【力扣】787. K 站中转内最便宜的航班加权——有向图最短路径
2024-10-21 05:39:41
前言
我感觉这题比较有代表性,所以记录一下,这题是加权有向图中求最短路径的问题。
题目
动态规划
假设有一条路径是[src, i, ..., j, dst],解法一子问题的定义是[src, i, ..., j],解法二子问题的定义是[i, ..., j, dst]。
解法一需要知道哪些节点指向dst,需要求入度。
解法二需要知道src指向哪些节点,需要求出度。
解法一
如下图所示,想要求src到dst的最短路径,如果知道了src到s1和src到s2的最短路径,那么问题就好解决了。
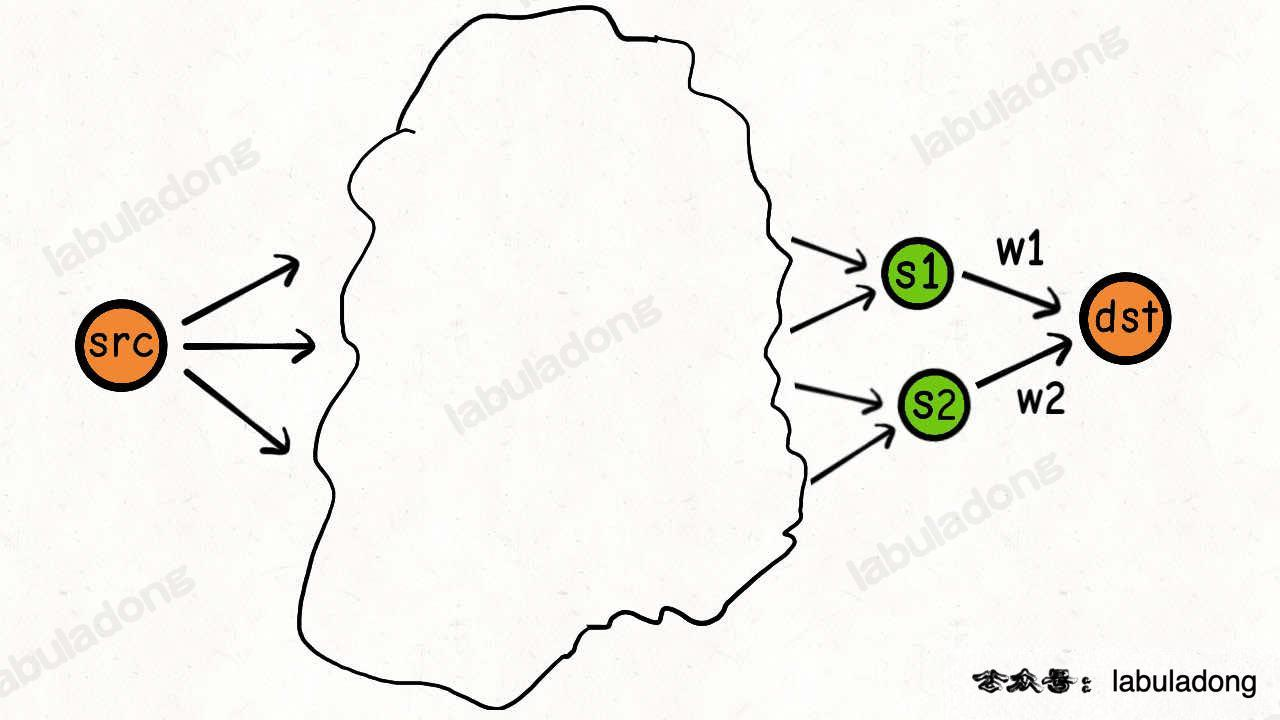
加上s1和s2到dst的花费取最小值即可,伪代码如下
minPrice(dst, k) =
min(minPrice(s1, k - 1) + w1,
minPrice(s2, k - 1) + w2)
最终代码
class Solution {
int n, src, dst;
int[][] flights;
int[][] memo;
HashMap<Integer, List<int[]>> indegree = new HashMap<>();
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
this.n = n;
this.flights = flights;
this.src = src;
this.dst = dst;
// 求入度
for(int[] flight : flights){
int from = flight[0], to = flight[1], price = flight[2];
indegree.putIfAbsent(to, new ArrayList<>());
indegree.get(to).add(new int[]{from, price});
}
memo = new int[n][k + 1];
for(int[] arr : memo){
Arrays.fill(arr, -2);
}
return dp(dst, k);
}
int dp(int dst, int k){
if(src == dst){
return 0;
}
if(k < 0){
return -1;
}
if(memo[dst][k] != -2){
return memo[dst][k];
}
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if(indegree.containsKey(dst)){
for(int[] v : indegree.get(dst)){
int subProblem = dp(v[0], k - 1);
if(subProblem == -1) continue;
res = Math.min(res, subProblem + v[1]);
}
}
memo[dst][k] = res == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : res;
return memo[dst][k];
}
}
解法二
如下图所示,想要求src到dst的最短路径,如果知道了s1到dst和s2到dst的最短路径,那么问题就好解决了。

加上src到s1和s2的花费取最小值即可,伪代码如下
minPrice(src, k) =
min(minPrice(s1, k - 1) + w1,
minPrice(s2, k - 1) + w2)
最终代码
class Solution {
int n, src, dst;
int[][] flights;
int[][] memo;
HashMap<Integer, List<int[]>> outdegree = new HashMap<>();
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
this.n = n;
this.flights = flights;
this.src = src;
this.dst = dst;
// 求出度
for(int[] flight : flights){
int from = flight[0], to = flight[1], price = flight[2];
outdegree.putIfAbsent(from, new ArrayList<>());
outdegree.get(from).add(new int[]{to, price});
}
memo = new int[n][k + 1];
for(int[] arr : memo){
Arrays.fill(arr, -2);
}
return dp(src, k);
}
int dp(int src, int k){
if(src == dst){
return 0;
}
if(k < 0){
return -1;
}
if(memo[src][k] != -2){
return memo[src][k];
}
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if(outdegree.containsKey(src)){
for(int[] v : outdegree.get(src)){
int subProblem = dp(v[0], k - 1);
if(subProblem == -1) continue;
res = Math.min(res, subProblem + v[1]);
}
}
memo[src][k] = res == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : res;
return memo[src][k];
}
}
小结
两种解法代码非常相似,具有对称性。对于有向图最短路径问题,常规思路都是 Dijkstra 等图论经典算法,没想到动态规划也可以,很奇妙。这也是我想记录这道题的原因吧。
BFS 算法思路
Dijkstra 算法
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int K) {
List<int[]>[] graph = new LinkedList[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
for (int[] edge : flights) {
int from = edge[0];
int to = edge[1];
int price = edge[2];
graph[from].add(new int[]{to, price});
}
// 启动 dijkstra 算法
// 计算以 src 为起点在 k 次中转到达 dst 的最短路径
K++;
return dijkstra(graph, src, K, dst);
}
class State {
// 图节点的 id
int id;
// 从 src 节点到当前节点的花费
int costFromSrc;
// 从 src 节点到当前节点经过的节点个数
int nodeNumFromSrc;
State(int id, int costFromSrc, int nodeNumFromSrc) {
this.id = id;
this.costFromSrc = costFromSrc;
this.nodeNumFromSrc = nodeNumFromSrc;
}
}
// 输入一个起点 src,计算从 src 到其他节点的最短距离
int dijkstra(List<int[]>[] graph, int src, int k, int dst) {
// 定义:从起点 src 到达节点 i 的最短路径权重为 distTo[i]
int[] distTo = new int[graph.length];
// 定义:从起点 src 到达节点 i 的最小权重路径至少要经过 nodeNumTo[i] 个节点
int[] nodeNumTo = new int[graph.length];
Arrays.fill(distTo, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
Arrays.fill(nodeNumTo, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// base case
distTo[src] = 0;
nodeNumTo[src] = 0;
// 优先级队列,costFromSrc 较小的排在前面
Queue<State> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> {
return a.costFromSrc - b.costFromSrc;
});
// 从起点 src 开始进行 BFS
pq.offer(new State(src, 0, 0));
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
State curState = pq.poll();
int curNodeID = curState.id;
int costFromSrc = curState.costFromSrc;
int curNodeNumFromSrc = curState.nodeNumFromSrc;
if (curNodeID == dst) {
// 找到最短路径
return costFromSrc;
}
if (curNodeNumFromSrc == k) {
// 中转次数耗尽
continue;
}
// 将 curNode 的相邻节点装入队列
for (int[] neighbor : graph[curNodeID]) {
int nextNodeID = neighbor[0];
int costToNextNode = costFromSrc + neighbor[1];
// 中转次数消耗 1
int nextNodeNumFromSrc = curNodeNumFromSrc + 1;
// 更新 dp table
if (distTo[nextNodeID] > costToNextNode) {
distTo[nextNodeID] = costToNextNode;
nodeNumTo[nextNodeID] = nextNodeNumFromSrc;
}
// 剪枝,如果中转次数更多,花费还更大,那必然不会是最短路径
if (costToNextNode > distTo[nextNodeID]
&& nextNodeNumFromSrc > nodeNumTo[nextNodeID]) {
continue;
}
pq.offer(new State(nextNodeID, costToNextNode, nextNodeNumFromSrc));
}
}
return -1;
}
参考资料
最新文章
- HTML基本元素(二)
- Linq to Xml读取复杂xml(带命名空间)
- 刀锋上前行!绕过Ramint蠕虫病毒直接脱壳
- linux网站服务Apache+php+mysql的安装
- linux 查看磁盘剩余命令
- Css中光标,DHTML,缩放的使用
- BZOJ 2753 [SCOI2012] 滑雪和时间胶囊 最小生成树
- 【贪心】 BZOJ 3252:攻略
- C#微信公众号开发 -- (一)开发之前的准备
- poj2975--Nim
- 14.2.3 InnoDB Redo Log
- .NET开源 FAQ
- TIdTCPClient 详解
- gradient渐变IE兼容处理
- 【webpack系列】从零搭建 webpack4+react 脚手架(二)
- java中伪共享问题
- Python这么强大, 怎样才能快速入坑?
- ascii、unicode、utf-8、gbk 区别
- CyclicBarrier源码解读
- 【Python】定时调度