广度优先搜索(BFS)思路及算法分析
2024-09-03 05:32:50
1、算法用途:
是一种图像搜索演算法。用于遍历图中的节点,有些类似于树的深度优先遍历。这里唯一的问题是,与树不同,图形可能包含循环,因此我们可能会再次来到同一节点。
2、主要思想:
主要借助一个队列、一个布尔类型数组、邻接矩阵完成(判断一个点是否查看过,用于避免重复到达同一个点,造成死循环等),先将各点以及各点的关系存入邻接矩阵。
再从第一个点开始,将一个点存入队列,然后在邻接表中找到他的相邻点,存入队列,每次pop出队列头部并将其打印出来(文字有些抽象,实际过程很简单),整个过程有点像往水中投入石子水花散开。
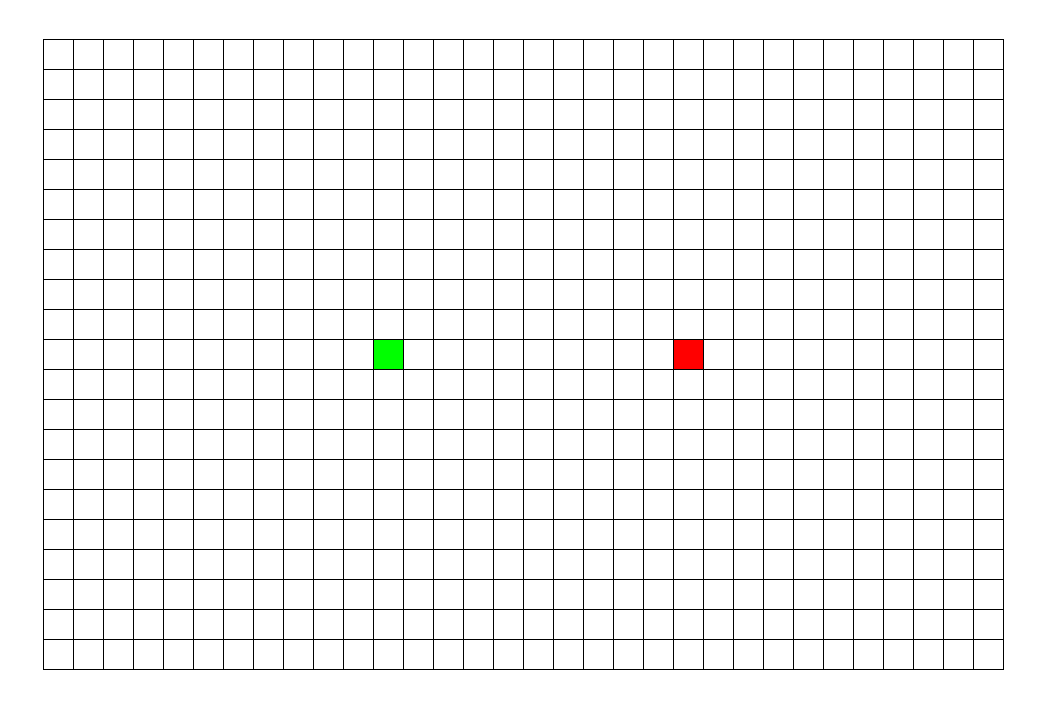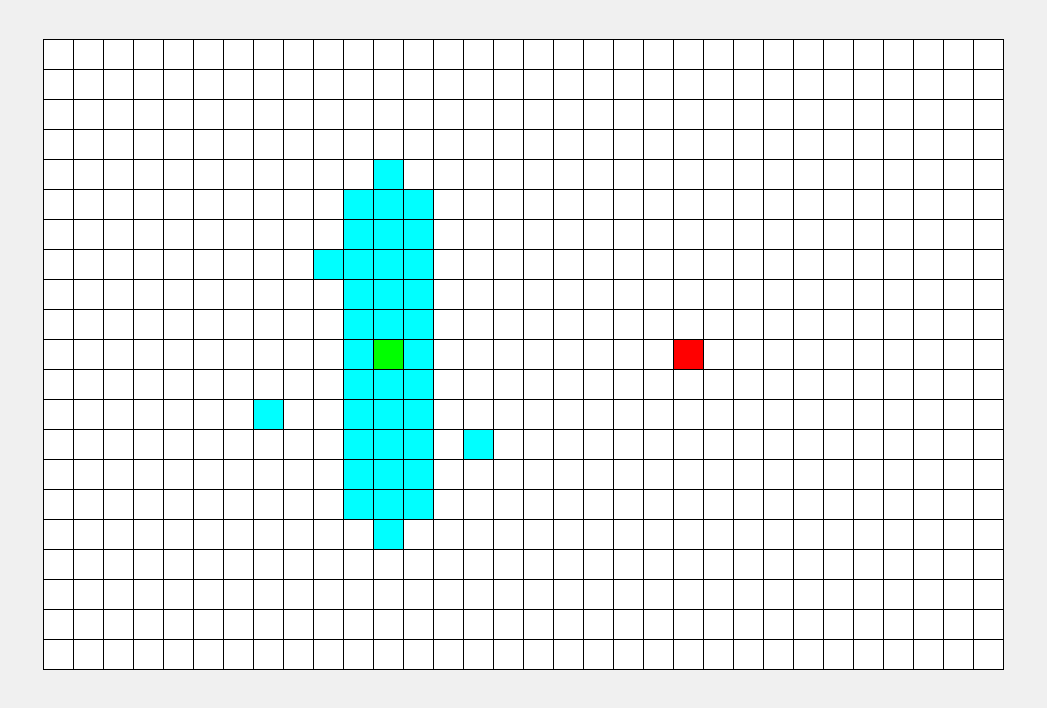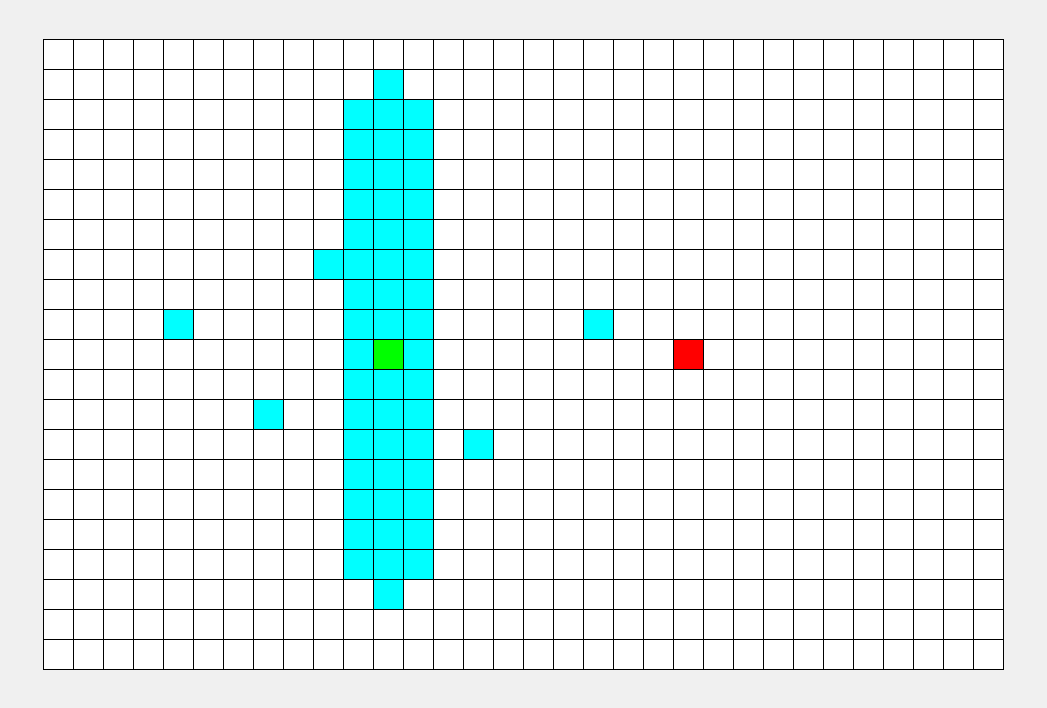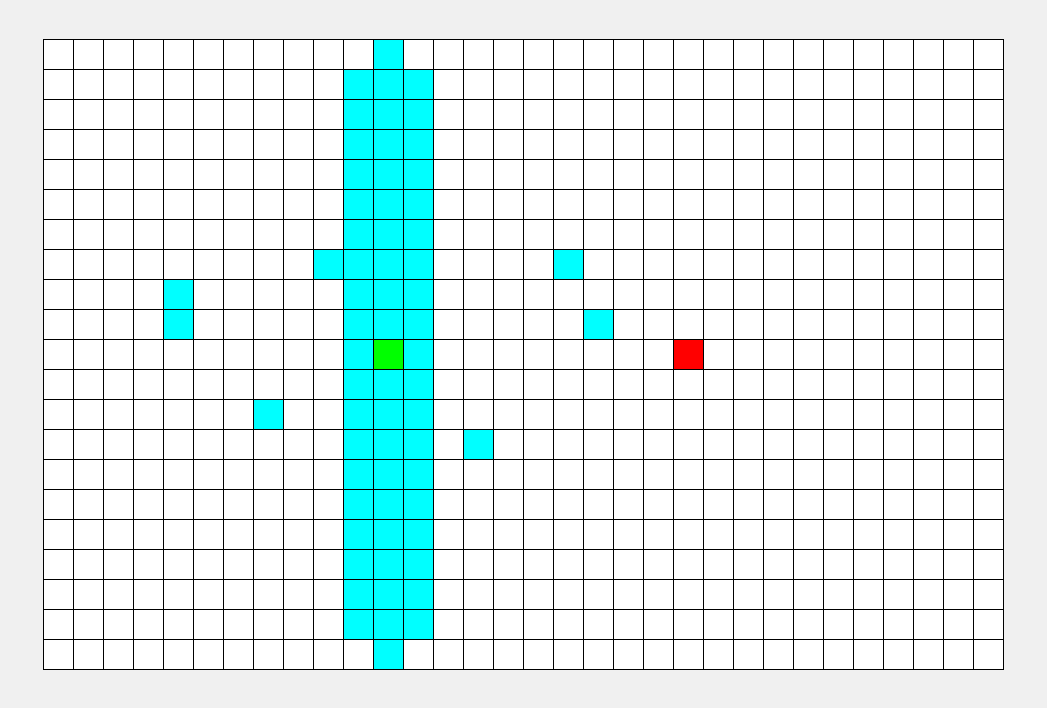

(邻接表是表示了图中与每一个顶点相邻的边集的集合,这里的集合指的是无序集)
3、代码(java):

(以上图为例的代码)
import java.util.*; //This class represents a directed graph using adjacency list
//representation
class Graph1 {
private static int V; // No. of vertices
private LinkedList<Integer> adj[]; // Adjacency Lists // Constructor
Graph1(int v) {
V = v;
adj = new LinkedList[v];
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i)
adj[i] = new LinkedList();
} // Function to add an edge into the graph
void addEdge(int v, int w) {
adj[v].add(w);
} // prints BFS traversal from a given source s
public void BFS() {
// Mark all the vertices as not visited(By default
// set as false)
boolean visited[] = new boolean[V];
// Create a queue for BFS
LinkedList<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>(); for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
BFSUtil(i, visited, queue);
}
}
} public void BFSUtil(int s, boolean visited[], LinkedList<Integer> queue) {
// Mark the current node as visited and enqueue it
visited[s] = true;
queue.add(s); while (queue.size() != 0) {
// Dequeue a vertex from queue and print it
s = queue.poll();
System.out.print(s + " "); // Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued vertex s
// If a adjacent has not been visited, then mark it
// visited and enqueue it
Iterator<Integer> i = adj[s].listIterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
int n = i.next();
if (!visited[n]) {
visited[n] = true;
queue.add(n);
}
}
}
} // Driver method to
public static void main(String args[]) {
Graph1 g = new Graph1(4); g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 3); System.out.println("Following is Breadth First Traversal " + "(starting from vertex 2)");
g.BFS();
}
}
4、复杂度分析:
算法借助了一个邻接表和队列,故它的空问复杂度为O(V)。 遍历图的过程实质上是对每个顶点查找其邻接点的过程,其耗费的时间取决于所采用结构。 邻接表表示时,查找所有顶点的邻接点所需时间为O(E),访问顶点的邻接点所花时间为O(V),此时,总的时间复杂度为O(V+E)。
最新文章
- JS工具
- linux 挂载命令详解
- 1020: [SHOI2008]安全的航线flight - BZOJ
- [译]Stairway to Integration Services Level 8 - SSIS 工作流管理高级
- Python多进程并发(multiprocessing)用法实例详解
- sql注入基础(原理)
- 5分钟搞定iOS抓包Charles,让数据一清二楚
- windows下Eclipse操作MapReduce例子报错:Failed to set permissions of path: \tmp\hadoop-Jerome\mapred\staging\
- 如何删除git远程仓库项目的所有内容,重新提交所有内容
- PHP 中的Trait
- 洛谷P4581 [BJOI2014]想法(玄学算法,拓扑排序)
- WebSocket 学习教程(二):Spring websocket实现消息推送
- SSM-网站后台管理系统制作(4)---Ajax前后端交互
- PythonStudy——字符串扩展方法 String extension method
- java了解哪些锁
- 三星固态sm863,pm863,sm865,sm865a颗粒
- day17(tomcat的安装,HTTP)
- ExpressRoute 连接模型
- ios UIImage图片拉伸 resizableImageWithCapInsets:
- 剑指offer相关问题