老齐python-基础6(循环 if while for)
2024-08-29 08:29:58
1、条件语句if
依据某个条件,满足这个条件后执行下面的内容
>>> if bool(conj): #语法
do something >>> a = 8
>>> if a == 8:
print(a)
8
1.1 if...elif...else
基本结构:
if 条件 1:
语句块1
elif 条件2:
语句块2
elif 条件3:
语句块3
...
else
语句块4
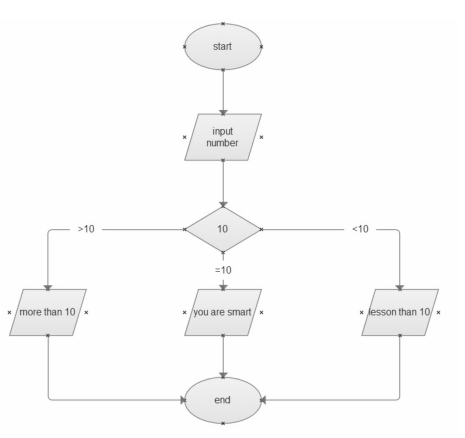
if使用示例程序
#!/usr/bin/env python #调用系统环境的python
#coding:utf-8 #支持中文 python3可省略 print("清输入任意一个整数数字:")
number = int(input()) #用户交互输入函数 if number == 10:
print("您输入的数字是:{}".format(number))
print("You are SMART")
elif number > 10:
print("您输入的数字是:{}".format(number))
print("This number is more than 10.")
else:
print("您输入的数字是:{}".format(number))
print("This number is less than 10.")
1.2三元操作符
三元操作,是条件语句中比较简练的一种赋值方式:
>>> name = "qiwsir" if 29 > 21 else "github"
>>> name
'qiwsir'
如果抽象成为一个公式,三元操作符就是这样的: A = Y if X else Z
如果X为真,那么就执行 A = Y
如果X为假,就执行A = Z
>>> x = 2
>>> y = 8
>>> a = "python" if x > y else "qiwsir"
>>> a
'qiwsir'
>>> b = "python" if x < y else "tajzhang"
>>> b
'python'
2、for循环
for 循环规则:
操作语句
2.1实例:
>>> hello = "world" #赋值语句
>>> for i in hello: #必须是可迭代的类型
print(i)
w
o
r
l
d
>>> for i in range(len(hello)): #得到hello引用字符串长度 为5
print(hello[i]) #对应每个索引输出值,直到最后一个 i=4为止
w
o
r
l
d
2.2多种序列类型for循环:
1)循环列表:
>>> names = ["Newton","Einstein","Hertz","Maxwell","Bohr","Cavendish","Feynman"]
>>> for name in names:
print(name,end="-*-") #end方法help(print)
Newton-*-Einstein-*-Hertz-*-Maxwell-*-Bohr-*-Cavendish-*-Feynman-*-
>>> for i in range(len(names)):
print(names[i])
Newton
Einstein
Hertz
Maxwell
Bohr
Cavendish
Feynman
>>>
2)循环字典:
>>> d = dict([("website","www.itdiffer.com"),("lang","python"),("author","laoqi")])
>>> d
{'website': 'www.itdiffer.com', 'lang': 'python', 'author': 'laoqi'}
>>> for k in d: #获取key
print(k)
website
lang
author
>>> d.keys()
dict_keys(['website', 'lang', 'author'])
>>> for k in d.keys(): #相同方法
print(k)
website
lang
author
>>> for k,v in d.items(): #获取键值
print (k + "-->" + v)
website-->www.itdiffer.com
lang-->python
author-->laoqi
2.3判断对象是否是可迭代的
>>> import collections
>>> isinstance(321,collections.Iterable)
False
>>> isinstance([1,2,3],collections.Iterable)
True
>>> isinstance({"name":"canglaoshi","work":"php"},collections.Iterable)
True
2.4 range(start,stop[,step])
start:开始数值,默认为0,也就是如果不写这项,则认为start=0
stop:结束的数值,这是必须要写的
step:变化的步长,默认是1,坚决不能为0
>>> range(0,9,2)
range(0, 9, 2)
>>> type(range(0,9,2)) #是一个Range类型的对象
<class 'range'>
>>> list(range(0,9,2))
[0, 2, 4, 6, 8
如果是从0开始,步长为1,可以写成range(9)
start=0,step=2,stop=9,值从0开始 结束是start + (n-1)step
>>> range(0,-9,-1)
range(0, -9, -1)
>>> list(range(0,-9,-1))
[0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, -6, -7, -8]
2.5并行迭代
可迭代(iterable):在python中的表现就是用for循环,从对象中获得一定数量的元素.
求两个可迭代对象每个元素的和zip():
>>> c = [1,2,3]
>>> d = [9,8,7,6]
>>> zip(c,d)
<zip object at 0x105912b88>
>>> list(zip(c,d))
[(1, 9), (2, 8), (3, 7)] >>> list(zip(d,c))
[(9, 1), (8, 2), (7, 3)]
>>> m = {"name","lang"}
>>> n = {"tajzhang","python"}
>>> list(zip(m,n))
[('name', 'tajzhang'), ('lang', 'python')]
>>> s = {"name":"tajzhang"}
>>> t = {"lang":"python"}
>>> list(zip(s,t))
[('name', 'lang')]
>>> a = 'tajzhang'
>>> c = [1,2,3]
>>> list(zip(c))
[(1,), (2,), (3,)]
>>> list(zip(a))
[('t',), ('a',), ('j',), ('z',), ('h',), ('a',), ('n',), ('g',)]
>>> a = [1,2,3,4,5]
>>> b = [9,8,7,6,5]
>>> d = []
>>> for x,y in zip(a,b): #使用zip使列表相加
d.append(x+y) >>> d
[10, 10, 10, 10, 10]
zip扩展用法
>>> for x,y in zip(a,b):
d.append(str(x) + ":" +y)
>>> d
['1:python', '2:www.itdiffer.com', '3:tajzhang']
>>> result = [(2,11),(4,13),(6,15),(8,17)]
>>> list(zip(*result))
[(2, 4, 6, 8), (11, 13, 15, 17)]
使用zip解决字典key value调换
方法1:使用for循环
>>> myinfor = {"name":"tajzhang","stie":"www.bokey.io","lang":"python"}
>>> infor = {}
>>> for k,v in myinfor.items():
infor[v] =k
>>> infor
{'tajzhang': 'name', 'www.bokey.io': 'stie', 'python': 'lang'}
方法2:使用zip()
>>> dict(zip(myinfor.values(),myinfor.keys()))
{'tajzhang': 'name', 'www.bokey.io': 'stie', 'python': 'lang'}
解析
>>> myinfor.values()
dict_values(['tajzhang', 'www.bokey.io', 'python'])
>>> myinfor.keys()
dict_keys(['name', 'stie', 'lang'])
>>> temp = zip(myinfor.values(),myinfor.keys()) #压缩成一个列表,每个元素是一个元祖,元祖中第一个是值,第二个是键
>>> temp
<zip object at 0x10239ee08>
>>> dict(temp) #这是函数dict()的功能
{'tajzhang': 'name', 'www.bokey.io': 'stie', 'python': 'lang'}
2.6 enumerate()
功能:类似同事得到元素索引和元素
>>> for i in range(len(week)):
print(week[i] + 'is' + str(i) ) mondayis0
sundayis1
fridayis2
>>> for (i,day) in enumerate(week):
print(day + 'is' + str(i)) mondayis0
sundayis1
fridayis2
使用举例:
>>> seasons = ['Spring','Summer','Fall','Winter']
>>> list(enumerate(seasons))
[(0, 'Spring'), (1, 'Summer'), (2, 'Fall'), (3, 'Winter')]
>>> list(enumerate(seasons,start=1))
[(1, 'Spring'), (2, 'Summer'), (3, 'Fall'), (4, 'Winter')]
>>> mylist = ["tajzhang",703,"python"]
>>> enumerate(mylist)
<enumerate object at 0x1023b6288>
>>> list(enumerate(mylist))
[(0, 'tajzhang'), (1, 703), (2, 'python')]
使用练习:
2.7列表解析
先得到1-9每个整数的平方
>>> power2 = []
>>> for i in range(1,10):
power2.append(i*i) >>> power2
[1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]
>>> squares = [x**2 for x in range(1,10)] #更pythonic的用法
>>> squares
[1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]
>>> mybag = [' glass',' apple',' green leaf']
>>> [one.strip() for one in mybag]
['glass', 'apple', 'green leaf']
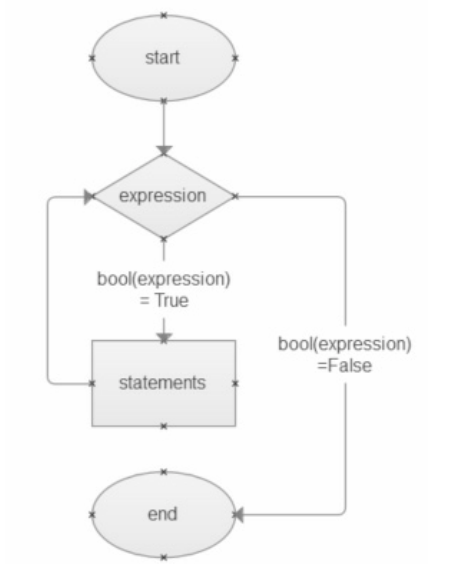
3、while循环
原理图
3.1猜数游戏:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#coding:UTF-8 import random i = 0 while i < 4:
print('*****************')
num = int(input('请输入0-9任意一个数字'))
xnum = random.randint(0,9)
x = 3 - i
if num == xnum:
print('运气真好,猜对了!')
break
elif num > xnum:
print('''您猜大了!\n 正确答案是:%s\n 您还有%s 次机会''' %(xnum,x))
elif num < xnum:
print('''您猜小了!\n 正确答案是:%s\n 您还有%s 次机会''' %(xnum,x))
print('******************')
i += 1
当用户不输入纯数字时候
num_input = ""
if not num_input.isdigit(): #判断输入字符串内是否是纯数字
print('Please input interger.')
elif int(num_input)<0 and int(num_input)>=100:
print("The number should be in 1 to 100.")
else:
print("xxx")
强化版猜数
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#coding:utf-8 import random number = random.randint(1,100) guess = 0 while True:
num_input = input("please input one integer that is in 1 to 100:")
guess += 1 if not num_input.isdigit():
print("Please input interger.")
elif int(num_input) < 0 or int(num_input) >= 100:
print("The number should be in 1 to 100.")
else:
if number == int(num_input):
print("OK,you are good. It is only %d,then you successed" % guess)
elif number > int(num_input):
print("your number is smaller.")
elif number < int(num_input):
print("your number is bigger.")
else:
print("There is something bad,I will not work")
3.2break 和 continue
break:跳出循环体
continue:返回循环开始继续执行
break
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#coding:utf-8 a = 9
while a:
if a%2 == 0:
break
else:
print("{} is odd number".format(a))
a -= 1
print("{} is even number".format(a))
continue
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#coding:utf-8 a = 9
while a:
if a%2 == 0:
a -= 1
continue
else:
print("{} is odd number".format(a))
a -= 1
3.3while..else
#!/usr/bin/env python3
count = 0
while count < 5:
print(conut,"is less than 5")
count = count + 1
else: #遇到else就意味着已经不在while循环内了
print(count,"is not less than 5")
3.4for..else 与上一样,也是跳出循环之后做的事
#!/usr/bin/env python3 from math import sqrt for n in range(99,1,-1):
root = sqrt(n)
if root == int(root):
print(n)
break
else:
print("Nothing")
最新文章
- C# DateTime.ToString的坑
- 华硕U303L通过U盘装系统
- ecshop的特点,持续加新
- 上传文件(单文件)(FormData)(前端代码+.NET服务器端)
- oracle 中触发器增加存储过程commit问题
- struts2文件下载相关信息
- python 练习 26
- about云资源汇总指引V1.4:包括hadoop,openstack,nosql,虚拟化
- [转]Delphi导出Excel的设置操作
- 驱动相关Error
- 小程序input输入框获取焦点时,文字会出现闪动
- python学习第31天
- JS中5种经典继承方式
- php 文件系统函数及目录函数
- 微信小程序:request合法域名检验出错,https://apis.map.qq.com 不在以下 request 合法域名列表中
- Linux 安装 lrzsz,使用 rz、sz 上传下载文件
- 蓝牙Profile的概念和常见种类(转)
- Java基础知识_毕向东_Java基础视频教程笔记(19-21 IO流)
- BZOJ.2806.[CTSC2012]Cheat(广义后缀自动机 DP 单调队列)
- Spark日志清洗