JDK源码分析(10)之 Hashtable 相关
本文的目的并不是让你对Hashtable更加了解,然后灵活运用;因为Hashtable的一个历史遗留的类,目前并不建议使用,所以本文主要和HashMap对比,感受同样功能的不同实现,知道什么是好的代码;所以在阅读本文之前最好先了解一下 HashMap,可以参考 HashMap 相关;
一、 类定义
public class Hashtable<K,V> extends Dictionary<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
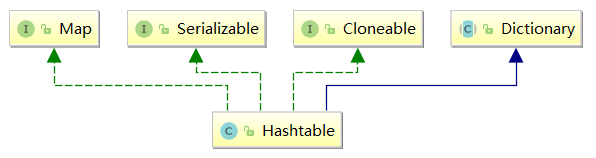
可以看到它和HashMap虽然都是哈希表,但是结构完全不一样,他是继承于Dictionary;
/**
* Maps the specified <code>key</code> to the specified
* <code>value</code> in this dictionary. Neither the key nor the
* value can be <code>null</code>.
*/
abstract public V put(K key, V value);
abstract public Enumeration<K> keys();
abstract public Enumeration<V> elements();
public interface Enumeration<E> {
boolean hasMoreElements();
E nextElement();
}
同AbstractMap相比功能结构基本一样,但是有两点很重要的区别:
Hashtable要求 key 和 value,都不能为 null,也就意味着这每次 put 元素的时候都需要判空,真是想想都好痛苦;- 另外 keys 和 elements 返回的居然是
Enumeration,这也是一个比较古老的接口,用于枚举(一次获得一个)对象集合中的元素;但是目前大多已经被Iterator给取代了;
二、构造方法和成员变量
private transient Entry<?,?>[] table; // 哈希槽
private int threshold; // 阈值
private float loadFactor; // 负载系数
以上三个应该就是 Map 中最重要的成员变量了,阈值和负载系数控制扩容时机,同HashMap的作用是一样的,哈希槽也是一样的,但是注意Entry<?,?>[]这里用的居然是通配符,而不是K V,也就意味着在取 entry 的时候,还需要强转类型,这也是非常神奇的地方;
public Hashtable(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: " + initialCapacity);
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Load: "+loadFactor);
if (initialCapacity==0)
initialCapacity = 1;
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
table = new Entry<?,?>[initialCapacity];
threshold = (int)Math.min(initialCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
}
public Hashtable(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0.75f);
}
public Hashtable() {
this(11, 0.75f);
}
public Hashtable(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> t) {
this(Math.max(2*t.size(), 11), 0.75f);
putAll(t);
}
如代码所示四个构造函数,主要就是为了初始化以上三个成员变量,但是注意table的容量;熟悉HashMap的肯定知道,HashMap的容量要求是2的幂,目的是为了使用hash % length = hash & (length-1),优化哈希槽的定位;但是如上面代码所示Hashtable的容量却不是,初始容量默认11,扩容是2倍加1;这样做的优缺点有什么呢:
- 缺点,不能利用“与”来优化哈希槽定位;
- 优点,减小了哈希冲突的几率(hashmap 的容量虽然是偶数,但是对哈希做了高位与低位,以及红黑树,使得即使hash冲突十分严重,性能也能得以保证),详情可以参考 为什么一般hashtable的桶数会取一个素数;
三、重要方法
1. 哈希槽定位
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
哈希表中最重要的方法肯定是哈希槽定位,如上面的原因Hashtable寻址的时候并不能做优化,所以只是用的典型除留余数法,(hash & 0x7FFFFFFF)则是为了保证第一位符号位是0,也就是正数,保证最终的余数是正数;
2. get 方法
public synchronized V get(Object key) {
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
return (V)e.value;
}
}
return null;
}
注意Hashtable的所有方法都是synchronized修饰的,所以Hashtable是线程安全的容器;
代码很简单,就是得到哈希,计算哈希桶,再一次遍历链表;但是需要注意:
int hash = key.hashCode();,这里是直接取的 key 的 hashCode,所以这里不能避免极端哈希的情况;- 另外就是不能使用可变 key (所有容器都不能使用可变 key),例如:
private static class A {
String name;
public A(String name) {this.name = name;}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) { ... }
@Override
public int hashCode() { ... }
}
private static void test01() {
Map<A, String> map = new Hashtable<>();
A a1 = new A("a");
A a2 = new A("a");
map.put(a1, "a");
map.put(a2, "a");
System.out.println(map.get(a1));
a1.name = "b";
System.out.println(map.get(a1));
}
// 打印:
a
null
3. put 方法
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Make sure the value is not null
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return old;
}
}
addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
return null;
}
Hashtable的put方法和HashMap相比,就显得十分清晰,先判空,在查找,找到就替换,找不到就插入新节点;但是在插入顺序(后面会讲到),红黑树性能保证等方面也就不能和HashMap相比了;另外这里取出来的Entry也是进行了类型强制转换;
4. addEntry 方法
private void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int index) {
modCount++;
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
if (count >= threshold) {
// Rehash the table if the threshold is exceeded
rehash();
tab = table;
hash = key.hashCode();
index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
}
// Creates the new entry.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>) tab[index];
tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
count++;
}
private static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
protected Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Entry<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
...
}
这里添加元素的时候首先判断是否扩容,然后添加节点;值得注意的是添加的节点是直接放在哈希槽里的(tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);)大部分的 Map 实现都是将添加的节点放在链表尾部;所以Hashtable中节点的相对顺序是不断变化的;
5. rehash 方法
protected void rehash() {
int oldCapacity = table.length;
Entry<?,?>[] oldMap = table;
// overflow-conscious code
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity << 1) + 1;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) {
if (oldCapacity == MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)
// Keep running with MAX_ARRAY_SIZE buckets
return;
newCapacity = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
Entry<?,?>[] newMap = new Entry<?,?>[newCapacity];
modCount++;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
table = newMap;
for (int i = oldCapacity ; i-- > 0 ;) {
for (Entry<K,V> old = (Entry<K,V>)oldMap[i] ; old != null ; ) {
Entry<K,V> e = old;
old = old.next;
int index = (e.hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % newCapacity;
e.next = (Entry<K,V>)newMap[index];
newMap[index] = e;
}
}
}
扩容的时候也是,先计算新容量,在得到一个新的哈希槽,然后将节点在依次放入;同添加节点一样是将节点直接放到哈希槽中,那么在扩容完毕之后,链表的相对顺序会反向;
总结
Hashtable的 key 和 value 都不能为 null,在使用的时候需要判空。。。。蛋疼- 哈希值完全依赖 key 的
hashCode方法,所以在使用的时候,需要额外注意 Hashtable的容量可以是任意值,默认是11,不能使用“与”来优化寻址Hashtable的节点相对位置是不断变化的;Hashtable是线程安全的;
最新文章
- 语义网 (Semantic Web)和 web 3.0
- JAVA基础学习——1.1 环境搭建 之jdk安装,环境变量配置 (系统Win10,64bit)
- Cannot open the disk 'D:\Program Files\VMOS\Centos.vmdk' or one of the snapshot disks it depends on
- VIM常用快捷键
- papi酱视频因违规遭下线整改,你知道原因吗?
- (转载)Android理解:显式和隐式Intent
- 第一个Android项目——计算器
- SQLCLUSTER sql数据库监测工具
- $.data()、$().data
- 提高Mysql查询速度的一些建议(转).
- npm install 插件 --save与 --save -dev的区别
- alibaba的springcloud孵化器项目
- PHP提交表单失败后如何保留填写的信息
- 阅读<构建之法>10、11、12章
- ltp执行过程总结
- 在使用MyCat和MySqL时的错误总结
- perl-我的第一个程序
- (转)WAMP多站点配置
- 【R】函数-其它实用函数
- 关于winform窗体关闭时弹出提示框,选择否时窗体也关闭的问题
热门文章
- wpf 的各个template
- Charles抓包软件简介
- 接口调试之Postman 使用方法详解
- [Swift]LeetCode26. 删除排序数组中的重复项 | Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array
- [Swift]LeetCode166. 分数到小数 | Fraction to Recurring Decimal
- [Swift]LeetCode385. 迷你语法分析器 | Mini Parser
- [Swift]LeetCode849. 到最近的人的最大距离 | Maximize Distance to Closest Person
- 优化之Sequence Generator组件
- JavaScript02-js使用
- [CERC2017] Intrinsic Interval