unix下网络编程之I/O复用(一)
什么是I/O复用?
What we need is the capability to tell the kernel that we want to be notified if one or more I/O conditions are ready (i.e., input is ready to be read, or the descriptor is capable of taking more output). This capability is called I/O multiplexing and is provided by the select and poll functions. ——来自《Unix网络编程》第三卷
在很多情况下,使用select或是poll,可以把事件的响应交给底层操作系统来管理,当有I/O事件发生时,操作系统会通知我们。
何时使用I/O复用:
1、When a client is handling multiple descriptors (normally interactive input and a network socket), I/O multiplexing should be used. This is the scenario we described previously.
2、It is possible, but rare, for a client to handle multiple sockets at the same time. We will show an example of this using select in Section 16.5 in the context of a Web client.
3、If a TCP server handles both a listening socket and its connected sockets, I/O multiplexing is normally used.
4、If a server handles both TCP and UDP, I/O multiplexing is normally used.
5、If a server handles multiple services and perhaps multiple protocols, I/O multiplexing is normally used.
——来自《Unix网络编程》第三卷
I/O模型
对于read而言,一般都会涉及到两个过程:
1. Waiting for the data to be ready
2. Copying the data from the kernel to the process
接下来的讨论,会根据这两阶段的操作进行描述。
I/O一共有5大模型:
1、阻塞I/O
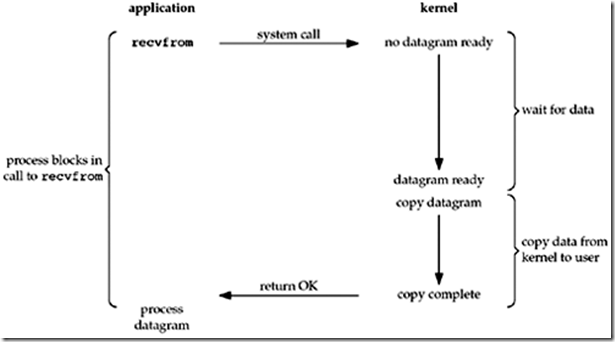
应用进程产生一个system call ,如果内核没有数据准备好,则会一直wait,处于阻塞,当内核数据准备好之后,将会把数据从内核再拷贝到应用进程,这一copy过程也处于阻塞状态。
2、非阻塞I/O
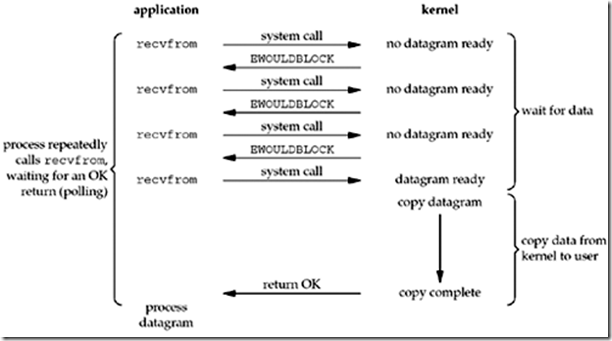
之所以称作为非阻塞I/O,就意味着当应用进程产生一个system call的时候,不管内核的数据是否准备好,都会立即返回。而后,再一次发起call,这是一个轮询的过程。当内核数据准备好之后,便可以正常进行响应。这一过程是非阻塞的。而当数据从内核copy到应用进程的过程,仍然是阻塞,应为要保证数据完整与一致。
3、I/O复用
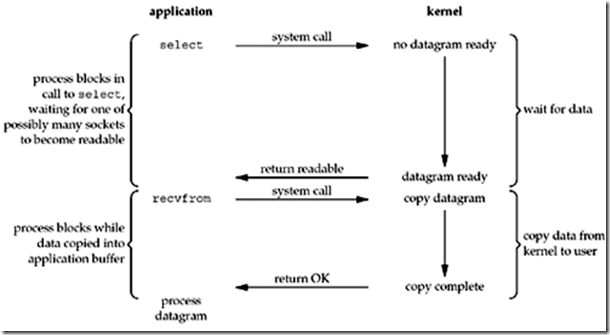
使用I/O复用,一个或多个 system call 阻塞于select 或是 poll,而不是阻塞与真正的调用。当内核有数据准备好的时候,会通知select或是poll,接下来,会发起真正的system call,也就是图片中的recvfrom。之后,便会正常copy数据到应用进程。值得注意的是,I/O复用产生了两次system call,一次select(poll),一次recvfrom。因此,如果进程只是处理单一描述字(descriptor)的话,使用I/O复用不但不会有好的效果,而且还会有额外的系统开销,所以,I/O复用一般都用于处理多个描述字(descriptors)的情况下。
4、信号驱动I/O
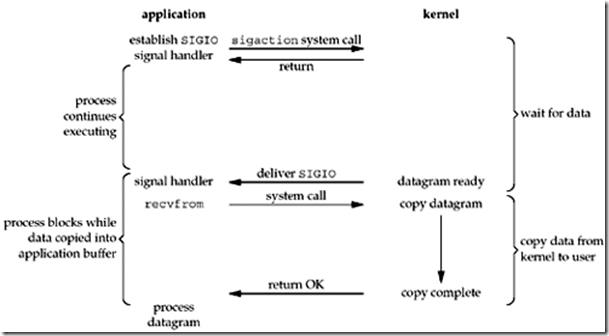
我们可以使用信号驱动I/O,当有描述字准备好后,内核会产生信号来通知应用进程。信号驱动模型不同于上述三种,对于应用进程而言,它在等待接受数据过程中,处于被通知状态。这一过程,相当于一个异步操作。但是,对于内核copy数据到应用进程这一过程,应用进程仍然处于阻塞的状态。
5、异步I/O
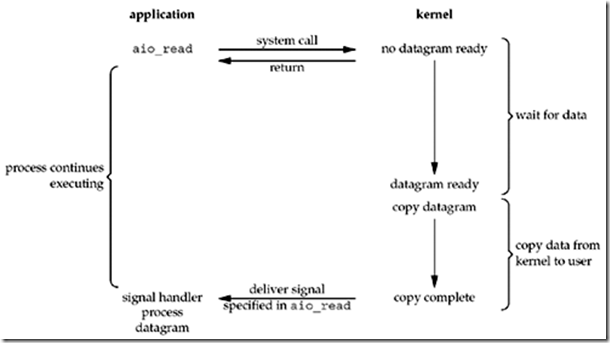
信号驱动I/O模型中,在等待内核数据准备阶段中,是一个异步的过程,而数据copy阶段则是阻塞的,也就是同步的。但是对于异步I/O模型而言,这两个阶段都是异步的。也就说,当引用进程产生一个aio_read后,它会继续执行其他操作,整个过程不会产生任何阻塞。
“We call aio_read (the POSIX asynchronous I/O functions begin with aio_ or lio_) and pass the kernel the descriptor, buffer pointer, buffer size (the same three arguments for read), file offset (similar to lseek), and how to notify us when the entire operation is complete.” ——来自《Unix网络编程》第三卷
5个I/O模型的比较总结:
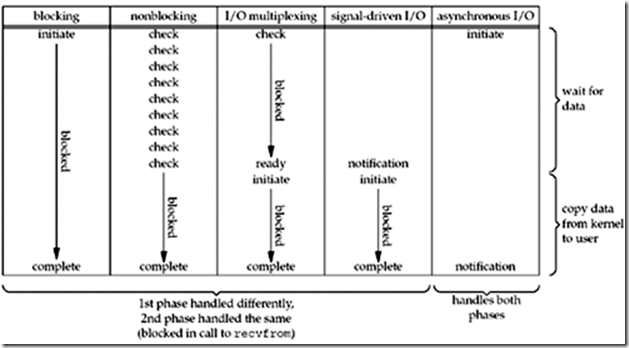
总结:
在本文中,主要介绍了什么是I/O复用,I/O复用的应用场景,已经5大I/O模型的介绍。 在下一篇博文中,会重点介绍Unix环境下select和poll的原理、实际应用以及代码实现。
最新文章
- handsontable学习
- win7 下配置Openssl
- 每天一个linux命令(6):mv命令
- ecshop后台导航修改教程说明
- Redis学习一 五种基本的数据类型
- BZOJ 3107 二进制a+b
- PL/SQL 9.0工具技巧
- UVA11988 Broken KeyBoard
- android xml解析 sax
- NSIS:使用nsWindows.nsh头文件调整窗体大小
- 第1阶段——uboot分析之启动函数bootm命令 (9)
- 入门-什么是webshell?
- Python并发编程协程(Coroutine)之Gevent
- I - Infinite Improbability Drive
- Java开发笔记(二十七)数值包装类型
- centos7下使用LVM给系统硬盘扩容超详细
- leetcode 703数据流中的第K大元素
- foreach 與 reference 的雷
- $Django 等web框架,交互,基础入门
- JPA(四):EntityManager