返回一个由actionMapping包装的如下结构
* <action name="login" class="com.gqx.framework.action.LoginAction" method="login" >
<result name="loginSuccess" type="redirect">/index.jsp</result>
<result name="loginFailed">/login.jsp</result> <!-- 默认是转发 -->
</action>
*/
/**
*
* @param actionName 当前返回路径
* @return 返回配置文件中代表action节点的actionMapping对象
*/
public ActionMapping getActionMapping(String actionName) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (actionName == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("传入参数不能为空!");
}
ActionMapping actionMapping=allAction.get(actionName);
if (actionMapping==null) {
throw new RuntimeException("路径在mystruct中找不到!请检查。");
}
return actionMapping;
} //初始化allAction集合
private void init() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
/****************dom4j读取配置文件**********/
try {
//1、得到解析器
SAXReader reader=new SAXReader();
//得到src/下的文件流
InputStream insStream=this.getClass().getResourceAsStream("/mystruct.xml");
//2、加载文件
Document doc=reader.read(insStream);
//3、得到根文件
Element rootElement=doc.getRootElement();
//4、得到package节点
Element elem_package=rootElement.element("package");
//5/5得到package节点下的所有action节点
List<Element> listAction=elem_package.elements("action");
//6、遍历action且封装
for (Element element : listAction) {
//6、1封装一个ActionMapping对象
ActionMapping actionMapping=new ActionMapping();
/**
* <action name="login" class="com.gqx.framework.action.LoginAction" method="login" >
<result name="loginSuccess" type="redirect">/index.jsp</result>
<result name="loginFailed">/login.jsp</result> <!-- 默认是转发 -->
</action>
*/
//封装action
actionMapping.setName(element.attributeValue("name"));
actionMapping.setClassName(element.attributeValue("class"));
actionMapping.setMethod(element.attributeValue("method")); //封装action下的result
Map<String, Result> results=new HashMap<String, Result>();
//得到当前action下所有的result子节点
Iterator<Element> iterator=element.elementIterator("result");
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
//当前迭代的每一result
Element element2 = (Element) iterator.next();
Result result =new Result();
//封装
result.setName(element2.attributeValue("name"));
result.setType(element2.attributeValue("type"));
result.setPage(element2.getTextTrim());
//添加到results中
results.put(result.getName(), result);
} actionMapping.setResult(results);
//6、2actionMapping添加到Map集合中
allAction.put(actionMapping.getName(), actionMapping); }
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
throw new RuntimeException("xml读取失败,初始化错误!");
}
} }
6、最后则是写全局的控制器ActionServlet,由它来管理ActionMappingManager中要跳转的页面信息,如外界通过访问http://localhost:8080/mystruct/login.jsp发来http://localhost:8080/mystruct/login.action请求,首先将其解析成login,根据这个login名字在mystruct中找到对应的class类(class="com.gqx.framework.action.LoginAction")和方法(method="login"),同时根据方法名称和参数得到类中的方法,通过反射得到调动其方法,便可得到一个返回的uri(表是状态,如:loginSuccess),然后由配置文件(管理类ActionMappingManager)依据uri来控制要跳转的相应页面。
package com.gqx.framework; import java.io.IOException; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import com.gqx.framework.bean.ActionMapping;
import com.gqx.framework.bean.ActionMappingManager;
import com.gqx.framework.bean.Result; public class ActionServlet extends HttpServlet { /**
* 核心控制器,此项目只有一个servlet
* 拦截所有的以action结尾的请求
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; ActionMappingManager actionMappingManager;
@Override
public void init() throws ServletException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//第一次访问时启动时候执行,希望启动的时候执行,在xml文件中配置load-on-startup在启动的是执行 //配置文件的读取,在ActionMappingManage的构造方法中调用了init方法。
actionMappingManager=new ActionMappingManager();
} public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
//1、获取请求的uri,得到请求的路径名称【login】
String uri=request.getRequestURI(); //得到login,根据login去mystruct.xml配置文件去第2步
String actionName=uri.substring(uri.lastIndexOf("/")+1,uri.indexOf(".action")); // 2、根据路径名称,读取配置文件,得到类的全名
ActionMapping actionMapping=actionMappingManager.getActionMapping(actionName);
String className=actionMapping.getClassName(); //当前请求的处理方法【method="login】
String method=actionMapping.getMethod();
//3、通过反射创建对象,调用方法,获取方法返回的标记
Class<?> clazz=Class.forName(className);
//实例化,创建对象
Object object=clazz.newInstance();
/**
* 这里的参数只能是HttpServletRequest.class,不能是request.class。
* 因为request是一个实现类,而这里必须是以接口.class为参数
*/
Method m=clazz.getDeclaredMethod(method, HttpServletRequest.class,HttpServletResponse.class); //调用方法返回的标记
String returnValue=(String) m.invoke(object,request,response); //4、拿到标记,读取配置文件,对应的标记页面
Result result=actionMapping.getResult().get(returnValue);
//跳转类型
String type=result.getType();
//页面
String page=result.getPage(); //5、跳转
if ("redirect".equals(type)) {
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+page);
}else {
request.getRequestDispatcher(page).forward(request, response);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} } public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doGet(request, response);
} }
最后则是配置这个Actionservlet在服务器的web.xml文件了
<!-- 核心控制器 -->
<servlet>
<description>This is the description of my J2EE component</description>
<display-name>This is the display name of my J2EE component</display-name>
<servlet-name>ActionServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.gqx.framework.ActionServlet</servlet-class>
<!-- 启动的时候执行servlet的初始化方法 -->
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet> <servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ActionServlet</servlet-name>
<!-- 拦截所有的action -->
<url-pattern>*.action</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
最后我们登入的时候就会看到这个效果了:

最新文章
- 2016 windows安装phing:安装成功
- Replication的犄角旮旯(七)-- 一个DDL引发的血案(下)(聊聊logreader的延迟)
- Spark入门实战系列--5.Hive(下)--Hive实战
- JavaScript高级程序设计学习笔记--变量、作用域和内存问题
- RUF MVC5 Repositories Framework Generator代码生成工具介绍和使用
- Maven3路程(六)用Maven创建Spring3 MVC项目
- 【linux】top命令详解
- javascript中的JSON序列化与反序列化
- ipython, 一个 python 的交互式 shell,比默认的python shell 好用得多,支持变量自动补全,自动缩进,支持 bash shell 命令,内置了许多很有用的功能和函数
- HDU POJ 1015 Jury Compromise(陪审团的人选,DP)
- Sublime Text 添加到右键菜单 带菜单图标
- (转)如何向map和reduce脚本传递参数
- SEO-长尾词与分词技术
- powershell-脚本运行权限政策
- Git 日常操作
- Jenkins 利用HTML Publisher plugin实现HTML文档报告展示
- LODOP中预览界面查看打印机的可打区域具体值
- Jquery EasyUI Combotree和 EasyUI tree展开所有父节点和获取完整路径
- vue中使用mui滑动条无法正常滑动
- [android] 手机卫士自定义组合控件