kubeDNS workflow(service registration and discovery)
2024-09-05 01:04:30
Service discovery
In k8s, we usually will more than make an application instance, and also the corresponding multiple pod, if through the pod IP access to the pod service will be hard to manage. Kubernetes provides the concept of service can be accessed through the VIP pod services, but in the use of the time there is a problem: how do you know an application of the VIP?We have two application, for example, an APP, one is the DB, manage each application using the rc, and provide services through service exposed the port.APP needs to connect to the DB application, we only know the name of a DB application, but do not know the VIP address.
The simplest way from kubernetes provides query API.But this is a bad practice, every application must first write queries at start-up time rely on the service logic, this itself is repeat and increases the complexity of the application;Second leading to applications rely on kubernetes, will not be able to deploy and run separately (of course, if by adding configuration option is also can be done, but it is increase in degrees).
At first, the method of kubernetes adopted docker used - environment variables.Start each pod, will be put through the environment variable is set all service of IP and port information, so that the application of the pod can be read by the environment variable to rely on the service address information.Matching relation between service and environment variables this way has a certain specification, use rise also relatively simple, but there is a big problem: rely on the service must be started in the pod existed before, otherwise will not appear in the environment variable.
A more ideal solution is: application can directly use the name of the service, don't need to care about it the IP address of the actual, in the middle of the conversion can be done automatically.DNS is name and IP conversion between the function of the system, so kubernetes is also provides the DNS method to solve this problem.
DNS Service
The DNS service is not independent of the system, but an addon, as a plug-in to install, not kubernetes cluster must (but very recommended installation).Can take it as a run on the application of the cluster, it's just the application is special.
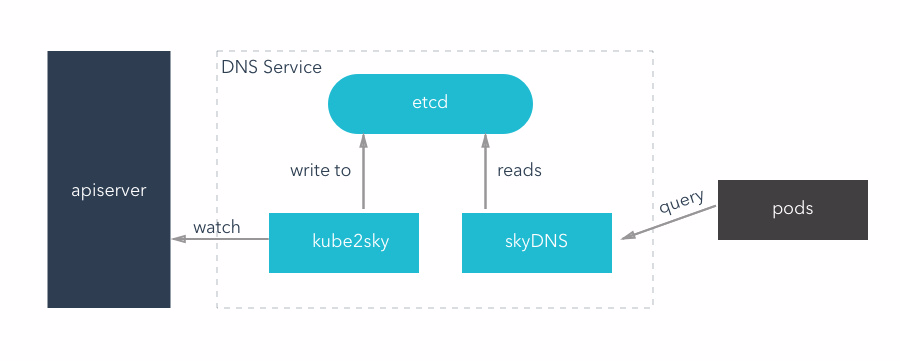
There are two kinds of DNS configuration mode, using etcd + kube2sky + skydns way before version 1.3, can be used after 1.3 kubedns + dnsmasq way.
kube2sky mode
This model mainly has three containers in operation:
- Kube2sky is responsible for the continuous monitoring k8s apiserver, once has the service creation, will obtain the service IP, and stored in the etcd
- Etcd in the form of the key - value is used to store the service name and the corresponding "ClusterIP"
- SkyDNS: according to the data of the etcd, external DNS query service
Service discovery
In k8s, we usually will more than make an application instance, and also the corresponding multiple pod, if through the pod IP access to the pod service will be hard to manage. Kubernetes provides the concept of service can be accessed through the VIP pod services, but in the use of the time there is a problem: how do you know an application of the VIP?We have two application, for example, an APP, one is the DB, manage each application using the rc, and provide services through service exposed the port.APP needs to connect to the DB application, we only know the name of a DB application, but do not know the VIP address.
The simplest way from kubernetes provides query API.But this is a bad practice, every application must first write queries at start-up time rely on the service logic, this itself is repeat and increases the complexity of the application;Second leading to applications rely on kubernetes, will not be able to deploy and run separately (of course, if by adding configuration option is also can be done, but it is increase in degrees).
At first, the method of kubernetes adopted docker used - environment variables.Start each pod, will be put through the environment variable is set all service of IP and port information, so that the application of the pod can be read by the environment variable to rely on the service address information.Matching relation between service and environment variables this way has a certain specification, use rise also relatively simple, but there is a big problem: rely on the service must be started in the pod existed before, otherwise will not appear in the environment variable.
A more ideal solution is: application can directly use the name of the service, don't need to care about it the IP address of the actual, in the middle of the conversion can be done automatically.DNS is name and IP conversion between the function of the system, so kubernetes is also provides the DNS method to solve this problem.
DNS Service
The DNS service is not independent of the system, but an addon, as a plug-in to install, not kubernetes cluster must (but very recommended installation).Can take it as a run on the application of the cluster, it's just the application is special.
There are two kinds of DNS configuration mode, using etcd + kube2sky + skydns way before version 1.3, can be used after 1.3 kubedns + dnsmasq way.
kube2sky mode
This model mainly has three containers in operation:
- Kube2sky is responsible for the continuous monitoring k8s apiserver, once has the service creation, will obtain the service IP, and stored in the etcd
- Etcd in the form of the key - value is used to store the service name and the corresponding "ClusterIP"
- SkyDNS: according to the data of the etcd, external DNS query service

example:
There is a DB, a APP server, APP server needs to connect DB for data reading and writing
1.DB server, through the RC created a pod, and at the same time to create a service for integration of the pod,DB service named DB_server.This is accomplished by k8s - apiserver,Will be a cluster IP for DB service distribution,for example: 192.168.20.3,ClusterIP can only be used for use within the cluster.
2.kube2sky listening to APIserver operations, access to the service name: DB_server and clusterIP: 192.168.20.3, and will write etcd.
3.APP server configured in the DB address for 'DB_server', this is the name of DB service,Use the service name instead of IP
4.Pod will send service name: DB_server to skyDNS, loading from etcd skyDNS service name corresponding IP, returned to the Pod
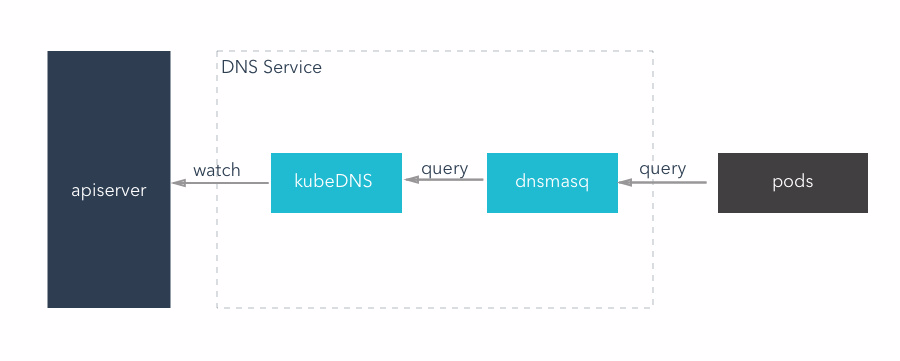
kubeDNS mode
This mode, kubeDNS container replace the function of the original three container, it will be to monitor apiserver and put all the service and the result of the endpoints using appropriate data structure stored in memory, and external DNS query service.
- KubeDNS: to provide the original kube2sky + etcd + skyDNS function, can provide DNS query service
- A lightweight DNS service software, can provide DNS cache function.KubeDNS mode, dnsmasq in memory set aside a block size (the default is 1g), save the current most commonly used DNS query record, if there is no to find records in the cache, it will into kubeDNS query, and the results are cached
- exec-healthz:In providing health checking
example:
1.DB server, through the RC created a pod, and at the same time to create a service for integration of the pod,DB service named DB_server.This is accomplished by k8s - apiserver,Will be a cluster IP for DB service distribution,for example: 192.168.20.3,ClusterIP can only be used for use within the cluster.
2. kubeDNS listening to APIserver operations,access to the service name: DB_server and clusterIP: 192.168.20.3, and use tree structure write cache.
3. dnsmasq:DNS rules obtained through kubedns container, in a cluster to provide DNS query service, equivalent to the DNS server.
4. APP server configured in the DB address for 'DB_server', this is the name of DB service,Use the service name instead of IP
5. Pod will send service name: DB_server to dnsmasq,dnsmasq query to the service of the corresponding IP is returned to the pod, if not checked, will contact the kubeDNS,If kubeDNS no record, it will return an error report to the APP server pod.
example:
There is a DB, a APP server, APP server needs to connect DB for data reading and writing
1.DB server, through the RC created a pod, and at the same time to create a service for integration of the pod,DB service named DB_server.This is accomplished by k8s - apiserver,Will be a cluster IP for DB service distribution,for example: 192.168.20.3,ClusterIP can only be used for use within the cluster.
2.kube2sky listening to APIserver operations, access to the service name: DB_server and clusterIP: 192.168.20.3, and will write etcd.
3.APP server configured in the DB address for 'DB_server', this is the name of DB service,Use the service name instead of IP
4.Pod will send service name: DB_server to skyDNS, loading from etcd skyDNS service name corresponding IP, returned to the Pod
kubeDNS mode
This mode, kubeDNS container replace the function of the original three container, it will be to monitor apiserver and put all the service and the result of the endpoints using appropriate data structure stored in memory, and external DNS query service.
- KubeDNS: to provide the original kube2sky + etcd + skyDNS function, can provide DNS query service
- A lightweight DNS service software, can provide DNS cache function.KubeDNS mode, dnsmasq in memory set aside a block size (the default is 1g), save the current most commonly used DNS query record, if there is no to find records in the cache, it will into kubeDNS query, and the results are cached
- exec-healthz:In providing health checking
example:
1.DB server, through the RC created a pod, and at the same time to create a service for integration of the pod,DB service named DB_server.This is accomplished by k8s - apiserver,Will be a cluster IP for DB service distribution,for example: 192.168.20.3,ClusterIP can only be used for use within the cluster.
2. kubeDNS listening to APIserver operations,access to the service name: DB_server and clusterIP: 192.168.20.3, and use tree structure write cache.
3. dnsmasq:DNS rules obtained through kubedns container, in a cluster to provide DNS query service, equivalent to the DNS server.
4. APP server configured in the DB address for 'DB_server', this is the name of DB service,Use the service name instead of IP
5. Pod will send service name: DB_server to dnsmasq,dnsmasq query to the service of the corresponding IP is returned to the pod, if not checked, will contact the kubeDNS,If kubeDNS no record, it will return an error report to the APP server pod.
最新文章
- python2.7高级编程 笔记一(Python中的with语句与上下文管理器学习总结)
- Python virtualenv with Sublime Text 3
- ASP.NET 字符编码的那些事
- 【图像处理】【SEED-VPM】2.接口
- SQLite的WAL机制
- ORACLE常见错误代码的分析与解决
- SpringMVC实战
- HDU 2841 Visible Trees 数论+容斥原理
- snowflake
- listview使用checkbox批量删除出现的问题
- linux 双网关双IP设置
- 小学生之Oracle分析函数
- 查看死锁原因 /data/anr/traces.txt
- 利用Arcgis for javascript API绘制GeoJSON并同时弹出多个Popup
- 201521123034《Java程序设计》第六周学习总结
- 201521123023《java程序设计》第三周学习总结
- 干货|人人都是翻译项目的Master
- 关于JQuery的绑定方法
- react dnd demo2
- iframe之间通信问题及iframe自适应高度问题