|
通过完成一个 todo 应用展示 Node.js + MySQL 增删改查的功能。这里后台使用 Koa 及其相应的一些中间件作为 server 提供服务。
初始化项目
$ mkdir node-crud && cd $_
$ yarn init -y && npx gitignore node
上面的命令创建了一个空文件夹 node-crud,进入之后初始化一个 package.json 以及创建 .gitignore 文件。
安装 Koa 并创建 app.js 以启动一个简单的 server:
$ yarn add koa
$ touch app.js
app.js
const Koa = require("koa");
const app = new Koa();
app.use(async ctx => {
ctx.body = "hello world!";
});
app.listen(3000);
console.log("server started at http://localhost:3000");
使用 node 启动服务后即可通过访问 http://localhost:3000 查看到页面。
$ node app.js
server started at http://localhost:3000
将启动服务的命令添加到 package.json 的 scripts 后,可通过 yarn 方便地调用。
package.json
"scripts": {
"start": "node app.js"
},
然后就可以这样来启动服务:
$ yarn start
server started at http://localhost:3000
hello world 页面
添加视图
现在页面还只能呈现简单的文本,通过让请求返回 HTML 文件,可渲染更加复杂的页面。比如:
app.use(async ctx => {
ctx.body = "<h1>hello world!</h1>";
});
但手动拼接 HTML 不是很方便,可通添加相应 Koa 中间件使得请求可从预先写好的模板文件返回 HTML 到页面。
安装 koa-views 并使用它来返回视图(view)。koa-views 需要配合另外的模板引擎来展示数据,这里使用 nunjucks。
$ yarn add koa-views nunjucks
在代码中使用上面两个 npm 模块来返回页面:
// 配置模板路径及所使用的模板引擎
app.use(
views(__dirname + "/views", {
map: {
html: "nunjucks"
}
})
);
app.use(async ctx => {
await ctx.render("form", {
todo: {}
});
});
然后创建 views 目录并在其中放置视图文件,比如创建一个 form.html 并在其中编辑一个 HTML 表单,后续使用它来提交数据。
views/form.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>todo crud - add todo</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/edit" method="POST">
<fieldset>
<legend>add todo</legend>
<input type="text" hidden name="id" value="{{ todo.id }}" />
<div class="form-row">
<label for="content">
todo content: <input name="content" type="text" placeholder="todo content..." id="content" value="{{ todo.content }}"
/>
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-row">
<label for="is_done">
is complete:
<input
name="is_done"
type="checkbox"
id="is_done"
value="1"
{%if not todo.is_done=='0'%}checked{%endif%}
/>
</label>
</div>
<button type="submit">submit</button>
</fieldset>
</form>
</body>
</html>
其中 {%...%} 为 nunjucks 的模板语法,更多可查看其文档。
再次启动服务器后,可看到如下的页面,包含一个表单以创建一个 todo。同时如果我们在渲染这个页面时,提供了 todo 数据,相应的数据会自动填充到表单中,此时该表单可用来编辑一个 todo。
表单页面
添加路由
除了这个表单页,应用中还会有一个展示所有 todo 的列表页。需要添加路由来分别展示这两个页面。同样是通过相应的 Koa 中间件来实现。这里不需要太复杂的功能,所以使用 koa-route 就能满足需求。
安装 koa-route :
在 views 目录下再创建一个 HTML 文件并写入列表页的代码:
views/list.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>todo crud - todo list</title>
<style>
li{
padding: 5px 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="/add">add</a>
<ul>
{% for item in list%}
<li>
<div class="todo-item">
<div class="content">#{{ loop.index }}[{%if item.is_done==0%}⏳{%else%}✅{%endif%}] {{ item.content }}</div>
</div>
</li>
{% else %}
<li>nothing yet. <a href="/add">add</a> some.</li>
{%endfor%}
</ul>
<a href="/add">add</a>
</body>
</html>
列表页中,通过 nunjucks 的 {% for item in list%} 语句遍历数据生成列表,需要展示的列表数据会在页面渲染时通过前面添加的 koa-view 来传递。
然后更新 app.js,添加路由逻辑以展示列表页和表单页。
const _ = require('koa-route');
app.use(
views(__dirname + "/views", {
map: {
html: "nunjucks"
}
})
);
app.use(
_.get("/", async function(ctx) {
const todos = await db.getAll();
await ctx.render("list", {
list: todos
});
})
);
app.use(
_.get("/add", async function(ctx) {
await ctx.render("form", { todo: {} });
})
);
因为 Koa 中间件是有顺序的。其中 views 的配置需要在路由之前,即 _.get 部分,这样后续中间件在路由分发时才能正确地设置上视图。
重新启动服务器,访问 http://localhost:3000 便能看到列表页。点击页面中 add 链接跳转到表单页以添加或编辑 todo。
列表页
现在我们有了可以提交数据的表单,也有了可以展示数据的列表页。接下来就是实现接收表单提交过来的数据并存入数据库。
表单数据的接收
通过添加相应的 Koa 中间件,以在代码中获取到页面提交过来的表单数据。
安装 koa-bodyparser 并在代码中启用。
$ yarn add koa-bodyparser
app.js
const bodyParser = require("koa-bodyparser");
app.use(bodyParser());
form 表单中,表单元素的 name 属性在数据提交时便是后端拿到的字段名,元素身上的 value 属性便是该字段的值。比如上面表单中 <input name="content" type="text" placeholder="todo content..." id="content" value="{{ todo.content }}"/> 在提交后会得到 {content:'...'}
添加新的路由以提供 POST 类型的接口来接收表单数据,因为该接口接收来的表单数据有可能是创建,有可能是编辑,这里取名 /edit:
app.use(
_.post("/edit", async function(ctx) {
try {
const todo = ctx.request.body;
// TODO: 保存到数据库
ctx.redirect("/");
} catch (error) {
ctx.body = error.stack;
}
})
);
这里 ctx.request.body 便是 koa-bodyparser 中间件解析数据后添加到 ctx.request 上的表单数据,等待被保存到数据库。
接下来便是数据库部分。
准备数据库
假设本地已经安装并正确配置了 MySQL,如果没有,可参考 MySQL 上手教程。
登录 MySQL 创建名为 todo 的数据库:
$ mysql -u wayou -p
# 输入密码...
mysql> CREATE DATABASE todo
切换到刚刚创建的数据库:
通过以下脚本创建名为 todo 的表:
CREATE TABLE `todo` (
`id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`content` varchar(500) COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`is_done` int(11) DEFAULT '0',
`date` date NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
)
数据库连接
在服务端代码中,同样,这里需要一个相应的 Koa 中间件来连接到数据库以进行相应的操作。
正常来讲,使用 mysql 即可,但它不提供 Promise 方式的接口调用,还是 callback 的方式,写起来有点不方便。所以这里使用另外一个 npm 模块 promise-mysql,是对它的 Promise 改装。
然后就可以愉快地使用 async/await 进行相关调用了。
创建 db.js 文件来专门处理数据库相关的操作,比如连接,数据的增删等,这样 app.js 中路由对应的 controller 只需要调用即可,不用掺杂数据库相关的逻辑。
db.js
const mysql = require("promise-mysql");
async function query(sql) {
const connection = await mysql.createConnection({
host: 'localhost',
user: 'wayou',
password: 'xxx',
database: "todo"
});
try {
const result = connection.query(sql);
connection.end();
return result;
} catch (error) {
throw error;
}
}
上面代码创建了一个接收 SQL 语句的方法,执行并返回结果。
小贴士:如果上面代码在后续测试执行时发现报如下的错误:
Error: ER_NOT_SUPPORTED_AUTH_MODE: Client does not support authentication protocol requested by server; consider upgrading MySQL client
多半是用来连接的帐户没有相应从程序进行连接的权限,可通过如下命令来配置 MySQL。
mysql> ALTER USER 'wayou'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'your_new_password';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
关于 mysql_native_password 可到这里了解更多。
FLUSH PRIVILEGES 用于刷新配置使其立即生效。
记录的插入
数据库连接准备好之后,就可以将接收到的表单数据插入到数据库中了。
在 db.js 中添加插入数据的方法:
db.js
async function update(todo) {
todo.is_done = todo.is_done == undefined ? 0 : todo.is_done;
if (todo.id) {
Object.assign(getTodoById(todo.id), todo);
return await query(</span></span> <span class="pl-s"> UPDATE todo</span> <span class="pl-s"> SET content='<span class="pl-s1"><span class="pl-pse">${</span><span class="pl-smi">todo</span>.<span class="pl-c1">content</span><span class="pl-pse">}</span></span>',is_done='<span class="pl-s1"><span class="pl-pse">${</span><span class="pl-smi">todo</span>.<span class="pl-smi">is_done</span><span class="pl-pse">}</span></span>'</span> <span class="pl-s"> WHERE todo.id=<span class="pl-s1"><span class="pl-pse">${</span><span class="pl-smi">todo</span>.<span class="pl-c1">id</span><span class="pl-pse">}</span></span></span> <span class="pl-s"> <span class="pl-pds">);
} else {
todo.date = new Date().toJSON().slice(0, 10);
return await query(</span></span> <span class="pl-s"> INSERT INTO todo (content,date,is_done) </span> <span class="pl-s"> VALUES ('<span class="pl-s1"><span class="pl-pse">${</span><span class="pl-smi">todo</span>.<span class="pl-c1">content</span><span class="pl-pse">}</span></span>','<span class="pl-s1"><span class="pl-pse">${</span><span class="pl-smi">todo</span>.<span class="pl-smi">date</span><span class="pl-pse">}</span></span>','<span class="pl-s1"><span class="pl-pse">${</span><span class="pl-smi">todo</span>.<span class="pl-smi">is_done</span><span class="pl-pse">}</span></span>')</span> <span class="pl-s"> <span class="pl-pds">);
}
}
该方法用于更新已有的记录或添加新的记录,这一点是通过判断传来的表单数据中是否有 id 字段,如果有,说明是编辑已有的数据,那么执行更新操作,如果没有 id 字段,则说明是新增一个 todo。
这里的 id 字段在 form 表单中是不展示的,参见上面表单页面的代码,但为了在表单提交时能够带上 id 字段,所以在表单中放置了一个隐藏的 <input> 来标识。
需要注意的是,HTML 中 form 表单中的 checkbox,其只在被勾选时才会被提交,未勾选时不会被提交到后台。所以这里对 is_done 进行一下兼容处理。
更新路由部分的代码,调用这里的 update 方法。
app.js
+ const db = require("./db");
app.use(
_.post("/edit", async function(ctx) {
try {
const todo = ctx.request.body;
- // TODO: 保存到数据库
+ await db.update(todo);
ctx.redirect("/");
} catch (error) {
ctx.body = error.stack;
}
})
);
重启服务器访问 http://localhost:3000/add 以提交表单来创建一条数据到数据库。
提交表单创建一条 todo
因为我们还没有将数据库中的列表展示到首页,所以这里提交成功后,跳回到首页时,数据没展现。不过我们可以去数据库查询刚刚创建的结果。
mysql> SELECT * FROM todo;
+----+---------+---------+------------+
| id | content | is_done | date |
+----+---------+---------+------------+
| 1 | 买菜 | 0 | 2019-04-26 |
+----+---------+---------+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
查询并展示数据到页面
刚刚已经写入了一条数据到数据库,现在可以通过 SELECT 语句将它查询出来并展示到首页的列表中。
添加相应的查询方法到 db.js 中。
db.js
async function getAll() {
return await query("select * from todo");
}
然后更新列表页的 controller,调用该方法获取数据并返回到页面。
app.js
app.use(
_.get("/", async function(ctx) {
- // TODO: 从数据库获取数据
- const todos = [];
+ const todos = await db.getAll();
await ctx.render("list", {
list: todos
});
})
);
重新启动服务后,如果一切顺利,访问首页可看到刚刚添加的 todo 展示了出来。
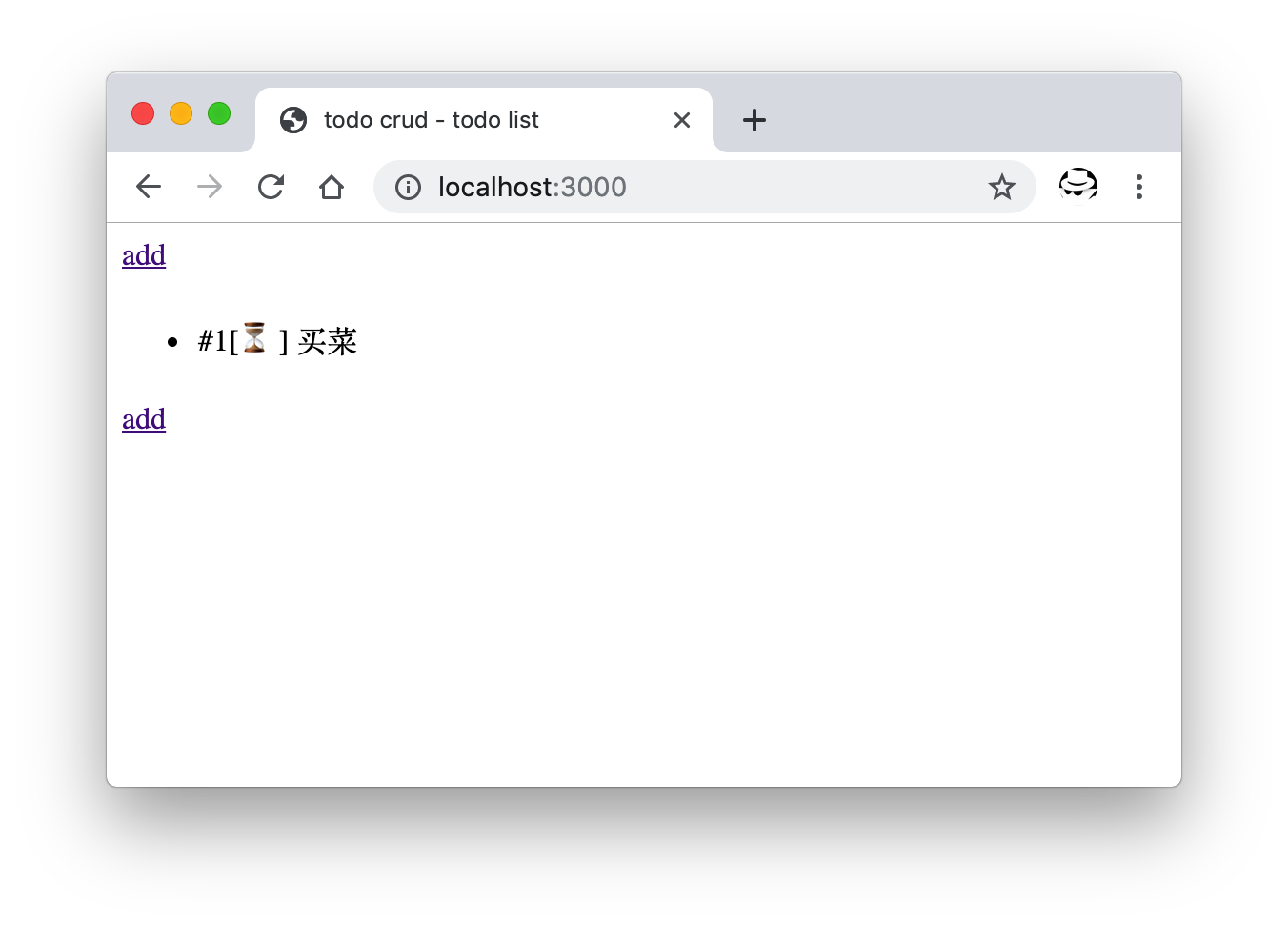
列表中展示来自数据库的数据
数据更新
下面为列表页中每条 todo 添加一个编辑按钮,点击后可跳转编辑页,同时跳转时连接上带上 todo 的 id。这样编辑页可从 url 中获取 id 并从数据库中将该 id 对应的数据取出来渲染到编辑页。
还需要添加一个新路由 /edit 展示和前面创建时一样的表单页,将根据 id 获取到的数据塞入表单提供编辑。
更新列表页 HTML 添加编辑按钮:
views/list.html
<div class="todo-item">
<div class="content">#{{ loop.index }}[{%if item.is_done==0%}⏳{%else%}✅{%endif%}] {{ item.content }}</div>
+ <div class="action">
+ <a href="/edit?id={{ item.id }}">edit</a>
+ </div>
</div>
添加编辑页的路由并返回这个表单:
app.js
app.use(
_.get("/edit", async function(ctx) {
const id = ctx.query.id;
if (!id) {
throw new Error("id is missing");
}
const todo = await db.getTodoById(id);
if (!todo) {
ctx.body = "item not found!";
} else {
await ctx.render("form", {
todo
});
}
})
);
因为参数是通过拼接到 url 传递而来,所以这里通过 query 部分来获取这个 id 参数。拿到之后调用了一个方法根据 id 获取数据。
更新 db.js 添加这个获取数据的方法:
db.js
async function getTodoById(id) {
const result = await query(`SELECT * FROM todo WHERE todo.id='${id}'`);
if (result[0]) {
return result[0];
}
return null;
}
重启后打开首页,可以看到新增的编辑按钮,点击后跳转到了新增的编辑页面,在这里可以对已经添加的条目进行更新。
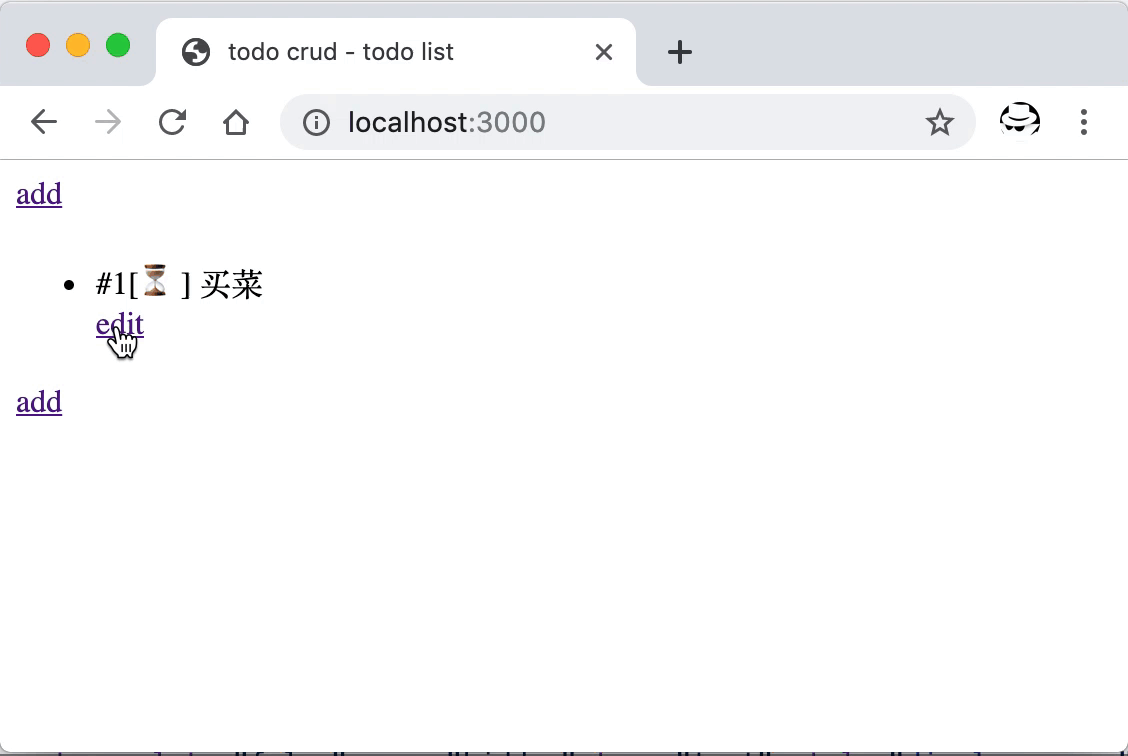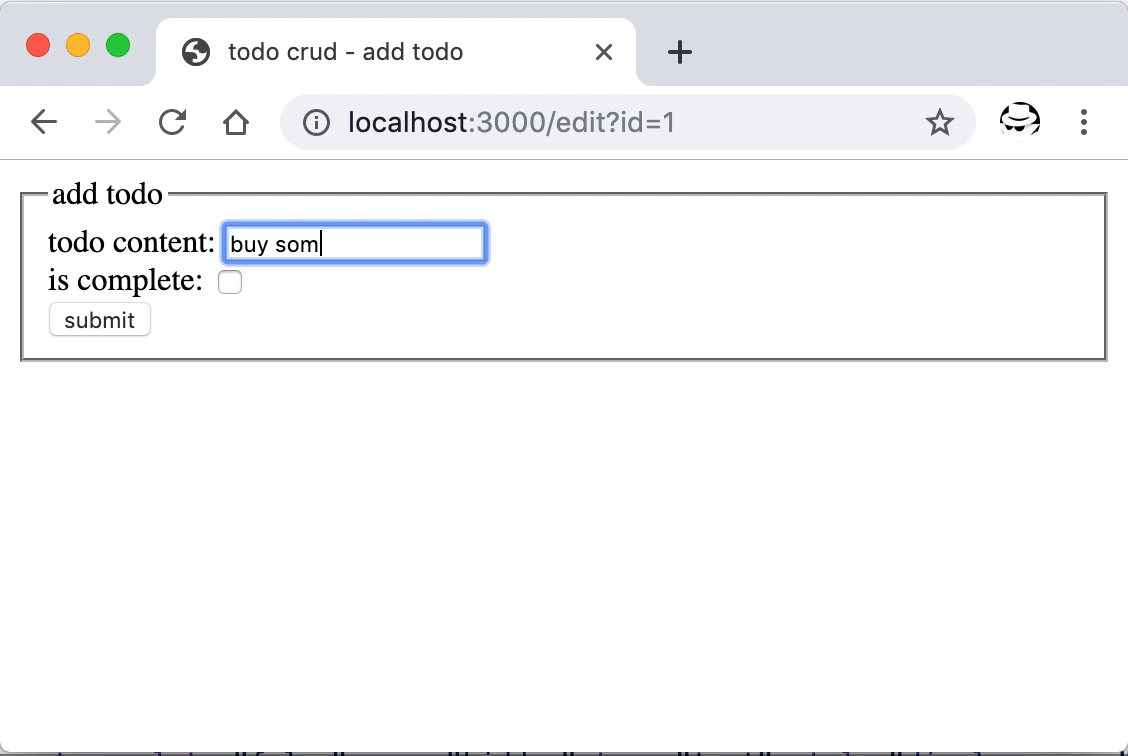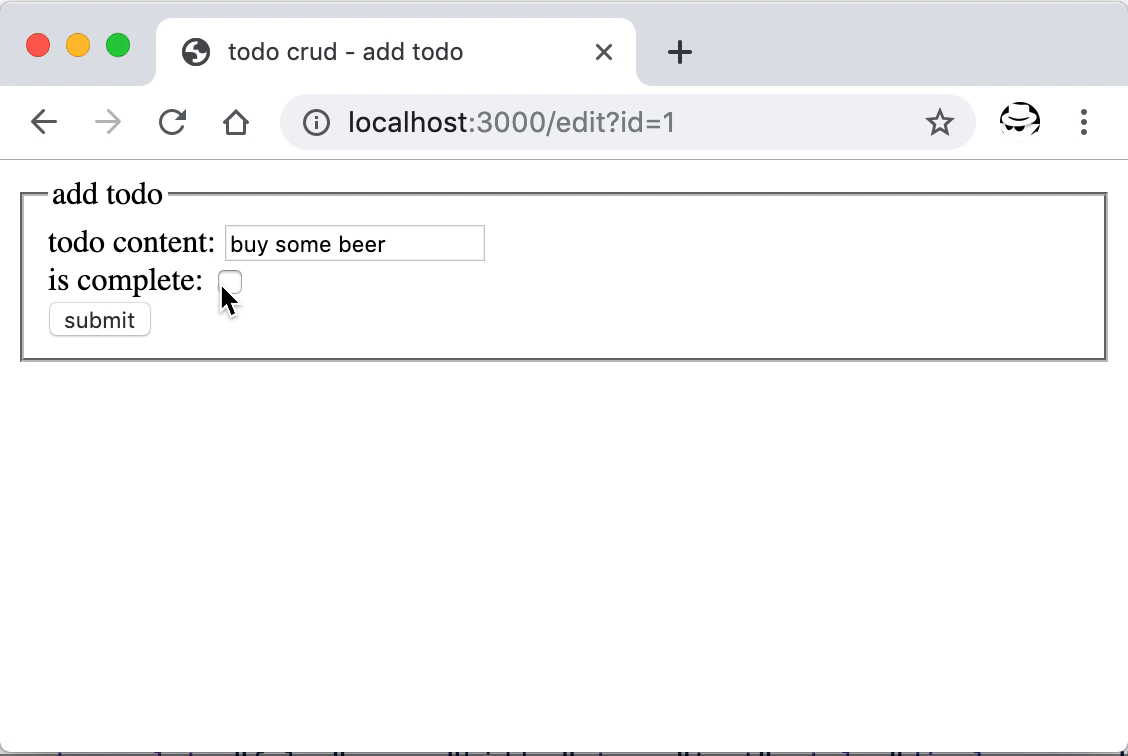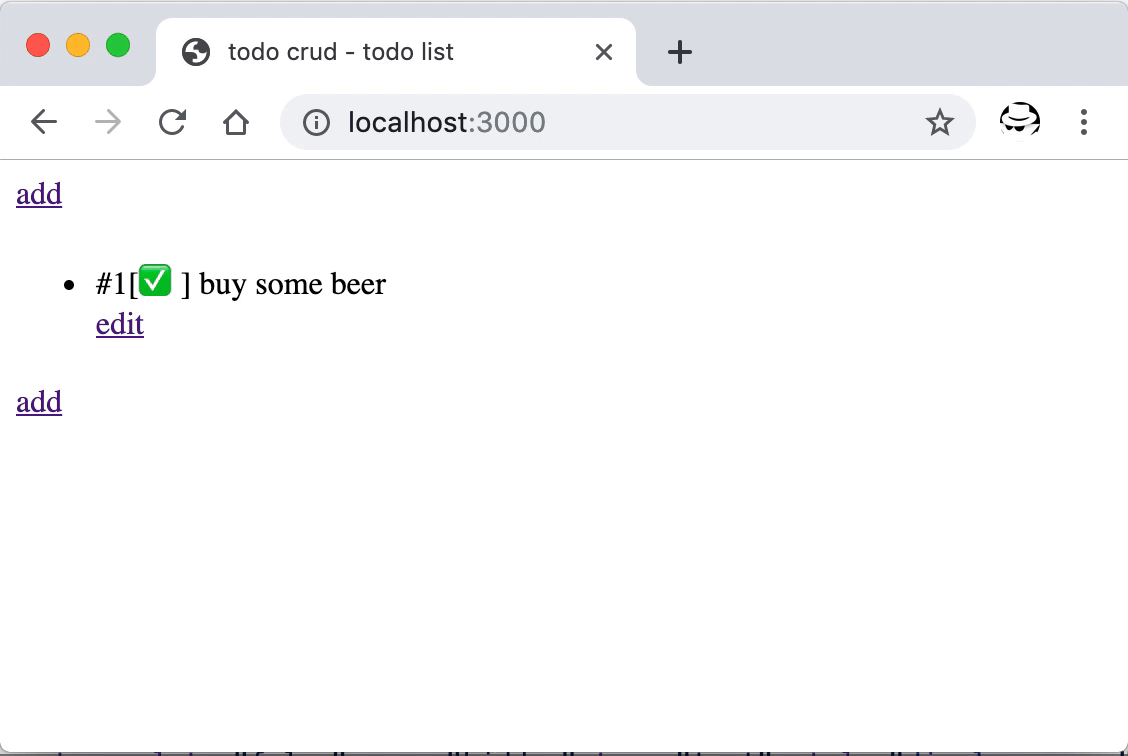
数据的更新
记录的删除
添加新的路由 '/remove' 提供删除操作的接口。
app.js
app.use(
_.post("/remove", async function(ctx) {
const id = ctx.request.body.id;
try {
console.log(`remove entry ${id}`);
await db.remove(id);
ctx.body = {
status: 0,
error_message: ""
};
} catch (error) {
ctx.body = error.stack;
}
})
);
这里 /remove 是个 POST 类型的接口,前台页面会将需要删除的条目 id 通过异步调用该接口传递过来。这里 POST 数据的获取也通过 koa-bodyparser 来获取,即 ctx.request.body 上面。
更新 db,js 添加从数据库删除条目的方法:
db.js
async function remove(id) {
return await query(`DELETE FROM todo WHERE todo.id='${id}'`);
}
万事具备,只差前台页面了。
更新列表页的模板,在刚刚添加编辑按钮的地方,添加一个删除按钮。
views/list.html
<div class="todo-item">
<div class="content">#{{ loop.index }}[{%if item.is_done==0%}⏳{%else%}✅{%endif%}] {{ item.content }}</div>
<div class="action">
+ <button onclick="remove({{ item.id }})">remove</button>
<a href="/edit?id={{ item.id }}">edit</a>
</div>
</div>
同时添加相应 JavaScript 代码发起删除的请求,调用上面添加的 POST 接口。
views/list.html
<script>
function remove(id) {
fetch("/remove", {
method: "post",
headers:{
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({ id })
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
if (data.status) {
alert(data.error_message);
} else {
alert("removed succussfully!");
location.reload();
}
})
.catch(error => alert(error));
}
</script>
前台在使用 fetch PSOT 数据时,需要指定正确的 Content-Type,否则后台 koa-bodyparser 无法解析。
重启后即可进行删除操作,成功后会提示并刷新页面。
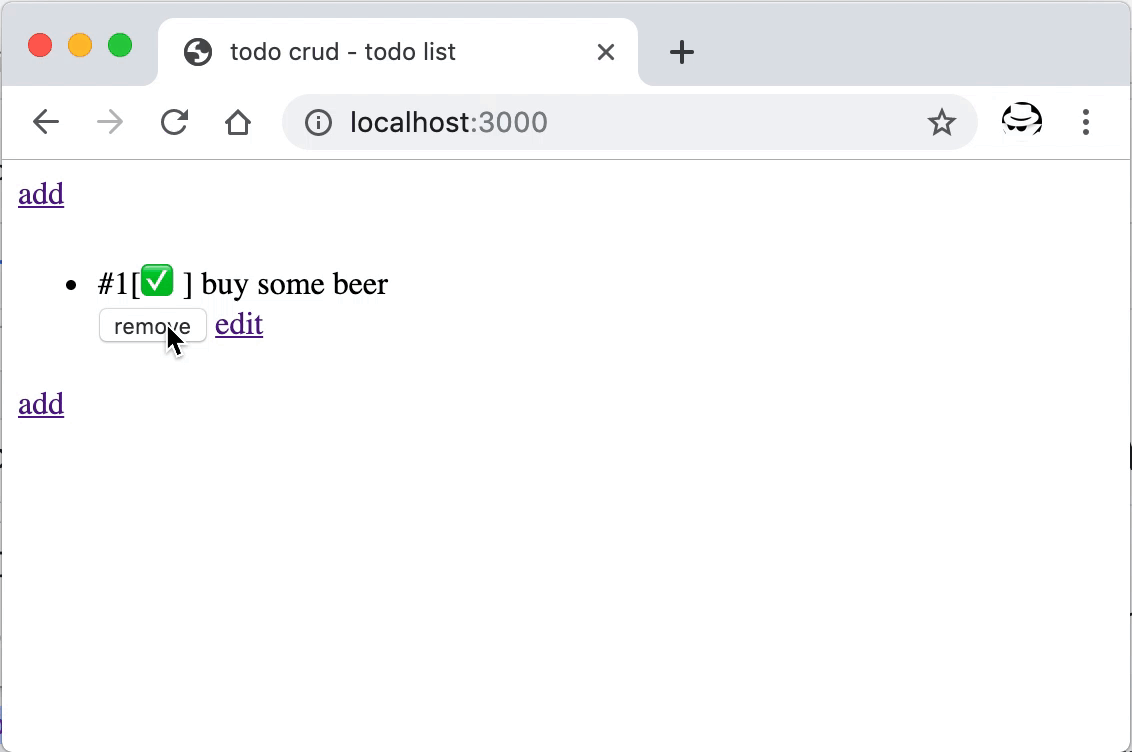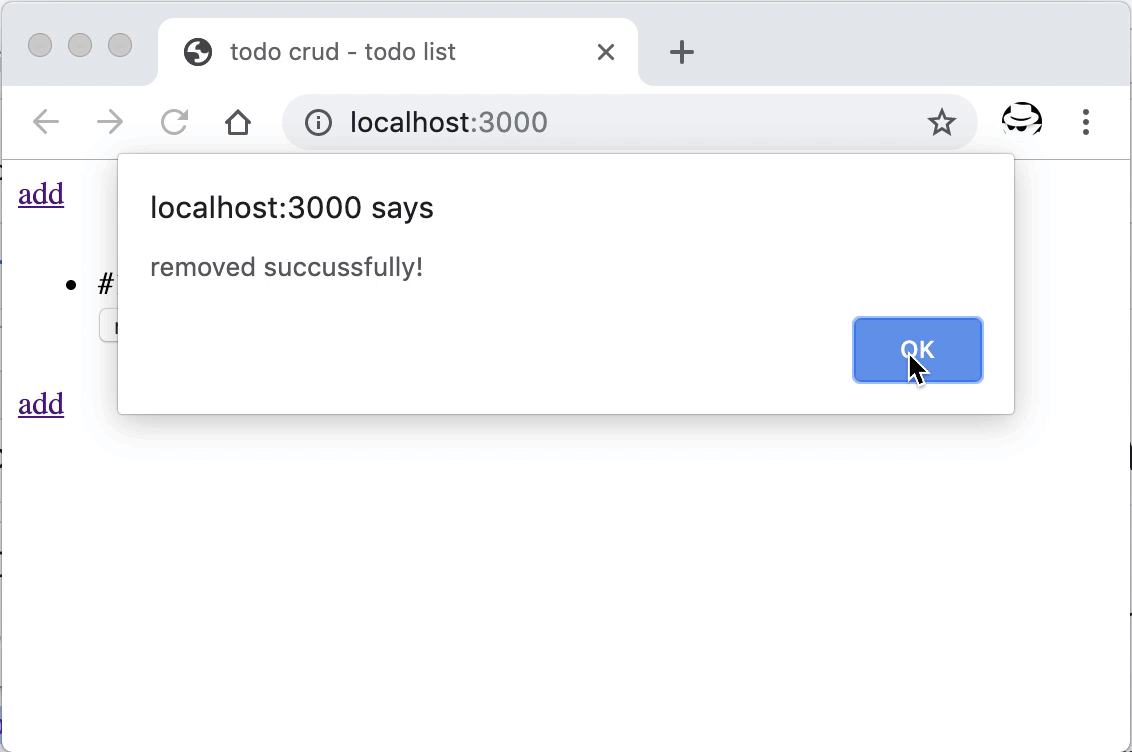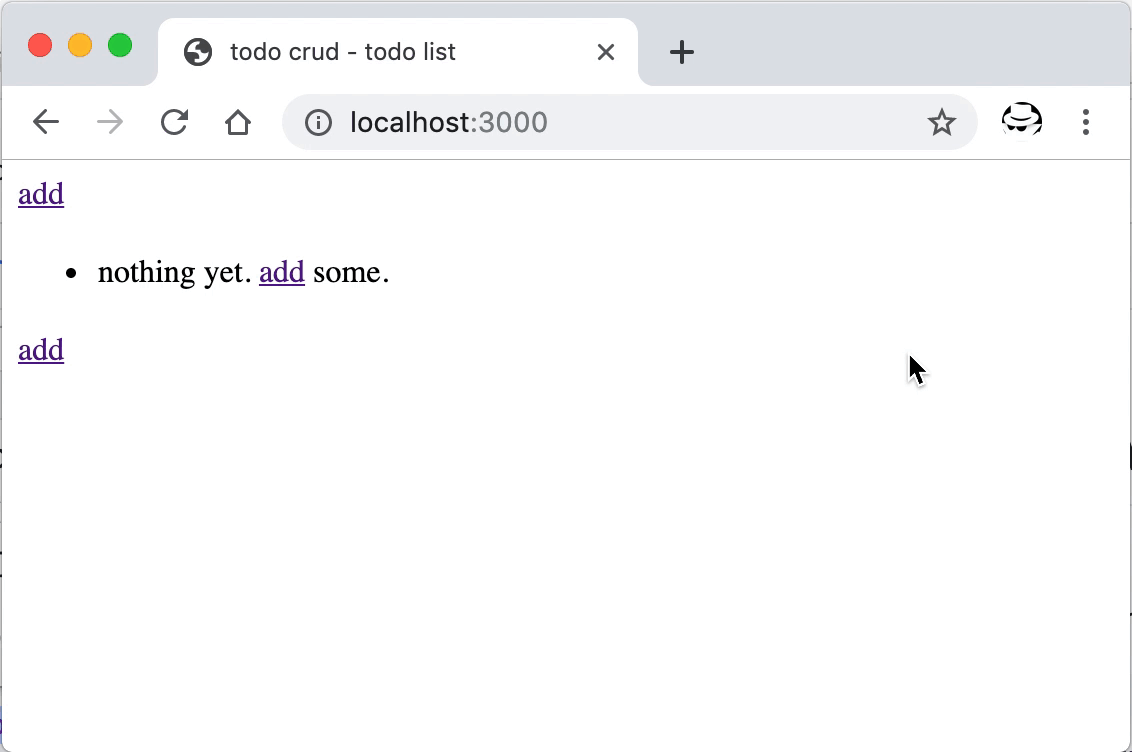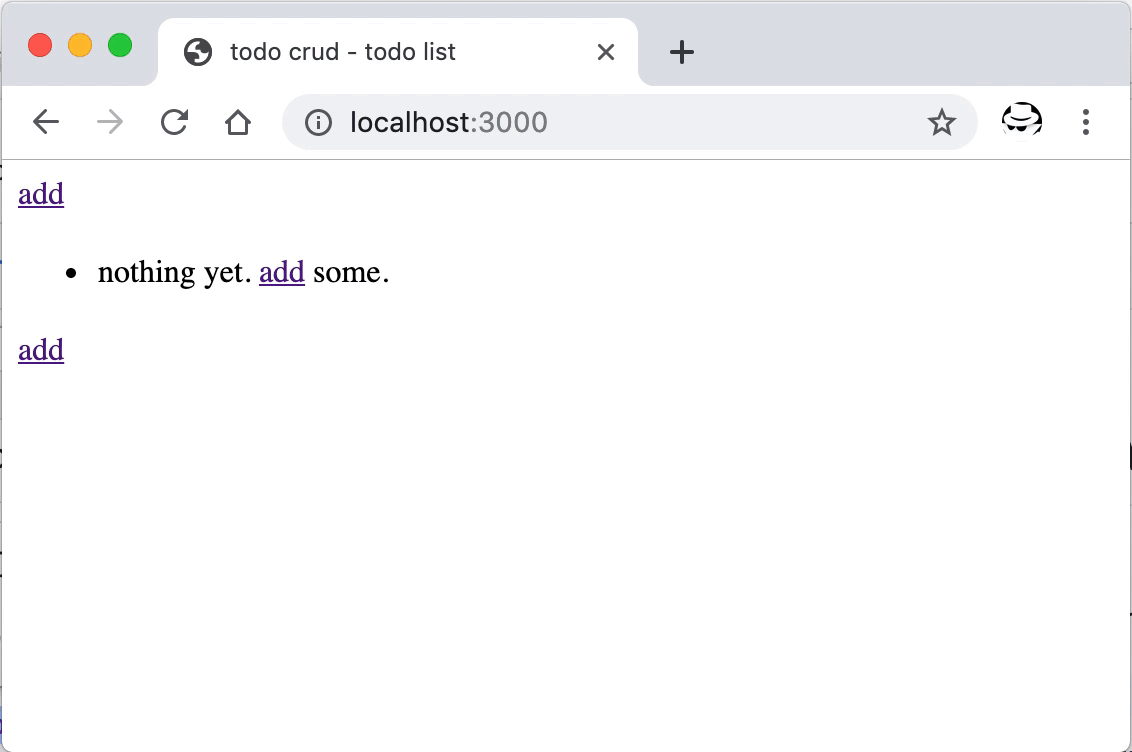
数据的删除操作
总结
完成本文的流程,实现了数据的增删改查等基本操作。其中包含表单数据的提交与接收,Koa 中间件的使用以及数据库连接,还有 SQL 语句的执行等。
本文中完整的示例代码可在 wayou/node-crud 仓库中找到。
相关资源
|






