C++11并发学习之三:线程同步(转载)
C++11并发学习之三:线程同步
1.<mutex> 头文件介绍
Mutex又称互斥量,C++ 11中与 Mutex 相关的类(包括锁类型)和函数都声明在 <mutex> 头文件中,所以如果你需要使用 std::mutex,就必须包含 <mutex> 头文件。
(1)Mutex系列类(四种)
std::mutex,最基本的 Mutex 类。
std::recursive_mutex,递归 Mutex 类。
std::time_mutex,定时 Mutex 类。
std::recursive_timed_mutex,定时递归 Mutex 类。
(2)Lock系列类(两种)
std::lock_guard,与 Mutex RAII 相关,方便线程对互斥量上锁。
std::unique_lock,与 Mutex RAII 相关,方便线程对互斥量上锁,但提供了更好的上锁和解锁控制。
(3)其他类型(结构体)
std::adopt_lock_t——它的常量对象定义为constexpr adopt_lock_t adopt_lock {};// constexpr 是 C++11 中的新关键字)
std::defer_lock_t——它的常量对象定义为constexpr defer_lock_t defer_lock {};// constexpr 是 C++11 中的新关键字)
std::try_to_lock_t——它的常量对象定义为constexpr try_to_lock_t try_to_lock {};// constexpr 是 C++11 中的新关键字)
(4)函数
std::try_lock,尝试同时对多个互斥量上锁。
std::lock,可以同时对多个互斥量上锁。
std::call_once,如果多个线程需要同时调用某个函数,call_once 可以保证多个线程对该函数只调用一次。
2.常用类型举例
(1)std::mutex类
☆构造函数,std::mutex不允许拷贝构造,也不允许 move 拷贝,最初产生的 mutex 对象是处于 unlocked 状态的。
☆lock(),调用线程将锁住该互斥量。线程调用该函数会发生下面 3 种情况:①如果该互斥量当前没有被锁住,则调用线程将该互斥量锁住,直到调用 unlock之前,该线程一直拥有该锁。②如果当前互斥量被其他线程锁住,则当前的调用线程被阻塞住。③如果当前互斥量被当前调用线程锁住,则会产生死锁(deadlock)。
☆unlock(), 解锁,释放对互斥量的所有权。
☆try_lock(),尝试锁住互斥量,如果互斥量被其他线程占有,则当前线程也不会被阻塞。线程调用该函数也会出现下面 3 种情况:① 如果该互斥量当前没有被锁住,则该线程锁住互斥量,直到该线程调用 unlock 释放互斥量。②如果当前互斥量被其他线程锁住,则当前调用线程返回 false,而并不会被阻塞掉。③如果当前互斥量被当前调用线程锁住,则会产生死锁(deadlock)。
不论是lock()还是try_lock()都需要和unlock()配套使用,下面举例说明lock()和try_lock()的区别。
- #include <thread>
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string>
- #include <chrono>
- #include <assert.h>
- #include <mutex>
- int counter=0;
- std::mutex mtx;
- void func()
- {
- for (int i=0; i<10000; ++i)
- {
- mtx.lock();
- ++counter;
- mtx.unlock();
- }
- }
- int main()
- {
- std::thread workerThreads[10];
- for (int i=0; i<10; ++i)
- {
- workerThreads[i] = std::thread(func);
- }
- for (auto& workerThread : workerThreads)
- {
- workerThread.join();
- }
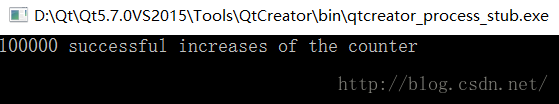
- std::cout << counter << " successful increases of the counter"<<std::endl;
- return 0;
- }
由于lock()的阻塞特性,所以每个线程都统计了10000次,一共是10*10000=100000次。
- #include <thread>
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string>
- #include <chrono>
- #include <assert.h>
- #include <mutex>
- int counter=0;
- std::mutex mtx;
- void func()
- {
- for (int i=0; i<10000; ++i)
- {
- if (mtx.try_lock())
- {
- ++counter;
- mtx.unlock();
- }
- }
- }
- int main()
- {
- std::thread workerThreads[10];
- for (int i=0; i<10; ++i)
- {
- workerThreads[i] = std::thread(func);
- }
- for (auto& workerThread : workerThreads)
- {
- workerThread.join();
- }
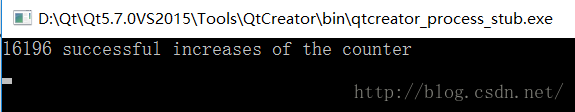
- std::cout << counter << " successful increases of the counter"<<std::endl;
- return 0;
- }
由于try_lock()的非阻塞特性,如果当前互斥量被其他线程锁住,则当前try_lock()返回 false,此时counter并不会增加1。所以这十个线程的统计结果具有随机性,下次运行程序时,统计值不一定是16191。
(2).std::lock_guard和std::unique_lock类
std::lock_guard使用起来比较简单,除了构造函数外没有其他成员函数。
std::unique_lock除了lock_guard的功能外,提供了更多的成员函数,相对来说更灵活一些。这些成员函数包括lock,try_lock,try_lock_for,try_lock_until、unlock等。
std::unique_lock::lock——用它所管理的Mutex对象的 lock 函数。
std::unique_lock::try_lock——用它所管理的Mutex对象的 try_lock函数。
std::unique_lock::unlock——用它所管理的Mutex对象的 unlock函数。
这两个类相比使用std::mutex的优势在于不用配对使用,无需担心忘记调用unlock而导致的程序死锁。
- #include <thread>
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string>
- #include <chrono>
- #include <assert.h>
- #include <mutex>
- int counter=0;
- std::mutex mtx;
- void func()
- {
- for (int i=0; i<10000; ++i)
- {
- //将std::lock_guard替换成std::unique_lock,效果是一样的
- std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lck (mtx);
- ++counter;
- }
- }
- int main()
- {
- std::thread workerThreads[10];
- for (int i=0; i<10; ++i)
- {
- workerThreads[i] = std::thread(func);
- }
- for (auto& workerThread : workerThreads)
- {
- workerThread.join();
- }
- std::cout << counter << " successful increases of the counter"<<std::endl;
- return 0;
- }
std::uniqure_lock构造函数的第二个参数可以是std::defer_lock,std::try_to_lock或std::adopt_lock
- #include <thread>
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string>
- #include <chrono>
- #include <assert.h>
- #include <mutex>
- int counter=0;
- std::mutex mtx;
- void func()
- {
- for (int i=0; i<10000; ++i)
- {
- mtx.lock();
- //注意此时Tag参数为std::adopt_lock表明当前线程已经获得了锁,
- //此后mtx对象的解锁操作交由unique_lock对象lck来管理,在lck的生命周期结束之后,
- //mtx对象会自动解锁。
- std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lck(mtx,std::adopt_lock);
- ++counter;
- }
- }
- int main()
- {
- std::thread workerThreads[10];
- for (int i=0; i<10; ++i)
- {
- workerThreads[i] = std::thread(func);
- }
- for (auto& workerThread : workerThreads)
- {
- workerThread.join();
- }
- std::cout << counter << " successful increases of the counter"<<std::endl;
- return 0;
- }
- #include <chrono>
- #include <assert.h>
- #include <mutex>
- int counter=0;
- std::mutex mtx;
- void func()
- {
- for (int i=0; i<10000; ++i)
- {
- //注意此时Tag参数为std::defer_lock表明当前线程没有获得了锁,
- //需要通过lck的lock和unlock来加锁和解锁,
- std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lck(mtx,std::defer_lock);
- lck.lock();
- ++counter;
- lck.unlock();
- }
- }
- int main()
- {
- std::thread workerThreads[10];
- for (int i=0; i<10; ++i)
- {
- workerThreads[i] = std::thread(func);
- }
- for (auto& workerThread : workerThreads)
- {
- workerThread.join();
- }
- std::cout << counter << " successful increases of the counter"<<std::endl;
- return 0;
- }
参考链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/haippy/p/3346477.html
最新文章
- PHP去重算法的优化过程
- canvas 画字
- express 转
- Linux 网络编程(epoll)
- Redis基本配置
- C#技术漫谈之垃圾回收机制(GC)(转)
- 代码片段------find批量处理
- IOS 类别与扩展的区别 (category & extensions)
- 23 读取excel
- grunt 前端开发环境搭建
- MS SQL Server Management Studio中提示不允许保长度出现不允许保存更改。您所做的更改要求删除并重新创建以下表
- Vmware虚拟机不能使用键盘的解决方法
- JavaScript 知识图谱
- websocket简单实现在线聊天
- DOS:第二天
- caffe的cancat层
- Centos7上安装mariadb
- Linux 为linux enterprises 6安装图形桌面教程
- webpack简单的打包体验
- C#.Net 持久化对象为XML文件