[贪心,dp] Educational Codeforces Round 71 (Rated for Div. 2) C. Gas Pipeline (1207C)
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You are responsible for installing a gas pipeline along a road. Let's consider the road (for simplicity) as a segment [0,n]
on OX axis. The road can have several crossroads, but for simplicity, we'll denote each crossroad as an interval (x,x+1) with integer x. So we can represent the road as a binary string consisting of n
characters, where character 0 means that current interval doesn't contain a crossroad, and 1 means that there is a crossroad.
Usually, we can install the pipeline along the road on height of 1
unit with supporting pillars in each integer point (so, if we are responsible for [0,n] road, we must install n+1 pillars). But on crossroads we should lift the pipeline up to the height 2
, so the pipeline won't obstruct the way for cars.
We can do so inserting several zig-zag-like lines. Each zig-zag can be represented as a segment [x,x+1]
with integer x consisting of three parts: 0.5 units of horizontal pipe + 1 unit of vertical pipe + 0.5 of horizontal. Note that if pipeline is currently on height 2, the pillars that support it should also have length equal to 2
units.
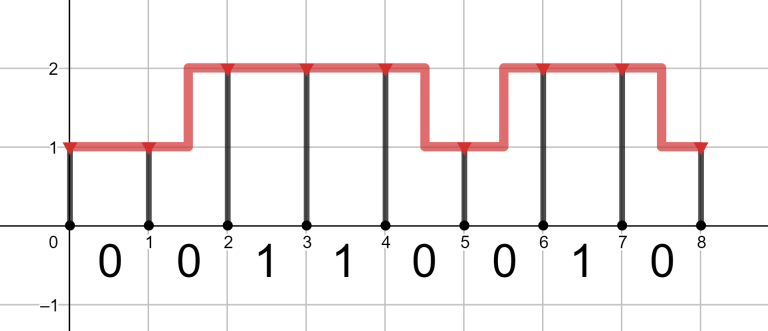
Each unit of gas pipeline costs us a
bourles, and each unit of pillar — b bourles. So, it's not always optimal to make the whole pipeline on the height 2
. Find the shape of the pipeline with minimum possible cost and calculate that cost.
Note that you must start and finish the pipeline on height 1
and, also, it's guaranteed that the first and last characters of the input string are equal to 0.
The fist line contains one integer T
(1≤T≤100) — the number of queries. Next 2⋅T
lines contain independent queries — one query per two lines.
The first line contains three integers n
, a, b (2≤n≤2⋅105, 1≤a≤108, 1≤b≤108
) — the length of the road, the cost of one unit of the pipeline and the cost of one unit of the pillar, respectively.
The second line contains binary string s
(|s|=n, si∈{0,1}, s1=sn=0
) — the description of the road.
It's guaranteed that the total length of all strings s
doesn't exceed 2⋅105
.
Print T
integers — one per query. For each query print the minimum possible cost of the constructed pipeline.
4
8 2 5
00110010
8 1 1
00110010
9 100000000 100000000
010101010
2 5 1
00
94
25
2900000000
13
The optimal pipeline for the first query is shown at the picture above.
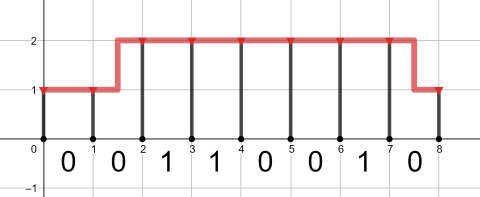
The optimal pipeline for the second query is pictured below:
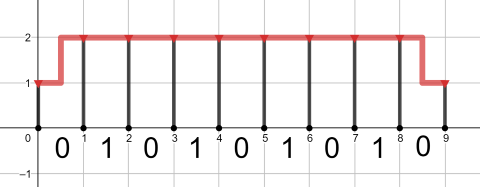
The optimal (and the only possible) pipeline for the third query is shown below:
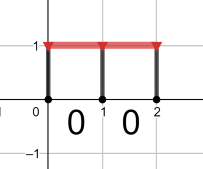
The optimal pipeline for the fourth query is shown below:
题意:
给一个长度为n的01串,和建单位长度的管道的代价a和单位长度的柱子b的代价,有4种柱子,低管道代价为a+b,高管道代价为a+2*b,上升管道代价为2*a+b,下降管道代价为2*a+2*b,01串中1代表要建高管道,一段高管道前要建上升管道,后要建下降管道,如果一个地方既要上升管道有要下降管道,则那个地方必须为高管道,问建这个区域管道和柱子的最小代价
思路:
读入01串后给管道分类,低管道为0,高管道为1,上升管道为2,下降管道为3,如果这个管道既要上升又要下降,则必须建高管道,再提取出上升管道和下降管道(这里设i从0开始),注意到只能是中间的某些下降管道到下一个上升管道这段看要不要换成全部都是高管道来比较代价,注意题中规定第1个管道必定是低管道或上升管道,最后一个必定是下降管道或低管道,下面的每个格子代价计算的是格子左边柱子的代价和格子管道的代价,在第一次访问时i为偶数是上升管道,但前面没有下降管道,故要算建低管道的代价和上升管道的代价,在最后一次访问时i为奇数时下降管道,但后面没有上升管道了,故要算建下降管道和低管道的代价,如果在中间,由于管道有升就有降且必定先升再降,而且才0开始存上升下降位置,所以偶数位存上升管道,奇数位置存下降管道,如果现在这个管道是下降管道,have计算从下降管道到上升管道之间有多少个高度低管道注意这里要开long long,不然会溢出,在可以先下降在上升的管道区域要判断是否这样建还是不下降而是继续全建高管道,选一个代价小的建,用2*a-b>=have*b这个公式判断,它是这样推出来的,设1类为这一段建下降管道,低管道,上升管道,2类为这一段全建高管道,1类的代价为(4*a+3*b+have*(a+b)),2类代价为(have+2)*(a+2*b),可见1类和2类在have不同时代价不同,所以可以做差来比较它们的大小,即推出此公式如果现在这个是上升管道则只算高管道有多少,因为第一个上升管道代价第一次时已经算过了,而中间碰到下降管道时计算代价是下降管道+低管道+上升管道.还要判断如果没有上升和下降的管道则全建低管道,输出答案时最后一个管道的右边柱子的代价要加上
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int amn=2e5+;
long long m[amn],jg[amn];
int main(){
long long T,n,a,b,st,ed,tp=;long long ans;char in;
ios::sync_with_stdio();
cin>>T;
while(T--){
tp=;
cin>>n>>a>>b;
st=-;ans=ed=;
for(int i=;i<n;i++){cin>>in;if(in=='')m[i]=;else m[i]=;}m[n]=;
for(int i=;i<n;i++){
if(m[i]==){
if(st==-)st=i-;
if(i>){
if(m[i-]==)m[i-]=;
else m[i-]=; ///如果这个管道既要上升又要下降,则必须建高管道
}
if(i+<n){
if(m[i+]==){m[i+]=;ed=i+;}
else m[i+]=; ///如果这个管道既要上升又要下降,则必须建高管道(其实这里不用判断,因为前面还没判断过,不可能有2,只可能时1或0
}
}
}
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
if(m[i]==||m[i]==)jg[tp++]=i;
for(int i=;i<tp;i++){ ///注意位置i从0开始哦! 注意题中规定第1个管道必定是低管道或上升管道,最后一个必定是下降管道或低管道,下面的每个格子代价计算的是格子左边柱子的代价和格子管道的代价,低管道a+b,高管道a+2*b,上升管道2*a+b,下降管道2*a+2*b
if(i==) ///在第一次访问时i为偶数是上升管道,但前面没有下降管道,故要算建低管道的代价和上升管道的代价
ans+=jg[i]*(a+b)+*a+b;
else if(i==tp-) ///在最后一次访问时i为奇数时下降管道,但后面没有上升管道了,故要算建下降管道和低管道的代价
ans+=(n--jg[i])*(a+b)+*a+*b;
if(i!=tp-){ ///如果在中间
if(i&){ ///由于管道有升就有降且必定先升再降,而且才0开始存上升下降位置,所以偶数位存上升管道,奇数位置存下降管道
long long have=jg[i+]-jg[i]-; ///have计算从下降管道到上升管道之间有多少个高度低管道注意这里要开long long,不然会溢出
if(*a-b>=have*b) ///在可以先下降在上升的管道区域要判断是否这样建还是不下降而是继续全建高管道,选一个代价小的建,用2*a-b>=have*b这个公式判断,它是这样推出来的,设1类为这一段建下降管道,低管道,上升管道,2类为这一段全建高管道,1类的代价为(4*a+3*b+have*(a+b)),2类代价为(have+2)*(a+2*b),可见1类和2类在have不同时代价不同,所以可以做差来比较它们的大小,即推出此公式
ans+=(have+)*(a+*b);
else
ans+=(*a+*b+have*(a+b));
}
else ///如果现在这个是上升管道则只算高管道有多少,因为第一个上升管道代价第一次时已经算过了,而中间碰到下降管道时计算代价是下降管道+低管道+上升管道
ans+=(jg[i+]-jg[i]-)*(a+*b);
}
}
if(tp==) ///如果没有上升和下降的管道则全建低管道
ans+=n*(a+b);
printf("%lld\n",ans+b); ///最后一个管道的右边柱子的代价要加上
}
}
/**
给一个长度为n的01串,和建单位长度的管道的代价a和单位长度的柱子b的代价,有4种柱子,低管道代价为a+b,高管道代价为a+2*b,上升管道代价为2*a+b,下降管道代价为2*a+2*b,01串中1代表要建高管道,一段高管道前要建上升管道,后要建下降管道,如果一个地方既要上升管道有要下降管道,则那个地方必须为高管道,问建这个区域管道和柱子的最小代价
读入01串后给管道分类,低管道为0,高管道为1,上升管道为2,下降管道为3,如果这个管道既要上升又要下降,则必须建高管道,再提取出上升管道和下降管道(这里设i从0开始),注意到只能是中间的某些下降管道到下一个上升管道这段看要不要换成全部都是高管道来比较代价,
注意题中规定第1个管道必定是低管道或上升管道,最后一个必定是下降管道或低管道,下面的每个格子代价计算的是格子左边柱子的代价和格子管道的代价,
在第一次访问时i为偶数是上升管道,但前面没有下降管道,故要算建低管道的代价和上升管道的代价,在最后一次访问时i为奇数时下降管道,但后面没有上升管道了,故要算建下降管道和低管道的代价,
如果在中间,由于管道有升就有降且必定先升再降,而且才0开始存上升下降位置,所以偶数位存上升管道,奇数位置存下降管道,
如果现在这个管道是下降管道,have计算从下降管道到上升管道之间有多少个高度低管道注意这里要开long long,不然会溢出,在可以先下降在上升的管道区域要判断是否这样建还是不下降而是继续全建高管道,选一个代价小的建,用2*a-b>=have*b这个公式判断,它是这样推出来的,设1类为这一段建下降管道,低管道,上升管道,2类为这一段全建高管道,1类的代价为(4*a+3*b+have*(a+b)),2类代价为(have+2)*(a+2*b),可见1类和2类在have不同时代价不同,所以可以做差来比较它们的大小,即推出此公式
如果现在这个是上升管道则只算高管道有多少,因为第一个上升管道代价第一次时已经算过了,而中间碰到下降管道时计算代价是下降管道+低管道+上升管道.
还要判断如果没有上升和下降的管道则全建低管道,
输出答案时最后一个管道的右边柱子的代价要加上
**/
最新文章
- C语言程序设计第十次作业
- Java算法-冒泡排序
- [转]开发Visual Studio风格的用户界面--MagicLibrary使用指南
- Cocos2d-X3.0 刨根问底(三)----- Director类源码分析
- sqlserver查询所有表的行数的sql语句
- (转)多个mapreduce工作相互依赖处理方法完整实例(JobControl)
- Iterator invalidation(迭代器失效)
- vue2 和 webpack 配置环境使用
- Spring之DAO模块
- mac 删除文件不经过废纸篓解决办法
- C#中的特性(Attributes)
- Luogu3613 睡觉困难综合征/BZOJ4811 Ynoi2017 由乃的OJ 树链剖分、贪心
- 键盘按键js效果
- [ovs] openvswitch 入门
- SEO--提高权重
- Android-Java控制多线程执行顺序
- 详解C#特性和反射(二)
- setuid、setgid、sticky的权限简单用法
- Assets/FollowDestination.cs(6,13): error CS0246: The type or namespace name `NavMeshAgent' could not be found. Are you missing `UnityEngine.AI' using directive?的解决方案
- sql-(Cross||Outer)Apply