tensorflow 13:多gpu 并行训练
多卡训练模式:
进行深度学习模型训练的时候,一般使用GPU来进行加速,当训练样本只有百万级别的时候,单卡GPU通常就能满足我们的需求,但是当训练样本量达到上千万,上亿级别之后,单卡训练耗时很长,这个时候通常需要采用多机多卡加速。深度学习多卡训练常见有两种方式,一种是数据并行化(data parallelism),另外一种是模型并行化(model parallelism)。
深度模型训练方法:
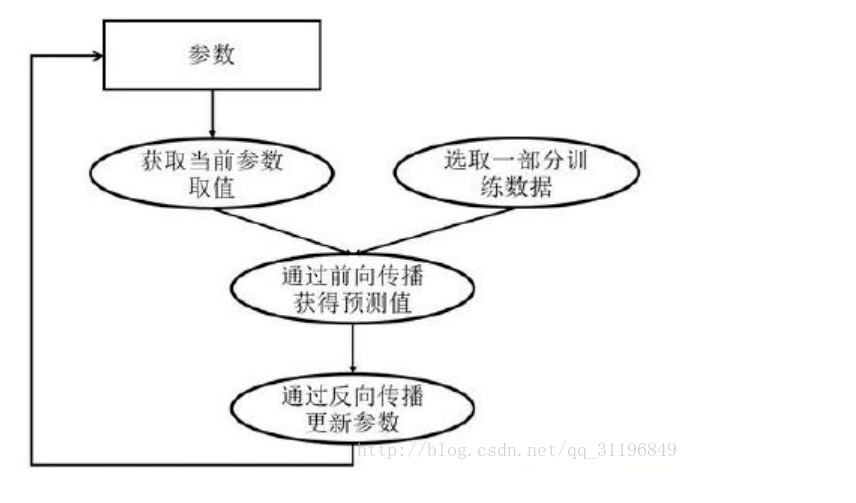
深度学习模型的训练是一个迭代的过程,在每一轮迭代过程中,前向传播算法会根据当前参数的取值,计算出在一小部分训练数据上的预测值,然后反向传播算法,再根据损失函数计算参数的梯度并且更新参数。
一、数据并行化
数据并行化:每个GPU上面跑一个模型,模型与模型之间结构参数相同,只是训练的数据不一样,每个模型通过最后的loss计算得到梯度之后,再把梯度传到一个parameter server(PS)上进行参数平均average gradient,然后再根据average gradient更新模型的参数。
深度学习算法由于数据量非常大、算法复杂度高等特点,常常需要采用并行机制。
### 常用的并行化深度学习模型训练方式有两种:同步模式和异步模式。
同步模式
同步模式:等到所有的数据分片都完成了梯度计算并把梯度传到PS之后统一的更新每个模型的参数。优点是训练稳定,训练出来的模型得到精度比较高;缺点是训练的时间取决于分片中最慢的那个片,所以同步模式适用于GPU之间性能差异不大情况下。
同步模式训练方法
在同步模式下,所有的设备同时读取参数的取值,并且当反向传播算法完成之后同步更新参数的取值,单个设备不会单独对参数进行更新,而会等所有设备都完成反向传播之后再统一更新参数。
同步模式训练流程图如下:
这里写图片描述
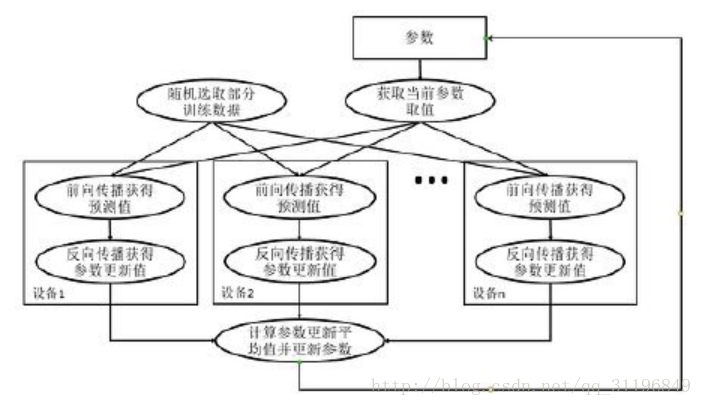
- 图中在迭代每一轮时,不同设备首先统一读取当前参数的取值,并随机获取一小部分数据
- 然后在不同设备上运行反向传播过程得到在各自训练数据上的参数的梯度
- 注意:虽然所有设备使用的参数是一致的,但是因为训练数据不同,所以得到的参数的梯度可能不一样
- 当所有设备完成反向传播的计算之后,需要计算出不同设备上参数梯度的平均值
- 最后再根据平均值对参数进行更新
异步模式
异步模式训练方法在并行化地训练深度学习模型时,不同设备(GPU或CPU)可以再不同训练数据上,运行整个迭代的过程,而不同并行模式的区别在于不同的参数更新方式。
异步模式训练流程图如下:
这里写图片描述
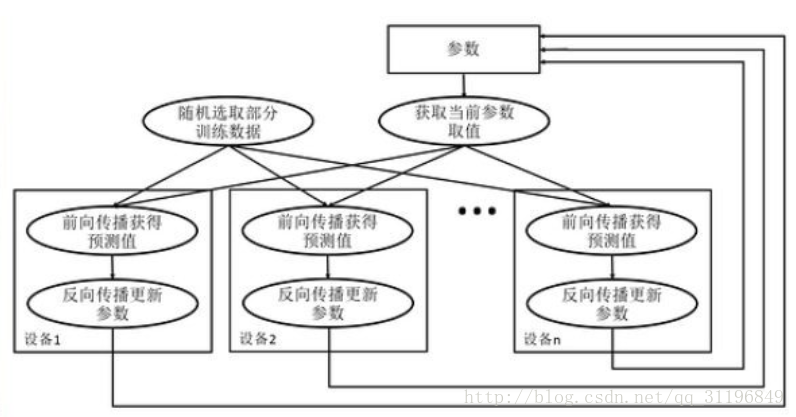
- 在每一轮迭代时,不同设备会读取参数最新的取值
- 因为设备不同,读取参数取值时间不一样,所以得到的值也可能不一样
- 根据当前参数的取值,和随机获取的一小部分训练数据,不同设备各自运行反向传播的过程,并且独立地更新参数
- 可以认为异步模式,就是单机模式复制了多份,每一份使用不同的训练数据进行训练。
- 在异步模式下,不同设备之前是完全独立的
同步/异步优劣比较
* 同步模式解决了异步模式中存在的参数更新问题,然而同步模式的效率却低于异步模式
* 在同步模式下,每一轮迭代都需要设备统一开始、统一结束
* 如果设备的运行速度不一致,那么每一轮训练都需要等待最慢的设备结束才能开始更新参数,于是很多时间将被花在等待上
* 虽然理论上异步模式存在缺陷,但是因为训练深度学习模型时,使用的随机梯度下降本身就是梯度下降的一个近似解法,而且即使是梯度下降也无法保证达到全局最优
* 所以在实际应用中,相同时间内,使用异步模式训练的模型不一定比同步模式差
代码示例
#将神经网络的优化过程跑在不同的GPU上
for i in range(N_GPU):
with tf.debice('/gpu:%d'%i)
with tf.name_scope('GPU_%d'%i) as scope:
cur_loss = get_loss(x,y_regularizer,scope)
#tf.get_variable的命名空间
tf.get_variable_scope().reuse_variables()
#使用当前gpu计算所有变量的梯度
grads= opt.compute_gradients(cur_loss)
tower_grads.append(grads)
#计算变量的平均梯度
grads = average_gradients(tower_grads)
#使用平均梯度更新参数
apply_gradient_op = opt.apply_gradients(grads,global_step = global)
二、模型并行化
模型并行化:当一个模型非常复杂,非常大,达到单机的内存根本没法容纳的时候,模型并行化就是一个好的选择。直观说就多多个GPU训练,每个GPU分别持有模型的一个片。它的优点很明显,大模型训练,缺点就是模型分片之间的通信和数据传输很耗时,所以不能简单说,模型并行就一定比数据并行要快。
还有数据并行和模型并行的混合模型:
数据并行适用于数据量比较小时快速训练模型,模型并行适用于大数据、大模型场景下。这里只是简单介绍,想要深入了解细节可以找其他资料学习一下。下面主要基于tensorflow讲一个数据并行化的实例。
1、 单机多卡训练:给个例子,比如一台机器上装有4个GPU卡,以cpu做为PS(master),主要保存一下参数和变量,进行梯度平均。其余4个GPU训练模型(worker),进行一些计算量比加大的操作。
- 1) 本地对数据切分为一个一个batch;
- 2) 把数据分别放到送到4个GPU进行模型训练,每个GPU拿到数据不一样;
- 3) 四个GPU训练,求loss得到梯度,并把梯度送回到CPU进行模型平均。
- 4) cpu接收4个gpu传来的梯度,进行梯度平均。
- 5) 四个GPU跟新参数
- 6) 重复2~5知道模型收敛。
2、 分布式的多久多卡:当是在一个多台机器的集群上训练的时候采用这种方式,在tensorflow中需要明确指定ps和worker的地址,这种方式兼容单机多卡,只是把ps和worker的地址设为local就可以了。
下面简要介绍下tensorflow中支持多卡训练和参数更新的几个API,具体介绍可以参考这篇文章(Distributedtensorflow实现原理)http://blog.csdn.net/lqfarmer/article/details/70214026。
Tensorflow进行重复性训练有In-graph replication和Between-graphreplication两种方式,In-graph replication就是数据并行化模式,Between-graphreplication就是数据并行化模式。梯度更新有异步Asynchronous training和同步Synchronous training两种模式。
Tensorflow官网也给了一个cifar10_multi_gpu_train.py 的例子,在单机多卡上运行,这里我给一个自己做的单机多卡训练的简单例子供参考,自己在搭建这个结构过程中也栽了很多坑,还在继续探索中,仅有训练部分。
程序主要分为五个部分:
- Main函数:定义主要运行逻辑;
- Run_epoch函数:定义主要训练逻辑;
- Generate_feed_dic函数:产生训练需要的batch样本;
- Multi_gpu_model函数:定义多个tower,每个tower对应一个gpu;
- Average_gradients函数:梯度平均计算。
一下是完整代码:
#critital class define
#getaverage gradient
defaverage_gradients(tower_grads):
average_grads = []
for grad_and_vars in zip(*tower_grads):
grads = []
for g, _ in grad_and_vars:
expanded_g = tf.expand_dims(g, 0)
grads.append(expanded_g)
grad = tf.concat(axis=0, values=grads)
grad = tf.reduce_mean(grad, 0)
v = grad_and_vars[0][1]
grad_and_var = (grad, v)
average_grads.append(grad_and_var)
return average_grads
#setupmultiple gpu tower
defmulti_gpu_model(num_gpus=4, word_embeddings = None):
grads = []
global_step = tf.Variable(0,name="global_step", trainable=False)
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-3)
withtf.variable_scope(tf.get_variable_scope()) as initScope:
for i in range(num_gpus):
withtf.device("/gpu:%d"%i):
withtf.name_scope("tower_%d"%i):
siameseModel = SiameseLSTM(
sequence_length=FLAGS.max_document_length,
embedding_size=FLAGS.embedding_dim,
hidden_units=FLAGS.hidden_units,
l2_reg_lambda=FLAGS.l2_reg_lambda,
batch_size=FLAGS.batch_size,
word_embeddings=word_embeddings)
tf.get_variable_scope().reuse_variables()
tf.add_to_collection("train_model", siameseModel)
grad_and_var =optimizer.compute_gradients(siameseModel.loss)
grads.append(grad_and_var)
tf.add_to_collection("loss",siameseModel.loss)
tf.add_to_collection("accuracy",siameseModel.accuracy)
tf.add_to_collection("distance",siameseModel.distance)
with tf.device("cpu:0"):
averaged_gradients =average_gradients(grads)
train_op =optimizer.apply_gradients(averaged_gradients, global_step=global_step)
return train_op,global_step
#generating training data
defgenerate_feed_dic(sess, batch_generator,feed_dict,train_op):
SMS =tf.get_collection("train_model")
for siameseModel in SMS:
x1_batch, x2_batch, y_batch =batch_generator.next()
if random()>0.5:
feed_dict[siameseModel.input_x1] =x1_batch
feed_dict[siameseModel.input_x2] =x2_batch
feed_dict[siameseModel.input_y] =y_batch
feed_dict[siameseModel.dropout_keep_prob]= FLAGS.dropout_keep_prob
else:
feed_dict[siameseModel.input_x1] =x2_batch
feed_dict[siameseModel.input_x2] =x1_batch
feed_dict[siameseModel.input_y] =y_batch
feed_dict[siameseModel.dropout_keep_prob]= FLAGS.dropout_keep_prob
return feed_dict
#define main trainingprocess
def run_epoch(sess,train_x1_idsList,train_x2_idsList,train_y,scope,global_step,train_op=None,is_training=False):
if is_training:
epoches = len(train_x1_idsList) //FLAGS.batch_size
batch_generator =datatool.data_iterator(train_x1_idsList, train_x2_idsList,train_y,FLAGS.batch_size,FLAGS.max_document_length)
# siameseModels =tf.get_collection("train_model")
while epoches > 0:
feed_dict = {}
epoches -= 1
feed_dict=generate_feed_dic(sess,batch_generator,feed_dict,train_op)
i = FLAGS.num_iteration
while i > 0:
i = i - 1
losses =tf.get_collection("loss")
accuracy =tf.get_collection("accuracy")
distance =tf.get_collection("distance")
total_accuracy =tf.add_n(losses, name='total_accu')
total_distance = tf.add_n(losses,name='total_distance')
total_loss = tf.add_n(losses,name='total_loss')
avg_losses = total_loss / 4
avg_accu = total_accuracy / 4
avg_dist = total_distance / 4
time_str =datetime.datetime.now().isoformat()
_,step,avg_losses,avg_accu,avg_dist =sess.run([train_op,global_step,total_loss,avg_accu,avg_dist],feed_dict)
#输出训练精度
print("TRAIN {}: step {},avg_loss {:g}, avg_dist {:g}, avg_acc {:g}".format(time_str, step,avg_losses, avg_dist, avg_accu))
#whole training process
defmain(argv=None):
print("\nParameters:")
for attr, value insorted(FLAGS.__flags.items()):
print("{}={}".format(attr.upper(),value))
print("")
#加载词向量
word2id, word_embeddings =datatool.load_word2vec("your dir for word2vec")
print("load train data")
(train_x1_idsList,train_x2_idsList,train_y),(valid_x1_idsList, valid_x2_lList,valid_y) =datatool.get_data_for_siamese(word2id, FLAGS.data_path)
print("starting graph def")
gpu_options =tf.GPUOptions(per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=0.8)
withtf.Graph().as_default():#,tf.device('/cpu:0')
session_conf = tf.ConfigProto(
allow_soft_placement=FLAGS.allow_soft_placement,
log_device_placement=FLAGS.log_device_placement,
gpu_options=gpu_options)
sess = tf.Session(config=session_conf)
print("started session")
print ("build multiplemodel")
with tf.name_scope("train")as train_scope:
print("define multiple gpumodel and init the training operation")
train_op,global_step =multi_gpu_model(FLAGS.num_gpus,word_embeddings)
print ("init allvariable")
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
print ("run epochestage")
run_epoch(sess,train_x1_idsList,train_x2_idsList,train_y,train_scope,global_step,train_op,True)
# Checkpoint directory. Tensorflowassumes this directory already exists so we need to create it
timestamp = str(int(time.time()))
checkpoint_dir =os.path.abspath(os.path.join(out_dir, "checkpoints"))
checkpoint_prefix =os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, "model")
if not os.path.exists(checkpoint_dir):
os.makedirs(checkpoint_dir)
out_dir =os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.curdir, "runs", timestamp))
print("Writing to {}\n".format(out_dir))
saver =tf.train.Saver(tf.global_variables(), max_to_keep=100)
注意:我用的是已经训练好的词向量,这里只需要加载进来就可以了。
最新文章
- javascript类型系统——包装对象
- C#中返回值封装
- 关于scrollbar-face-color只支持ie的解决办法!
- AutoLayout那些坑
- 在 eclipse 中设置每行的字数
- offer--链表反转和从尾到头打印链表
- centOS 一键php环境安装-php博弈
- Docker创建MySQL集装箱
- Vue声明式渲染
- clear read-only status问题的解决
- C# - 为值类型重定义相等性
- 用 pdf.js兼容部分安卓显示PDF在线预览 时,a标签直接链接参数文件不能含中文的解决办法
- Python【每日一问】09
- 跑步“无核心,不PB”
- Java 支付宝支付,退款,单笔转账到支付宝账户(支付宝支付)
- PAT A1132 Cut Integer (20 分)——数学题
- border重叠的问题
- [leetcode 50]remove element
- Delphi 包的设计思想及它与PAS、BPL、DCU、DLL、OXC的关系
- mysql使用一条sql删除多条数据