201771010135 杨蓉庆《面对对象程序设计(java)》第十二周学习总结
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握Java GUI中框架创建及属性设置中常用类的API;
(2) 掌握Java GUI中2D图形绘制常用类的API;
(3) 了解Java GUI中2D图形中字体与颜色的设置方法;
(4) 了解Java GUI中2D图像的载入方法。
一、理论知识
10.1 AWT与Swing简介
(1)用户界面(User Interface) :用户与计算机系统(各种程序)交互的接口
(2)图形用户界面(Graphical User Interface) :以图形方式呈现的用户界面
(3)Java的抽象窗口工具箱(AbstractWindow Toolkit,AWT)包含在java.awt包中,它提供了许 多用来设计GUI的组件类和容器类
(4)AWT库处理用户界面元素的方法:把图形元素的创 建和行为委托给本地GUI工具箱进行处理
(5)Swing用户界面库是非基于对等体的GUI工具箱。Swing具有更丰富并且更方便的用户界面元素集合。
Swing对底层平台的依赖很少,因此与平台相关的bug很少。
(6) AWT与Swing的关系:大部分AWT组件都有其Swing的等价组件。
(7)Swing组件的名字一般是在AWT组件名前面添加一个字母“J”,如:JButton,JFrame,JPanel等。
10.2 框架的创建
(1)组件:由Component类的子类或间接子类创建的对象;
(2)容器是Java中能容纳和排列组件的组件。 常用的容器是框架(Frame,JFrame)
(3)Container类提供了一个方法add(),用来在容器类 组件对象中添加其他组件。 例如fra.add(button); fra.add(textField);
(4)容器本身也是一个组件,可以把一个容器添加到 另一个容器里,实现容器嵌套;
(5)创建空框架:在Java中,常采用框架(Frame)创建初始界面, 即GUI的顶层窗口 ,AWT库中有一个基于对等体的Frame类。
- 定位:常用Component类的setLocation和setBounds方法
- 常用属性 —— Title:框架标题 IconImage:框架图;
- 通过调用Toolkit类的方法来得到屏幕尺寸信息。
(6)Swing程序员最关心的是内容面板,也称为内容 窗格;
(7)在AWT中可调用add()方法把组件直接添加到AWT Frame中,在Swing中组件则添加到内容窗格里;
10.3 图形程序设计
(1)2D对象 :Java SE了包含一个Java 2D库,该库提供了一个 非常强大的图形操作集,Java 2D图形类使用浮点数坐标系,这样可为坐标指定单位。
(2)2D库为每个图形类提供两个版本的静态内部类: –Retangle2D.Float –Retangle2D.Double
(3)颜色的使用:Graphics2D类的setPaint方法(Graphics类为 setColor方法)用来设置颜色。
(4)复合色:通过指定红绿蓝三色比例,用Color类对象来复合成 一种新的颜色。 Color构造器如下: Color(intredness,intgreenness,intblueness)
(5)字体的使用:(1)AWT中定义的五种逻辑字体名 SanaSerif Serif Monospaced Dialog DialogInput ,这些逻辑字体在不同语言和操作系统上映射为不同的物理字体;
(2)字体风格:Font.PLAIN Font.BOLD Fond.ITALIC Fond.BOLD+ Font.ITALIC
(3)设置字体 : Font serif=new Font(“Serif”,Font.BOLD,14); g2.setFont(serif);
10.4显示图像
(1)在Java应用程序中,一旦图像保存在本地或因 特网的某个位置上,就可以将它们直接读入到java 应用程序中;
(2)完成将一个图像文件加载到程序中,再调用 Graphics类提供的DrawImage()显示它。
二、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第10章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
运行下列程序,观察程序运行结果。
package simpleFrame;
import javax.swing.*;
public class Sf
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
JFrame frame = new JFrame(); //生成一个JFrame类
frame.setBounds(0, 0,300, 200);//给窗口设置位置、大小
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);//设置窗口可见
}
}
结果如下:

- 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材407页程序10-1,结合程序运行结果理解程序;与上面程序对比,思考异同;
- 掌握空框架创建方法;
- 了解主线程与事件分派线程概念;
- 掌握GUI顶层窗口创建技术。
package simpleFrame; import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* @version 1.33 2015-05-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class SimpleFrameTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() ->//lamdba函数
{
SimpleFrame frame = new SimpleFrame();//构建一个SimpleFrame对象
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//退出窗口
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
} class SimpleFrame extends JFrame
{
//定义两个私有属性
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200; public SimpleFrame()
{
setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT);//数组大小
}
}
结果如下:

测试程序2:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材412页程序10-2,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握确定框架常用属性的设置方法。
package sizedFrame; import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* @version 1.34 2015-06-16
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class SizedFrameTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() ->
{
JFrame frame = new SizedFrame();//生成GUI界面对象
frame.setTitle("SizedFrame");//定义属性
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//关闭窗口
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
} class SizedFrame extends JFrame//SizedFrame类继承JFrame
{
public SizedFrame()
{
// get screen dimensions Toolkit kit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();//生成Toolkit对象
Dimension screenSize = kit.getScreenSize();
int screenHeight = screenSize.height;//通过对象访问属性,获得Dimension对象屏幕的长度
int screenWidth = screenSize.width; // set frame width, height and let platform pick screen location setSize(screenWidth / 2, screenHeight / 2);
setLocationByPlatform(true); // set frame icon Image img = new ImageIcon("icon.gif").getImage();//定义图形用户界面图标
setIconImage(img);
}
}
SizedFrameTest
结果如下:
测试程序3:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材418页程序10-3,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握在框架中添加组件;
l 掌握自定义组件的用法。
package notHelloWorld; import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*; /**
* @version 1.33 2015-05-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class NotHelloWorld
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() ->
{
JFrame frame = new NotHelloWorldFrame();//生成GUI界面对象
frame.setTitle("NotHelloWorld");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//退出窗口
frame.setVisible(true);//设置窗口可见
});
}
} /**
* A frame that contains a message panel
*/
class NotHelloWorldFrame extends JFrame
{
public NotHelloWorldFrame()
{
add(new NotHelloWorldComponent());//add方法的使用
pack();//调整窗口大小
}
} /**
* A component that displays a message.
*/
class NotHelloWorldComponent extends JComponent
{
//定义两个公共属性
public static final int MESSAGE_X = 75;
public static final int MESSAGE_Y = 100;
//定义两个私有属性
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200; public void paintComponent(Graphics g)//覆盖这个方法来描述应该如何绘制自己的组件
{
g.drawString("Not a Hello, World program", MESSAGE_X, MESSAGE_Y);
} public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); }
// 访问器
}
NotHelloWorld
结果如下:

测试程序4:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材424 -425页程序10-4,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握2D图形的绘制方法。
package draw; import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* @version 1.33 2007-05-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class DrawTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() ->
{
JFrame frame = new DrawFrame();
frame.setTitle("DrawTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
} /**
* A frame that contains a panel with drawings
*/
class DrawFrame extends JFrame
{
public DrawFrame()
{
add(new DrawComponent());
pack();
}
} /**
* A component that displays rectangles and ellipses.
*/
class DrawComponent extends JComponent
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 400;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 400; public void paintComponent(Graphics g)
{
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g; // draw a rectangle double leftX = 100;
double topY = 100;
double width = 200;
double height = 150;
//返回闭合矩形的长、宽、x、y坐标值 Rectangle2D rect = new Rectangle2D.Double(leftX, topY, width, height);
g2.draw(rect); // draw the enclosed ellipse Ellipse2D ellipse = new Ellipse2D.Double();
ellipse.setFrame(rect);
g2.draw(ellipse); // draw a diagonal line g2.draw(new Line2D.Double(leftX, topY, leftX + width, topY + height)); // draw a circle with the same center double centerX = rect.getCenterX();
double centerY = rect.getCenterY();
double radius = 150; Ellipse2D circle = new Ellipse2D.Double();//构造一个圆
circle.setFrameFromCenter(centerX, centerY, centerX + radius, centerY + radius);
g2.draw(circle);//定义属性
} public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); }
}
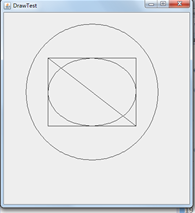
DrawTest
结果如下:
测试程序5:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材432页-433程序10-5,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 了解2D图形中字体的设置的方法;
package font; import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.font.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* @version 1.34 2015-05-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class FontTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() ->
{
JFrame frame = new FontFrame();
frame.setTitle("FontTest");//定义属性
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//退出窗口
frame.setVisible(true);//设置窗口可见
});
}
} /**
* A frame with a text message component
*/
class FontFrame extends JFrame
{
public FontFrame()
{
add(new FontComponent());//add了组件
pack();//调整窗口大小
}
} /**
* A component that shows a centered message in a box.
*/
class FontComponent extends JComponent//继承JComponent容器
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200; public void paintComponent(Graphics g)
{
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g; String message = "Hello, World!"; Font f = new Font("Serif", Font.BOLD, 36);
g2.setFont(f); // measure the size of the message
//测量信息大小
FontRenderContext context = g2.getFontRenderContext();
Rectangle2D bounds = f.getStringBounds(message, context);//获取矩形的2D边界 // set (x,y) = top left corner of text double x = (getWidth() - bounds.getWidth()) / 2;
double y = (getHeight() - bounds.getHeight()) / 2; // add ascent to y to reach the baseline double ascent = -bounds.getY();
double baseY = y + ascent; // draw the message g2.drawString(message, (int) x, (int) baseY); g2.setPaint(Color.LIGHT_GRAY); // draw the baseline g2.draw(new Line2D.Double(x, baseY, x + bounds.getWidth(), baseY)); // draw the enclosing rectangle Rectangle2D rect = new Rectangle2D.Double(x, y, bounds.getWidth(), bounds.getHeight());
g2.draw(rect);
} public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); }
}
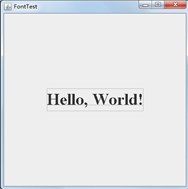
FontTest
结果如下:
测试程序6:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材436页-437程序10-6,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 了解2D图形图像的显示方法。
package image; import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* @version 1.34 2015-05-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ImageTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() ->
{
JFrame frame = new ImageFrame();
frame.setTitle("ImageTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
} /**
* A frame with an image component
*/
class ImageFrame extends JFrame
{
public ImageFrame()
{
add(new ImageComponent());
pack();//调整图片大小
}
} /**
* A component that displays a tiled image
*/
class ImageComponent extends JComponent //继承
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT =200;
//定义私有属性
private Image image; public ImageComponent()
{
image = new ImageIcon("E:\\t01e7d4d9d2529f5500.gif").getImage();
} public void paintComponent(Graphics g)
{
if (image == null) return; int imageWidth = image.getWidth(null);
int imageHeight = image.getHeight(null);
// draw the image in the upper-left corner
//获取图片的 宽和高
g.drawImage(image, 0, 0, null);
// tile the image across the component for (int i = 0; i * imageWidth <= getWidth(); i++)
for (int j = 0; j * imageHeight <= getHeight(); j++)
if (i + j > 0)
g.copyArea(0, 0, imageWidth, imageHeight, i * imageWidth, j * imageHeight);
} public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); }
}
ImageTest
结果如下:

三、总结
本章我们学习了图形程序设计,我们学习了java GUI中框架创建及属性设置中常用类的API、Java GUI中2D图形绘制常用类的API,虽然不用全部记下,但我觉得在闲暇时刻还是要多看这些API,才能更好的运用到程序中去,其次我了解Java GUI中2D图形中字体与颜色的设置方法,可以自己设置想要的字体和颜色,通过老师学长的讲解和代码注释,我也能更好的理解新接触到的那些知识,感觉收获颇丰。
最新文章
- C与CPP 在线手册查找
- Android入门之GPS定位详解
- CentOS6系升级Python2.7版本
- 第七章 美化DetailView界面
- Alternative Representations for 4-Bit Integers
- Java学习笔记(五):异常处理
- 通过Jquery中Ajax获取json文件数据
- mybatis 入门进阶之 pojo
- 把angular项目整合到.net mvc中
- Linux查看日志方法总结(1)
- 网络分层和Http协议原理
- Java内存模型-final域的内存语义--没明白,预留以后继续理解
- HDU 2000 ASCII码排序
- JS 测试网络速度与网络延迟
- Microsoft Visual Studio 2010(vs10)安装与使用
- 记录css的常用属性
- 实例化Flask的参数 及 对app的配置
- JS touch
- openfire聊天记录插件
- 【kafka学习之三】kafka集群运维