20145310《Java程序设计》第3周学习总结
20145310 《Java程序设计》第3周学习总结
教材学习内容总结
本周学习内容比较多,主要是第四第五章的学习。
第四章
类与对象
类是对象的设计图,对象是类的实例。
类(Class)的含义可以理解为,具有相同属性和行为的一组对象的集合,用于组合各个对象所共有操作和属性的一种机制。
对象(Object)的含义:存在的具体实体,具有明确的状态和行为。
书上的例子是设计一件衣服,分别从color和size两方面考虑。而这个的设计图就是
{
String color;
char size;
}
Clothes c1 = new Clothes();中,将c1名称参考至新建对象。c1与c语言中的指针相似。
c1是引用,在栈上
new Clothes()在堆上生成对象
//定义两个值域成员
class Clothes //定义clothes类
{
String color;
char size;
}
public class Field
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Clothes sun = new Clothes();
Clothes spring = new Clothes(); //建立Clothes实例
sun.color = "red";
sun.size = 'S';
spring.color = "green";
spring.size = 'M';
//为个别对象的数据成员指定值
System.out.printf("sun (%s,%c)%n", sun.color,sun.size);
System.out.printf("sun (%s,%c)%n", spring.color,spring.size);
//显示个别对象的数据或成员值
}
}
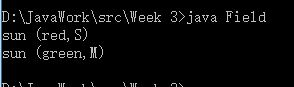
如果想在建立对象时,一并进行某个初始流程,像是指定数据成员值,则可以定义构造函数。
class Clothes2
{
String color;
char size;
Clothes2(String color,char size) //从这里开始就定义构造了一个函数。
{
this.color = color; //color参数的值指定给这个对象的color成员
this.size = size;
}
}
public class Field2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Clothes2 sun = new Clothes2("red",'S'); //使用上面指定的构造函数建立对象
Clothes2 spring = new Clothes2("green",'M');
System.out.printf("sun (%s,%c)%n",sun.color,sun.size);
System.out.printf("spring (%s,%c)%n",spring.color,spring.size); //输出结果
}
}

使用标准类
java SE提供了标准API,这些API由许多类组成。 java.util.Scanner与java.math.BigDecimal
使用java.util.Scanner:
import java.util.Scanner; //使用import偷懒
class Guess
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); //建立Scanner实例
int number = (int) (Math.random()*10); //readom随机数,10以内
int guess;
do{
System.out.print("猜数字(0~9):");
guess = scanner.nextInt(); //取得下一个int整数
}
while(guess != number);
System.out.println("猜中了...XD");
}
}

(这次比较惨,最后一次才猜中)
程序偷懒之后只要输入Scanner就可以了。
为了得到更好的精确度,可以使用java.math.BigDecimal类
import java.math.BigDecimal; //同样,让程序偷懒
class DecimalDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BigDecimal operand1 = new BigDecimal ("1.0");
BigDecimal operand2 = new BigDecimal ("0.8");
BigDecimal result = operand1.subtract (operand2); //将上面两个数做减法
System.out.println(result); //输出结果
}
}
运行结果:

改成比较大小是否相等的代码
import java.math.BigDecimal;
class DecimalDemo2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BigDecimal op1 = new BigDecimal("0.1");
BigDecimal op2 = new BigDecimal("0.1");
BigDecimal op3 = new BigDecimal("0.1");
BigDecimal result = new BigDecimal("0.3");
if(op1.add(op2).add(op3).equals(result)) //add为加 equals为比较两个bigdecimal实质上是否相同
{
System.out.println("等于 0.3"); //相同的输出"等于 0.3"
}
else {
System.out.println("不等于 0.3");
}
}
}
运行结果:

基本类型打包器
基本类型打包器:Long、Integer、Double、Float、Boolean等类是所谓的打包器,正如此名称所示,这些类主要目的就是提供对象实例作为“壳”,将基本类型打包在对象之中。
//Integer打包实例
class IntegerDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int data1 = 10;
int data2 = 20;
Integer wrapper1 = new Integer(data1); //打包基本类型
Integer wrapper2 = new Integer(data2);
System.out.println(data1/3); //基本类型运算
System.out.println(wrapper1.doubleValue()/3); //操作打包器的方法
System.out.println(wrapper1.compareTo(wrapper2));
}
}
运行结果:

从java SE 5.0之后提供了自动装箱、拆箱功能。
数组对象
Java中,数组是对象。
与C语言不同,Java检查数组边界,越界会触发ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException异常
定义数组的方式:int[] scores ={88,81,74,69,79,76,77,85,95,93};
//定义数组并依次输出
class Score
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] scores = {88,81,74,68,78,76,77,85,95,93}; //定义数组
for(int i = 0;i <scores.length;i++);//自增i
{
System.out.printf("学生分数:%d %n", scores[i]); //依次输出
}
}
}
运行结果:

二维数组实例:
class XY
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[][]cords = {
{1,2,3},
{4,5,6} //声明二维数组,并赋给他们初始值
};
for(int x = 0;x < cords.length;x++) //得知有几列
{
for(int y = 0;y < cords[x].length;y++) //取得每列的长度
{
System.out.printf("%2d",cords[x][y]); //指定列、行索引取得数组元素
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
运行结果:

如果事先不知道元素值,只知道元素个数,可以使用new关键词指定长度来建立数组。
如果默认初始值不符合需求,可以使用java.util.Arrays的fill()方法设定新建数组的元素值。
import java.util.Arrays; //使用import进行偷懒
class Score2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] scores = new int[10];
for(int score : scores)
{
System.out.printf("%2d",score);
}
System.out.println();
Arrays.fill(scores,60); //新建数组的元素值
for(int score : scores)
{
System.out.printf("%3d",score);
}
}
}
运行结果:

也可以建立不规则数组
class IrregularArry
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[][]arr = new int[2][]; //声明arr参考的对象会有两个索引
arr[0] = new int[] {1,2,3,4,5}; //arr[0]是长度为5的一维数组
arr[1] = new int[] {1,2,3}; //arr[1]是长度为3的一维数组
for (int[] row : arr)
{
for(int value : row)
{
System.out.printf("%2d",value);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
运行结果:

上面的程序片段建立了0个Integer对象。每个索引其实都是Integer类型。
class IntegerArray
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Integer [] scores = new Integer [3];
for(Integer score : scores)
{
System.out.println(score);
}
scores[0] = new Integer(99);
scores[1] = new Integer(87);
scores[2] = new Integer(66);
for(Integer score : scores)
{
System.out.println(score);
}
}
}
运行结果

Arrays.copyOf()的方法可以方便的复制数组
import java.util.Arrays;
class CopyArray
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] scores1 = {88,81,74,69,78,76,77,85,95,93}; //定义数组
int[] scores2 = Arrays.copyOf(scores1,scores1.length);
for(int score : scores2){
System.out.printf("%3d",score);
}
System.out.println();
scores2[0] = 99;
//不影响score1 参考的数组对象
for(int score : scores1)
{
System.out.printf("%3d",score);
}
}
}
运行结果:

对于类类型声明的数组则要注意参考的行为。
class Clothes
{
String color;
char size;
Clothes(String color,char size)
{
this.color = color;
this.size = size;
}
}
public class ShallowCopy
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Clothes[] c1 = {new Clothes("red",'L'),new Clothes("blue",'M')};
Clothes[] c2 = new Clothes[c1.length];
for(int i = 0;i < c1.length;i++) //复制元素
{
c2[i] = c1 [i];
}
c1[0].color = "yellow"; //通过c1修改索引0对象
System.out.println(c2[0].color); //通过c2取得索引0对象的颜色
}
}
运行结果:
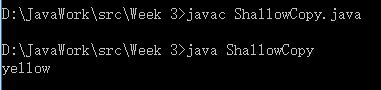
深层复制行为Deepcopy
class Clothes2
{
String color;
char size;
Clothes2(String color,char size)
{
this.color = color;
this.size = size;
}
}
public class DeepCopy
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Clothes2[] c1 = {new Clothes2("red",'L'),new Clothes2("blue",'M')};
Clothes2[] c2 = new Clothes2[c1.length];
for(int i = 0;i < c1.length;i++)
{
Clothes2 c = new Clothes2(c1[i].color,c1[i].size); //自行复制元素
c2[i] = c;
}
c1[0].color = "yellow";
System.out.println(c2[0].color);
}
}
运行结果:

字符串对象
字符串的本质是打包字符数组的对象,是java.lang.string类的实例。
以下程序是让用户输入整数,输入0后会计算所有整数总和并显示。
import java.util.Scanner;
class sum
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
long sum = 0;
long number = 0;
do{
System.out.print("输入数字:");
number = Long.parseLong(scanner.nextLine());
sum += number; //计算加和
}
while(number != 0);
System.out.println("总和:" + sum);
}
}
运行结果:

计算出所有整数平均:
class Average
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
long sum = 0;
for(String arg : args)
{
sum += Long.parseLong(arg);
}
System.out.println("平均:" + (float) sum / args.length);
}
}
运行结果:

使用stringBuilder来实现显示1+到100
class OneTo100
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
for (int i=1;i < 100 ;i++ )
{
builder.append(i).append('+');
}
System.out.println(builder.append(100).toString());
}
}
运行结果:

第五章
封装
封装(Encapsulation)实际上使用方法(Method)将类的数据隐藏起来,控制用户对类的修改和访问数据的程度,隐藏对象细节,将对象当作黑箱进行操作。
假设要写个可以管理储值卡的应用程序,首先要定义储值卡会记录那些数据,比如储值卡号码、余额、红利点数。这些可以用class定义。
java定义构造函数:
class CashCard
{
String number;
int balance;
int bonus;
CashCard(String number,int balanve,int bonus)
{
this.number = number;
this.balance = balance;
this.bonus = bonus;
}
}
如果用户想建立5个CashCard对象,可以用数组。
public class CardApp
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
CashCard[] cards = {
new CashCard("A001",500,0),
new CashCard("A002",300,0),
new CashCard("A003",1000,1),
new CashCard("A004",2000,2),
new CashCard("A005",3000,3)
};
for(CashCard card : cards)
{
System.out.printf("(%s,%d,%d)%n",card.number,card.balance,card.bonus);
}
}
}
运行结果:

储值不能是负的,储值大于1000的话,就给予红利一点。定义(method方法)
class CashCard
{
String number;
int balance;
int bonus;
CashCard(String number,int balance,int bonus)
{
this.number = number;
this.balance = balance;
this.bonus = bonus;
}
void store(int money) //储值时调用的方法
{
if(money > 0)
{
this.balance += money;
if(money >=1000)
{
this.bonus++;
}
}
else
{
System.out.println("储值怎么可能是负的??");
}//封装储值流程
}
void charge(int money)
{
if(money > 0)
{
if (money <= this.balance)
{
this.balance -= money;
}
else{
System.out.println("钱不够了");
}
}
else
{
System.out.println("扣负数?这不是叫我储值嘛?");
}
}
int exchange(int bonus) //兑换红利点数时调用的方法
{
if(bonus > 0)
{
this.bonus -= bonus;
}
return this.bonus;
}
}
相应的app可以这样写数组。
public class CardApp2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
CashCard[] cards = {
new CashCard("A001",500,0),
new CashCard("A002",300,0),
new CashCard("A003",1000,1),
};
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
for(CashCard card : cards)
{
System.out.printf("为(%s,%d,%d)储值:",card.number,card.balance,card.bonus);
card.store(scanner.nextInt());
System.out.printf("明细(%s,%d,%d)%n",card.number,card.balance,card.bonus);
}
}
}
程序运行结果如下

换个数字再次运行一下

类语法细节
public 用在类前,用在方法前,用在成员变量前。
在定义类时,可以使用构造函数定义对象建立的初始流程。
可以定义多个构造函数,只要参数类型或个数不同,这成为重载构造函数。
要注意自动装箱、拆箱的问题。
class Some
{
void somemethod(int i)
{
System.out.println("int 版本被调用");
}
void someMethod(Integer integer)
{
System.out.println("Integer 版本被调用");
}
}
public class OverloadBoxing
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Some s = new Some();
s.someMethod(1);
}
}
结果是显示int版本被调用,如图。

this()调用只能出现在构造函数第一行。
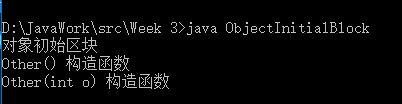
在创建对象之后,调用构造函数之前,若有想执行的流程,可以使用{}定义。
class Other
{
{
System.out.println("对象初始区块");
}
Other()
{
System.out.println("Other() 构造函数");
}
Other(int o)
{
this();
System.out.println("Other(int o) 构造函数");
}
}
public class ObjectInitialBlock
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
new Other(1);
}
}
运行结果:
新增的import static语法:
import java.util.Scanner;
import static java.lang.System.in;
import static java.lang.System.out;
public class ImportStatic
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(in);
out.print("请输入姓名:");
out.printf("%s 你好! %n",scanner.nextLine());
}
}
运行结果:

不定长度自变量:
class MathTool
{
public static int sum(int ... numbers)
{
int sum = 0;
for(int number : numbers)
{
sum += number;
}
return sum;
}
}
java中只有传值调用。传值(Pass By Value,Call by Value)
public class CallByValue
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Customer c1 = new Customer("Justin");
some(c1); //c1与参数c参考同一对象
System.out.println(c1.name);
Customer c2 = new Customer("Justin");
other(c2); //c2与参数c参考同一对象
System.out.println(c2.name);
}
static void some(Customer c)
{
c.name = "John";
}
static void other(Customer c)
{
c = new Customer("Bill");//c参考至新建的对象
}
}
class Customer
{
String name;
Customer(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
}
程序运行结果: 
代码调试中的问题和解决过程
这次的代码比较多,所出现的问题也比较多。

上图的原因找了好久,原来是最后一个括号不是英文环境下的括号。
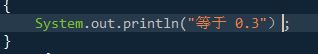

显然大括号与普通括号没有分清。

这个是Score的S小写了。在java中是很严格的区分大小写的。
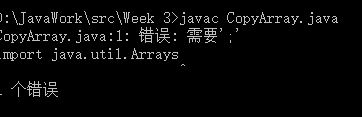
Import一行也是需要写分号的。

这是因为最后的大括号个数错误、

这也是大小写问题造成的。
同时我还在编写过程中遇到了汉字编码的问题,我打算写一篇博客讨论这个问题。
其他(感悟、思考等,可选)
这周学习的内容比较多,并且比较难于理解。可能一周的时间还不够好好消化新学的知识,还需要多看看书,视频。但这周敲得代码数量确实很多。其实编程、敲代码并不是一个无聊的过程。细细的品读代码的意义,不断解决代码调试过程中的各种错误,也是一件很有意思的事情。并且,随着代码数量的越来越多,所犯的错误也越来越少了。
学习java没有捷径,只有通过编写越来越多的代码,做越来越多的练习才能学好。
图片:
托管代码图片:


学习进度条
| 代码行数(新增/累积) | 博客量(新增/累积) | 学习时间(新增/累积) | 重要成长 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标 | 5000行 | 30篇 | 400小时 | |
| 第一周 | 100/100 | 2/2 | 10/10 | 初部认识java |
| 第二周 | 150/250 | 1/3 | 12/22 | 掌握Java基础语法 |
| 第三周 | 537/787 | 2/4 | 20/42 | 认识对象,对象封装 |
参考资料
最新文章
- Neutron 架构 - 每天5分钟玩转 OpenStack(67)
- jQuery 简单过滤选择器
- [tools] Sublime text 3 神器
- swift(一)
- STL--vector(转载)
- Java栈实现
- sql连接查询 2011-10-10 23:13 (QQ空间)
- linux 安装php的redis拓展
- MVC5的控制器,使用HttpPost方式时,接收的参数为null的原因
- BZOJ 1492: [NOI2007]货币兑换Cash [CDQ分治 斜率优化DP]
- 学习python 检测字符串的方法
- AJAX返回值问题
- Java自带RPC实现,RMI框架入门
- cmd常用
- 《转》Babel 入门教程
- 【大数据系列】基于MapReduce的数据处理 SequenceFile序列化文件
- MVC文件上传05-使用客户端jQuery-File-Upload插件和服务端Backload组件自定义上传文件夹
- 关于EF的一点小记录
- 【python】Django设置SESSION超时时间没有生效?
- CPU制造全过程(图文全解)