Flask(3)- Flask 中的 HTTP 方法
2024-10-08 22:20:39
查看 app.route() 源代码
def route(self, rule: str, **options: t.Any) -> t.Callable:
"""Decorate a view function to register it with the given URL
rule and options. Calls :meth:`add_url_rule`, which has more
details about the implementation. .. code-block:: python @app.route("/")
def index():
return "Hello, World!" See :ref:`url-route-registrations`. The endpoint name for the route defaults to the name of the view
function if the ``endpoint`` parameter isn't passed. The ``methods`` parameter defaults to ``["GET"]``. ``HEAD`` and
``OPTIONS`` are added automatically. :param rule: The URL rule string.
:param options: Extra options passed to the
:class:`~werkzeug.routing.Rule` object.
""" def decorator(f: t.Callable) -> t.Callable:
endpoint = options.pop("endpoint", None)
self.add_url_rule(rule, endpoint, f, **options)
return f return decorator
重点
- Calls:meth: add_url_rule,需要关注下这个方法
- end_poiont 如果未传递 endpoint 参数,则路由的端点名称默认为视图函数的名称,如果已为注册函数,则会引发错误
- methods 参数默认值是 ["GET"],所以当你不传 methods 参数时,只有发送 GET 请求才能匹配上对应的路由
来看看 add_url_rule 方法
打个断点,进入 debug 调试模式,运行后,一直 F7 就能看到源码
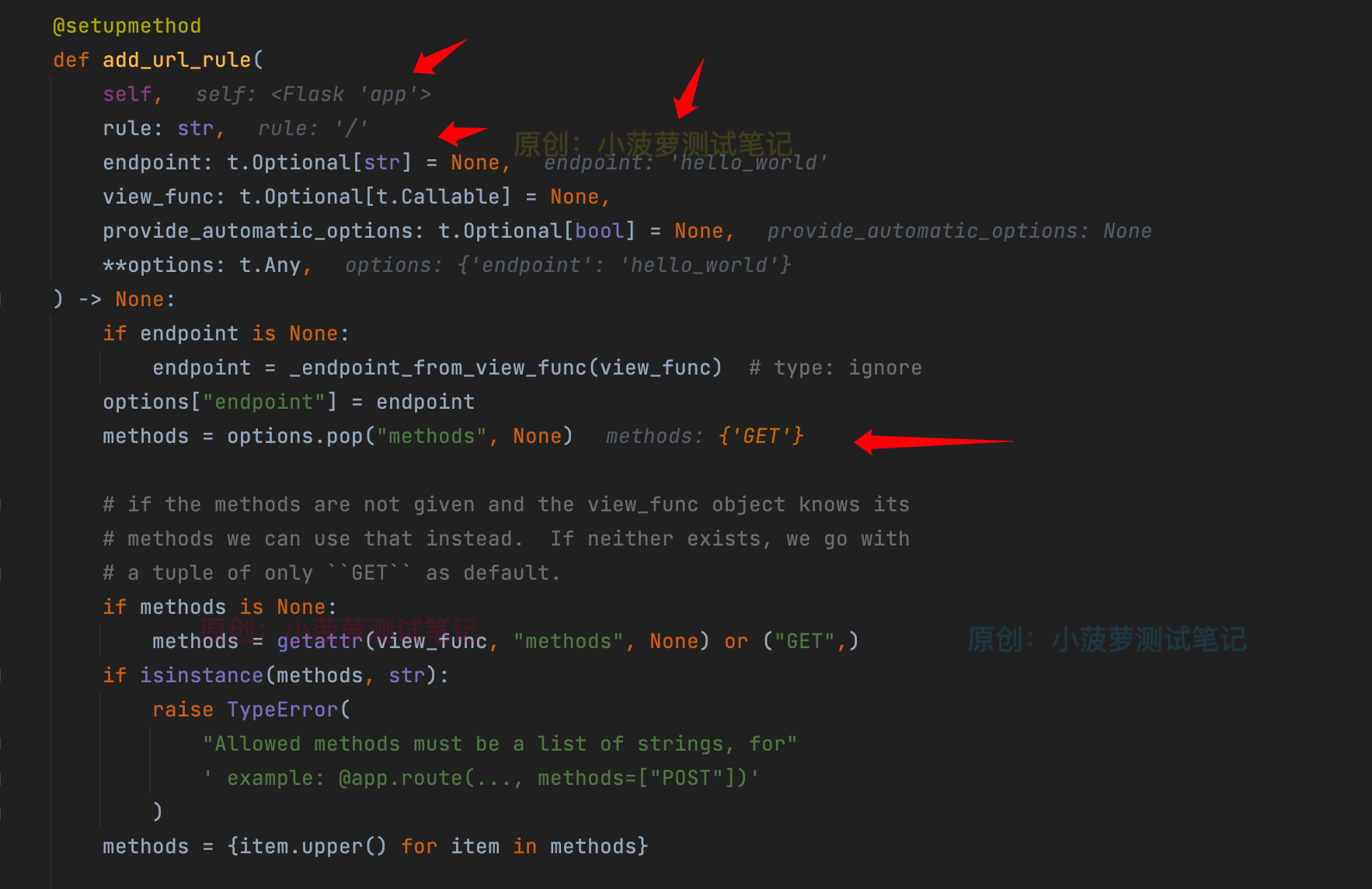
- self:就是 Flask 类的实例
- rule:其实就是路由规则
- end_point:函数名
- methods:如果没有传,那么会先通过 view_func 获取 methods 属性,如果还是没有,那默认就是 GET,记得这是个列表 [ ]
结论
默认的 app.route() 是仅支持 GET 请求的,如果想通过 POST、PUT、DELTE 等方法正常请求的话,需要添加 methods 参数哦
GET 请求的栗子
代码
# 不指定 methods,默认就是 GET
@app.route('/')
def hello_world():
# 返回字符串
return '<b>Hello World</b>' @app.route('/get', methods=["GET"])
def get_():
# 返回字符串
return '这是get请求'
postman 请求结果

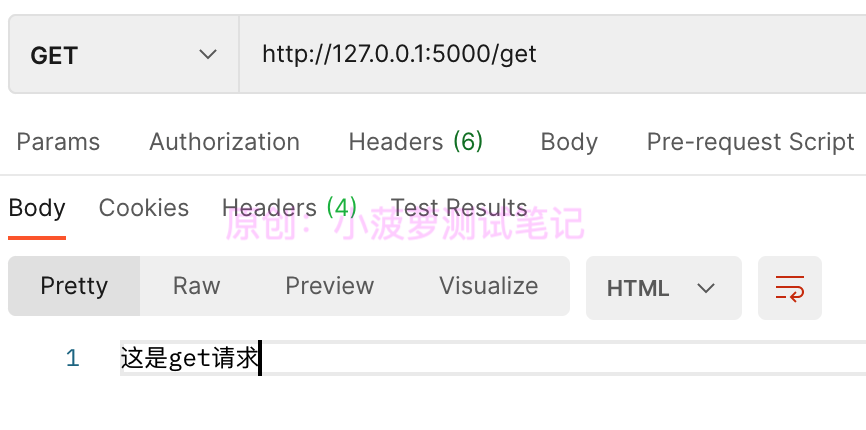
没啥特别的~
POST 请求的栗子
代码
@app.route('/post', methods=["POST"])
def post_():
# 返回字符串
return {"messgage": "这是post请求"}
返回的是一个 python 字典,那么最后请求得到响应会是啥呢?
postman 请求结果

踩坑之一:哎呀,假设我用 GET 方法发起请求,那么就会直接报 405,说你的请求方法是不允许的!记住了哦!
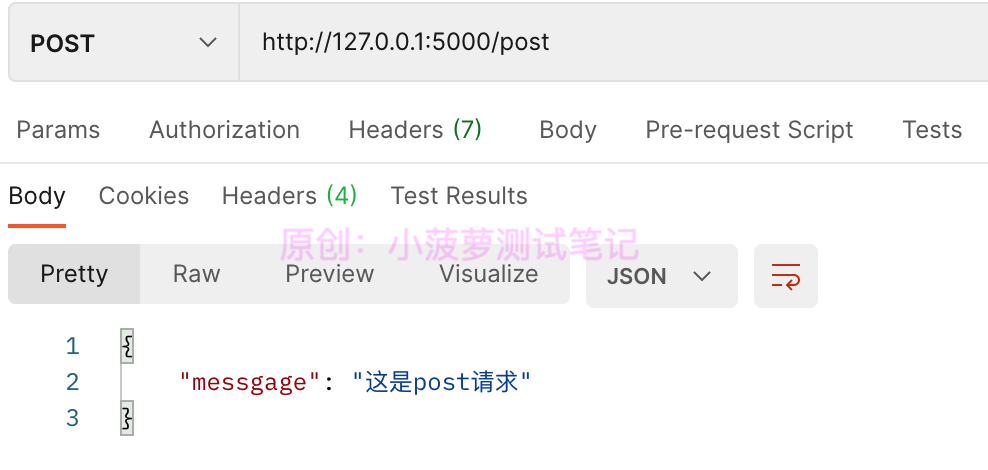
要记住,如果 return 的是字典,那么请求得到的响应数据是 Json 格式哦
PUT、DELETE 请求的栗子
代码
@app.route('/delandput', methods=["DELETE", "PUT"])
def delandput():
# 返回字符串
return ["delete", "put"]
一个视图函数,允许 DELETE、PUT 方法
postman 请求结果
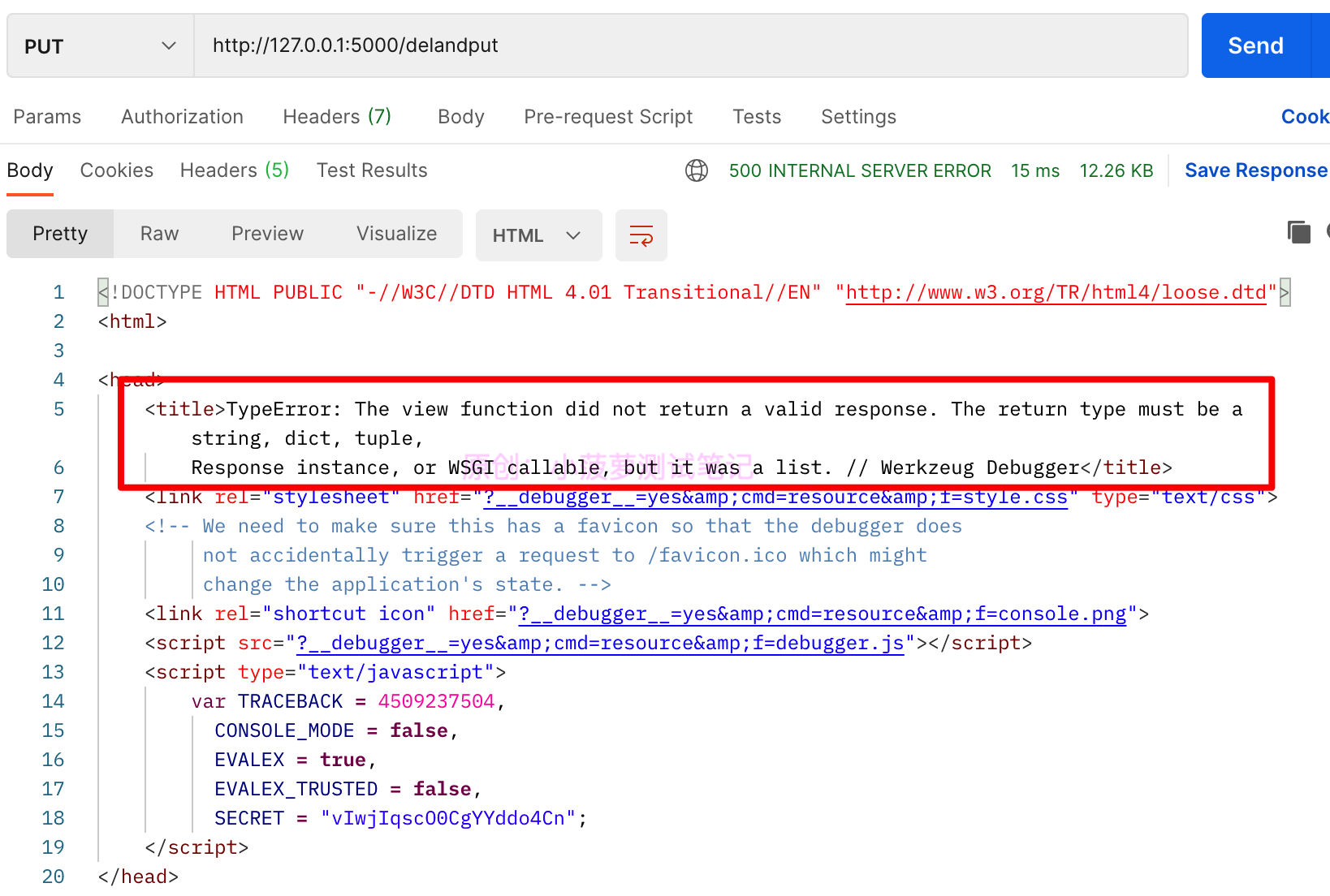
踩坑之二:我去!怎么报错了...仔细一看,错误信息已经提示的很清楚了,视图函数的返回值类型只能是 string、dict、tuple
正确的代码
@app.route('/delandput', methods=["DELETE", "PUT"])
def delandput():
# 返回字符串
return {"result": ["delete", "put"]}
postman 请求结果
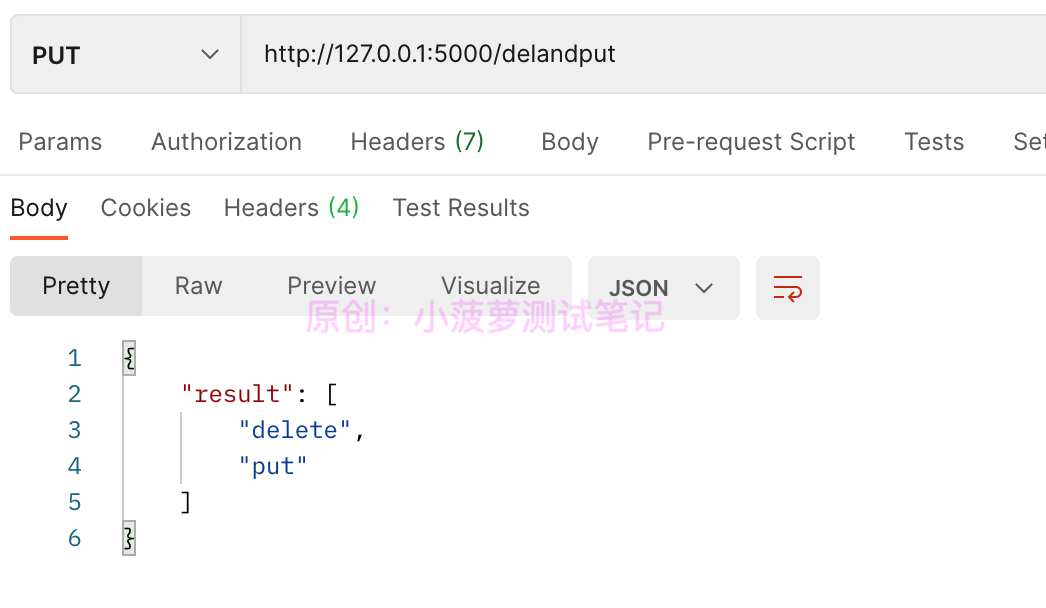
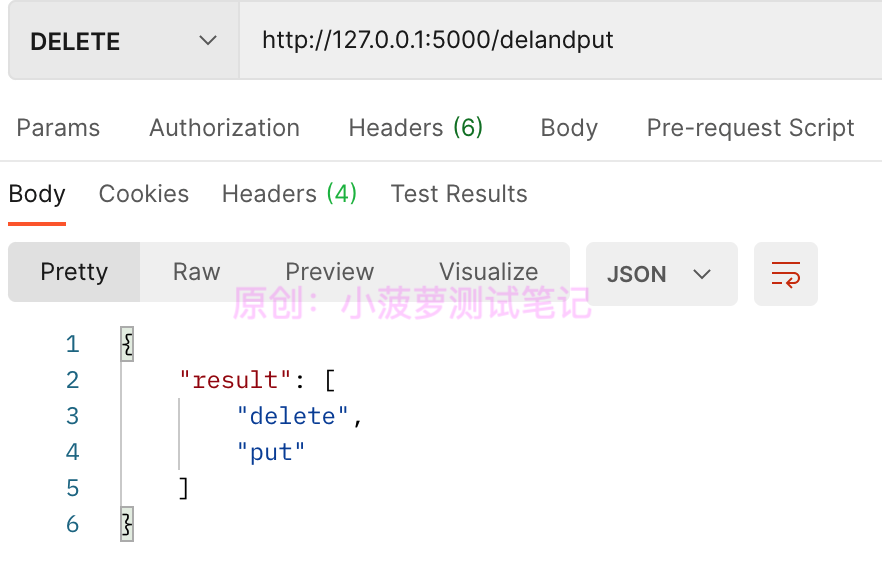
put 和 delete 都成功啦
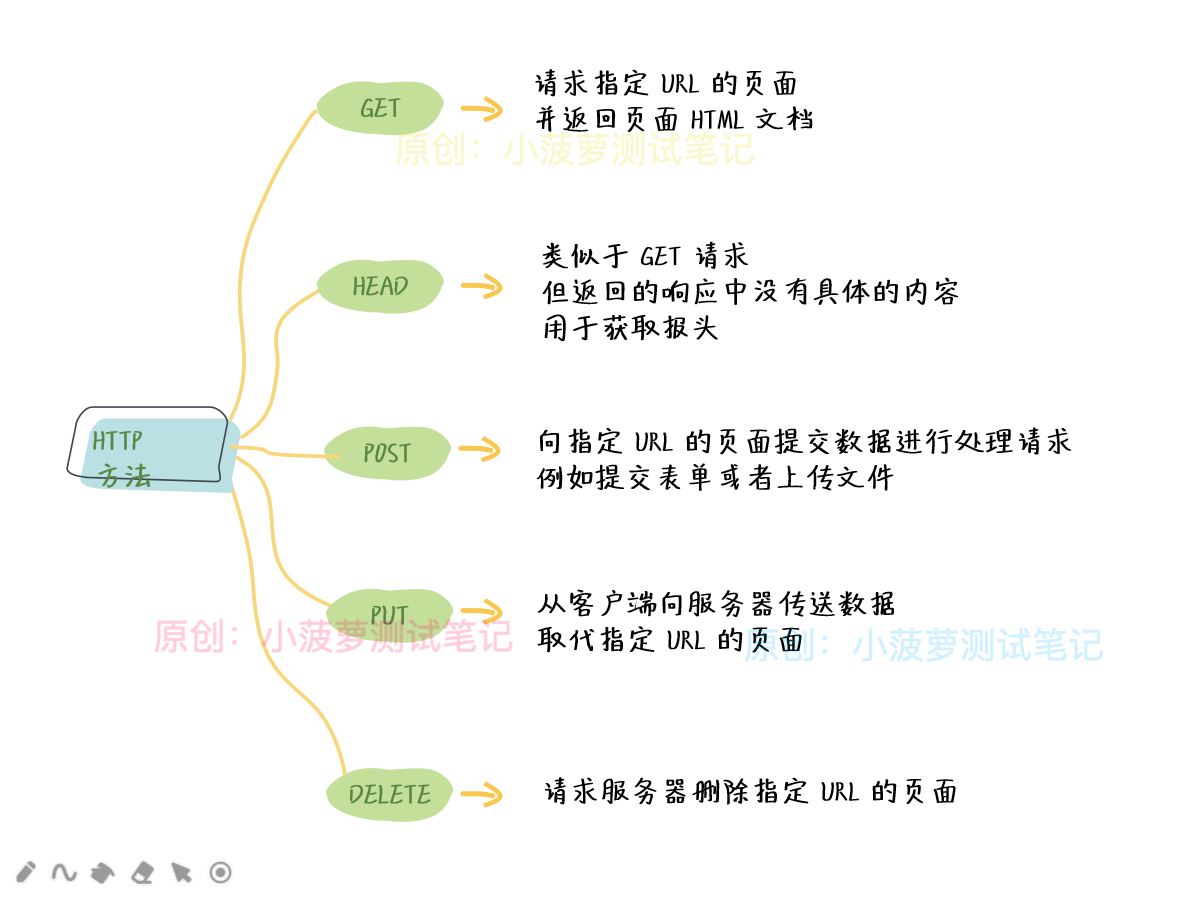
总结
最新文章
- maven管理本地jar包注意事项
- mysql 语法
- Centos6 换源
- [hihoCoder] 博弈游戏·Nim游戏
- Centos文本方式安装情况下lvm分区的创建
- ADO.NET知识的运用一(Day 26)
- mysqldump 备份数据说明+ 避免锁表
- ubuntu文本界面乱码的中国解决方案
- 微信小程序开源项目库集合
- STM32F2系列低功耗总结
- Linux运行级别简介
- jQuery实现用户输入自动完成功能
- 基于Java Mail 进行发送(带附件和压缩附件)的邮件
- Unity 3d游戏逆向及.NET Reflector工具使用介绍
- CSS布局(圣杯、双飞翼、flex)
- 三、后门的编写和 ShellCode 的提取
- jmeter获取cookies信息(配置)
- 『实践』VirtualBox 5.1.18+Centos 6.8+hadoop 2.7.3搭建hadoop完全分布式集群及基于HDFS的网盘实现
- Spring源码分析(一)基本介绍
- 网页正文提取,降噪的实现(readability/Document)