golang开发:类库篇(五)go测试工具goconvey的使用
2024-09-01 02:06:33
为什么要使用goconvey测试程序
goconvey 集成go test,go test 无缝接入。管理运行测试用例,而且提供了丰富的函数断言、非常友好的WEB界面,直观的查看测试结果。
如果没有goconvey的话,编写一个测试结果,首先运行被测试函数,然后判断被测试函数的运行结果,各种if判断,各种输出提示信息,而且回归测试也比较麻烦。但是如果使用了goconvey这些都就变得无比的简单。
还是看些使用代码比较简单明了。
怎么使用goconvey测试程序
第一步当然是安装goconvey
go get github.com/smartystreets/goconvey
看下被测试的代码
package main
import "fmt"
type Student struct {
Num int
Name string
Chinaese int
English int
Math int
}
func NewStudent(num int, name string) (*Student,error) {
if num < 1 || len(name) < 1 {
return nil,fmt.Errorf("num name empty")
}
stu := new(Student)
stu.Num = num
stu.Name = name
return stu,nil
}
func (this *Student) GetAve() (int,error) {
score := this.Chinaese + this.English + this.Math
if score == 0 {
return 0,fmt.Errorf("score is 0")
}
return score/3,nil
}
主要看下goconvey的测试代码
package main
import (
"testing"
. "github.com/smartystreets/goconvey/convey"
)
func TestNew(t *testing.T) {
Convey("start test new", t, func() {
stu,err := NewStudent(0,"")
Convey("have error", func() {
So(err, ShouldBeError)
})
Convey("stu is nil", func() {
So(stu, ShouldBeNil)
})
})
}
func TestScore(t *testing.T) {
stu,_ := NewStudent(1,"test")
Convey("if error", t, func() {
_,err := stu.GetAve()
Convey("have error", func() {
So(err, ShouldBeError)
})
})
Convey("normal", t, func() {
stu.Math = 60
stu.Chinaese = 70
stu.English = 80
score,err := stu.GetAve()
Convey("have error", func() {
So(err, ShouldBeError)
})
Convey("score > 60", func() {
So(score, ShouldBeGreaterThan, 60)
})
})
}
进入到test代码目录,执行 go test
=== RUN TestNew
start test new
have error ✔
stu is nil ✔
2 total assertions
--- PASS: TestNew (0.00s)
=== RUN TestScore
if error
have error ✔
3 total assertions
normal
have error ✘
score > 60 ✔
Failures:
* /data/www/go/src/test/student_test.go
Line 35:
其实命令行显示的是有颜色标识的。期望出现的结果都会打上对勾,如果期望出现而没有出现的都会打上叉。
还有更好玩的WEB界面。进入的test代码的目录,然后执行 goconvey 会打开一个WEB界面,更加友好的标识出了测试的结果,测试了多少次,有几个通过,几个失败,一目了然。
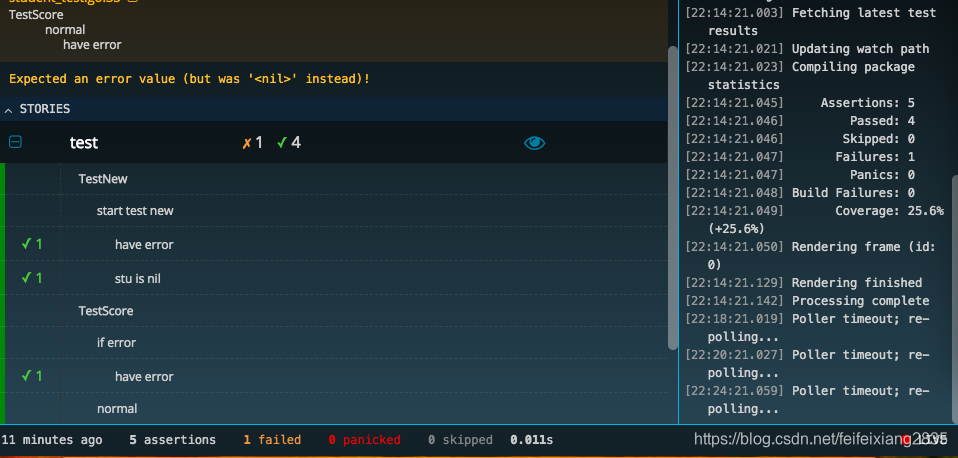
其实使用特别简单
引入类库,启动Convey函数,剩下的就是调用So各种断言各种比较
import (
"testing"
. "github.com/smartystreets/goconvey/convey"
)
Convey("desc", t, func() {
So(var, function)
})
基本平常开发中的比较函数基本都有,看下比较的函数列表,看着貌似都涵盖了。
Convey("Equality assertions should be accessible", t, func() {
thing1a := thing{a: "asdf"}
thing1b := thing{a: "asdf"}
thing2 := thing{a: "qwer"}
So(1, ShouldEqual, 1)
So(1, ShouldNotEqual, 2)
So(1, ShouldAlmostEqual, 1.000000000000001)
So(1, ShouldNotAlmostEqual, 2, 0.5)
So(thing1a, ShouldResemble, thing1b)
So(thing1a, ShouldNotResemble, thing2)
So(&thing1a, ShouldPointTo, &thing1a)
So(&thing1a, ShouldNotPointTo, &thing1b)
So(nil, ShouldBeNil)
So(1, ShouldNotBeNil)
So(true, ShouldBeTrue)
So(false, ShouldBeFalse)
So(0, ShouldBeZeroValue)
So(1, ShouldNotBeZeroValue)
})
Convey("Numeric comparison assertions should be accessible", t, func() {
So(1, ShouldBeGreaterThan, 0)
So(1, ShouldBeGreaterThanOrEqualTo, 1)
So(1, ShouldBeLessThan, 2)
So(1, ShouldBeLessThanOrEqualTo, 1)
So(1, ShouldBeBetween, 0, 2)
So(1, ShouldNotBeBetween, 2, 4)
So(1, ShouldBeBetweenOrEqual, 1, 2)
So(1, ShouldNotBeBetweenOrEqual, 2, 4)
})
Convey("Container assertions should be accessible", t, func() {
So([]int{1, 2, 3}, ShouldContain, 2)
So([]int{1, 2, 3}, ShouldNotContain, 4)
So(map[int]int{1: 1, 2: 2, 3: 3}, ShouldContainKey, 2)
So(map[int]int{1: 1, 2: 2, 3: 3}, ShouldNotContainKey, 4)
So(1, ShouldBeIn, []int{1, 2, 3})
So(4, ShouldNotBeIn, []int{1, 2, 3})
So([]int{}, ShouldBeEmpty)
So([]int{1}, ShouldNotBeEmpty)
So([]int{1, 2}, ShouldHaveLength, 2)
})
Convey("String assertions should be accessible", t, func() {
So("asdf", ShouldStartWith, "a")
So("asdf", ShouldNotStartWith, "z")
So("asdf", ShouldEndWith, "df")
So("asdf", ShouldNotEndWith, "as")
So("", ShouldBeBlank)
So("asdf", ShouldNotBeBlank)
So("asdf", ShouldContainSubstring, "sd")
So("asdf", ShouldNotContainSubstring, "af")
})
Convey("Panic recovery assertions should be accessible", t, func() {
So(panics, ShouldPanic)
So(func() {}, ShouldNotPanic)
So(panics, ShouldPanicWith, "Goofy Gophers!")
So(panics, ShouldNotPanicWith, "Guileless Gophers!")
})
Convey("Type-checking assertions should be accessible", t, func() {
// NOTE: Values or pointers may be checked. If a value is passed,
// it will be cast as a pointer to the value to avoid cases where
// the struct being tested takes pointer receivers. Go allows values
// or pointers to be passed as receivers on methods with a value
// receiver, but only pointers on methods with pointer receivers.
// See:
// http://golang.org/doc/effective_go.html#pointers_vs_values
// http://golang.org/doc/effective_go.html#blank_implements
// http://blog.golang.org/laws-of-reflection
So(1, ShouldHaveSameTypeAs, 0)
So(1, ShouldNotHaveSameTypeAs, "1")
So(bytes.NewBufferString(""), ShouldImplement, (*io.Reader)(nil))
So("string", ShouldNotImplement, (*io.Reader)(nil))
})
Convey("Time assertions should be accessible", t, func() {
january1, _ := time.Parse(timeLayout, "2013-01-01 00:00")
january2, _ := time.Parse(timeLayout, "2013-01-02 00:00")
january3, _ := time.Parse(timeLayout, "2013-01-03 00:00")
january4, _ := time.Parse(timeLayout, "2013-01-04 00:00")
january5, _ := time.Parse(timeLayout, "2013-01-05 00:00")
oneDay, _ := time.ParseDuration("24h0m0s")
So(january1, ShouldHappenBefore, january4)
So(january1, ShouldHappenOnOrBefore, january1)
So(january2, ShouldHappenAfter, january1)
So(january2, ShouldHappenOnOrAfter, january2)
So(january3, ShouldHappenBetween, january2, january5)
So(january3, ShouldHappenOnOrBetween, january3, january5)
So(january1, ShouldNotHappenOnOrBetween, january2, january5)
So(january2, ShouldHappenWithin, oneDay, january3)
So(january5, ShouldNotHappenWithin, oneDay, january1)
So([]time.Time{january1, january2}, ShouldBeChronological)
})
特别实用的一个测试类库,养成写完代码使用goconvey做测试的好习惯,也顺便覆盖下使用方法和案例,定能让开发事半功倍,减少Bug率。
最新文章
- break与continue的区别
- Android开发自学笔记(Android Studio)—4.4 AdapterView及其子类
- Linux服务器搬迁记(一)
- Java关键字总结及详解
- GET到新技能,SharpCEF,C#和JS的互相调用
- 第八篇 SQL Server安全数据加密
- mysql的distinct理解
- 前端编辑神器Brackets
- CF 508D Tanya and Password(无向图+输出欧拉路)
- Windows系统下文件的概念及c语言对其的基本操作(乙)
- bzoj 3261最大异或和
- DigitalClock的替代者TextClock
- C++ 文件流的方式操作文件(一个简单的写入,读取)
- linux搭建所遇到的坑elasticsearch-6.3.0
- 使用Spring MVC实现数据绑定
- 测试工具之Fiddler
- JavaScript输入表单数据正则验证规则
- MySQL--派生表Condition Pushdown优化
- N的多次方Python实现
- [原]IOS 设备基本信息