2、Flume1.7.0入门:安装、部署、及flume的案例
一、什么是Flume?
flume 作为 cloudera 开发的实时日志收集系统,受到了业界的认可与广泛应用。
flume的特点:
flume是一个分布式、可靠、和高可用的海量日志采集、聚合和传输的系统。支持在日志系统中定制各类数据发送方,用于收集数据;同时,Flume提供对数据进行简单处理,并写到各种数据接受方(比如文本、HDFS、Hbase等)的能力 。
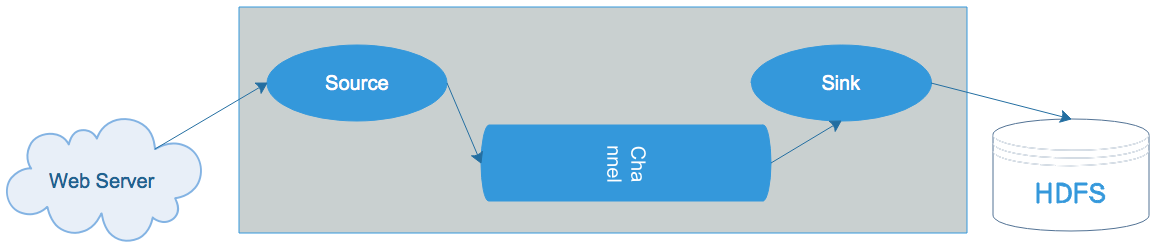
flume的数据流由事件(Event)贯穿始终。事件是Flume的基本数据单位,它携带日志数据(字节数组形式)并且携带有头信息,这些Event由Agent外部的Source生成,当Source捕获事件后会进行特定的格式化,然后Source会把事件推入(单个或多个)Channel中。你可以把Channel看作是一个缓冲区,它将保存事件直到Sink处理完该事件。Sink负责持久化日志或者把事件推向另一个Source。
flume的可靠性
当节点出现故障时,日志能够被传送到其他节点上而不会丢失。Flume提供了三种级别的可靠性保障,从强到弱依次分别为:end-to-end(收到数据agent首先将event写到磁盘上,当数据传送成功后,再删除;如果数据发送失败,可以重新发送。),Store on failure(这也是scribe采用的策略,当数据接收方crash时,将数据写到本地,待恢复后,继续发送),Besteffort(数据发送到接收方后,不会进行确认)。
flume的可恢复性:
还是靠Channel。推荐使用FileChannel,事件持久化在本地文件系统里(性能较差)。
flume的一些核心概念:
- Agent:使用JVM 运行Flume。每台机器运行一个agent,但是可以在一个agent中包含多个sources和sinks。
- Client:生产数据,运行在一个独立的线程。
- Source:从Client专门用来收集数据,传递给Channel,可以处理各种类型、各种格式的日志数据,包括avro、thrift、exec、jms、spooling directory、netcat、sequence generator、syslog、http、legacy、自定义。
- Sink:从Channel收集数据,运行在一个独立线程,sink组件是用于把数据发送到目的地的组件,目的地包括hdfs、logger、avro、thrift、ipc、file、null、Hbase、solr、自定义。
- Channel:连接 sources 和 sinks ,这个有点像一个队列,source组件把数据收集来以后,临时存放在channel中,即channel组件在agent中是专门用来存放临时数据的——对采集到的数据进行简单的缓存,可以存放在memory、jdbc、file等等。
- Events:可以是日志记录、 avro 对象等。
Agent的概念
Flume以agent为最小的独立运行单位。一个agent就是一个JVM,agent本身是一个Java进程,运行在日志收集节点—所谓日志收集节点就是服务器节点。
单agent由Source、Sink和Channel三大组件构成,类似生产者、仓库、消费者的架构.如下图:
Event的概念
flume的核心是把数据从数据源(source)收集过来,在将收集到的数据送到指定的目的地(sink)。为了保证输送的过程一定成功,在送到目的地(sink)之前,会先缓存数据(channel),待数据真正到达目的地(sink)后,flume在删除自己缓存的数据。
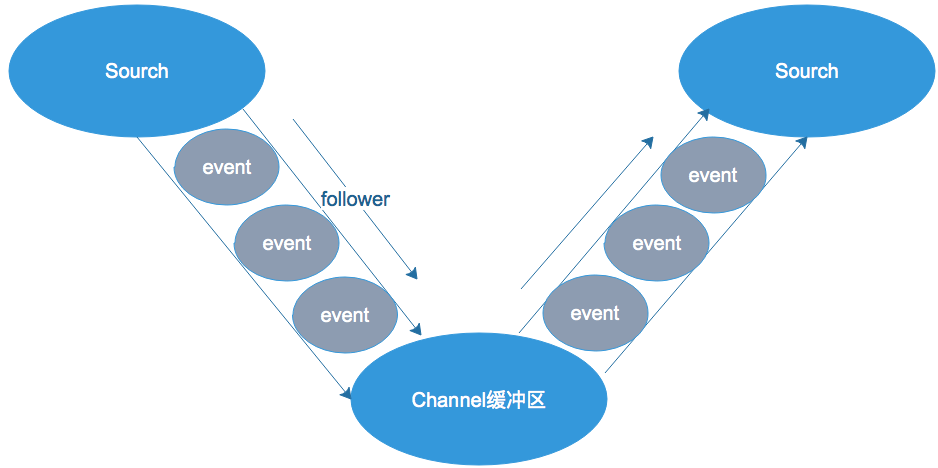
在整个数据的传输的过程中,流动的是event,即事务保证是在event级别进行的。那么什么是event呢?—–event将传输的数据进行封装,是flume传输数据的基本单位,如果是文本文件,通常是一行记录,event也是事务的基本单位。event从source,流向channel,再到sink,本身为一个字节数组,并可携带headers(头信息)信息。event代表着一个数据的最小完整单元,从外部数据源来,向外部的目的地去。
为了方便大家理解,给出一张event的数据流向图:
一个完整的event包括:event headers、event body、event信息(即文本文件中的单行记录),如下所以:
2017-03-29 14:00:58,227 (SinkRunner-PollingRunner-DefaultSinkProcessor) [INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.LoggerSink.process(LoggerSink.java:95)] Event: { headers:{} body: 68 65 6C 6C 6F 20 77 6F 72 64 hello word }
其中event信息就是flume收集到的日记记录。
flume的运行机制
flume的核心就是一个agent,这个agent对外有两个进行交互的地方,一个是接受数据的输入——source,一个是数据的输出sink,sink负责将数据发送到外部指定的目的地。source接收到数据之后,将数据发送给channel,chanel作为一个数据缓冲区会临时存放这些数据,随后sink会将channel中的数据发送到指定的地方—-例如HDFS等,注意:只有在sink将channel中的数据成功发送出去之后,channel才会将临时数据进行删除,这种机制保证了数据传输的可靠性与安全性。
flume的广义用法
flume可以支持多级flume的agent,即flume可以前后相继,例如sink可以将数据写到下一个agent的source中,这样的话就可以连成串了,可以整体处理了。flume还支持扇入(fan-in)、扇出(fan-out)。所谓扇入就是source可以接受多个输入,所谓扇出就是sink可以将数据输出多个目的地destination中。
值得注意的是,Flume提供了大量内置的Source、Channel和Sink类型。不同类型的Source,Channel和Sink可以自由组合。组合方式基于用户设置的配置文件,非常灵活。比如:Channel可以把事件暂存在内存里,也可以持久化到本地硬盘上。Sink可以把日志写入HDFS, HBase,甚至是另外一个Source等等。Flume支持用户建立多级流,也就是说,多个agent可以协同工作,并且支持Fan-in、Fan-out、Contextual Routing、Backup Routes。如下图所示:

二、安装Flume
1、下载Flume
http://apache.mirrors.hoobly.com/flume/1.7.0/apache-flume-1.7.0-bin.tar.gz
2、安装Flume
1)将下载的flume包,解压到/opt目录中.
2)修改 flume-env.sh 配置文件,主要是JAVA_HOME变量设置
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ cp conf/flume-env.sh.template conf/flume-env.sh
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ vi conf/flume-env.sh
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
# or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
# distributed with this work for additional information
# regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
# to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
# "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
# with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# If this file is placed at FLUME_CONF_DIR/flume-env.sh, it will be sourced
# during Flume startup.
# Enviroment variables can be set here.
export JAVA_HOME=/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_111.jdk/Contents/Home
# Give Flume more memory and pre-allocate, enable remote monitoring via JMX
# export JAVA_OPTS="-Xms100m -Xmx2000m -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote"
# Let Flume write raw event data and configuration information to its log files for debugging
# purposes. Enabling these flags is not recommended in production,
# as it may result in logging sensitive user information or encryption secrets.
# export JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Dorg.apache.flume.log.rawdata=true -Dorg.apache.flume.log.printconfig=true "
# Note that the Flume conf directory is always included in the classpath.
#FLUME_CLASSPATH=""
3)验证是否安装成功
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ bin/flume-ng version
Flume 1.7.0
Source code repository: https://git-wip-us.apache.org/repos/asf/flume.git
Revision: 511d868555dd4d16e6ce4fedc72c2d1454546707
Compiled by bessbd on Wed Oct 12 20:51:10 CEST 2016
From source with checksum 0d21b3ffdc55a07e1d08875872c00523
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$
出现上面的信息,表示安装成功了.
三、flume的案例
对于flume的原理其实很容易理解,我们更应该掌握flume的具体使用方法,flume提供了大量内置的Source、Channel和Sink类型。而且不同类型的Source、Channel和Sink可以自由组合—–组合方式基于用户设置的配置文件,非常灵活。比如:Channel可以把事件暂存在内存里,也可以持久化到本地硬盘上。Sink可以把日志写入HDFS, HBase,甚至是另外一个Source等等。下面我将用具体的案例详述flume的具体用法。
其实flume的用法很简单—-书写一个配置文件,在配置文件当中描述source、channel与sink的具体实现,而后运行一个agent实例,在运行agent实例的过程中会读取配置文件的内容,这样flume就会采集到数据。
配置文件的编写原则:
0)、案例1:Netcat
NetCat Source:监听一个指定的网络端口,即只要应用程序向这个端口里面写数据,这个source组件就可以获取到信息。
1>从整体上描述代理agent中sources、sinks、channels所涉及到的组件
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
2>详细描述agent中每一个source、sink与channel的具体实现:即在描述source的时候,需要指定source到底是什么类型的,即这个source是接受文件的、还是接受http的、还是接受thrift的;对于sink也是同理,需要指定结果是输出到HDFS中,还是Hbase中啊等等;对于channel需要指定是内存啊,还是数据库啊,还是文件啊等等。
# Describe configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost
a1.sources.r1.port = 44444
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
3>通过channel将source与sink连接起来
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
启动agent的shell操作:
flume-ng agent -n a1 -c conf -f conf/example.file -Dflume.root.logger=DEBUG,console
参数说明:
-n 指定agent名称(与配置文件中代理的名字相同)
-c 指定flume中配置文件的目录
-f 指定配置文件
-Dflume.root.logger=DEBUG,console 设置日志等级
1)、案例1:Avro
Avro可以发送一个给定的文件给Flume,Avro 源使用AVRO RPC机制。
a)创建agent配置文件
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ vi conf/avro.conf
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = avro
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sources.r1.bind = 0.0.0.0
a1.sources.r1.port = 4141
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
b)启动flume agent a1
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ bin/flume-ng agent -n a1 -c conf -f conf/avro.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
c)创建指定文件
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ echo "hello word" > log.00
d)使用avro-client发送文件
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ bin/flume-ng avro-client -c conf -H mbp -p 4141 -F log.00
e)在mbp的控制台,可以看到以下信息,注意最后一行:
2017-03-29 13:52:19,139 (lifecycleSupervisor-1-0) [INFO - org.apache.flume.node.PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider.start(PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider.java:62)] Configuration provider starting
.
.
.
2017-03-29 14:00:58,227 (SinkRunner-PollingRunner-DefaultSinkProcessor) [INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.LoggerSink.process(LoggerSink.java:95)] Event: { headers:{} body: 68 65 6C 6C 6F 20 77 6F 72 64 hello word }
2)、案例2:Spool
监听一个指定的目录,即只要应用程序向这个指定的目录中添加新的文件,source组件就可以获取到该信息,并解析该文件的内容,然后写入到channle。写入完成后,标记该文件已完成或者删除该文件。
Spool监测配置的目录下新增的文件,并将文件中的数据读取出来。需要注意两点:
1) 拷贝到spool目录下的文件不可以再打开编辑。
2) spool目录下不可包含相应的子目录
a)创建agent配置文件
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ vi conf/spool.conf
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = spooldir
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sources.r1.spoolDir = /opt/apache-flume-1.7.0-bin/logs
a1.sources.r1.fileHeader = true
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
b)启动flume agent a1
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ bin/flume-ng agent -n a1 -c conf -f conf/spool.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
c)追加文件到/opt/apache-flume-1.7.0-bin/logs目录
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ echo "spool test1" > logs/spool_text.log
d)在mbp的控制台,可以看到以下相关信息:
2017-03-29 14:31:04,921 (SinkRunner-PollingRunner-DefaultSinkProcessor) [INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.LoggerSink.process(LoggerSink.java:95)] Event: { headers:{file=/opt/apache-flume-1.7.0-bin/logs/spool_text.log} body: 73 70 6F 6F 6C 20 74 65 73 74 31 spool test1 }
3)、案例3:Exec
监听一个指定的命令,获取一条命令的结果作为它的数据源
常用的是tail -F file指令,即只要应用程序向日志(文件)里面写数据,source组件就可以获取到日志(文件)中最新的内容 。
EXEC执行一个给定的命令获得输出的源,如果要使用tail命令,必选使得file足够大才能看到输出内容
a)创建agent配置文件
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ vi conf/exec_tail.conf
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = exec
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /opt/apache-flume-1.7.0-bin/log_exec_tail
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
b)启动flume agent a1
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ bin/flume-ng agent -n a1 -c conf -f conf/exec_tail.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
c)生成足够多的内容在文件里
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ for i in {1..100};do echo "exec tail$i" >> /opt/apache-flume-1.7.0-bin/logs/log_exec_tail done
e)在mbp的控制台,可以看到以下信息:
2017-03-29 15:26:25,990 (lifecycleSupervisor-1-0) [INFO - org.apache.flume.node.PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider.start(PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider.java:62)] Configuration provider starting
.
.
.
2017-03-29 15:26:44,336 (SinkRunner-PollingRunner-DefaultSinkProcessor) [INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.LoggerSink.process(LoggerSink.java:95)] Event: { headers:{} body: 65 78 65 63 20 74 61 69 6C 39 34 exec tail94 }
2017-03-29 15:26:44,336 (SinkRunner-PollingRunner-DefaultSinkProcessor) [INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.LoggerSink.process(LoggerSink.java:95)] Event: { headers:{} body: 65 78 65 63 20 74 61 69 6C 39 35 exec tail95 }
2017-03-29 15:26:44,336 (SinkRunner-PollingRunner-DefaultSinkProcessor) [INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.LoggerSink.process(LoggerSink.java:95)] Event: { headers:{} body: 65 78 65 63 20 74 61 69 6C 39 36 exec tail96 }
2017-03-29 15:26:44,336 (SinkRunner-PollingRunner-DefaultSinkProcessor) [INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.LoggerSink.process(LoggerSink.java:95)] Event: { headers:{} body: 65 78 65 63 20 74 61 69 6C 39 37 exec tail97 }
2017-03-29 15:26:44,336 (SinkRunner-PollingRunner-DefaultSinkProcessor) [INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.LoggerSink.process(LoggerSink.java:95)] Event: { headers:{} body: 65 78 65 63 20 74 61 69 6C 39 38 exec tail98 }
2017-03-29 15:26:44,337 (SinkRunner-PollingRunner-DefaultSinkProcessor) [INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.LoggerSink.process(LoggerSink.java:95)] Event: { headers:{} body: 65 78 65 63 20 74 61 69 6C 39 39 exec tail99 }
2017-03-29 15:26:44,337 (SinkRunner-PollingRunner-DefaultSinkProcessor) [INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.LoggerSink.process(LoggerSink.java:95)] Event: { headers:{} body: 65 78 65 63 20 74 61 69 6C 31 30 30 exec tail100 }
4)、案例4:Syslogtcp
Syslogtcp监听TCP的端口做为数据源
a)创建agent配置文件
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ vi conf/syslog_tcp.conf
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = syslogtcp
a1.sources.r1.port = 5140
a1.sources.r1.host = localhost
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
b)启动flume agent a1
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ bin/flume-ng agent -n a1 -c conf -f conf/syslog_tcp.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
c)测试产生syslog
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ echo "hello idoall.org syslog" | nc localhost 5140
d)在mbp的控制台,可以看到以下信息:
2017-03-29 15:33:43,305 (New I/O worker #1) [WARN - org.apache.flume.source.SyslogUtils.buildEvent(SyslogUtils.java:317)] Event created from Invalid Syslog data.
2017-03-29 15:33:46,303 (SinkRunner-PollingRunner-DefaultSinkProcessor) [INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.LoggerSink.process(LoggerSink.java:95)] Event: { headers:{Severity=0, Facility=0, flume.syslog.status=Invalid} body: 68 65 6C 6C 6F 20 69 64 6F 61 6C 6C 2E 6F 72 67 hello idoall.org }
5)、案例5:JSONHandler
a)创建agent配置文件
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ vi conf/post_json.conf
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = org.apache.flume.source.http.HTTPSource
a1.sources.r1.port = 8888
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
b)启动flume agent a1
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ bin/flume-ng agent -n a1 -c conf -f conf/post_json.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
c)生成JSON 格式的POST request
curl -X POST -d '[{ "headers" :{"a" : "a1","b" : "b1"},"body" : "idoall.org_body"}]' http://localhost:8888
d)在mbp的控制台,可以看到以下信息:
2017-03-29 15:37:30,565 (lifecycleSupervisor-1-0) [INFO - org.mortbay.log.Slf4jLog.info(Slf4jLog.java:67)] jetty-6.1.26
2017-03-29 15:37:30,713 (lifecycleSupervisor-1-0) [INFO - org.mortbay.log.Slf4jLog.info(Slf4jLog.java:67)] Started SelectChannelConnector@0.0.0.0:8888
2017-03-29 15:37:30,713 (lifecycleSupervisor-1-0) [INFO - org.apache.flume.instrumentation.MonitoredCounterGroup.register(MonitoredCounterGroup.java:119)] Monitored counter group for type: SOURCE, name: r1: Successfully registered new MBean.
2017-03-29 15:37:30,713 (lifecycleSupervisor-1-0) [INFO - org.apache.flume.instrumentation.MonitoredCounterGroup.start(MonitoredCounterGroup.java:95)] Component type: SOURCE, name: r1 started
2017-03-29 15:38:00,451 (SinkRunner-PollingRunner-DefaultSinkProcessor) [INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.LoggerSink.process(LoggerSink.java:95)] Event: { headers:{a=a1, b=b1} body: 69 64 6F 61 6C 6C 2E 6F 72 67 5F 62 6F 64 79 idoall.org_body }
总结Exec source:Exec source和Spooling Directory Source是两种常用的日志采集的方式,其中Exec source可以实现对日志的实时采集,Spooling Directory Source在对日志的实时采集上稍有欠缺,尽管Exec source可以实现对日志的实时采集,但是当Flume不运行或者指令执行出错时,Exec source将无法收集到日志数据,日志会出现丢失,从而无法保证收集日志的完整性。
6)、案例6:Avro Source
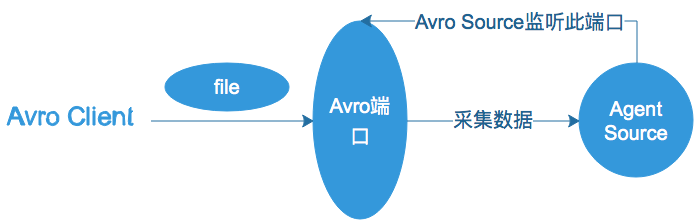
监听一个指定的Avro 端口,通过Avro 端口可以获取到Avro client发送过来的文件 。即只要应用程序通过Avro 端口发送文件,source组件就可以获取到该文件中的内容。 其中 Sink:hdfs Channel:file
(注:Avro和Thrift都是一些序列化的网络端口–通过这些网络端口可以接受或者发送信息,Avro可以发送一个给定的文件给Flume,Avro 源使用AVRO RPC机制)
Avro Source运行原理如下图:
flume配置文件的书写是相当灵活的—-不同类型的Source、Channel和Sink可以自由组合!
最后对上面用的几个flume source进行适当总结:
① NetCat Source:监听一个指定的网络端口,即只要应用程序向这个端口里面写数据,这个source组件
就可以获取到信息。
②Spooling Directory Source:监听一个指定的目录,即只要应用程序向这个指定的目录中添加新的文
件,source组件就可以获取到该信息,并解析该文件的内容,然后写入到channle。写入完成后,标记
该文件已完成或者删除该文件。
③Exec Source:监听一个指定的命令,获取一条命令的结果作为它的数据源
常用的是tail -F file指令,即只要应用程序向日志(文件)里面写数据,source组件就可以获取到日志(文件)中最新的内容 。
④Avro Source:监听一个指定的Avro 端口,通过Avro 端口可以获取到Avro client发送过来的文件 。即只要应用程序通过Avro 端口发送文件,source组件就可以获取到该文件中的内容。
7)、案例7:Hadoop sink
a)创建agent配置文件
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ vi conf/hdfs_sink.conf
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = syslogtcp
a1.sources.r1.port = 5140
a1.sources.r1.host = localhost
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://localhost:8020/user/flume/syslogtcp
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = Syslog
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 10
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = minute
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
b)启动flume agent a1
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ bin/flume-ng agent -n a1 -c conf -f conf/hdfs_sink.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
c)测试产生syslog
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ echo "hello idoall flume -> hadoop testing one" | nc localhost 5140
d)在mbp的控制台,可以看到以下信息:
2017-03-29 19:10:14,820 (SinkRunner-PollingRunner-DefaultSinkProcessor) [INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.hdfs.HDFSSequenceFile.configure(HDFSSequenceFile.java:63)] writeFormat = Writable, UseRawLocalFileSystem = false
2017-03-29 19:10:14,834 (SinkRunner-PollingRunner-DefaultSinkProcessor) [INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.hdfs.BucketWriter.open(BucketWriter.java:231)] Creating hdfs://localhost:8020/user/flume/syslogtcp/Syslog.1490785814821.tmp
2017-03-29 19:10:44,861 (hdfs-k1-roll-timer-0) [INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.hdfs.BucketWriter.close(BucketWriter.java:357)] Closing hdfs://localhost:8020/user/flume/syslogtcp/Syslog.1490785814821.tmp
2017-03-29 19:10:44,880 (hdfs-k1-call-runner-9) [INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.hdfs.BucketWriter$8.call(BucketWriter.java:618)] Renaming hdfs://localhost:8020/user/flume/syslogtcp/Syslog.1490785814821.tmp to hdfs://localhost:8020/user/flume/syslogtcp/Syslog.1490785814821
2017-03-29 19:10:44,884 (hdfs-k1-roll-timer-0) [INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.hdfs.HDFSEventSink$1.run(HDFSEventSink.java:382)] Writer callback called.
e)在mbp上再打开一个窗口,去hadoop上检查文件是否生成
mbp:hadoop-2.7.3$ bin/hadoop fs -ls /user/flume/syslogtcp
Found 1 items
-rw-r--r-- 3 liudebin supergroup 175 2017-03-29 19:10 /user/flume/syslogtcp/Syslog.1490785779051
mbp:hadoop-2.7.3$ bin/hadoop fs -cat /user/flume/syslogtcp/Syslog.1490785779051
SEQ!org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable"org.apache.hadoop.io.BytesWritable?L????ˌ?ܞ ??[???(hello idoall flume -> hadoop testing one?????L????ˌ?ܞ ??
8)、案例8:File Roll Sink
a)创建agent配置文件
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ vi conf/file_roll.conf
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = syslogtcp
a1.sources.r1.port = 5555
a1.sources.r1.host = localhost
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = file_roll
a1.sinks.k1.sink.directory = /opt/apache-flume-1.7.0-bin/logs
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
b)启动flume agent a1
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ bin/flume-ng agent -n a1 -c conf -f conf/file_roll.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
c)测试产生log
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ echo "hello idoall.org syslog" | nc localhost 5555
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ echo "hello idoall.org syslog 2" | nc localhost 5555
d)查看/home/hadoop/flume-1.5.0-bin/logs下是否生成文件,默认每30秒生成一个新文件
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ ls -l logs/
total 24
-rw-r--r-- 1 liudebin wheel 50 3 30 13:06 1490850370723-1
-rw-r--r-- 1 liudebin wheel 0 3 30 13:06 1490850370723-2
-rw-r--r-- 1 liudebin wheel 6429 3 29 14:06 flume.log.COMPLETED
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ cat logs/1490850370723-1 logs/1490850370723-2
hello idoall.org syslog
hello idoall.org syslog 2
9)、案例9:Replicating Channel Selector
Flume支持Fan out流从一个源到多个通道。有两种模式的Fan out,分别是复制和复用。在复制的情况下,流的事件被发送到所有的配置通道。在复用的情况下,事件被发送到可用的渠道中的一个子集。Fan out流需要指定源和Fan out通道的规则。
这次我们需要用到mbp1,mbp2两台机器
a)在mbp1创建replicating_Channel_Selector.conf配置文件
mbp1:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ vi conf/replicating_Channel_Selector.conf
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.channels = c1 c2
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = syslogtcp
a1.sources.r1.port = 5140
a1.sources.r1.host = localhost
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sources.r1.selector.type = replicating
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = mbp1
a1.sinks.k1.port = 5555
a1.sinks.k2.type = avro
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2
a1.sinks.k2.hostname = mbp2
a1.sinks.k2.port = 5555
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.channels.c2.type = memory
a1.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
b)在mbp1创建replicating_Channel_Selector_avro.conf配置文件
mbp1:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ vi conf/replicating_Channel_Selector_avro.conf
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = avro
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sources.r1.bind = 0.0.0.0
a1.sources.r1.port = 5555
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
c)在mbp1上将2个配置文件复制到mbp2上一份
mbp1:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ scp -r conf/replicating_Channel_Selector.conf vagrant@mbp2:/opt/apache-flume-1.7.0/conf/
mbp1:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ scp -r conf/replicating_Channel_Selector_avro.conf vagrant@mbp2:/opt/apache-flume-1.7.0/conf/
d)打开4个窗口,在mbp1和mbp2上同时启动两个flume agent
mbp1:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ bin/flume-ng agent -c . -f conf/replicating_Channel_Selector.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
mbp1:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ bin/flume-ng agent -c . -f conf/replicating_Channel_Selector_avro.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
e)然后在mbp1或mbp2的任意一台机器上,测试产生syslog
mbp1:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ echo "hello idoall.org syslog" | nc localhost 5140
f)在mbp1和mbp2的sink窗口,分别可以看到以下信息,这说明信息得到了同步:
17/04/05 14:08:18 INFO ipc.NettyServer: Connection to /192.168.1.51:46844 disconnected.
17/04/05 14:08:52 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0x90f8fe1f, /192.168.1.50:35873 => /192.168.1.50:5555] OPEN
17/04/05 14:08:52 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0x90f8fe1f, /192.168.1.50:35873 => /192.168.1.50:5555] BOUND: /192.168.1.50:5555
17/04/05 14:08:52 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0x90f8fe1f, /192.168.1.50:35873 => /192.168.1.50:5555] CONNECTED: /192.168.1.50:35873
17/04/05 14:08:59 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0xd6318635, /192.168.1.51:46858 => /192.168.1.50:5555] OPEN
17/04/05 14:08:59 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0xd6318635, /192.168.1.51:46858 => /192.168.1.50:5555] BOUND: /192.168.1.50:5555
17/04/05 14:08:59 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0xd6318635, /192.168.1.51:46858 => /192.168.1.50:5555] CONNECTED: /192.168.1.51:46858
17/04/05 14:09:20 INFO sink.LoggerSink: Event: { headers:{Severity=0, flume.syslog.status=Invalid, Facility=0} body: 68 65 6C 6C 6F 20 69 64 6F 61 6C 6C 2E 6F 72 67 hello idoall.org }
10)、案例10:Multiplexing Channel Selector
a)在mbp1创建Multiplexing_Channel_Selector配置文件
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ vi conf/Multiplexing_Channel_Selector.conf
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.channels = c1 c2
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = org.apache.flume.source.http.HTTPSource
a1.sources.r1.port = 5140
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sources.r1.selector.type = multiplexing
a1.sources.r1.selector.header = type
#映射允许每个值通道可以重叠。默认值可以包含任意数量的通道。
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.baidu = c1
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.ali = c2
a1.sources.r1.selector.default = c1
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = mbp1
a1.sinks.k1.port = 5555
a1.sinks.k2.type = avro
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2
a1.sinks.k2.hostname = mbp2
a1.sinks.k2.port = 5555
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.channels.c2.type = memory
a1.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
b)在mbp1创建Multiplexing_Channel_Selector_avro配置文件
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ vi conf/Multiplexing_Channel_Selector_avro.conf
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = avro
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sources.r1.bind = 0.0.0.0
a1.sources.r1.port = 5555
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
c)将2个配置文件复制到mbp2上一份
mbp1:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$scp -r conf/Multiplexing_Channel_Selector.conf root@mbp2:/opt/apache-flume-1.7.0-bin/conf/Multiplexing_Channel_Selector.conf
mbp1:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$scp -r conf/Multiplexing_Channel_Selector_avro.conf root@mbp2:/opt/apache-flume-1.7.0-bin/conf/Multiplexing_Channel_Selector_avro.conf
d)打开4个窗口,在mbp1和mbp2上同时启动两个flume agent
mbp1:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$bin/flume-ng agent -c . -f conf/Multiplexing_Channel_Selector_avro.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
mbp1:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$bin/flume-ng agent -c . -f conf/Multiplexing_Channel_Selector.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
e)然后在mbp1或mbp2的任意一台机器上,测试产生syslog
mbp1:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$curl -X POST -d '[{ "headers" :{"type" : "baidu"},"body" : "idoall_TEST1"}]' http://localhost:5140 && curl -X POST -d '[{ "headers" :{"type" : "ali"},"body" : "idoall_TEST2"}]' http://localhost:5140 && curl -X POST -d '[{ "headers" :{"type" : "qq"},"body" : "idoall_TEST3"}]' http://localhost:5140
f)在mbp1的sink窗口,可以看到以下信息:
17/04/05 14:32:21 INFO node.Application: Starting Sink k1
17/04/05 14:32:21 INFO node.Application: Starting Source r1
17/04/05 14:32:21 INFO source.AvroSource: Starting Avro source r1: { bindAddress: 0.0.0.0, port: 5555 }...
17/04/05 14:32:21 INFO instrumentation.MonitoredCounterGroup: Monitored counter group for type: SOURCE, name: r1: Successfully registered new MBean.
17/04/05 14:32:21 INFO instrumentation.MonitoredCounterGroup: Component type: SOURCE, name: r1 started
17/04/05 14:32:21 INFO source.AvroSource: Avro source r1 started.
17/04/05 14:32:36 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0xcf00eea6, /192.168.1.50:35916 => /192.168.1.50:5555] OPEN
17/04/05 14:32:36 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0xcf00eea6, /192.168.1.50:35916 => /192.168.1.50:5555] BOUND: /192.168.1.50:5555
17/04/05 14:32:36 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0xcf00eea6, /192.168.1.50:35916 => /192.168.1.50:5555] CONNECTED: /192.168.1.50:35916
17/04/05 14:32:44 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0x432f5468, /192.168.1.51:46945 => /192.168.1.50:5555] OPEN
17/04/05 14:32:44 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0x432f5468, /192.168.1.51:46945 => /192.168.1.50:5555] BOUND: /192.168.1.50:5555
17/04/05 14:32:44 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0x432f5468, /192.168.1.51:46945 => /192.168.1.50:5555] CONNECTED: /192.168.1.51:46945
17/04/05 14:34:11 INFO sink.LoggerSink: Event: { headers:{type=baidu} body: 69 64 6F 61 6C 6C 5F 54 45 53 54 31 idoall_TEST1 }
17/04/05 14:34:57 INFO sink.LoggerSink: Event: { headers:{type=qq} body: 69 64 6F 61 6C 6C 5F 54 45 53 54 33
g)在mbp2的sink窗口,可以看到以下信息:
17/04/05 14:32:27 INFO node.Application: Starting Sink k1
17/04/05 14:32:27 INFO node.Application: Starting Source r1
17/04/05 14:32:27 INFO source.AvroSource: Starting Avro source r1: { bindAddress: 0.0.0.0, port: 5555 }...
17/04/05 14:32:27 INFO instrumentation.MonitoredCounterGroup: Monitored counter group for type: SOURCE, name: r1: Successfully registered new MBean.
17/04/05 14:32:27 INFO instrumentation.MonitoredCounterGroup: Component type: SOURCE, name: r1 started
17/04/05 14:32:27 INFO source.AvroSource: Avro source r1 started.
17/04/05 14:32:36 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0x7c2f0aec, /192.168.1.50:38104 => /192.168.1.51:5555] OPEN
17/04/05 14:32:36 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0x7c2f0aec, /192.168.1.50:38104 => /192.168.1.51:5555] BOUND: /192.168.1.51:5555
17/04/05 14:32:36 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0x7c2f0aec, /192.168.1.50:38104 => /192.168.1.51:5555] CONNECTED: /192.168.1.50:38104
17/04/05 14:32:44 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0x3d36f553, /192.168.1.51:48599 => /192.168.1.51:5555] OPEN
17/04/05 14:32:44 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0x3d36f553, /192.168.1.51:48599 => /192.168.1.51:5555] BOUND: /192.168.1.51:5555
17/04/05 14:32:44 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0x3d36f553, /192.168.1.51:48599 => /192.168.1.51:5555] CONNECTED: /192.168.1.51:48599
17/04/05 14:34:33 INFO sink.LoggerSink: Event: { headers:{type=ali} body: 69 64 6F 61 6C 6C 5F 54 45 53 54 32 idoall_TEST2 }
可以看到,根据header中不同的条件分布到不同的channel上
11)、案例11:Flume Sink Processors
failover的机器是一直发送给其中一个sink,当这个sink不可用的时候,自动发送到下一个sink。
a)在m1创建Flume_Sink_Processors配置文件
- root@m1:/home/hadoop# vi /home/hadoop/flume-1.5.0-bin/conf/Flume_Sink_Processors.conf
- a1.sources = r1
- a1.sinks = k1 k2
- a1.channels = c1 c2
- #这个是配置failover的关键,需要有一个sink group
- a1.sinkgroups = g1
- a1.sinkgroups.g1.sinks = k1 k2
- #处理的类型是failover
- a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = failover
- #优先级,数字越大优先级越高,每个sink的优先级必须不相同
- a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.priority.k1 = 5
- a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.priority.k2 = 10
- #设置为10秒,当然可以根据你的实际状况更改成更快或者很慢
- a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.maxpenalty = 10000
- # Describe/configure the source
- a1.sources.r1.type = syslogtcp
- a1.sources.r1.port = 5140
- a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2
- a1.sources.r1.selector.type = replicating
- # Describe the sink
- a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
- a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
- a1.sinks.k1.hostname = m1
- a1.sinks.k1.port = 5555
- a1.sinks.k2.type = avro
- a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2
- a1.sinks.k2.hostname = m2
- a1.sinks.k2.port = 5555
- # Use a channel which buffers events in memory
- a1.channels.c1.type = memory
- a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
- a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
- a1.channels.c2.type = memory
- a1.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
- a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
b)在m1创建Flume_Sink_Processors_avro配置文件
- root@m1:/home/hadoop# vi /home/hadoop/flume-1.5.0-bin/conf/Flume_Sink_Processors_avro.conf
- a1.sources = r1
- a1.sinks = k1
- a1.channels = c1
- # Describe/configure the source
- a1.sources.r1.type = avro
- a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
- a1.sources.r1.bind = 0.0.0.0
- a1.sources.r1.port = 5555
- # Describe the sink
- a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
- # Use a channel which buffers events in memory
- a1.channels.c1.type = memory
- a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
- a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
- # Bind the source and sink to the channel
- a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
- a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
c)将2个配置文件复制到m2上一份
- root@m1:/home/hadoop/flume-1.5.0-bin# scp -r /home/hadoop/flume-1.5.0-bin/conf/Flume_Sink_Processors.conf root@m2:/home/hadoop/flume-1.5.0-bin/conf/Flume_Sink_Processors.conf
- root@m1:/home/hadoop/flume-1.5.0-bin# scp -r /home/hadoop/flume-1.5.0-bin/conf/Flume_Sink_Processors_avro.conf root@m2:/home/hadoop/flume-1.5.0-bin/conf/Flume_Sink_Processors_avro.conf
d)打开4个窗口,在m1和m2上同时启动两个flume agent
- root@m1:/home/hadoop# /home/hadoop/flume-1.5.0-bin/bin/flume-ng agent -c . -f /home/hadoop/flume-1.5.0-bin/conf/Flume_Sink_Processors_avro.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
- root@m1:/home/hadoop# /home/hadoop/flume-1.5.0-bin/bin/flume-ng agent -c . -f /home/hadoop/flume-1.5.0-bin/conf/Flume_Sink_Processors.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
e)然后在m1或m2的任意一台机器上,测试产生log
- root@m1:/home/hadoop# echo "idoall.org test1 failover" | nc localhost 5140
f)因为m2的优先级高,所以在m2的sink窗口,可以看到以下信息,而m1没有:
- 14/08/10 15:02:46 INFO ipc.NettyServer: Connection to /192.168.1.51:48692 disconnected.
- 14/08/10 15:03:12 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0x09a14036, /192.168.1.51:48704 => /192.168.1.51:5555] OPEN
- 14/08/10 15:03:12 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0x09a14036, /192.168.1.51:48704 => /192.168.1.51:5555] BOUND: /192.168.1.51:5555
- 14/08/10 15:03:12 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0x09a14036, /192.168.1.51:48704 => /192.168.1.51:5555] CONNECTED: /192.168.1.51:48704
- 14/08/10 15:03:26 INFO sink.LoggerSink: Event: { headers:{Severity=0, flume.syslog.status=Invalid, Facility=0} body: 69 64 6F 61 6C 6C 2E 6F 72 67 20 74 65 73 74 31 idoall.org test1 }
g)这时我们停止掉m2机器上的sink(ctrl+c),再次输出测试数据:
- root@m1:/home/hadoop# echo "idoall.org test2 failover" | nc localhost 5140
h)可以在m1的sink窗口,看到读取到了刚才发送的两条测试数据:
- 14/08/10 15:02:46 INFO ipc.NettyServer: Connection to /192.168.1.51:47036 disconnected.
- 14/08/10 15:03:12 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0xbcf79851, /192.168.1.51:47048 => /192.168.1.50:5555] OPEN
- 14/08/10 15:03:12 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0xbcf79851, /192.168.1.51:47048 => /192.168.1.50:5555] BOUND: /192.168.1.50:5555
- 14/08/10 15:03:12 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0xbcf79851, /192.168.1.51:47048 => /192.168.1.50:5555] CONNECTED: /192.168.1.51:47048
- 14/08/10 15:07:56 INFO sink.LoggerSink: Event: { headers:{Severity=0, flume.syslog.status=Invalid, Facility=0} body: 69 64 6F 61 6C 6C 2E 6F 72 67 20 74 65 73 74 31 idoall.org test1 }
- 14/08/10 15:07:56 INFO sink.LoggerSink: Event: { headers:{Severity=0, flume.syslog.status=Invalid, Facility=0} body: 69 64 6F 61 6C 6C 2E 6F 72 67 20 74 65 73 74 32 idoall.org test2 }
i)我们再在m2的sink窗口中,启动sink:
- root@m1:/home/hadoop# /home/hadoop/flume-1.5.0-bin/bin/flume-ng agent -c . -f /home/hadoop/flume-1.5.0-bin/conf/Flume_Sink_Processors_avro.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
j)输入两批测试数据:
- root@m1:/home/hadoop# echo "idoall.org test3 failover" | nc localhost 5140 && echo "idoall.org test4 failover" | nc localhost 5140
k)在m2的sink窗口,我们可以看到以下信息,因为优先级的关系,log消息会再次落到m2上:
- 14/08/10 15:09:47 INFO node.Application: Starting Sink k1
- 14/08/10 15:09:47 INFO node.Application: Starting Source r1
- 14/08/10 15:09:47 INFO source.AvroSource: Starting Avro source r1: { bindAddress: 0.0.0.0, port: 5555 }...
- 14/08/10 15:09:47 INFO instrumentation.MonitoredCounterGroup: Monitored counter group for type: SOURCE, name: r1: Successfully registered new MBean.
- 14/08/10 15:09:47 INFO instrumentation.MonitoredCounterGroup: Component type: SOURCE, name: r1 started
- 14/08/10 15:09:47 INFO source.AvroSource: Avro source r1 started.
- 14/08/10 15:09:54 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0x96615732, /192.168.1.51:48741 => /192.168.1.51:5555] OPEN
- 14/08/10 15:09:54 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0x96615732, /192.168.1.51:48741 => /192.168.1.51:5555] BOUND: /192.168.1.51:5555
- 14/08/10 15:09:54 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0x96615732, /192.168.1.51:48741 => /192.168.1.51:5555] CONNECTED: /192.168.1.51:48741
- 14/08/10 15:09:57 INFO sink.LoggerSink: Event: { headers:{Severity=0, flume.syslog.status=Invalid, Facility=0} body: 69 64 6F 61 6C 6C 2E 6F 72 67 20 74 65 73 74 32 idoall.org test2 }
- 14/08/10 15:10:43 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0x12621f9a, /192.168.1.50:38166 => /192.168.1.51:5555] OPEN
- 14/08/10 15:10:43 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0x12621f9a, /192.168.1.50:38166 => /192.168.1.51:5555] BOUND: /192.168.1.51:5555
- 14/08/10 15:10:43 INFO ipc.NettyServer: [id: 0x12621f9a, /192.168.1.50:38166 => /192.168.1.51:5555] CONNECTED: /192.168.1.50:38166
- 14/08/10 15:10:43 INFO sink.LoggerSink: Event: { headers:{Severity=0, flume.syslog.status=Invalid, Facility=0} body: 69 64 6F 61 6C 6C 2E 6F 72 67 20 74 65 73 74 33 idoall.org test3 }
- 14/08/10 15:10:43 INFO sink.LoggerSink: Event: { headers:{Severity=0, flume.syslog.status=Invalid, Facility=0} body: 69 64 6F 61 6C 6C 2E 6F 72 67 20 74 65 73 74 34 idoall.org test4 }
12)、案例12:Load balancing Sink Processor
load balance type和failover不同的地方是,load balance有两个配置,一个是轮询,一个是随机。两种情况下如果被选择的sink不可用,就会自动尝试发送到下一个可用的sink上面。
a)在m1创建Load_balancing_Sink_Processors配置文件
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ vi conf/load_balancing_sink_processors.conf
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.channels = c1
#这个是配置Load balancing的关键,需要有一个sink group
a1.sinkgroups = g1
a1.sinkgroups.g1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = load_balance
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.backoff = true
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.selector = round_robin
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = syslogtcp
a1.sources.r1.port = 5140
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = m1
a1.sinks.k1.port = 5555
a1.sinks.k2.type = avro
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k2.hostname = m2
a1.sinks.k2.port = 5555
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
b)在m1创建Load_balancing_Sink_Processors_avro配置文件
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ vi conf/load_balancing_sink_processors_avro.conf
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = avro
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sources.r1.bind = 0.0.0.0
a1.sources.r1.port = 5555
# Describe the sink
sinks.k1.type = logger
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
c)将2个配置文件复制到mbp2上一份
root@mbp1:/opt/apache-flume-1.7.0-bin# scp -r conf/Load_balancing_Sink_Processors.conf root@mbp2:/opt/apache-flume-1.7.0-bin/conf/Load_balancing_Sink_Processors.conf
root@mbp1:/opt/apache-flume-1.7.0-bin# scp -r conf/Load_balancing_Sink_Processors_avro.conf root@mbp2:/opt/apache-flume-1.7.0-bin/conf/Load_balancing_Sink_Processors_avro.conf
d)打开4个窗口,在mbp1和mbp2上同时启动两个flume agent
root@mbp1:/opt# /opt/apache-flume-1.7.0-bin/bin/flume-ng agent -c . -f conf/Load_balancing_Sink_Processors_avro.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
root@mbp1:/opt# /opt/apache-flume-1.7.0-bin/bin/flume-ng agent -c . -f conf/Load_balancing_Sink_Processors.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
e)然后在mbp1或mbp2的任意一台机器上,测试产生log,一行一行输入,输入太快,容易落到一台机器上
root@mbp1:/opt# echo "idoall.org test1" | nc localhost 5140
root@mbp1:/opt# echo "idoall.org test2" | nc localhost 5140
root@mbp1:/opt# echo "idoall.org test3" | nc localhost 5140
root@mbp1:/opt# echo "idoall.org test4" | nc localhost 5140
f)在mbp1的sink窗口,可以看到以下信息:
17/04/05 15:35:29 INFO sink.LoggerSink: Event: { headers:{Severity=0, flume.syslog.status=Invalid, Facility=0} body: 69 64 6F 61 6C 6C 2E 6F 72 67 20 74 65 73 74 32 idoall.org test2 }
17/04/05 15:35:33 INFO sink.LoggerSink: Event: { headers:{Severity=0, flume.syslog.status=Invalid, Facility=0} body: 69 64 6F 61 6C 6C 2E 6F 72 67 20 74 65 73 74 34 idoall.org test4 }
g)在mbp2的sink窗口,可以看到以下信息:
17/04/05 15:35:27 INFO sink.LoggerSink: Event: { headers:{Severity=0, flume.syslog.status=Invalid, Facility=0} body: 69 64 6F 61 6C 6C 2E 6F 72 67 20 74 65 73 74 31 idoall.org test1 }
17/08/05 15:35:29 INFO sink.LoggerSink: Event: { headers:{Severity=0, flume.syslog.status=Invalid, Facility=0} body: 69 64 6F 61 6C 6C 2E 6F 72 67 20 74 65 73 74 33 idoall.org test3 }
说明轮询模式起到了作用。
13)、案例13:Hbase sink
a)在测试之前,请先参考《ubuntu12.04+hadoop2.2.0+zookeeper3.4.5+hbase0.96.2+hive0.13.1分布式环境部署》将hbase启动
b)然后将以下文件复制到flume中:
cp hbase-1.3.0-bin/lib/protobuf-java-2.5.0.jar apache-flume-1.7.0-bin/lib/
cp hbase-1.3.0-bin/lib/habase-client-1.3.0.jar apache-flume-1.7.0-bin/lib/
cp hbase-1.3.0-bin/lib/hbase-common-1.3.0.jar apache-flume-1.7.0-bin/lib/
cp hbase-1.3.0-bin/lib/hbase-protocol-1.3.0.jar apache-flume-1.7.0-bin/lib/
cp hbase-1.3.0-bin/lib/hbase-server-1.3.0.jar apache-flume-1.7.0-bin/lib/
cp hbase-1.3.0-bin/lib/hbase-hadoop2-compat-1.3.0.jar apache-flume-1.7.0-bin/lib/
cp hbase-1.3.0-bin/lib/hbase-hadoop-compat-1.3.0.jar apache-flume-1.7.0-bin/lib/
cp hbase-1.3.0-bin/lib/htrace-core-3.1.0-incubating.jar apache-flume-1.7.0-bin/lib/
c)确保test_idoall_org表在hbase中已经存在
d)在m1创建hbase_simple配置文件
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ vi conf/hbase_simple.conf
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = syslogtcp
a1.sources.r1.port = 5140
a1.sources.r1.host = localhost
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
a1.sinks.k1.type = hbase
a1.sinks.k1.table = test_idoall_org
a1.sinks.k1.columnFamily = name
a1.sinks.k1.column = idoall
a1.sinks.k1.serializer = org.apache.flume.sink.hbase.RegexHbaseEventSerializer
a1.sinks.k1.channel = memoryChannel
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
e)启动flume agent
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ bin/flume-ng agent -n a1 -c conf -f conf/hbase_simple.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
f)测试产生syslog
mbp:apache-flume-1.7.0-bin$ echo "hello idoall.org from flume" | nc localhost 5140
g)这时登录到hbase中,可以发现新数据已经插入
mbp@opt# hbase-1.3.0/bin/hbase shell
2017-04-05 16:09:48,984 INFO [main] Configuration.deprecation: hadoop.native.lib is deprecated. Instead, use io.native.lib.available
HBase Shell; enter 'help<RETURN>' for list of supported commands.
Type "exit<RETURN>" to leave the HBase Shell
Version 0.96.2-hadoop2, r1581096, Mon Mar 24 16:03:18 PDT 2017
hbase(main):001:0> list
TABLE
SLF4J: Class path contains multiple SLF4J bindings.
SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/opt/hbase-1.3.0/lib/slf4j-log4j12-1.6.4.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]
SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/opt/hadoop-2.8.0/share/hadoop/common/lib/slf4j-log4j12-1.7.5.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]
SLF4J: See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#multiple_bindings for an explanation.
hbase2hive_idoall
hive2hbase_idoall
test_idoall_org
3 row(s) in 2.6880 seconds
=> ["hbase2hive_idoall", "hive2hbase_idoall", "test_idoall_org"]
hbase(main):002:0> scan "test_idoall_org"
ROW COLUMN+CELL
10086 column=name:idoall, timestamp=1406424831473, value=idoallvalue
1 row(s) in 0.0550 seconds
hbase(main):003:0> scan "test_idoall_org"
ROW COLUMN+CELL
10086 column=name:idoall, timestamp=1406424831473, value=idoallvalue
1407658495588-XbQCOZrKK8-0 column=name:payload, timestamp=1407658498203, value=hello idoall.org from flume
2 row(s) in 0.0200 seconds
hbase(main):004:0> quit
经过这么多flume的例子测试,如果你全部做完后,会发现flume的功能真的很强大,可以进行各种搭配来完成你想要的工作,俗话说师傅领进门,修行在个人,如何能够结合你的产品业务,将flume更好的应用起来,快去动手实践吧。
最新文章
- 夺命雷公狗----Git---6---GitHub基本使用
- VS2010部署Asp.net程序到本地IIS 7
- Raspberry Pi Resources-Using the UART
- 超好用的plsql设置
- Part 12 DateTime functions in SQL Server
- OK335xS LAN8710 phy driver hacking
- textarea中的空格与换行
- 为什么使用 Containjs 模块化管理工具效率高?
- nova创建虚拟机源码分析系列之五 nova源码分发实现
- python第一天2.28
- 5.04-requests_cookies
- ELK之安装了search guard认证后安装elasticsearch-head
- Saiku本地编译运行后Debug调试(十二)
- 数据库和ado连接语句的使用总结
- nfs共享文件搭建
- 20145315何佳蕾《网络对抗》Web安全基础
- Python3 tkinter基础 Label imag显示图片
- ViewPager的简单用法+适配器+监听器的介绍
- Jenkins+Ant+Jmeter搭建持续集成的接口测试平台(转)
- C#调用DLL报“试图加载格式不正确的程序”