Openfoam Pstream类探索
对于数值仿真而言,无论是商软或者开源并行计算都是非常重要的,而且想把自身数值仿真能力提升一个层次,必须对并行计算有很好的理解与应用
openfoam并行通信主要通过Pstream类完成
本篇文章进行说明解释
Pstream类,类如其名,parallel_stream,并行计算时使用的信息流
类似的命名方法我们在c++文件读取时说过,std有fstream类读取写入文件/二进制文件,比如说我们要读取文件,会把读取内容放入缓存区内进行操作
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream> // ifstream类需要包含的头文件。
#include <string> // getline()函数需要包含的头文件。
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string filename = R"(./test.txt)";
//ifstream fin(filename, ios::in);
ifstream fin;
fin.open(filename , ios::in);
// 判断打开文件是否成功。
// 失败的原因主要有:1)目录不存在;2)文件不存在;3)没有权限,Linux平台下很常见。
if (fin.is_open() == false)
{
cout << "打开文件" << filename << "失败。\n"; return 0;
}
string buffer;
while (fin >> buffer)
{
cout << buffer << endl;
}
fin.close(); // 关闭文件,fin对象失效前会自动调用close()。
cout << "操作文件完成。\n";
}
类似的openfoam也有PstreamBuffers类进行并行通信缓冲
可以这样使用:
PstreamBuffers pBuffers(Pstream::commsTypes::nonBlocking);
for (label proci = 0; proci < Pstream::nProcs(); proci++)
{
if (proci != Pstream::myProcNo())
{
someObject vals;
UOPstream str(proci, pBuffers);
str << vals;
}
}
pBuffers.finishedSends(); // no-op for blocking
for (label proci = 0; proci < Pstream::nProcs(); proci++)
{
if (proci != Pstream::myProcNo())
{
UIPstream str(proci, pBuffers);
someObject vals(str);
}
}
上面这个程序可以看到,先后使用UOPstream与UIPstream进行缓冲区的文件输出与读取,这就很像ofstream类与ifstream类,甚至命名方式上都有几分相似,我们打开相应的继承关系图
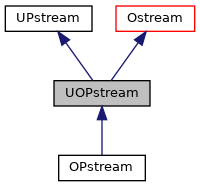
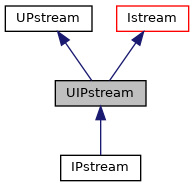
二者分别服务于IPstream类与OPstream类,我们再打开今天文章的主角,Pstream类继承关系图
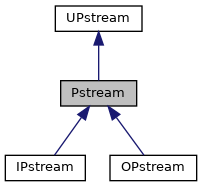
发现IPstream类与OPstream类是Pstream类的衍生类,Pstream类是其基础
打开Pstream类的源码:
点击查看代码
namespace Foam
{
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*\
Class Pstream Declaration
\*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
class Pstream
:
public UPstream
{
protected:
// Protected data
//- Transfer buffer
DynamicList<char> buf_;
public:
// Declare name of the class and its debug switch
ClassName("Pstream");
// Constructors
//- Construct given optional buffer size
Pstream
(
const commsTypes commsType,
const label bufSize = 0
)
:
UPstream(commsType),
buf_(0)
{
if (bufSize)
{
buf_.setCapacity(bufSize + 2*sizeof(scalar) + 1);
}
}
// Gather and scatter
//- Gather data. Apply bop to combine Value
// from different processors
template<class T, class BinaryOp>
static void gather
(
const List<commsStruct>& comms,
T& Value,
const BinaryOp& bop,
const int tag,
const label comm
);
//- Like above but switches between linear/tree communication
template<class T, class BinaryOp>
static void gather
(
T& Value,
const BinaryOp& bop,
const int tag = Pstream::msgType(),
const label comm = Pstream::worldComm
);
//- Scatter data. Distribute without modification. Reverse of gather
template<class T>
static void scatter
(
const List<commsStruct>& comms,
T& Value,
const int tag,
const label comm
);
//- Like above but switches between linear/tree communication
template<class T>
static void scatter
(
T& Value,
const int tag = Pstream::msgType(),
const label comm = Pstream::worldComm
);
// Combine variants. Inplace combine values from processors.
// (Uses construct from Istream instead of <<)
template<class T, class CombineOp>
static void combineGather
(
const List<commsStruct>& comms,
T& Value,
const CombineOp& cop,
const int tag,
const label comm
);
//- Like above but switches between linear/tree communication
template<class T, class CombineOp>
static void combineGather
(
T& Value,
const CombineOp& cop,
const int tag = Pstream::msgType(),
const label comm = Pstream::worldComm
);
//- Scatter data. Reverse of combineGather
template<class T>
static void combineScatter
(
const List<commsStruct>& comms,
T& Value,
const int tag,
const label comm
);
//- Like above but switches between linear/tree communication
template<class T>
static void combineScatter
(
T& Value,
const int tag = Pstream::msgType(),
const label comm = Pstream::worldComm
);
// Combine variants working on whole List at a time.
template<class T, class CombineOp>
static void listCombineGather
(
const List<commsStruct>& comms,
List<T>& Value,
const CombineOp& cop,
const int tag,
const label comm
);
//- Like above but switches between linear/tree communication
template<class T, class CombineOp>
static void listCombineGather
(
List<T>& Value,
const CombineOp& cop,
const int tag = Pstream::msgType(),
const label comm = Pstream::worldComm
);
//- Scatter data. Reverse of combineGather
template<class T>
static void listCombineScatter
(
const List<commsStruct>& comms,
List<T>& Value,
const int tag,
const label comm
);
//- Like above but switches between linear/tree communication
template<class T>
static void listCombineScatter
(
List<T>& Value,
const int tag = Pstream::msgType(),
const label comm = Pstream::worldComm
);
// Combine variants working on whole map at a time. Container needs to
// have iterators and find() defined.
template<class Container, class CombineOp>
static void mapCombineGather
(
const List<commsStruct>& comms,
Container& Values,
const CombineOp& cop,
const int tag,
const label comm
);
//- Like above but switches between linear/tree communication
template<class Container, class CombineOp>
static void mapCombineGather
(
Container& Values,
const CombineOp& cop,
const int tag = Pstream::msgType(),
const label comm = UPstream::worldComm
);
//- Scatter data. Reverse of combineGather
template<class Container>
static void mapCombineScatter
(
const List<commsStruct>& comms,
Container& Values,
const int tag,
const label comm
);
//- Like above but switches between linear/tree communication
template<class Container>
static void mapCombineScatter
(
Container& Values,
const int tag = Pstream::msgType(),
const label comm = UPstream::worldComm
);
// Gather/scatter keeping the individual processor data separate.
// Values is a List of size UPstream::nProcs() where
// Values[UPstream::myProcNo()] is the data for the current processor.
//- Gather data but keep individual values separate
template<class T>
static void gatherList
(
const List<commsStruct>& comms,
List<T>& Values,
const int tag,
const label comm
);
//- Like above but switches between linear/tree communication
template<class T>
static void gatherList
(
List<T>& Values,
const int tag = Pstream::msgType(),
const label comm = UPstream::worldComm
);
//- Scatter data. Reverse of gatherList
template<class T>
static void scatterList
(
const List<commsStruct>& comms,
List<T>& Values,
const int tag,
const label comm
);
//- Like above but switches between linear/tree communication
template<class T>
static void scatterList
(
List<T>& Values,
const int tag = Pstream::msgType(),
const label comm = UPstream::worldComm
);
// Exchange
//- Helper: exchange contiguous data. Sends sendData, receives into
// recvData. If block=true will wait for all transfers to finish.
template<class Container, class T>
static void exchange
(
const UList<Container>& sendData,
const labelUList& recvSizes,
List<Container>& recvData,
const int tag = UPstream::msgType(),
const label comm = UPstream::worldComm,
const bool block = true
);
//- Helper: exchange sizes of sendData. sendData is the data per
// processor (in the communicator). Returns sizes of sendData
// on the sending processor.
template<class Container>
static void exchangeSizes
(
const Container& sendData,
labelList& sizes,
const label comm = UPstream::worldComm
);
//- Exchange contiguous data. Sends sendData, receives into
// recvData. Determines sizes to receive.
// If block=true will wait for all transfers to finish.
template<class Container, class T>
static void exchange
(
const UList<Container>& sendData,
List<Container>& recvData,
const int tag = UPstream::msgType(),
const label comm = UPstream::worldComm,
const bool block = true
);
};
我们看到Pstream类有一个构造函数,剩下的都是静态成员函数,而这些成员函数就是并行通讯的工具箱
这里多问一句,为什么工具箱的函数都是静态成员函数
为什么这里用静态成员函数呢
用静态成员可以变量实现多个对象间的数据共享,比全局变量更安全
这里我详细说下,举个例子
Time mytime1;
mytime1.hour=2;
Time mytime2;
mytime2.hour=4;
这段程序中成员变量是跟着对象走的,他们的对象各自占用不同的内存地址,彼此互不影响
那我们想做类内的全局变量满足相互通信需求,在不同对象mytime1和mytime2中共享一个副本,怎么办
这时static关键字就派上用场了,增加了static关键字或成员函数不隶属整个对象,而隶属于整个类
因为这个变量跟着类走,所以调用时用“类名::成员变量名”或“类名::成员变量函数”进行调用(当然也可用“对象名.静态函数名”),表示明确的隶属关系,不创建对象也可进行访问编辑
在Pstream类调用工具箱中函数时,我们常见到这样的调用方式,而且不创建Pstream对象也可进行调用
// 在head节点收集信息
Pstream::gatherList(nInternalFaces);
Pstream::gatherList(nBoundaries);
因为类的静态成员脱离了与对象的关系,普通成员变量的内存分配是在对象初始化时完成的,对于静态成员必须在程序的全局区进行清晰的初始化
全局区的初始化过程可由某个.cpp源文件的开头的静态成员函数完成,如下所示:
void Time::func(int testValue)
{
mystatic = testValue ;
}
或者在全局区这样写:
int Time::mystatic=10;
这样能保证这个静态成员变量能够被正常使用。
此外静态成员函数只能调用静态成员变量,也没有this指针可以使用
这里上一张图可能更方便理解
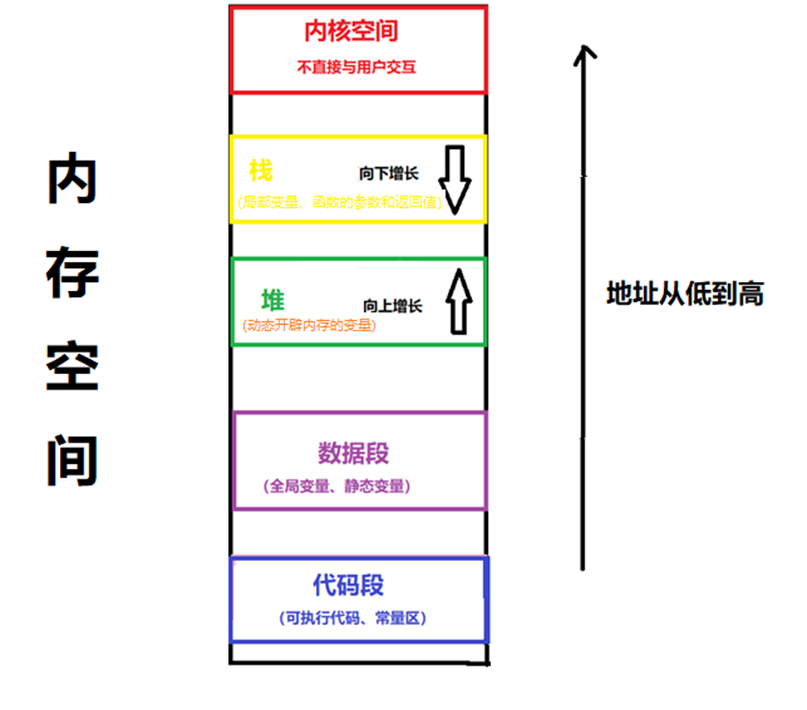
C++程序运行时,静态变量和全局变量存储在数据段,所以需要在全局区通过直接分配内存或者静态函数进行分配内存
因而静态成员的生命周期与程序运行周期相同,在程序中只有一份,无论创建对象与否,或者创建多少对象
说到这里可能大家对Openfoam的并行通信多了一些理解,只要开始了并行计算那么就可以通过Pstream类内的成员函数进行通信调用,在同样的数据段副本上进行信息流沟通
接下来依次说下各个工具的使用
收发数据
Pstream::gather()与Pstream::scatter()分别有两个重载,分别是收集以及散布数据,不如后面Pstream::gatherList()与Pstream::scatterList()常用,这里不细说了
Pstream::combineGather()、Pstream::combineScatter()重载情况与上同,用于就地集中收集或散布的数据,不太常用
Pstream::listCombineGather()、Pstream::listCombineScatter()重载情况与上同,用于一次整合list容器中的变量
Pstream::mapCombineGather()、Pstream::mapCombineScatter()重载情况与上同,用于一次整合整个map容器中的变量
Pstream::gatherList()以及Pstream::scatterList()的第二个重载比较常用,
template<class T>
static void gatherList
(
List<T>& Values,
const int tag = Pstream::msgType(),
const label comm = UPstream::worldComm
);
template<class T>
static void scatterList
(
List<T>& Values,
const int tag = Pstream::msgType(),
const label comm = UPstream::worldComm
);
Pstream::gatherList()以及Pstream::scatterList()的输入第一个参数是Values
这个Values需要自己整合下,Values是UPstream::nProcs()数量大小的List,比如说我要收集内部面可以这样创建需要收集的List,
List<label> nIternalFaces(Pstream::nProcs());
nIternalFaces[Pstream::myProcNo()] = mesh.Cf().size();//比如说看看每个节点分到了多少网格
Pstream::gatherList(nIternalFaces);//在头结点收集数据
Pstream::scatterList()与之类似
Pstream::gatherList()以及Pstream::scatterList()的输入第二个参数是Pstream::msgType(),默认为1,可以不输入
int Foam::UPstream::msgType_(1);
Pstream::gatherList()以及Pstream::scatterList()的输入第三个参数是Pstream::msgType(),默认为0,可以不输入
Foam::label Foam::UPstream::worldComm(0);
交换数据
Pstream::exchange()有两个重载,用于交换连续的数据,一般情况下等待其他所有传输完成再传输,可通过默认参数block()修改优先权
Pstream::exchangeSizes()用于交换数据的大小
下面是Pstream类函数相互关系
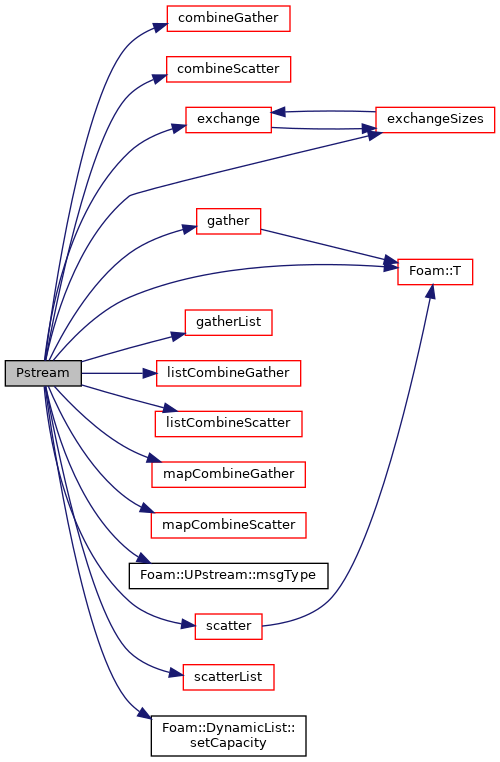
结语
并行开发远不止收发数据这么简单,还有很多类可说的,后续会一一进行介绍,并对openfoam并行计算进行优化
自从这个月15号找到人生支点后,基本上每天都在肝一篇说明书,逐渐开启这个季度的狂飙
一起探索openfoam也是相当有趣的一件事,非常欢迎私信讨论
指正的价值要比打赏更重要,下面是个人联系方式,能结交到志同道合的朋友是我的荣幸

最新文章
- Download Free Oracle Reports Building Guide eBook
- Extjs中引入JSP页面
- 理解python的with语句
- 现在不能使用foxmail同步qq记事本功能,可能是对字数的大小有限制
- Java实现文件的读写,复制
- 2015GitWebRTC编译实录7
- 【dapper】.net平台下的框架
- 微软Hololens学院教程-Hologram 211-Gestures(手势)【微软教程已经更新,本文是老版本】
- 反射实体自动生成EasyUi DataGrid模板
- Uber能知道你是不是在开车的时候玩手机
- Java基础知识强化之IO流笔记29:BufferedOutputStream / BufferedInputStream(字节缓冲流)之BufferedInputStream读取数据
- 关于FPGA随笔
- 网络流 E - Escape HDU - 3605
- [转帖]关于CPU Cache -- 程序猿需要知道的那些事
- Coursera, Deep Learning 1, Neural Networks and Deep Learning - week4, Deep Neural Networks
- allegro画电路板
- CentOS安装vmtools后 共享文件不能显示的问题
- 使用Word批量删除换行和空白行
- 字符集和编码——Unicode(UTF&UCS)深度历险
- angular把echarts封装为指令(配合requirejs)
热门文章
- 在链表上实现 Partition 以及荷兰国旗问题
- 深入浅出学习透析Nginx服务器的基本原理和配置指南「Keepalive性能分析实战篇」
- 如何使用C#在Excel中插入分页符
- pandas中loc和iloc的使用细节
- 【基础篇】一文带你掌握 Redis
- [python] 基于matplotlib实现圆环图的绘制
- 51NOD5213A 【提高组/高分-省选预科 第一场【M】】序列
- 洛谷P2036 PERKET题解
- ORM哪家强?java,c#,php,python,go 逐一对比, 网友直呼:全面客观
- 基于NOSTR协议的“公有制”版本的Twitter,去中心化社交软件Damus用后感,一个极端走向另一个极端