JavaScript内置一些方法的实现原理--new关键字,call/apply/bind方法--实现
先学习下new操作符吧
new关键字调用函数的心路历程:
1.创建一个新对象
2.将函数的作用域赋给新对象(this就指向这个对象)
3.执行函数中的代码
4.返回这个对象
根据这个的思路,来实现一个简单的new操作吧,代码演示:
function myNew(Func, ...args) {
if (typeof Func !== 'function') throw new Error(`${Func} is not a constructor`);
const obj = Object.create(Func.prototype);
const res = Func.apply(obj, args);
if (res instanceof Object) return res;
return obj;
}
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
const p1 = new Person('xm', 20);
const p2 = myNew(Person, 'xm', 20);
首先,先判断传进来的第一个参数是不是函数,不是函数抛出错误。
接着以传进来的函数的原型对象为原型创建一个新对象。
这步相当于obj.__proto__ = Func.prototype或者Object.setPrototypeOf(obj, Func.prototype)。
(Object.create()是推荐用法,ie11以下不支持上面那些东西、const,ie11不支持...)
调用函数,通过apply方法把函数的this绑定到obj。如果函数有返回值,且为对象,则返回该对象。
否则返回obj。
稍微兼容一点的写法(到ie9):
function myNew(Func) {
if (typeof Func !== 'function') throw new Error( Func + 'is not a constructor');
var obj = Object.create(Func.prototype);
var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 1);
var res = Func.apply(obj, args);
if (res instanceof Object) return res;
return obj;
}
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
var p1 = new Person('xm', 20);
var p2 = myNew(Person, 'xm', 20);
验证:

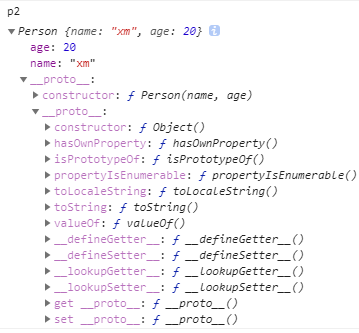
call方法
call方法最常见的用法就是改变函数的this指向。
该方法的第一个参数为函数的this指向。后面的参数为函数的参数,按顺序传入。
根据这个思路,来实现这样一个功能简单的call方法吧。代码演示:
Function.prototype.myCall = function(context, ...args) {
let self = this;
context = context || window;
Object.defineProperty(context, 'myFn', {
configurable: true,
get() {
return self;
}
});
const res = context.myFn(...args);
delete context.myFn;
return res;
};
以上代码,在Function的原型对象上添加一个myCall方法,就可以实现fn.myCall()如此模样的操作了。
接着定义一个变量保存方法函数内部this,this指向调用该方法的函数。
然后做一个简单的短路操作,如果传进来的第一个参数是undefined、null,则指向window。
当然,如果瞎传,那就只能下一行执行时报错了。
接着在context上添加一个属性,并把该属性设置成可以删除的,设置get方法。
访问该属性时触发get方法,返回的是调用myCall方法的函数。接下来调用函数,返回值保存到res。
最后删除context.myFn属性,返回res。
验证:

稍微兼容一些的写法:
Function.prototype.myCall = Function.prototype.call || function(context) {
var self = this, args = [], res, i, len;
context = context || window;
Object.defineProperty(context, 'myFn', {
configurable: true,
get() {
return self;
}
});
for (i = 1, len = arguments.length; i < len; i++) {
args.push('arguments[' + i + ']');
}
res = eval('context.myFn(' + args + ')');
delete context.myFn;
return res;
};
当然,测试的时候先把前面的短路操作去掉。。
apply方法
apply方法与call方法很相似,只在传参上有点区别。apply第二个参数是数组或类数组对象。
接下来就来实现一个功能相对单一的apply方法吧。代码演示:
Function.prototype.myApply = function(context, arr) {
let self = this;
context = context || window;
Object.defineProperty(context, 'myFn', {
configurable: true,
get() {
return self;
}
});
const res = context.myFn(...arr);
delete context.myFn;
return res;
};
几乎和call方法的实现一模一样。。
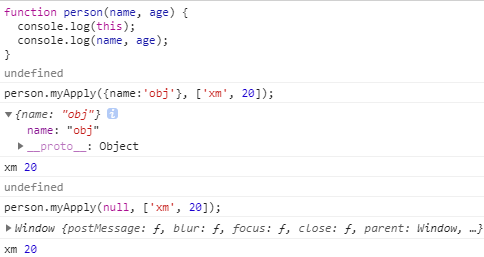
稍微兼容一些的写法:
Function.prototype.myApply = Function.prototype.apply || function(context) {
var self = this, args = [], _args = [], res, i, len;
context = context || window;
Object.defineProperty(context, 'myFn', {
configurable: true,
get() {
return self;
}
});
for (i = 0, len = arguments[1].length; i < len; i++) {
args.push('_args[' + i + ']');
_args.push(arguments[1][i]);
}
res = eval('context.myFn(' + args + ')');
delete context.myFn;
return res;
};
需要注意的是,传进的参数只有两个,第二个是数组或类数组,像myCall方法中传入eval函数的字符串直接映射arguments对象是行不通的。
可以再创建一个数组,把传进来的第二个参数全部push进去,eval函数的字符串直接映射该数组。
当然,测试的时候先把前面的短路操作去掉。。
bind方法
bind方法略有不同,函数调用bind方法,返回的是一个函数。当函数只是普通调用时,this指向bind方法的第一个参数。
如果返回的函数被当做构造函数调用时,前面绑定的this又无效了,此时指向new操作符创建的对象。
如:
function person() {
console.log(this);
}
const P1 = person.bind({name: 'xm'});
P1();// {name: 'xm'}
new P1();// person实例
还需要注意的是,当返回的函数被当做对象的方法调用时,此时this仍然指向bind方法绑定的对象。如:
const obj = {
P1
};
obj.P1();// {name: 'xm'}
接下来,来实现这样的一个bind方法吧。代码演示:
Function.prototype.myBind = function(context, ...args) {
const self = this;
context = context || window;
const Bound = function() {
const _args = [...args, ...arguments];
let _context = context;
if (this instanceof Bound) _context = this;
return self.apply(_context, _args);
}
const _Fn = function () {};
_Fn.prototype = this.prototype;
Bound.prototype = new _Fn();
return Bound;
};
以上代码,在Function的原型对象上添加一个myBind方法,就可以实现fn.myBind()如此模样的操作了。
接着保存函数的this,这个this指向调用myBind()方法的函数。
然后简单处理下传进来的第一个参数,为null、undefined时指向window。
接下来就是创建一个Bound函数,这个Bound函数是一个闭包,它可以访问外层函数的变量。
最后它是要作为myBind()方法的返回值,返回出去的。
在Bound函数里,第五行代码先处理了下参数。除第一个context参数,其他参数有时候会在myBind方法里传,有时候会在返回的函数里传。
这里不管三七二十一,都转成数组,然后拼接成一个数组。然后通过apply方法传参。(使用eval函数也行,就是麻烦了些)
第七行代码判断this 和 Bound的关系,如果Bound函数被new操作符调用,则函数内部的this指向Bound的实例(即new创建的对象)。
此时instanceof会返回真,然后这里处理下_context参数,把this赋给_context。
最后通过apply方法调用self(即外层函数保存的this),最后把函数返回值return出去。
测试代码:
function person(name, age) {
console.log(this);
console.log(name, age);
}
const Bound = person.myBind({name: 'xm'}, 'xh' );
const person1 = new Bound(20);
以上代码,person函数先调用myBind()方法,并把返回的函数(Bound)保存到Bound。
然后通过new调用Bound函数。结果:

对比:
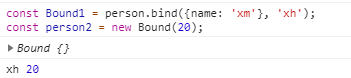
方法没有大的问题,基本是实现了。
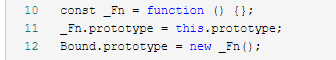
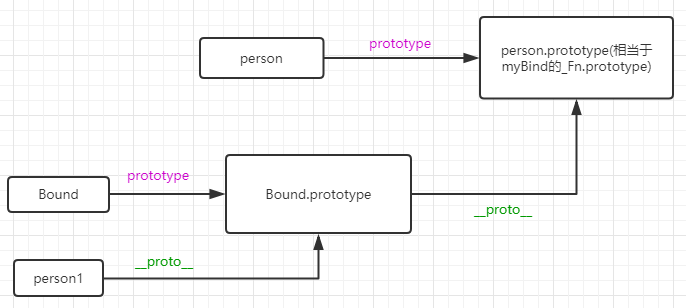
然后,这三行代码的作用是处理Bound函数的原型链。这样做的一个好处是,
Bound函数原型对象是空函数_Fn的一个实例。可以随意扩展。_Fn函数的原型对象又是person函数的原型对象。
这就等于Bound函数的原型对象的原型指针指向了person函数的原型对象。。。代码描述就是 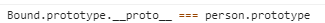
因此,Bound函数的实例不仅拥有Bound.prototype上的方法和属性,还拥有person函数原型对象的方法和属性。
原型链,如图:
验证:
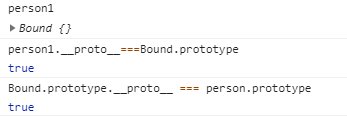
稍微兼容一些的写法:
Function.prototype.myBind = Function.prototype.bind || function(context) {
var self = this;
var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 1);
context = context || window;
var Bound = function() {
var _args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 0);
var _context = context;
if (this instanceof Bound) _context = this;
return self.apply(_context, args.concat(_args));
}
var _Fn = function () {};
_Fn.prototype = this.prototype;
Bound.prototype = new _Fn();
return Bound;
};
最新文章
- Servlet技术(使用myeclipse)
- dp 走格子问题
- 欧洲宇航局(ESA)的协同设计室(CDF)
- JavaScript学习09 函数本质及Function对象深入探索
- Java语言基础(八)
- auto space advisor
- Django学习(七)---添加新文章页面
- angular/cli 常用指令
- POI以SAX方式解析Excel2007大文件(包含空单元格的处理) Java生成CSV文件实例详解
- Linux基础命令---arp
- Log4j 日志记录
- 42.scrapy爬取数据入库mongodb
- WEB中会话跟踪
- luncene 查询字符串的解析-QueryParser类
- WEB安全扫描器Netsparker推荐给大家
- 为Android添加开机启动脚本
- 获取DOM
- C# 面试题 (三)
- JS中Document节点总结
- Node.js的http模块理解