面试——String的比较总结
2024-09-29 02:52:06
public class StringTest {
private static String getA() {return "a";}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "ab";
String s2 = "a"+"b";
String a = "a";
String s3 = a+"b";
//s1.equals(s2);
//Object
//HashMap
/*HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
map.put("语文", 1);
map.put("数学", 2);
map.put("英语", 3);
map.put("历史", 4);
map.put("政治", 5);
map.put("地理", 6);
map.put("生物", 7);
map.put("化学", 8);
for(Entry<String, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ": " + entry.getValue());
}
更多了解:https://yikun.github.io/2015/04/01/Java-HashMap%E5%B7%A5%E4%BD%9C%E5%8E%9F%E7%90%86%E5%8F%8A%E5%AE%9E%E7%8E%B0/
*/
final String aa = "a";
String s4 = aa +"b";
String s5 = getA() +"b";
String s6 = new String("ab");
System.out.println(s1==s2);//true
System.out.println(s1==s3);//false
System.out.println(s1==s4);//true
System.out.println(s1==s5);//false
System.out.println(s1==s6);//false
System.out.println(s1==s6.intern());//true
System.out.println(s2.intern()==s6.intern());//true
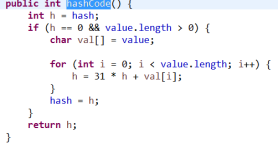
System.out.println(s1.hashCode());//
System.out.println(s2.hashCode());//
System.out.println(s3.hashCode());//
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(s1));//
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(s2));//
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(s3));//
/**
* 问:
* 1、为什么是true? 这里涉及到基础知识点有哪些?
* 答:
* 1、
* a、首先这里要明白"=="是干什么的?
* "=="是匹配内存单元上的内容是否相等,其实就是一个数字,因为计算机内存中也只有数字0和1;
* 原始类型"byte,boolean,short,char,int,float,double,long",就直接比较它们的值;
* 引用类型"Reference",就比较引用的值,通常指对象的逻辑地址,也就是比较两个引用是否是同一个对象;
* 空值"null",JVM也会赋予给它一个特定的值;
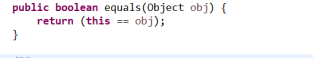
* b、equals()方法?
* 首先是在Object类中定义的,equals()方法只所以存在Object类,是希望子类去重写该方法,因为业务场景不一样,所以比较的
* 标准就不一样。String类就重写了该方法。
* 

* 重写equals()方法,一般会重写hashCode()方法?
* 首先明白HashCode是什么?
* hashCode值是hashCode()方法提供了对象的hashCode值,它的返回值默认与System.identityHashCode(object)相同
* hashCode具体是对象头部的一部分二进制组成的数字,有标识对象的作用,但是不等价于地址。
* 为什么存在hashCode? 因为对象要用于算法中,而算法建立在数字基础上。
* 
* 这里Object.hashCode()与System.identityHashCode(Object)值为什么不一致?
* 因为System.identityHashCode()方法是java根据对象在内存中的地址计算出来的一个数值,不同的地址计算出来数值不一样
* 所以s2和s3不是同一个对象,所以计算不是同一个值
* 又因为String重写了hashCode()方法,所以值也不一样。
*
* Hashmap,HashSet等类似集合中,如果用某个对象作为key,,也是要基于这个对象实现hash的写入和查找。
* Hash算法可以将对象相对离散开,这样就可以在查找数据的时候根据这个key快速地缩小数据的范围。
* 这个时候key就如同数组里面的key,而value就是链表,hashcode值不能说是唯一的,所以在Hash算法中定位
* 到具体链表之后,需要进一步循环链表,然后通过equals()来对比Key的值是否一样的,所以在这个时候,hashCode()
* 与equals()似乎成了一对儿,换句话说,HashCode是为了算法快速定位数据而存在,equals()是为了对比真实值
* 存在的。
* 需要注意的是,我们可以重写HashCode()方法,但最好是返回值最好是能将对象相对离散的数据,如果始终是返回一个值
* 那就是一个key,链表将会很长,查询链表还慢。
* 更多了解HashMap底层。
*
* c、编译时优化方案
* s1==s3//false 因为a不是常量,而是局部变量,并且可以通过字节码增强技术改变,所以不会编译时优化
* s1==s4//true 因为c是final修饰不可变,编译可以优化
* s1==s5//false 来源方法,编译器不知道方法做了什么,即是返回是常量,也是对引用实现的拷贝,拷贝并不是final
*
* 因为s1,s2是引用同一个对象,对象比较用"=="所以为true.
* 2、
* s1==s6// false 两个不同的对象 ,new
* intern() 保存在方法区的常量池中 ,效率不高
*/ } }
最新文章
- Hadoop学习之旅三:MapReduce
- 3.Code-First 约定(EF Code-First系列)
- POJ2239 Selecting Courses(二分图最大匹配)
- WCF初探-9:WCF服务承载 (下)
- [Js]面向对象的选项卡实例
- EL表达式-例子
- css 去除input 获取焦点的蓝色边框
- IE浏览器Ajax缓存问题小结
- My way to Python - Day05 - 面向对象-思维导图
- 网站注册信息的JS全码
- POI数据下载器
- windows下架设SVN服务器并设置开机启动
- 刨根究底字符编码之十二——UTF-8究竟是怎么编码的
- Davinci DM6446开发攻略——DSP开发工程建立
- js前端对后台数据的获取,如果是汉字则需要添上引号
- Android 性能优化之减少UI过度绘制
- QT获取本机IP和Mac地址
- 自己动手,打造轻量级VSCode/C#环境代替LinqPad
- Python+Pycharm—学习1—封装&导入
- 跟我一起学习vue2(熟悉vue.js)[一]
热门文章
- [poj] 3041 Asteroids || 最小点覆盖=最大二分图匹配
- College student reflects on getting started in open source(二)
- iOS_自定义毛玻璃效果
- 关于"implicit declaration of function 'gettimeofday' is invalid in c99"的解决
- Ubuntu16.10 +python3.5+Tensorflow 1.1
- [python] win7 64位 安装pygame
- Codeforces Round #444 (Div. 2)A. Div. 64【进制思维】
- Python的并发并行[1] -> 线程[2] -> 锁与信号量
- spark完整的数据倾斜解决方案
- 【bzoj1485:】【 [HNOI2009]有趣的数列】模任意数的卡特兰数