Java开发工程师(Web方向) - 04.Spring框架 - 第3章.AOP技术
第3章--AOP技术
Spring框架 - AOP概述 笔记https://my.oschina.net/hava/blog/758873
Spring框架 - AOP使用 笔记https://my.oschina.net/hava/blog/758881
AOP概述
在第1章中讲到AOP的一个例子:calculator中使用logger时将业务逻辑分离
public class Calculator {
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
}
public class Calculator {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(Calculator.class);
public int add(int a, int b) {
logger.info("Enter into Calculator.add(a,b) method");
int result = 0;
try {
result = a + b;
} catch (Exception ex {
logger.info("Exception in Calculator.add(a,b) method");
}
logger.info("Leaving Calculator.add(a,b) method");
return result;
}
}
缺点:
代码重复
耦合业务逻辑(计算)与非业务逻辑(Logger)
AOP-->
public class Calculator {
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
public int sub(int a, int b) {
return a - b;
}
}
public class MyLogger {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(MyLogger.class);
public void methodEnter (Method method) {
logger.info("Enter into " + method.getMethodInfo() + " method");
}
public void methodException (Method method) {
logger.info("Exception in " + method.getMethodInfo() + " method");
}
public void methodLeave (Method method) {
logger.info("Leaving " + method.getMethodInfo() + " method");
}
}
优点:
代码重用
解耦业务逻辑与非业务逻辑
AOP (面向切面)
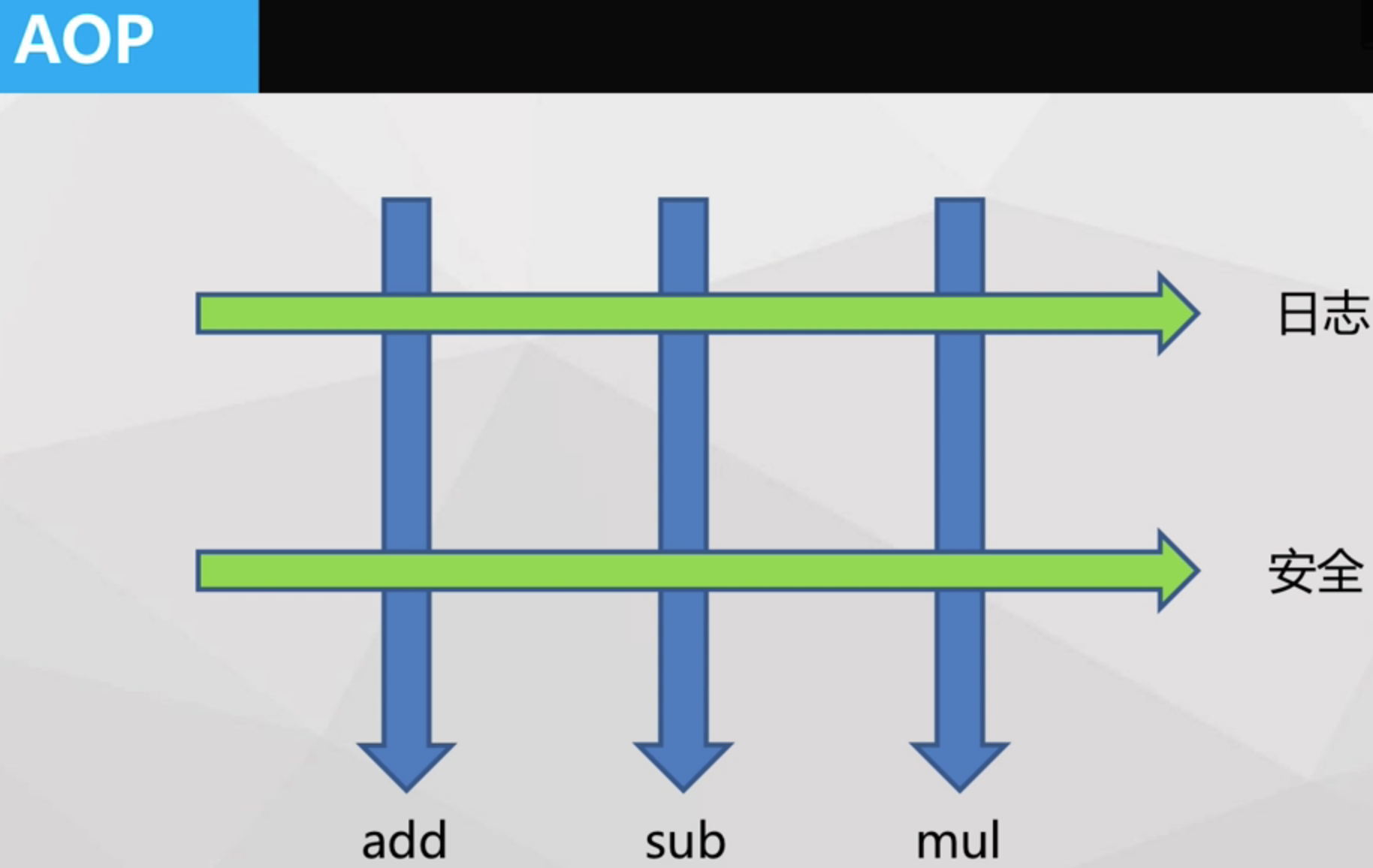
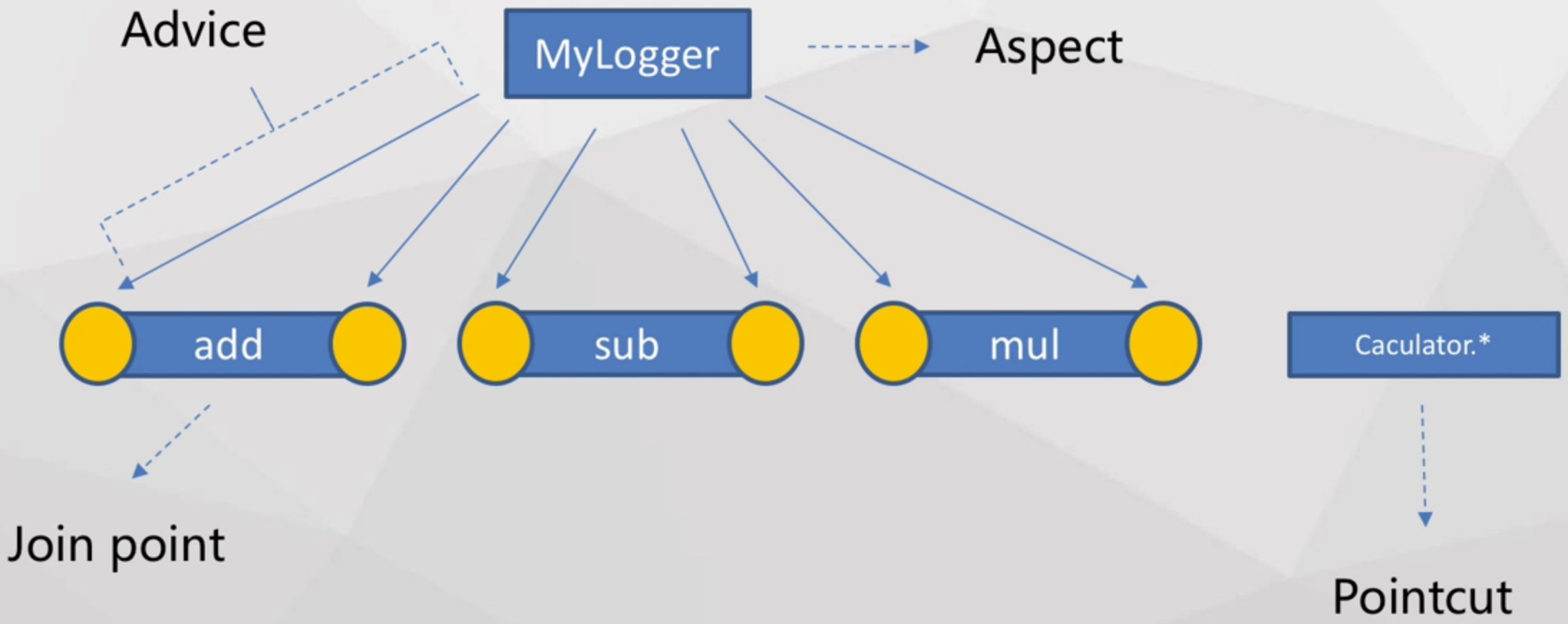
Aspect: 切面(如MyLogger等日志、安全横切功能)
Join point: 函数执行/属性访问的过程(Spring中没有提供AOP的属性访问操作)
Advice: 定义了在某个特定函数执行点的切面功能 (如MyLogger打印日志的行为)
Advice类型:
Before: 函数执行之前
After returning: 函数正常返回之后
After throwing: 函数抛出异常之后
After finally: 函数返回之后
Around: 函数执行前后(入口和出口)
Pointcut: 匹配横切目标函数的表达式(哪些业务逻辑需要进行该AOP)
Spring AOP:
非完整AOP实现(如果想要更完整的AOP实现,可以使用AspectJ)
整合了AOP和IoC
通过XML schema-based AOP供使用(Spring本身提供的,通过XML声明的方式)
通过@AspectJ annotation-based AOP供使用(整合了AspectJ中的某些功能)
AOP使用
@AspectJ AOP
添加aspectjweaver.jar包
pom.xml中:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>4.2.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency> <dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.8.7</version>
</dependency> <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>4.2.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
application-context.xml中
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.0.xsd"> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy /> </beans>
xmlns的作用跟package name的作用类似,用于区分两个相同类名(不同位置)的类
aop的属性tag比如aop:aspectj-autoproxy, 会通过spring-aop-2.0.xsd文件来验证属性配置是否正确
定义Aspect
application-context.xml中
<bean id="loggingAspect" class="com.netease.nanodegree.LoggingAspect"></bean>
新建类LoggingAspect.java中
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; @Aspect
public class LoggingAspect { }
定义Pointcut
@Pointcut("execution(* com.netease.nanodegree.Calculator.*(..))")
private void arithmetic() {
}
将该AOP匹配到Calculator类中的所有函数
表达式名称为arithmetic,后续使用可以直接通过该名称使用
Pointcut表达式:designator(modifiers? return-type declaring-type? name(para,) throws?)
designator: 如execution表示函数执行, within表示在某个包/类下运行的函数
modifiers: public/private(可选)
return-type: 返回类型,*表示匹配所有返回类型
declaring-type: 包名/类名(可选)
name: 函数名
param: 参数列表:()无参;(..)任意参数
throws: 抛出的异常类型(可选)
示例:
匹配所有public的函数--@Pointcut("execution(public * *(..))") private void publicMethod()
匹配所有DAO模块中的public函数--@Pointcut("execution(public * com.netease.dao.*.*(..))") private void publicDaoMethod()
匹配所有以save开头的函数--@Pointcut("execution(* save*(..))") private void saveMethod()
匹配所有以save开头的public函数--@Pointcut("execution(publicMethod() && saveMethod())") private void publicSaveMethod()
定义Advice
实例:在函数操作前执行打印日志的功能
// 在函数操作前执行打印日志的功能
@Before("com.netease.nanodegree.LoggingAspect.arithmetic()")
// 可以直接写pointcut表达式
// @Before("execution(* com.netease.nanodegree.Calculator.*(..))")
public void doLog() { }
同样,还有@AfterReturning/@AfterThrowing/@After等等
但是,doLog()函数如何得到函数的上下文信息呢?
public void doLog(JoinPoint jp) {
System.out.println(jp.getSignature() + ", " + jp.getArgs());
}
getSignature()返回的为函数签名
getArgs()返回的为无类型的Object对象
但是,@Around和其他类型有所不同,需要注入的为ProceedingJoinPoint(JoinPoint的子类)
@Around("com.netease.nanodegree.LoggingAspect.arithmetic()")
public void doLog(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) {
System.out.println("start method: " + pjp.toString());
Object retVal = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("stop method: " + pjp.toString());
return retVal;
}
要想得到调用函数的返回值
@AfterReturning (
pointcut="com.netease.nanodegree.LoggingAspect.arithmetic()",
returning="retVal")
public void doLog(Object retVal) {
// do something with retVal
}
要想得到调用函数抛出的异常
@AfterThrowing (
pointcut="com.netease.nanodegree.LoggingAspect.arithmetic()",
throwing="ex")
public void doLog(IllegalArgumentException ex) {
// do something with ex
}
要想得到目标函数的参数(有类型的对象)
@Before("com.netease.nanodegree.LoggingAspect.arithmetic() && args(a, ..)")
public void doLog(JoinPoint jp, int a) {
// do something with parameters
}
匹配第一个参数并命名为a,不管后面其他的参数
实例:
1. 新建Maven项目
2. 在pom.xml中添加依赖
org.springframework: spring-aop
org.aspectj: aspectjweaver
3. application-context.xml初始化如上
4. 新建Calculator.java类
public class Calculator {
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
public int sub(int a, int b) {
return a - b;
}
}
5. 新建LoggingAspect.java
@Aspect
public class LoggingAspect { }
6. 在application-context.xml中定义关于LoggingAspect的bean
<bean id="loggingAspect" class="com.netease.nanodegree.LoggingAspect"></bean>
<bean id="calculator" class="com.netease.nanodegree.Calculator"></bean>
7. 在LoggingAspect.java中
@Before("execution(* com.netease.nanodegree.Calculator.*(..)")
private void arithmeticDoLog(Joinpoint jp) {
System.out.println(jp.toString());
}
8. 新建TestApp.java
public class TestApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application-context.xml");
Calculator calculator = context.getBean("calculator", Calculator.class);
System.out.println(calculator.add(1, 1));
((ConfigurableApplicationContext) context).close();
}
}
9. 运行

10. 功能扩展
得到函数参数列表等等
@Before("execution(* com.netease.nanodegree.Calculator.*(..)) && args(a, ..)")
private void arithmeticDoLog(JoinPoint jp, int a) {
System.out.println(a + ": " + jp.toString());
}
输出:
1: execution(int com.netease.nanodegree.Calculator.add(int,int))
5: execution(int com.netease.nanodegree.Calculator.sub(int,int))
Schema-based AOP:
application-context.xml的文件相同,但是不需要 <aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
Aspect的定义
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="loggingAspect" ref="loggingBean">
...
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
Pointcut的定义
<!-- 3种方法定义pointcut -->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="arithmetic" expression="execution(* com.netease.nanodegree.Calculator.*(..))"/>
</aop:config>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="arithmetic" expression="com.netease.nanodegree.LoggingAspect.arithmetic()"/>
</aop:config>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="loggingAspect" ref="loggingBean">
<aop:pointcut id="arithmetic" expression="execution(* com.netease.nanodegree.Calculator.*(..))"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
Advice的定义
<!-- 定义各种Advice -->
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="loggingAspect" ref="loggingBean">
<aop:before pointcut-ref="arithmetic" method="doLog"/>
</aop:aspect>
<aop:aspect id="loggingAspect" ref="loggingBean">
<aop:before pointcut="execution(* com.netease.nanodegree.Calculator.*(..))" method="doLog"/>
</aop:aspect>
<aop:aspect id="loggingAspect" ref="loggingBean">
<aop:after-returning pointcut-ref="arithmetic" returning="retVal" method="doLog"/>
</aop:aspect>
<aop:aspect id="loggingAspect" ref="loggingBean">
<aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref="arithmetic" throwing="ex" method="doLog"/>
</aop:aspect>
<aop:aspect id="loggingAspect" ref="loggingBean">
<aop:around pointcut-ref="arithmetic" method="doLog"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
Schema or @AspectJ
Schema: 配置集中
@AspectJ: 配置分散,但兼容AspectJ
AOP技术单元测试
如下关于AOP的描述中错误的是:
- A.AOP可以对代码进行解耦;
- B.AOP可以作用于函数执行;
- C.AOP可以简化代码;
- D.AOP只能作用于public函数;2.00/2.00
下面哪个不属于AOP的Advice类型:
- A.Before returning;2.00/2.00
- B.After finally;
- C.After returning;
- D.Before;
关于Pointcut表达式,说法错误的是:
- A.必须得声明函数的参数列表匹配模式;
- B.必须得声明函数的modifiers;1.00/3.00
- C.必须得声明函数抛出异常的匹配模式;1.00/3.00
- D.必须得声明函数所在类的包的匹配模式;1.00/3.00
AOP技术作业
http://zhanjingbo.site/14759932535473.html
完成一个基本的应用,提供若干个Service(>=2),每个Service提供基本的增删查改的接口(实现随意,比如输出一行信息),通过AOP保证所有所有的Service接口在正常调用返回后以及抛出异常时(Service接口模拟),打出如下信息:函数名称,函数参数,并说明发生的事件:正常返回或者抛出异常。
(注:需要查找资料,了解JoinPoint的API)
基本要求:必须附加一个项目说明文档,说明每个功能点对应程序的运行结果(截图),项目的接口说明或者关键代码(不要把全部代码贴出来)等可以反映项目结果的内容。提交作业的时候必须有这个项目说明文档,否则会影响最终评分。
最新文章
- 常用SQL[ORACLE]
- 用自己赚的钱第一次坐飞机 那feel倍儿爽
- 64位系统使用Access 数据库文件的彻底解决方法
- SQL基础之XML
- Linux下6种优秀的邮件传输代理
- 【iCore2双核心板】SRAM 读写实验(基于Verilog语言)
- class属性添加多个类
- 移动端的click
- LanSoEditor_common ---android平台的视频编辑SDK
- 【Linux】查看进程号
- SQL常用增删改查语句
- 034_nginx报错总结
- Linux命令:ssh-copy-id
- 服务化实战之 dubbo、dubbox、motan、thrift、grpc等RPC框架比较及选型
- 知物由学 | AI在Facebook清理有害内容上扮演了什么角色?
- PetaPoco源代码学习--0.目录贴
- 求一个正实数X的开方
- SVN Error: Unreadable path encountered; access denied;
- python selenium 问题汇总
- 用PL/pgSQL写postgreSQL的存储过程[转]