【atcoder F - Namori】**
F- Namori
http://agc004.contest.atcoder.jp/tasks/agc004_f
Time limit : 2sec / Memory limit : 256MB
Score : 2200 points
Problem Statement
You are given an undirected graph with N vertices and M edges. Here, N−1≤M≤N holds and the graph is connected. There are no self-loops or multiple edges in this graph.
The vertices are numbered 1 through N, and the edges are numbered 1 through M. Edge i connects vertices ai and bi.
The color of each vertex can be either white or black. Initially, all the vertices are white. Snuke is trying to turn all the vertices black by performing the following operation some number of times:
- Select a pair of adjacent vertices with the same color, and invert the colors of those vertices. That is, if the vertices are both white, then turn them black, and vice versa.
Determine if it is possible to turn all the vertices black. If the answer is positive, find the minimum number of times the operation needs to be performed in order to achieve the objective.
Constraints
- 2≤N≤105
- N−1≤M≤N
- 1≤ai,bi≤N
- There are no self-loops or multiple edges in the given graph.
- The given graph is connected.
Partial Score
- In the test set worth 1500 points, M=N−1.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
NMa1b1a2b2:aMbMOutput
If it is possible to turn all the vertices black, print the minimum number of times the operation needs to be performed in order to achieve the objective. Otherwise, print
-1instead.
Sample Input 1
Copy6 5
1 2
1 3
1 4
2 5
2 6Sample Output 1
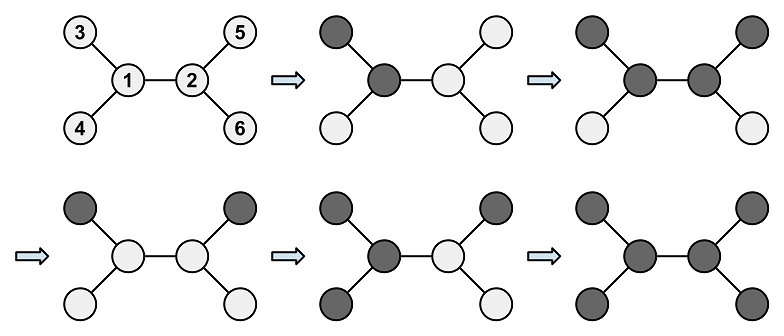
Copy5For example, it is possible to perform the operations as shown in the following diagram:
Sample Input 2
Copy3 2
1 2
2 3Sample Output 2
Copy-1It is not possible to turn all the vertices black.
Sample Input 3
Copy4 4
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 1Sample Output 3
Copy2This case is not included in the test set for the partial score.
Sample Input 4
Copy6 6
1 2
2 3
3 1
1 4
1 5
1 6Sample Output 4
Copy7This case is not included in the test set for the partial score.
【分析】
这题真神!!
如果是一棵树的话。
树是二分图,所以我们将他黑白染色,问题变成了,可以交换相邻的黑色和白色,使得最后图黑白倒置。
把白色看成空格,黑色看成棋子,就是树上有x个棋子,你可以往空格里面移动,问你最少多少步到达目标状态。
在树上,其实方案是唯一的,你求一下子树里面现在有多少个棋子,目标是多少个棋子,你就知道一定会从父亲那里运过来多少棋子(或者从这个运向父亲多少个棋子)
这个是直接求就可以了的,就是$\sum ai-bi$
黑点个数初末态不同则无解。
当有环怎么办?
我们分类讨论:
1、构成奇环,多了的一条边连向的两点是同色的,就是说两个点那里可以同时加2个黑点或者同时减两个黑点,加/减多少个黑点你是知道的,(黑点奇偶初末态不同则无解),你就直接把那些黑点加上去,然后做法跟前面一样了。
2、构成偶环,就是说多了的那条边也可以运棋子,假设这条边向上运了x个棋子,然后就也是树上的问题。你的ans最后会写成|Ai-x|或|Ai+x|或|Ai|的形式,这种形式的和很经典啦,就是数轴上的距离和,我们x取其中的中位数就能算出最优解。
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define Maxn 100010
#define LL long long
const int INF=; int mymin(int x,int y) {return x<y?x:y;} struct node
{
int x,y,next;
}t[Maxn*];
int len,first[Maxn]; void ins(int x,int y)
{
t[++len].x=x;t[len].y=y;
t[len].next=first[x];first[x]=len;
} int r1,r2,ad;
int sm[Maxn],ss[Maxn],ans,d[Maxn],h[Maxn];
int dfs(int x,int fa,int dep)
{
sm[x]=;ss[x]=dep;d[x]=dep;
if(x==r1||x==r2) sm[x]+=ad,ss[x]+=ad;
int tt=;
for(int i=first[x];i;i=t[i].next) if(t[i].y!=fa)
{
int y=t[i].y;
tt+=dfs(y,x,-dep);
sm[x]+=sm[y];ss[x]+=ss[y];
}
if(x==r1) tt++;
if(x==r2) tt--;
if(tt==-) h[++h[]]=ss[x]-(sm[x]-ss[x]);
else if(tt==) h[++h[]]=(sm[x]-ss[x])-ss[x];
else ans+=abs(ss[x]-(sm[x]-ss[x]));
// ans+=abs(ss[x]-(sm[x]-ss[x]));
return tt;
} int ff[Maxn];
int ffa(int x)
{
if(ff[x]!=x) ff[x]=ffa(ff[x]);
return ff[x];
} int main()
{
// int T;
// scanf("%d",&T);
// while(T--)
{
int n,m;r1=r2=;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
len=;
memset(first,,sizeof(first));
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) ff[i]=i;
for(int i=;i<=m;i++)
{
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
if(ffa(x)!=ffa(y))
{
ff[ffa(x)]=ffa(y);
ins(x,y);ins(y,x);
}
else r1=x,r2=y;
}
if(m==n-)
{
dfs(,,);
ans=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) ans+=abs(ss[i]-(sm[i]-ss[i]));
if(sm[]-ss[]!=ss[]) printf("-1\n");
else printf("%d\n",ans);
}
else
{
// printf("-2\n");
ad=;
dfs(,,);
if(d[r1]==d[r2])
{
ad=abs(ss[]-(sm[]-ss[]));
if(ad&) printf("-1\n");
else
{
ad/=;
if(ss[]>sm[]-ss[]) dfs(,,);
else dfs(,,);
ans=ad;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) ans+=abs(ss[i]-(sm[i]-ss[i]));
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
}
else
{
h[]=;h[++h[]]=;
ans=;
dfs(,,);
if(sm[]-ss[]!=ss[]) printf("-1\n");
else
{
sort(h+,h++h[]);
int x=h[h[]/+];
for(int i=;i<=h[];i++) ans+=abs(h[i]-x);
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
}
}
}
return ;
}
【代码有点丑。。
2017-04-19 09:43:00
最新文章
- AlloyTouch 0.2.0发布--鱼和熊掌兼得
- c语言数据结构复习
- JavaScript对象状态
- Hadoop的核心组件和生态圈
- Sublime Text3 快捷键
- MultiTouch camera controls source code
- 重启sql server服务两种方式
- WM_PAINT在微软官方定义中,wParam和lParam都没有使用,所以就被Delphi给重定义了这个消息,还增加了DC(Delphi可任意改写消息的结构)
- Visual Studio 2013 新增web项目IIS Express的64位版 转载来源http://www.cnblogs.com/jianyus/p/3524335.html
- python学习:猜数字游戏
- Scapy的使用
- JQuery.validate 错误信息对话框
- Linux 下Shell的学习3-service编程
- App store 应用审核由于 IPv6 网络问题被拒的一点分析
- LayDate 时间选择插件的使用介绍 (低版本1.0好像是)
- elasticsearch(一) 之 elasticsearch初识
- Hibernate主键生成策略详解
- 条款1:将c++视作一个语言联邦
- windowns 查看端口占用
- linux(ubuntu16.04)下安装和破解pycharm专业版