10.2 Hibernate持久层

点击项目右键->MyEclipse->Add Hibernate Capabilities




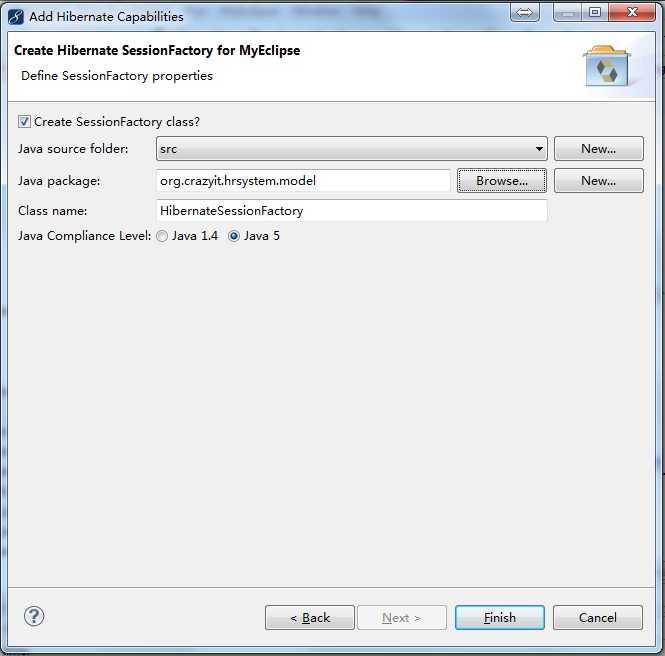
打开MyEclipse Hibernate Perspective(MyEclipse Hibernate 视图)


<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> <!-- Generated by MyEclipse Hibernate Tools. -->
<hibernate-configuration> <session-factory>
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql:///hibernate3_day03</property>
<property name="connection.username">root</property>
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="myeclipse.connection.profile">local</property> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration>



换一台电脑又要重新创建数据库。





Shit,MySQL在Windows下都不区分大小写。
















<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> <!-- Generated by MyEclipse Hibernate Tools. -->
<hibernate-configuration> <session-factory>
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql:///hrSystem</property>
<property name="connection.username">root</property>
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="myeclipse.connection.profile">local</property> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration>




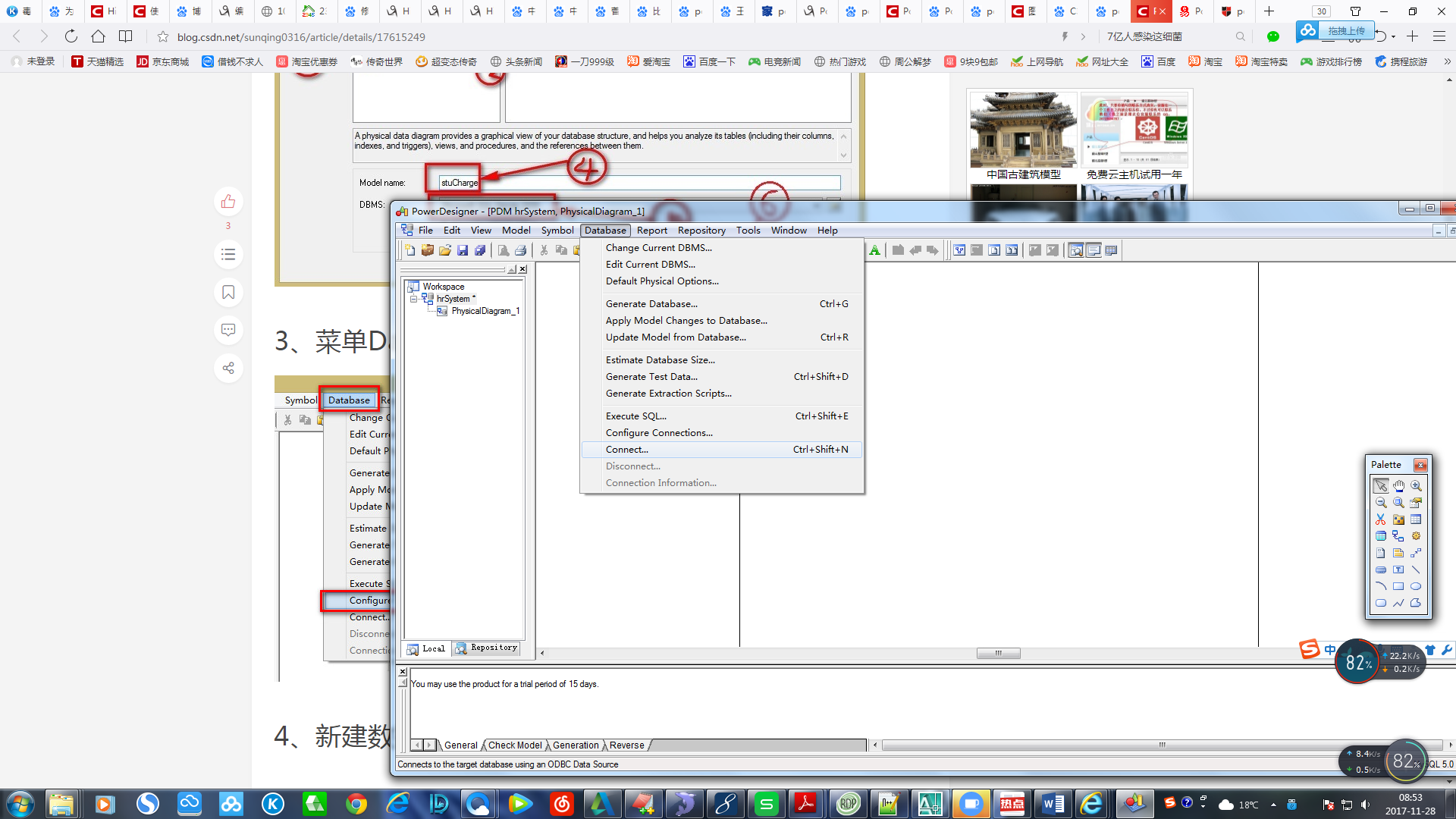

PowerDesignerfang反向工程连接MySql没有mySql odbc驱动
需要安装 MySql ODBC驱动,百度下载吧mysql-connector-odbc-5.3.4-win32.msi





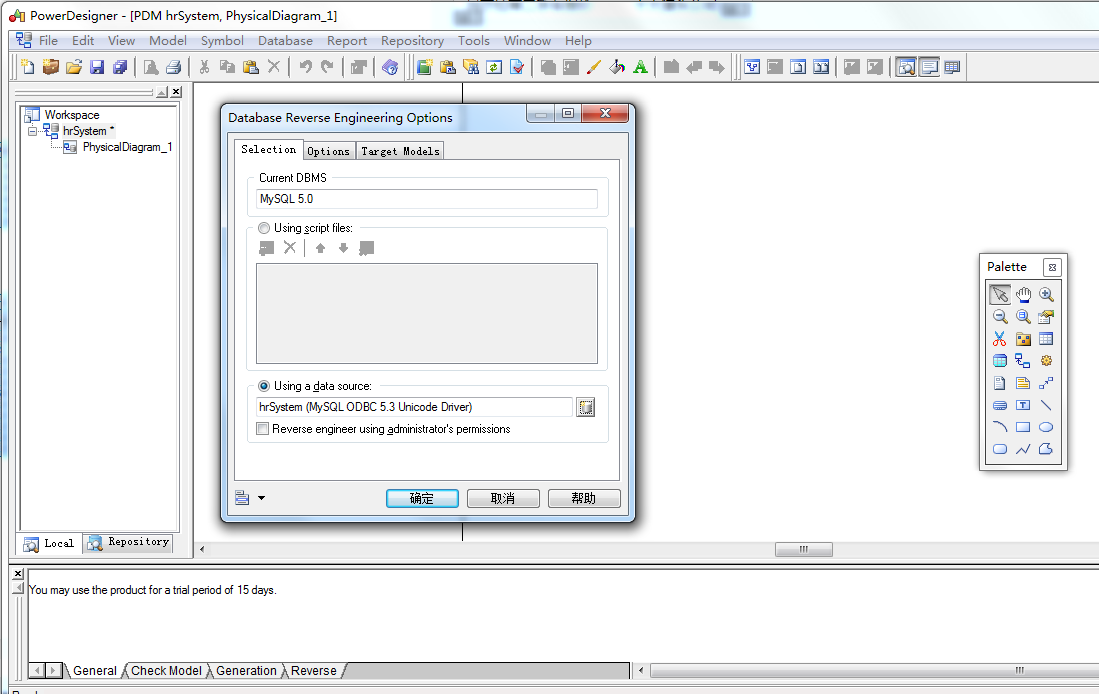



退出登录:
package org.crazyit.hrsystem.action; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession; import org.apache.struts2.interceptor.ServletRequestAware; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
/**
*
* @author zhongzh
*
*/
public class LogoutAction extends ActionSupport implements ServletRequestAware{
//定义一个HttpServletRequest对象
private HttpServletRequest request;
//实现SerlvetRequestAware接口必须重写的方法
@Override
public void setServletRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.request = request;
}
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//获取HttpSession
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
//使Session失效
session.invalidate(); return SUCCESS;
} }
3. 增加校验配置文件(RegisterXAction-validation.xml)
3.1 命名规范
校验文件命名规则:ActionName-validation.xml,其中ActionName就是需要校验的action的类名。
如果需要在Action中对某个特定的方法进行校验,则需要为此特定方法专门定义一个校验文件(否则,调用默认的)。该文件命名规则为:actionNme-methodNae-validation.xml;同时,还需要在struts.xml文件配置action时指定其method属性(否则,调用默认的)。
3.2 位置规范
该文件应该与action类的文件位于同一个路径下。
3.3 该文件的定义
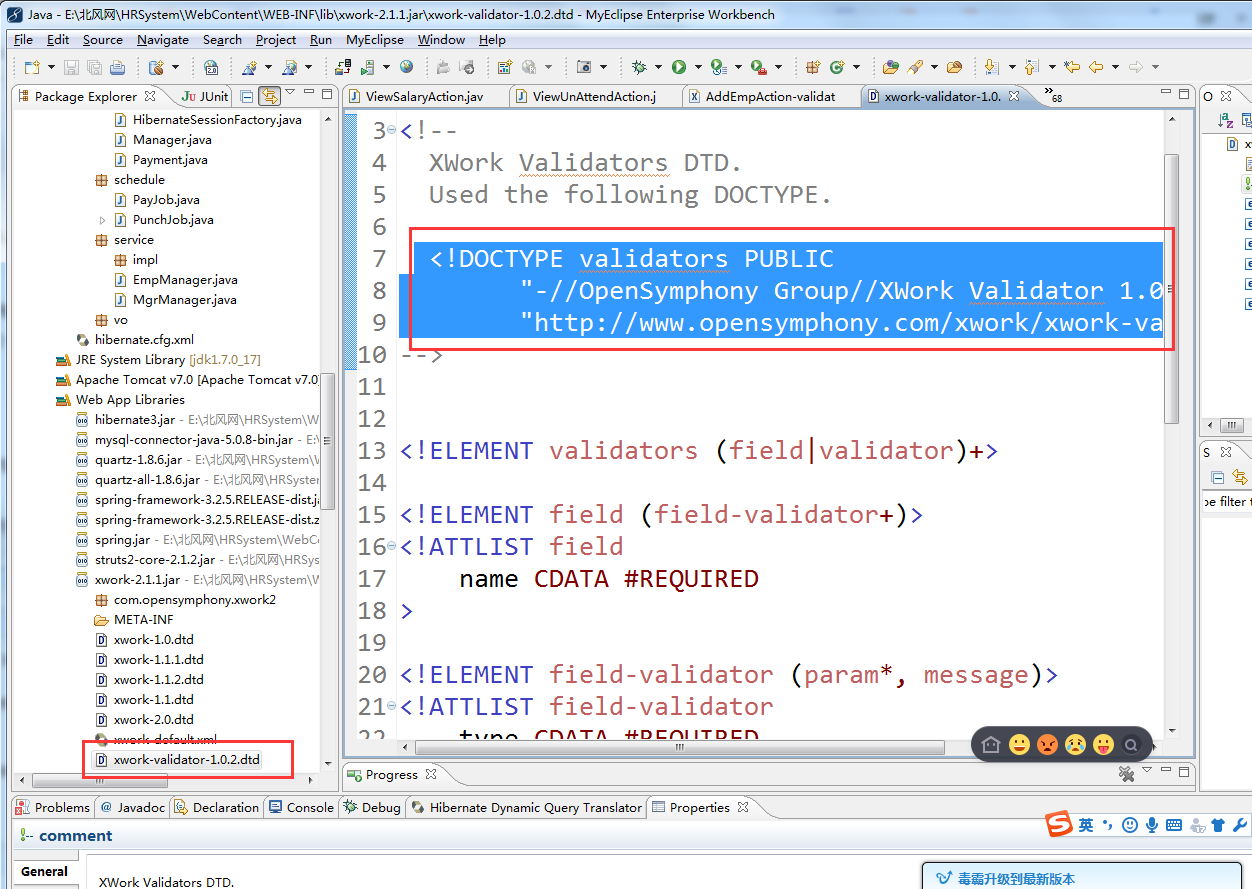
参考:struts-2.3.x\lib\xwork-core-2.3.x.jar包中xwork-validator-1.0.x.dtd文件的描述。
<!DOCTYPE validators PUBLIC
"-//OpenSymphony Group//XWork Validator 1.0.2//EN"
"http://www.opensymphony.com/xwork/xwork-validator-1.0.2.dtd">
3.4 该文件中validator的种类
参考:xwork-core-2.3.x.jar\com\opensymphony\xwork2\validator\validators中的default.xml文件。
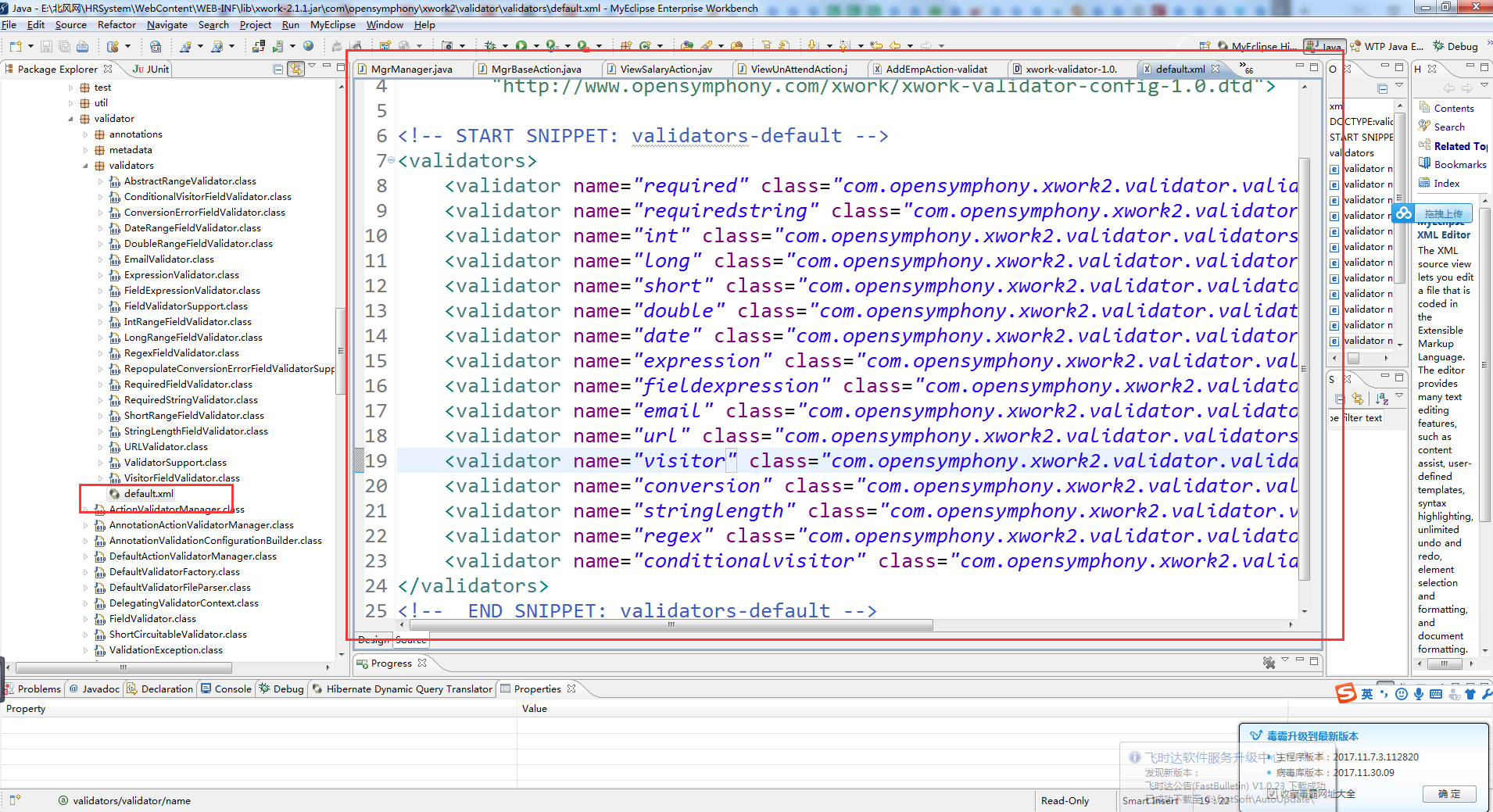
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE validators PUBLIC
"-//OpenSymphony Group//XWork Validator Config 1.0//EN"
"http://www.opensymphony.com/xwork/xwork-validator-config-1.0.dtd"> <!-- START SNIPPET: validators-default -->
<validators>
<validator name="required" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.RequiredFieldValidator"/>
<validator name="requiredstring" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.RequiredStringValidator"/>
<validator name="int" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.IntRangeFieldValidator"/>
<validator name="long" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.LongRangeFieldValidator"/>
<validator name="short" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.ShortRangeFieldValidator"/>
<validator name="double" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.DoubleRangeFieldValidator"/>
<validator name="date" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.DateRangeFieldValidator"/>
<validator name="expression" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.ExpressionValidator"/>
<validator name="fieldexpression" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.FieldExpressionValidator"/>
<validator name="email" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.EmailValidator"/>
<validator name="url" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.URLValidator"/>
<validator name="visitor" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.VisitorFieldValidator"/>
<validator name="conversion" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.ConversionErrorFieldValidator"/>
<validator name="stringlength" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.StringLengthFieldValidator"/>
<validator name="regex" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.RegexFieldValidator"/>
<validator name="conditionalvisitor" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.ConditionalVisitorFieldValidator"/>
</validators>
<!-- END SNIPPET: validators-default -->
设置JSP页面自动提示
Ehcache是用来管理缓存的一个工具,其缓存的数据可以是存放在内存里面的,也可以是存放在硬盘上的。其核心是CacheManager,一切Ehcache的应用都是从CacheManager开始的。它是用来管理Cache(缓存)的,一个应用可以有多个CacheManager,而一个CacheManager下又可以有多个Cache。Cache内部保存的是一个个的Element,而一个Element中保存的是一个key和value的配对,相当于Map里面的一个Entry。
1 CacheManager
CacheManager是Ehcache的核心,它的主要职责是对Cache的创建、移除和访问。只有CacheManager里面的Cache才能实现缓存数据的功能。一切使用Ehcache的应用都是从构建CacheManager开始的。构建CacheManager时,我们可以直接通过其构造方法来进行构建,也可以通过使用CacheManager提供的静态方法来进行构建。
当我们使用CacheManager的无参构造方法来构造CacheManager时就是使用的默认配置。这种情况最终还是会寻找默认的配置文件进行配置。Ehcache首先会到类根路径下寻找一个叫ehcache.xml的配置文件来配置CacheManager,如果没有找到该文件,则会加载CacheManager的默认配置ehcache-failsafe.xml文件,这个文件是在ehcache.jar里面的。关于配置文件如何配置的问题将在后续的文章中再做一个详细的讲解,这里先来简单看一个配置文件。
Xml代码
配置 quartz.properties
配置 applicationContext.xml
c3p0-0.9.1.2.jar
AbstractComboPooledDataSource的源码:
/*
* Distributed as part of c3p0 v.0.9.5.2
*
* Copyright (C) 2015 Machinery For Change, Inc.
*
* Author: Steve Waldman <swaldman@mchange.com>
*
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of EITHER:
*
* 1) The GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL), version 2.1, as
* published by the Free Software Foundation
*
* OR
*
* 2) The Eclipse Public License (EPL), version 1.0
*
* You may choose which license to accept if you wish to redistribute
* or modify this work. You may offer derivatives of this work
* under the license you have chosen, or you may provide the same
* choice of license which you have been offered here.
*
* This software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
*
* You should have received copies of both LGPL v2.1 and EPL v1.0
* along with this software; see the files LICENSE-EPL and LICENSE-LGPL.
* If not, the text of these licenses are currently available at
*
* LGPL v2.1: http://www.gnu.org/licenses/old-licenses/lgpl-2.1.html
* EPL v1.0: http://www.eclipse.org/org/documents/epl-v10.php
*
*/ package com.mchange.v2.c3p0; import java.beans.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.naming.*;
import com.mchange.v2.log.*;
import com.mchange.v2.naming.*;
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.impl.*; import javax.sql.DataSource;
import com.mchange.v2.beans.BeansUtils;
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.cfg.C3P0Config;
import com.mchange.v2.lang.ObjectUtils; /**
* <p>For the meaning of most of these properties, please see c3p0's top-level documentation!</p>
*/
public abstract class AbstractComboPooledDataSource extends AbstractPoolBackedDataSource implements PooledDataSource, Serializable, Referenceable
{
final static MLogger logger = MLog.getLogger( AbstractComboPooledDataSource.class ); final static Set TO_STRING_IGNORE_PROPS = new HashSet( Arrays.asList( new String[] {
"connection",
"lastAcquisitionFailureDefaultUser",
"lastCheckinFailureDefaultUser",
"lastCheckoutFailureDefaultUser",
"lastConnectionTestFailureDefaultUser",
"lastIdleTestFailureDefaultUser",
"logWriter",
"loginTimeout",
"numBusyConnections",
"numBusyConnectionsAllUsers",
"numBusyConnectionsDefaultUser",
"numConnections",
"numConnectionsAllUsers",
"numConnectionsDefaultUser",
"numFailedCheckinsDefaultUser",
"numFailedCheckoutsDefaultUser",
"numFailedIdleTestsDefaultUser",
"numIdleConnections",
"numIdleConnectionsAllUsers",
"numThreadsAwaitingCheckoutDefaultUser",
"numIdleConnectionsDefaultUser",
"numUnclosedOrphanedConnections",
"numUnclosedOrphanedConnectionsAllUsers",
"numUnclosedOrphanedConnectionsDefaultUser",
"numUserPools",
"effectivePropertyCycleDefaultUser",
"parentLogger",
"startTimeMillisDefaultUser",
"statementCacheNumCheckedOutDefaultUser",
"statementCacheNumCheckedOutStatementsAllUsers",
"statementCacheNumConnectionsWithCachedStatementsAllUsers",
"statementCacheNumConnectionsWithCachedStatementsDefaultUser",
"statementCacheNumStatementsAllUsers",
"statementCacheNumStatementsDefaultUser",
"statementDestroyerNumConnectionsInUseAllUsers",
"statementDestroyerNumConnectionsWithDeferredDestroyStatementsAllUsers",
"statementDestroyerNumDeferredDestroyStatementsAllUsers",
"statementDestroyerNumConnectionsInUseDefaultUser",
"statementDestroyerNumConnectionsWithDeferredDestroyStatementsDefaultUser",
"statementDestroyerNumDeferredDestroyStatementsDefaultUser",
"statementDestroyerNumThreads",
"statementDestroyerNumActiveThreads",
"statementDestroyerNumIdleThreads",
"statementDestroyerNumTasksPending",
"threadPoolSize",
"threadPoolNumActiveThreads",
"threadPoolNumIdleThreads",
"threadPoolNumTasksPending",
"threadPoolStackTraces",
"threadPoolStatus",
"overrideDefaultUser",
"overrideDefaultPassword",
"password",
"reference",
"upTimeMillisDefaultUser",
"user",
"userOverridesAsString",
"allUsers",
"connectionPoolDataSource",
"propertyChangeListeners",
"vetoableChangeListeners"
} ) ); // just so we have a unified syntax when we guard against degenerate parameter changes, which
// otherwise might needlessly reset pools.
private static boolean diff( int a, int b ) { return a != b; }
private static boolean diff( boolean a, boolean b ) { return a != b; }
private static boolean diff( Object a, Object b ) { return !ObjectUtils.eqOrBothNull(a, b ); } // not reassigned post-ctor; mutable elements protected by their own locks
// when (very rarely) necessery, we sync this -> wcpds -> dmds // note that serialization of these guys happens via our superclass
// we just have to make sure they get properly reset on deserialization
transient DriverManagerDataSource dmds;
transient WrapperConnectionPoolDataSource wcpds; public AbstractComboPooledDataSource()
{ this( true ); } public AbstractComboPooledDataSource( boolean autoregister )
{
super( autoregister ); // System.err.println("...Initializing ComboPooledDataSource."); dmds = new DriverManagerDataSource();
wcpds = new WrapperConnectionPoolDataSource(); wcpds.setNestedDataSource( dmds ); try
{ this.setConnectionPoolDataSource( wcpds ); }
catch (PropertyVetoException e)
{
logger.log(MLevel.WARNING, "Hunh??? This can't happen. We haven't set up any listeners to veto the property change yet!", e);
throw new RuntimeException("Hunh??? This can't happen. We haven't set up any listeners to veto the property change yet! " + e);
} // set things up in case there are future changes to our ConnectionPoolDataSource
//
setUpPropertyEvents();
} private void setUpPropertyEvents()
{
VetoableChangeListener wcpdsConsistencyEnforcer = new VetoableChangeListener()
{
// always called within synchronized mutators of the parent class... needn't explicitly sync here
public void vetoableChange( PropertyChangeEvent evt ) throws PropertyVetoException
{
String propName = evt.getPropertyName();
Object val = evt.getNewValue(); if ( "connectionPoolDataSource".equals( propName ) )
{
if (val instanceof WrapperConnectionPoolDataSource)
{
DataSource nested = (DataSource) ((WrapperConnectionPoolDataSource)val).getNestedDataSource();
if (! (nested instanceof DriverManagerDataSource) )
throw new PropertyVetoException(this.getClass().getName() + " requires that its unpooled DataSource " +
" be set at all times, and that it be a" +
" com.mchange.v2.c3p0.DriverManagerDataSource. Bad: " + nested, evt);
}
else
throw new PropertyVetoException(this.getClass().getName() + " requires that its ConnectionPoolDataSource " +
" be set at all times, and that it be a" +
" com.mchange.v2.c3p0.WrapperConnectionPoolDataSource. Bad: " + val, evt);
}
}
};
this.addVetoableChangeListener( wcpdsConsistencyEnforcer ); PropertyChangeListener wcpdsStateUpdater = new PropertyChangeListener()
{
public void propertyChange( PropertyChangeEvent evt )
{
String propName = evt.getPropertyName();
Object val = evt.getNewValue(); if ( "connectionPoolDataSource".equals( propName ) )
updateLocalVarsFromCpdsProp();
}
};
this.addPropertyChangeListener( wcpdsStateUpdater );
} private void updateLocalVarsFromCpdsProp()
{
this.wcpds = (WrapperConnectionPoolDataSource) this.getConnectionPoolDataSource();
this.dmds = (DriverManagerDataSource) wcpds.getNestedDataSource();
} public AbstractComboPooledDataSource(String configName)
{
this();
initializeNamedConfig( configName, true );
} // // workaround sun big id #6342411 (in which reflective
// // access to a public method of a non-public class fails,
// // even if the non-public class is accessed via a public
// // subclass)
// public String getDataSourceName()
// { return super.getDataSourceName(); } // DriverManagerDataSourceProperties (count: 4)
public String getDescription()
{ return dmds.getDescription(); } public void setDescription( String description )
{ dmds.setDescription( description ); } public String getDriverClass()
{ return dmds.getDriverClass(); } public void setDriverClass( String driverClass ) throws PropertyVetoException
{
dmds.setDriverClass( driverClass );
// System.err.println("setting driverClass: " + driverClass);
} public boolean isForceUseNamedDriverClass()
{ return dmds.isForceUseNamedDriverClass(); } public void setForceUseNamedDriverClass( boolean forceUseNamedDriverClass )
{
dmds.setForceUseNamedDriverClass( forceUseNamedDriverClass );
} public String getJdbcUrl()
{
// System.err.println("getting jdbcUrl: " + dmds.getJdbcUrl());
return dmds.getJdbcUrl();
} public void setJdbcUrl( String jdbcUrl )
{
if ( diff( dmds.getJdbcUrl(), jdbcUrl ) )
{
dmds.setJdbcUrl( jdbcUrl );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
// System.err.println("setting jdbcUrl: " + jdbcUrl + " [dmds@" + C3P0ImplUtils.identityToken( dmds ) + "]");
// if (jdbcUrl == null)
// new Exception("*** NULL SETTER ***").printStackTrace();
}
} public Properties getProperties()
{
//System.err.println("getting properties: " + dmds.getProperties());
return dmds.getProperties();
} public void setProperties( Properties properties )
{
if ( diff( dmds.getProperties(), properties ) )
{
//System.err.println("setting properties: " + properties);
dmds.setProperties( properties );
this.resetPoolManager(false);
}
} // DriverManagerDataSource "virtual properties" based on properties
public String getUser()
{ return dmds.getUser(); } public void setUser( String user )
{
if ( diff( dmds.getUser(), user ) )
{
dmds.setUser( user );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public String getPassword()
{ return dmds.getPassword(); } public void setPassword( String password )
{
if ( diff( dmds.getPassword(), password ) )
{
dmds.setPassword( password );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} // WrapperConnectionPoolDataSource properties
public int getCheckoutTimeout()
{ return wcpds.getCheckoutTimeout(); } public void setCheckoutTimeout( int checkoutTimeout )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getCheckoutTimeout(), checkoutTimeout ) )
{
wcpds.setCheckoutTimeout( checkoutTimeout );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public int getAcquireIncrement()
{ return wcpds.getAcquireIncrement(); } public void setAcquireIncrement( int acquireIncrement )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getAcquireIncrement(), acquireIncrement ) )
{
wcpds.setAcquireIncrement( acquireIncrement );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public int getAcquireRetryAttempts()
{ return wcpds.getAcquireRetryAttempts(); } public void setAcquireRetryAttempts( int acquireRetryAttempts )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getAcquireRetryAttempts(), acquireRetryAttempts ) )
{
wcpds.setAcquireRetryAttempts( acquireRetryAttempts );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public int getAcquireRetryDelay()
{ return wcpds.getAcquireRetryDelay(); } public void setAcquireRetryDelay( int acquireRetryDelay )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getAcquireRetryDelay(), acquireRetryDelay ) )
{
wcpds.setAcquireRetryDelay( acquireRetryDelay );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public boolean isAutoCommitOnClose()
{ return wcpds.isAutoCommitOnClose(); } public void setAutoCommitOnClose( boolean autoCommitOnClose )
{
if ( diff(wcpds.isAutoCommitOnClose(), autoCommitOnClose) )
{
wcpds.setAutoCommitOnClose( autoCommitOnClose );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public String getContextClassLoaderSource()
{ return wcpds.getContextClassLoaderSource(); } public void setContextClassLoaderSource( String contextClassLoaderSource ) throws PropertyVetoException
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getContextClassLoaderSource(), contextClassLoaderSource ) )
{
wcpds.setContextClassLoaderSource( contextClassLoaderSource );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public String getConnectionTesterClassName()
{ return wcpds.getConnectionTesterClassName(); } public void setConnectionTesterClassName( String connectionTesterClassName ) throws PropertyVetoException
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getConnectionTesterClassName(), connectionTesterClassName ) )
{
wcpds.setConnectionTesterClassName( connectionTesterClassName );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public String getAutomaticTestTable()
{ return wcpds.getAutomaticTestTable(); } public void setAutomaticTestTable( String automaticTestTable )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getAutomaticTestTable(), automaticTestTable ) )
{
wcpds.setAutomaticTestTable( automaticTestTable );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public boolean isForceIgnoreUnresolvedTransactions()
{ return wcpds.isForceIgnoreUnresolvedTransactions(); } public void setForceIgnoreUnresolvedTransactions( boolean forceIgnoreUnresolvedTransactions )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.isForceIgnoreUnresolvedTransactions(), forceIgnoreUnresolvedTransactions ) )
{
wcpds.setForceIgnoreUnresolvedTransactions( forceIgnoreUnresolvedTransactions );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public boolean isPrivilegeSpawnedThreads()
{ return wcpds.isPrivilegeSpawnedThreads(); } public void setPrivilegeSpawnedThreads( boolean privilegeSpawnedThreads )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.isPrivilegeSpawnedThreads(), privilegeSpawnedThreads ) )
{
wcpds.setPrivilegeSpawnedThreads( privilegeSpawnedThreads );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public int getIdleConnectionTestPeriod()
{ return wcpds.getIdleConnectionTestPeriod(); } public void setIdleConnectionTestPeriod( int idleConnectionTestPeriod )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getIdleConnectionTestPeriod(), idleConnectionTestPeriod ) )
{
wcpds.setIdleConnectionTestPeriod( idleConnectionTestPeriod );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public int getInitialPoolSize()
{ return wcpds.getInitialPoolSize(); } public void setInitialPoolSize( int initialPoolSize )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getInitialPoolSize(), initialPoolSize ) )
{
wcpds.setInitialPoolSize( initialPoolSize );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public int getMaxIdleTime()
{ return wcpds.getMaxIdleTime(); } public void setMaxIdleTime( int maxIdleTime )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getMaxIdleTime(), maxIdleTime ) )
{
wcpds.setMaxIdleTime( maxIdleTime );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public int getMaxPoolSize()
{ return wcpds.getMaxPoolSize(); } public void setMaxPoolSize( int maxPoolSize )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getMaxPoolSize(), maxPoolSize ) )
{
wcpds.setMaxPoolSize( maxPoolSize );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public int getMaxStatements()
{ return wcpds.getMaxStatements(); } public void setMaxStatements( int maxStatements )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getMaxStatements(), maxStatements ) )
{
wcpds.setMaxStatements( maxStatements );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public int getMaxStatementsPerConnection()
{ return wcpds.getMaxStatementsPerConnection(); } public void setMaxStatementsPerConnection( int maxStatementsPerConnection )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getMaxStatementsPerConnection(), maxStatementsPerConnection ) )
{
wcpds.setMaxStatementsPerConnection( maxStatementsPerConnection );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public int getMinPoolSize()
{ return wcpds.getMinPoolSize(); } public void setMinPoolSize( int minPoolSize )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getMinPoolSize(), minPoolSize ) )
{
wcpds.setMinPoolSize( minPoolSize );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public String getOverrideDefaultUser()
{ return wcpds.getOverrideDefaultUser(); } public void setOverrideDefaultUser(String overrideDefaultUser)
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getOverrideDefaultUser(), overrideDefaultUser ) )
{
wcpds.setOverrideDefaultUser( overrideDefaultUser );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public String getOverrideDefaultPassword()
{ return wcpds.getOverrideDefaultPassword(); } public void setOverrideDefaultPassword(String overrideDefaultPassword)
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getOverrideDefaultPassword(), overrideDefaultPassword ) )
{
wcpds.setOverrideDefaultPassword( overrideDefaultPassword );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public int getPropertyCycle()
{ return wcpds.getPropertyCycle(); } public void setPropertyCycle( int propertyCycle )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getPropertyCycle(), propertyCycle ) )
{
wcpds.setPropertyCycle( propertyCycle );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public boolean isBreakAfterAcquireFailure()
{ return wcpds.isBreakAfterAcquireFailure(); } public void setBreakAfterAcquireFailure( boolean breakAfterAcquireFailure )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.isBreakAfterAcquireFailure(), breakAfterAcquireFailure ) )
{
wcpds.setBreakAfterAcquireFailure( breakAfterAcquireFailure );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public boolean isTestConnectionOnCheckout()
{ return wcpds.isTestConnectionOnCheckout(); } public void setTestConnectionOnCheckout( boolean testConnectionOnCheckout )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.isTestConnectionOnCheckout(), testConnectionOnCheckout ) )
{
wcpds.setTestConnectionOnCheckout( testConnectionOnCheckout );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public boolean isTestConnectionOnCheckin()
{ return wcpds.isTestConnectionOnCheckin(); } public void setTestConnectionOnCheckin( boolean testConnectionOnCheckin )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.isTestConnectionOnCheckin(), testConnectionOnCheckin ) )
{
wcpds.setTestConnectionOnCheckin( testConnectionOnCheckin );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public boolean isUsesTraditionalReflectiveProxies()
{ return wcpds.isUsesTraditionalReflectiveProxies(); } public void setUsesTraditionalReflectiveProxies( boolean usesTraditionalReflectiveProxies )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.isUsesTraditionalReflectiveProxies(), usesTraditionalReflectiveProxies ) )
{
wcpds.setUsesTraditionalReflectiveProxies( usesTraditionalReflectiveProxies );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public String getPreferredTestQuery()
{ return wcpds.getPreferredTestQuery(); } public void setPreferredTestQuery( String preferredTestQuery )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getPreferredTestQuery(), preferredTestQuery ) )
{
wcpds.setPreferredTestQuery( preferredTestQuery );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public int getMaxAdministrativeTaskTime()
{ return wcpds.getMaxAdministrativeTaskTime(); } public void setMaxAdministrativeTaskTime( int maxAdministrativeTaskTime )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getMaxAdministrativeTaskTime(), maxAdministrativeTaskTime ) )
{
wcpds.setMaxAdministrativeTaskTime( maxAdministrativeTaskTime );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public int getMaxIdleTimeExcessConnections()
{ return wcpds.getMaxIdleTimeExcessConnections(); } public void setMaxIdleTimeExcessConnections( int maxIdleTimeExcessConnections )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getMaxIdleTimeExcessConnections(), maxIdleTimeExcessConnections ) )
{
wcpds.setMaxIdleTimeExcessConnections( maxIdleTimeExcessConnections );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public int getMaxConnectionAge()
{ return wcpds.getMaxConnectionAge(); } public void setMaxConnectionAge( int maxConnectionAge )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getMaxConnectionAge(), maxConnectionAge ) )
{
wcpds.setMaxConnectionAge( maxConnectionAge );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public String getConnectionCustomizerClassName()
{ return wcpds.getConnectionCustomizerClassName(); } public void setConnectionCustomizerClassName( String connectionCustomizerClassName )
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getConnectionCustomizerClassName(), connectionCustomizerClassName ) )
{
wcpds.setConnectionCustomizerClassName( connectionCustomizerClassName );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public int getUnreturnedConnectionTimeout()
{ return wcpds.getUnreturnedConnectionTimeout(); } public void setUnreturnedConnectionTimeout(int unreturnedConnectionTimeout)
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getUnreturnedConnectionTimeout(), unreturnedConnectionTimeout ) )
{
wcpds.setUnreturnedConnectionTimeout( unreturnedConnectionTimeout );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public String getUserOverridesAsString()
{ return wcpds.getUserOverridesAsString(); } public void setUserOverridesAsString(String uoas) throws PropertyVetoException
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getUserOverridesAsString(), uoas ) )
{
wcpds.setUserOverridesAsString( uoas );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public Map getUserOverrides()
{ return wcpds.getUserOverrides(); } public boolean isDebugUnreturnedConnectionStackTraces()
{ return wcpds.isDebugUnreturnedConnectionStackTraces(); } public void setDebugUnreturnedConnectionStackTraces(boolean debugUnreturnedConnectionStackTraces)
{
if ( diff( wcpds.isDebugUnreturnedConnectionStackTraces(), debugUnreturnedConnectionStackTraces ) )
{
wcpds.setDebugUnreturnedConnectionStackTraces( debugUnreturnedConnectionStackTraces );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public boolean isForceSynchronousCheckins()
{ return wcpds.isForceSynchronousCheckins(); } public void setForceSynchronousCheckins(boolean forceSynchronousCheckins)
{
if ( diff( wcpds.isForceSynchronousCheckins(), forceSynchronousCheckins ) )
{
wcpds.setForceSynchronousCheckins( forceSynchronousCheckins );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} public int getStatementCacheNumDeferredCloseThreads()
{ return wcpds.getStatementCacheNumDeferredCloseThreads(); } public void setStatementCacheNumDeferredCloseThreads(int statementCacheNumDeferredCloseThreads)
{
if ( diff( wcpds.getStatementCacheNumDeferredCloseThreads(), statementCacheNumDeferredCloseThreads ) )
{
wcpds.setStatementCacheNumDeferredCloseThreads( statementCacheNumDeferredCloseThreads );
this.resetPoolManager( false );
}
} // shared properties (count: 1)
public String getFactoryClassLocation()
{ return super.getFactoryClassLocation(); } public void setFactoryClassLocation( String factoryClassLocation )
{
if (
diff( dmds.getFactoryClassLocation(), factoryClassLocation ) ||
diff( wcpds.getFactoryClassLocation(), factoryClassLocation ) ||
diff( super.getFactoryClassLocation(), factoryClassLocation )
)
{
dmds.setFactoryClassLocation( factoryClassLocation );
wcpds.setFactoryClassLocation( factoryClassLocation );
super.setFactoryClassLocation( factoryClassLocation );
}
} public String toString() { return toString( false ); } public String toString(boolean show_config)
{
if ( show_config )
{
//System.err.println("ComboPooledDataSource.toString()"); StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(512);
sb.append( this.getClass().getName() );
sb.append(" [ ");
try { BeansUtils.appendPropNamesAndValues(sb, this, TO_STRING_IGNORE_PROPS); }
catch (Exception e)
{
sb.append( e.toString() );
//e.printStackTrace();
}
sb.append(" ]"); // Map userOverrides = wcpds.getUserOverrides();
// if (userOverrides != null)
// sb.append("; userOverrides: " + userOverrides.toString()); return sb.toString();
}
else
{
return this.getClass().getName() + "[ identityToken -> " + this.getIdentityToken() + ", dataSourceName -> " + this.getDataSourceName() + " ]";
}
} // serialization stuff -- set up bound/constrained property event handlers on deserialization
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1;
private static final short VERSION = 0x0001; private void writeObject( ObjectOutputStream oos ) throws IOException
{
oos.writeShort( VERSION );
} private void readObject( ObjectInputStream ois ) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
{
short version = ois.readShort();
switch (version)
{
case VERSION:
updateLocalVarsFromCpdsProp();
setUpPropertyEvents();
break;
default:
throw new IOException("Unsupported Serialized Version: " + version);
}
} // JDBC4 Wrapper stuff
private boolean isWrapperForDmds(Class<?> iface)
{ return iface.isAssignableFrom( dmds.getClass() ); } public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException
{ return isWrapperForDmds( iface ) || isWrapperForThis( iface ); } public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException
{
if (this.isWrapperForDmds( iface ))
return dmds.unwrap( iface );
else if ( this.isWrapperForThis( iface ) )
return (T) this;
else
throw new SQLException(this + " is not a wrapper for or implementation of " + iface.getName());
}
} //now, referenceability happens exactly the same way it does for PoolBackedDataSource
//all this stuff (and the maintenance hassle of it) should be unnecessary /*
// WrapperConnectionPoolDataSource properties -- count: 28
//
// ("checkoutTimeout");
// ("acquireIncrement");
// ("acquireRetryAttempts");
// ("acquireRetryDelay");
// ("autoCommitOnClose");
// ("connectionTesterClassName");
// ("forceIgnoreUnresolvedTransactions");
// ("idleConnectionTestPeriod");
// ("initialPoolSize");
// ("maxIdleTime");
// ("maxPoolSize");
// ("maxStatements");
// ("maxStatementsPerConnection");
// ("minPoolSize");
// ("propertyCycle");
// ("breakAfterAcquireFailure");
// ("testConnectionOnCheckout");
// ("testConnectionOnCheckin");
// ("usesTraditionalReflectiveProxies");
// ("preferredTestQuery");
// ("automaticTestTable");
// ("userOverridesAsString");
// ("overrideDefaultUser");
// ("overrideDefaultPassword");
// ("maxAdministrativeTaskTime");
// ("maxIdleTimeExcessConnections");
// ("maxConnectionAge");
// ("connectionTesterClassName"); final static JavaBeanReferenceMaker referenceMaker = new JavaBeanReferenceMaker(); static
{
referenceMaker.setFactoryClassName( C3P0JavaBeanObjectFactory.class.getName() ); // DriverManagerDataSource properties (count: 4)
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("description");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("driverClass");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("jdbcUrl");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("properties"); // WrapperConnectionPoolDataSource properties (count: 27)
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("checkoutTimeout");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("acquireIncrement");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("acquireRetryAttempts");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("acquireRetryDelay");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("autoCommitOnClose");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("connectionTesterClassName");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("forceIgnoreUnresolvedTransactions");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("idleConnectionTestPeriod");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("initialPoolSize");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("maxIdleTime");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("maxPoolSize");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("maxStatements");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("maxStatementsPerConnection");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("minPoolSize");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("propertyCycle");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("breakAfterAcquireFailure");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("testConnectionOnCheckout");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("testConnectionOnCheckin");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("usesTraditionalReflectiveProxies");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("preferredTestQuery");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("automaticTestTable");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("userOverridesAsString");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("overrideDefaultUser");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("overrideDefaultPassword");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("maxAdministrativeTaskTime");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("maxIdleTimeExcessConnections");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("maxConnectionAge"); // PoolBackedDataSource properties (count: 2)
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("dataSourceName");
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("numHelperThreads"); // identity token
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("identityToken"); // shared properties (count: 1)
referenceMaker.addReferenceProperty("factoryClassLocation");
} public Reference getReference() throws NamingException
{
synchronized ( this )
{
synchronized ( wcpds )
{
synchronized( dmds )
{
//System.err.println("ComboPooledDataSource.getReference()!!!!");
//new Exception("PRINT-STACK-TRACE").printStackTrace();
//javax.naming.Reference out = referenceMaker.createReference( this );
//System.err.println(out);
//return out; return referenceMaker.createReference( this );
}
}
}
}
*/

找Spring.jar的源码,在Eclipse用SVN检出源码




在https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/tree/master/spring-orm/src/main/java/org/springframework/orm/hibernate5上下载LocalSessionFactoryBean的源码

从https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/tree/4.3.x/spring-orm/src/main/java/org/springframework/orm可以下载hibernate3的源码


/*
* Copyright 2002-2014 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.orm.hibernate3; import java.io.File;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import javax.transaction.TransactionManager; import org.hibernate.HibernateException;
import org.hibernate.Interceptor;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cache.RegionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Environment;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Mappings;
import org.hibernate.cfg.NamingStrategy;
import org.hibernate.dialect.Dialect;
import org.hibernate.engine.FilterDefinition;
import org.hibernate.engine.SessionFactoryImplementor;
import org.hibernate.event.EventListeners;
import org.hibernate.tool.hbm2ddl.DatabaseMetadata;
import org.hibernate.transaction.JTATransactionFactory; import org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanClassLoaderAware;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy;
import org.springframework.jdbc.support.JdbcUtils;
import org.springframework.jdbc.support.lob.LobHandler;
import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; /**
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean} that creates a
* Hibernate {@link org.hibernate.SessionFactory}. This is the usual way to
* set up a shared Hibernate SessionFactory in a Spring application context;
* the SessionFactory can then be passed to Hibernate-based DAOs via
* dependency injection.
*
* <p>Configuration settings can either be read from a Hibernate XML file,
* specified as "configLocation", or completely via this class. A typical
* local configuration consists of one or more "mappingResources", various
* "hibernateProperties" (not strictly necessary), and a "dataSource" that the
* SessionFactory should use. The latter can also be specified via Hibernate
* properties, but "dataSource" supports any Spring-configured DataSource,
* instead of relying on Hibernate's own connection providers.
*
* <p>This SessionFactory handling strategy is appropriate for most types of
* applications, from Hibernate-only single database apps to ones that need
* distributed transactions. Either {@link HibernateTransactionManager} or
* {@link org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager} can be
* used for transaction demarcation, with the latter only necessary for
* transactions which span multiple databases.
*
* <p>This factory bean will by default expose a transaction-aware SessionFactory
* proxy, letting data access code work with the plain Hibernate SessionFactory
* and its {@code getCurrentSession()} method, while still being able to
* participate in current Spring-managed transactions: with any transaction
* management strategy, either local or JTA / EJB CMT, and any transaction
* synchronization mechanism, either Spring or JTA. Furthermore,
* {@code getCurrentSession()} will also seamlessly work with
* a request-scoped Session managed by
* {@link org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.OpenSessionInViewFilter} /
* {@link org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.OpenSessionInViewInterceptor}.
*
* <p>Requires Hibernate 3.6.x, as of Spring 4.0.
* Note that this factory will use "on_close" as default Hibernate connection
* release mode, unless in the case of a "jtaTransactionManager" specified,
* for the reason that this is appropriate for most Spring-based applications
* (in particular when using Spring's HibernateTransactionManager).
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 1.2
* @see HibernateTemplate#setSessionFactory
* @see HibernateTransactionManager#setSessionFactory
* @see #setExposeTransactionAwareSessionFactory
* @see #setJtaTransactionManager
* @see org.hibernate.SessionFactory#getCurrentSession()
* @see HibernateTransactionManager
* @deprecated as of Spring 4.3, in favor of Hibernate 4.x/5.x
*/
@Deprecated
public class LocalSessionFactoryBean extends AbstractSessionFactoryBean implements BeanClassLoaderAware { private static final ThreadLocal<DataSource> configTimeDataSourceHolder =
new ThreadLocal<DataSource>(); private static final ThreadLocal<TransactionManager> configTimeTransactionManagerHolder =
new ThreadLocal<TransactionManager>(); private static final ThreadLocal<Object> configTimeRegionFactoryHolder =
new ThreadLocal<Object>(); private static final ThreadLocal<LobHandler> configTimeLobHandlerHolder =
new ThreadLocal<LobHandler>(); /**
* Return the DataSource for the currently configured Hibernate SessionFactory,
* to be used by LocalDataSourceConnectionProvoder.
* <p>This instance will be set before initialization of the corresponding
* SessionFactory, and reset immediately afterwards. It is thus only available
* during configuration.
* @see #setDataSource
* @see LocalDataSourceConnectionProvider
*/
public static DataSource getConfigTimeDataSource() {
return configTimeDataSourceHolder.get();
} /**
* Return the JTA TransactionManager for the currently configured Hibernate
* SessionFactory, to be used by LocalTransactionManagerLookup.
* <p>This instance will be set before initialization of the corresponding
* SessionFactory, and reset immediately afterwards. It is thus only available
* during configuration.
* @see #setJtaTransactionManager
* @see LocalTransactionManagerLookup
*/
public static TransactionManager getConfigTimeTransactionManager() {
return configTimeTransactionManagerHolder.get();
} /**
* Return the RegionFactory for the currently configured Hibernate SessionFactory,
* to be used by LocalRegionFactoryProxy.
* <p>This instance will be set before initialization of the corresponding
* SessionFactory, and reset immediately afterwards. It is thus only available
* during configuration.
* @see #setCacheRegionFactory
*/
static Object getConfigTimeRegionFactory() {
return configTimeRegionFactoryHolder.get();
} /**
* Return the LobHandler for the currently configured Hibernate SessionFactory,
* to be used by UserType implementations like ClobStringType.
* <p>This instance will be set before initialization of the corresponding
* SessionFactory, and reset immediately afterwards. It is thus only available
* during configuration.
* @see #setLobHandler
* @see org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.ClobStringType
* @see org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.BlobByteArrayType
* @see org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.BlobSerializableType
*/
public static LobHandler getConfigTimeLobHandler() {
return configTimeLobHandlerHolder.get();
} private Class<? extends Configuration> configurationClass = Configuration.class; private Resource[] configLocations; private String[] mappingResources; private Resource[] mappingLocations; private Resource[] cacheableMappingLocations; private Resource[] mappingJarLocations; private Resource[] mappingDirectoryLocations; private Properties hibernateProperties; private TransactionManager jtaTransactionManager; private RegionFactory cacheRegionFactory; private LobHandler lobHandler; private Interceptor entityInterceptor; private NamingStrategy namingStrategy; private TypeDefinitionBean[] typeDefinitions; private FilterDefinition[] filterDefinitions; private Properties entityCacheStrategies; private Properties collectionCacheStrategies; private Map<String, Object> eventListeners; private boolean schemaUpdate = false; private ClassLoader beanClassLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader(); private Configuration configuration; /**
* Specify the Hibernate Configuration class to use.
* <p>Default is {@link org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration}; any subclass
* of this default Hibernate Configuration class can be specified.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void setConfigurationClass(Class<?> configurationClass) {
if (configurationClass == null || !Configuration.class.isAssignableFrom(configurationClass)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"'configurationClass' must be assignable to [org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration]");
}
this.configurationClass = (Class<? extends Configuration>) configurationClass;
} /**
* Set the location of a single Hibernate XML config file, for example as
* classpath resource "classpath:hibernate.cfg.xml".
* <p>Note: Can be omitted when all necessary properties and mapping
* resources are specified locally via this bean.
* @see org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration#configure(java.net.URL)
*/
public void setConfigLocation(Resource configLocation) {
this.configLocations = new Resource[] {configLocation};
} /**
* Set the locations of multiple Hibernate XML config files, for example as
* classpath resources "classpath:hibernate.cfg.xml,classpath:extension.cfg.xml".
* <p>Note: Can be omitted when all necessary properties and mapping
* resources are specified locally via this bean.
* @see org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration#configure(java.net.URL)
*/
public void setConfigLocations(Resource... configLocations) {
this.configLocations = configLocations;
} /**
* Set Hibernate mapping resources to be found in the class path,
* like "example.hbm.xml" or "mypackage/example.hbm.xml".
* Analogous to mapping entries in a Hibernate XML config file.
* Alternative to the more generic setMappingLocations method.
* <p>Can be used to add to mappings from a Hibernate XML config file,
* or to specify all mappings locally.
* @see #setMappingLocations
* @see org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration#addResource
*/
public void setMappingResources(String... mappingResources) {
this.mappingResources = mappingResources;
} /**
* Set locations of Hibernate mapping files, for example as classpath
* resource "classpath:example.hbm.xml". Supports any resource location
* via Spring's resource abstraction, for example relative paths like
* "WEB-INF/mappings/example.hbm.xml" when running in an application context.
* <p>Can be used to add to mappings from a Hibernate XML config file,
* or to specify all mappings locally.
* @see org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration#addInputStream
*/
public void setMappingLocations(Resource... mappingLocations) {
this.mappingLocations = mappingLocations;
} /**
* Set locations of cacheable Hibernate mapping files, for example as web app
* resource "/WEB-INF/mapping/example.hbm.xml". Supports any resource location
* via Spring's resource abstraction, as long as the resource can be resolved
* in the file system.
* <p>Can be used to add to mappings from a Hibernate XML config file,
* or to specify all mappings locally.
* @see org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration#addCacheableFile(java.io.File)
*/
public void setCacheableMappingLocations(Resource... cacheableMappingLocations) {
this.cacheableMappingLocations = cacheableMappingLocations;
} /**
* Set locations of jar files that contain Hibernate mapping resources,
* like "WEB-INF/lib/example.hbm.jar".
* <p>Can be used to add to mappings from a Hibernate XML config file,
* or to specify all mappings locally.
* @see org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration#addJar(java.io.File)
*/
public void setMappingJarLocations(Resource... mappingJarLocations) {
this.mappingJarLocations = mappingJarLocations;
} /**
* Set locations of directories that contain Hibernate mapping resources,
* like "WEB-INF/mappings".
* <p>Can be used to add to mappings from a Hibernate XML config file,
* or to specify all mappings locally.
* @see org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration#addDirectory(java.io.File)
*/
public void setMappingDirectoryLocations(Resource... mappingDirectoryLocations) {
this.mappingDirectoryLocations = mappingDirectoryLocations;
} /**
* Set Hibernate properties, such as "hibernate.dialect".
* <p>Can be used to override values in a Hibernate XML config file,
* or to specify all necessary properties locally.
* <p>Note: Do not specify a transaction provider here when using
* Spring-driven transactions. It is also advisable to omit connection
* provider settings and use a Spring-set DataSource instead.
* @see #setDataSource
*/
public void setHibernateProperties(Properties hibernateProperties) {
this.hibernateProperties = hibernateProperties;
} /**
* Return the Hibernate properties, if any. Mainly available for
* configuration through property paths that specify individual keys.
*/
public Properties getHibernateProperties() {
if (this.hibernateProperties == null) {
this.hibernateProperties = new Properties();
}
return this.hibernateProperties;
} /**
* Set the JTA TransactionManager to be used for Hibernate's
* TransactionManagerLookup. Allows for using a Spring-managed
* JTA TransactionManager for Hibernate's cache synchronization.
* <p>Note: If this is set, the Hibernate settings should not define a
* transaction manager lookup to avoid meaningless double configuration.
* @see LocalTransactionManagerLookup
*/
public void setJtaTransactionManager(TransactionManager jtaTransactionManager) {
this.jtaTransactionManager = jtaTransactionManager;
} /**
* Set the Hibernate RegionFactory to use for the SessionFactory.
* Allows for using a Spring-managed RegionFactory instance.
* <p>Note: If this is set, the Hibernate settings should not define a
* cache provider to avoid meaningless double configuration.
* @see org.hibernate.cache.RegionFactory
*/
public void setCacheRegionFactory(RegionFactory cacheRegionFactory) {
this.cacheRegionFactory = cacheRegionFactory;
} /**
* Set the LobHandler to be used by the SessionFactory.
* Will be exposed at config time for UserType implementations.
* @see #getConfigTimeLobHandler
* @see org.hibernate.usertype.UserType
* @see org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.ClobStringType
* @see org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.BlobByteArrayType
* @see org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.BlobSerializableType
*/
public void setLobHandler(LobHandler lobHandler) {
this.lobHandler = lobHandler;
} /**
* Set a Hibernate entity interceptor that allows to inspect and change
* property values before writing to and reading from the database.
* Will get applied to any new Session created by this factory.
* <p>Such an interceptor can either be set at the SessionFactory level, i.e. on
* LocalSessionFactoryBean, or at the Session level, i.e. on HibernateTemplate,
* HibernateInterceptor, and HibernateTransactionManager. It's preferable to set
* it on LocalSessionFactoryBean or HibernateTransactionManager to avoid repeated
* configuration and guarantee consistent behavior in transactions.
* @see HibernateTemplate#setEntityInterceptor
* @see HibernateInterceptor#setEntityInterceptor
* @see HibernateTransactionManager#setEntityInterceptor
* @see org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration#setInterceptor
*/
public void setEntityInterceptor(Interceptor entityInterceptor) {
this.entityInterceptor = entityInterceptor;
} /**
* Set a Hibernate NamingStrategy for the SessionFactory, determining the
* physical column and table names given the info in the mapping document.
* @see org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration#setNamingStrategy
*/
public void setNamingStrategy(NamingStrategy namingStrategy) {
this.namingStrategy = namingStrategy;
} /**
* Specify the Hibernate type definitions to register with the SessionFactory,
* as Spring TypeDefinitionBean instances. This is an alternative to specifying
* <<typedef> elements in Hibernate mapping files.
* <p>Unfortunately, Hibernate itself does not define a complete object that
* represents a type definition, hence the need for Spring's TypeDefinitionBean.
* @see TypeDefinitionBean
* @see org.hibernate.cfg.Mappings#addTypeDef(String, String, java.util.Properties)
*/
public void setTypeDefinitions(TypeDefinitionBean... typeDefinitions) {
this.typeDefinitions = typeDefinitions;
} /**
* Specify the Hibernate FilterDefinitions to register with the SessionFactory.
* This is an alternative to specifying <<filter-def> elements in
* Hibernate mapping files.
* <p>Typically, the passed-in FilterDefinition objects will have been defined
* as Spring FilterDefinitionFactoryBeans, probably as inner beans within the
* LocalSessionFactoryBean definition.
* @see FilterDefinitionFactoryBean
* @see org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration#addFilterDefinition
*/
public void setFilterDefinitions(FilterDefinition... filterDefinitions) {
this.filterDefinitions = filterDefinitions;
} /**
* Specify the cache strategies for entities (persistent classes or named entities).
* This configuration setting corresponds to the <class-cache> entry
* in the "hibernate.cfg.xml" configuration format.
* <p>For example:
* <pre class="code">
* <property name="entityCacheStrategies">
* <props>
* <prop key="com.mycompany.Customer">read-write</prop>
* <prop key="com.mycompany.Product">read-only,myRegion</prop>
* </props>
* </property></pre>
* @param entityCacheStrategies properties that define entity cache strategies,
* with class names as keys and cache concurrency strategies as values
* @see org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration#setCacheConcurrencyStrategy(String, String)
*/
public void setEntityCacheStrategies(Properties entityCacheStrategies) {
this.entityCacheStrategies = entityCacheStrategies;
} /**
* Specify the cache strategies for persistent collections (with specific roles).
* This configuration setting corresponds to the <collection-cache> entry
* in the "hibernate.cfg.xml" configuration format.
* <p>For example:
* <pre class="code">
* <property name="collectionCacheStrategies">
* <props>
* <prop key="com.mycompany.Order.items">read-write</prop>
* <prop key="com.mycompany.Product.categories">read-only,myRegion</prop>
* </props>
* </property></pre>
* @param collectionCacheStrategies properties that define collection cache strategies,
* with collection roles as keys and cache concurrency strategies as values
* @see org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration#setCollectionCacheConcurrencyStrategy(String, String)
*/
public void setCollectionCacheStrategies(Properties collectionCacheStrategies) {
this.collectionCacheStrategies = collectionCacheStrategies;
} /**
* Specify the Hibernate event listeners to register, with listener types
* as keys and listener objects as values. Instead of a single listener object,
* you can also pass in a list or set of listeners objects as value.
* <p>See the Hibernate documentation for further details on listener types
* and associated listener interfaces.
* <p>See {@code org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration#setListener(String, Object)}
* @param eventListeners Map with listener type Strings as keys and
* listener objects as values
*/
public void setEventListeners(Map<String, Object> eventListeners) {
this.eventListeners = eventListeners;
} /**
* Set whether to execute a schema update after SessionFactory initialization.
* <p>For details on how to make schema update scripts work, see the Hibernate
* documentation, as this class leverages the same schema update script support
* in org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration as Hibernate's own SchemaUpdate tool.
* @see org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration#generateSchemaUpdateScript
* @see org.hibernate.tool.hbm2ddl.SchemaUpdate
*/
public void setSchemaUpdate(boolean schemaUpdate) {
this.schemaUpdate = schemaUpdate;
} @Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader beanClassLoader) {
this.beanClassLoader = beanClassLoader;
} @Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected SessionFactory buildSessionFactory() throws Exception {
// Create Configuration instance.
Configuration config = newConfiguration(); DataSource dataSource = getDataSource();
if (dataSource != null) {
// Make given DataSource available for SessionFactory configuration.
configTimeDataSourceHolder.set(dataSource);
}
if (this.jtaTransactionManager != null) {
// Make Spring-provided JTA TransactionManager available.
configTimeTransactionManagerHolder.set(this.jtaTransactionManager);
}
if (this.cacheRegionFactory != null) {
// Make Spring-provided Hibernate RegionFactory available.
configTimeRegionFactoryHolder.set(this.cacheRegionFactory);
}
if (this.lobHandler != null) {
// Make given LobHandler available for SessionFactory configuration.
// Do early because mapping resource might refer to custom types.
configTimeLobHandlerHolder.set(this.lobHandler);
} // Analogous to Hibernate EntityManager's Ejb3Configuration:
// Hibernate doesn't allow setting the bean ClassLoader explicitly,
// so we need to expose it as thread context ClassLoader accordingly.
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
ClassLoader threadContextClassLoader = currentThread.getContextClassLoader();
boolean overrideClassLoader =
(this.beanClassLoader != null && !this.beanClassLoader.equals(threadContextClassLoader));
if (overrideClassLoader) {
currentThread.setContextClassLoader(this.beanClassLoader);
} try {
if (isExposeTransactionAwareSessionFactory()) {
// Set Hibernate 3.1+ CurrentSessionContext implementation,
// providing the Spring-managed Session as current Session.
// Can be overridden by a custom value for the corresponding Hibernate property.
config.setProperty(
Environment.CURRENT_SESSION_CONTEXT_CLASS, SpringSessionContext.class.getName());
} if (this.jtaTransactionManager != null) {
// Set Spring-provided JTA TransactionManager as Hibernate property.
config.setProperty(
Environment.TRANSACTION_STRATEGY, JTATransactionFactory.class.getName());
config.setProperty(
Environment.TRANSACTION_MANAGER_STRATEGY, LocalTransactionManagerLookup.class.getName());
}
else {
// Makes the Hibernate Session aware of the presence of a Spring-managed transaction.
// Also sets connection release mode to ON_CLOSE by default.
config.setProperty(
Environment.TRANSACTION_STRATEGY, SpringTransactionFactory.class.getName());
} if (this.entityInterceptor != null) {
// Set given entity interceptor at SessionFactory level.
config.setInterceptor(this.entityInterceptor);
} if (this.namingStrategy != null) {
// Pass given naming strategy to Hibernate Configuration.
config.setNamingStrategy(this.namingStrategy);
} if (this.typeDefinitions != null) {
// Register specified Hibernate type definitions.
Mappings mappings = config.createMappings();
for (TypeDefinitionBean typeDef : this.typeDefinitions) {
mappings.addTypeDef(typeDef.getTypeName(), typeDef.getTypeClass(), typeDef.getParameters());
}
} if (this.filterDefinitions != null) {
// Register specified Hibernate FilterDefinitions.
for (FilterDefinition filterDef : this.filterDefinitions) {
config.addFilterDefinition(filterDef);
}
} if (this.configLocations != null) {
for (Resource resource : this.configLocations) {
// Load Hibernate configuration from given location.
config.configure(resource.getURL());
}
} if (this.hibernateProperties != null) {
// Add given Hibernate properties to Configuration.
config.addProperties(this.hibernateProperties);
} if (dataSource != null) {
Class<?> providerClass = LocalDataSourceConnectionProvider.class;
if (isUseTransactionAwareDataSource() || dataSource instanceof TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy) {
providerClass = TransactionAwareDataSourceConnectionProvider.class;
}
else if (config.getProperty(Environment.TRANSACTION_MANAGER_STRATEGY) != null) {
providerClass = LocalJtaDataSourceConnectionProvider.class;
}
// Set Spring-provided DataSource as Hibernate ConnectionProvider.
config.setProperty(Environment.CONNECTION_PROVIDER, providerClass.getName());
} if (this.cacheRegionFactory != null) {
// Expose Spring-provided Hibernate RegionFactory.
config.setProperty(Environment.CACHE_REGION_FACTORY, LocalRegionFactoryProxy.class.getName());
} if (this.mappingResources != null) {
// Register given Hibernate mapping definitions, contained in resource files.
for (String mapping : this.mappingResources) {
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource(mapping.trim(), this.beanClassLoader);
config.addInputStream(resource.getInputStream());
}
} if (this.mappingLocations != null) {
// Register given Hibernate mapping definitions, contained in resource files.
for (Resource resource : this.mappingLocations) {
config.addInputStream(resource.getInputStream());
}
} if (this.cacheableMappingLocations != null) {
// Register given cacheable Hibernate mapping definitions, read from the file system.
for (Resource resource : this.cacheableMappingLocations) {
config.addCacheableFile(resource.getFile());
}
} if (this.mappingJarLocations != null) {
// Register given Hibernate mapping definitions, contained in jar files.
for (Resource resource : this.mappingJarLocations) {
config.addJar(resource.getFile());
}
} if (this.mappingDirectoryLocations != null) {
// Register all Hibernate mapping definitions in the given directories.
for (Resource resource : this.mappingDirectoryLocations) {
File file = resource.getFile();
if (!file.isDirectory()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Mapping directory location [" + resource + "] does not denote a directory");
}
config.addDirectory(file);
}
} // Tell Hibernate to eagerly compile the mappings that we registered,
// for availability of the mapping information in further processing.
postProcessMappings(config);
config.buildMappings(); if (this.entityCacheStrategies != null) {
// Register cache strategies for mapped entities.
for (Enumeration<?> classNames = this.entityCacheStrategies.propertyNames(); classNames.hasMoreElements();) {
String className = (String) classNames.nextElement();
String[] strategyAndRegion =
StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(this.entityCacheStrategies.getProperty(className));
if (strategyAndRegion.length > 1) {
config.setCacheConcurrencyStrategy(className, strategyAndRegion[0], strategyAndRegion[1]);
}
else if (strategyAndRegion.length > 0) {
config.setCacheConcurrencyStrategy(className, strategyAndRegion[0]);
}
}
} if (this.collectionCacheStrategies != null) {
// Register cache strategies for mapped collections.
for (Enumeration<?> collRoles = this.collectionCacheStrategies.propertyNames(); collRoles.hasMoreElements();) {
String collRole = (String) collRoles.nextElement();
String[] strategyAndRegion =
StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(this.collectionCacheStrategies.getProperty(collRole));
if (strategyAndRegion.length > 1) {
config.setCollectionCacheConcurrencyStrategy(collRole, strategyAndRegion[0], strategyAndRegion[1]);
}
else if (strategyAndRegion.length > 0) {
config.setCollectionCacheConcurrencyStrategy(collRole, strategyAndRegion[0]);
}
}
} if (this.eventListeners != null) {
// Register specified Hibernate event listeners.
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : this.eventListeners.entrySet()) {
String listenerType = entry.getKey();
Object listenerObject = entry.getValue();
if (listenerObject instanceof Collection) {
Collection<Object> listeners = (Collection<Object>) listenerObject;
EventListeners listenerRegistry = config.getEventListeners();
Object[] listenerArray =
(Object[]) Array.newInstance(listenerRegistry.getListenerClassFor(listenerType), listeners.size());
listenerArray = listeners.toArray(listenerArray);
config.setListeners(listenerType, listenerArray);
}
else {
config.setListener(listenerType, listenerObject);
}
}
} // Perform custom post-processing in subclasses.
postProcessConfiguration(config); // Build SessionFactory instance.
logger.info("Building new Hibernate SessionFactory");
this.configuration = config;
return newSessionFactory(config);
} finally {
if (dataSource != null) {
configTimeDataSourceHolder.remove();
}
if (this.jtaTransactionManager != null) {
configTimeTransactionManagerHolder.remove();
}
if (this.cacheRegionFactory != null) {
configTimeRegionFactoryHolder.remove();
}
if (this.lobHandler != null) {
configTimeLobHandlerHolder.remove();
}
if (overrideClassLoader) {
// Reset original thread context ClassLoader.
currentThread.setContextClassLoader(threadContextClassLoader);
}
}
} /**
* Subclasses can override this method to perform custom initialization
* of the Configuration instance used for SessionFactory creation.
* The properties of this LocalSessionFactoryBean will be applied to
* the Configuration object that gets returned here.
* <p>The default implementation creates a new Configuration instance.
* A custom implementation could prepare the instance in a specific way,
* or use a custom Configuration subclass.
* @return the Configuration instance
* @throws HibernateException in case of Hibernate initialization errors
* @see org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration#Configuration()
*/
protected Configuration newConfiguration() throws HibernateException {
return BeanUtils.instantiateClass(this.configurationClass);
} /**
* To be implemented by subclasses that want to register further mappings
* on the Configuration object after this FactoryBean registered its specified
* mappings.
* <p>Invoked <i>before</i> the {@code Configuration.buildMappings()} call,
* so that it can still extend and modify the mapping information.
* @param config the current Configuration object
* @throws HibernateException in case of Hibernate initialization errors
* @see org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration#buildMappings()
*/
protected void postProcessMappings(Configuration config) throws HibernateException {
} /**
* To be implemented by subclasses that want to perform custom
* post-processing of the Configuration object after this FactoryBean
* performed its default initialization.
* <p>Invoked <i>after</i> the {@code Configuration.buildMappings()} call,
* so that it can operate on the completed and fully parsed mapping information.
* @param config the current Configuration object
* @throws HibernateException in case of Hibernate initialization errors
* @see org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration#buildMappings()
*/
protected void postProcessConfiguration(Configuration config) throws HibernateException {
} /**
* Subclasses can override this method to perform custom initialization
* of the SessionFactory instance, creating it via the given Configuration
* object that got prepared by this LocalSessionFactoryBean.
* <p>The default implementation invokes Configuration's buildSessionFactory.
* A custom implementation could prepare the instance in a specific way,
* or use a custom SessionFactoryImpl subclass.
* @param config Configuration prepared by this LocalSessionFactoryBean
* @return the SessionFactory instance
* @throws HibernateException in case of Hibernate initialization errors
* @see org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration#buildSessionFactory
*/
protected SessionFactory newSessionFactory(Configuration config) throws HibernateException {
return config.buildSessionFactory();
} /**
* Return the Configuration object used to build the SessionFactory.
* Allows for access to configuration metadata stored there (rarely needed).
* @throws IllegalStateException if the Configuration object has not been initialized yet
*/
public final Configuration getConfiguration() {
if (this.configuration == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Configuration not initialized yet");
}
return this.configuration;
} /**
* Executes schema update if requested.
* @see #setSchemaUpdate
* @see #updateDatabaseSchema()
*/
@Override
protected void afterSessionFactoryCreation() throws Exception {
if (this.schemaUpdate) {
updateDatabaseSchema();
}
} /**
* Allows for schema export on shutdown.
*/
@Override
public void destroy() throws HibernateException {
DataSource dataSource = getDataSource();
if (dataSource != null) {
// Make given DataSource available for potential SchemaExport,
// which unfortunately reinstantiates a ConnectionProvider.
configTimeDataSourceHolder.set(dataSource);
}
try {
super.destroy();
}
finally {
if (dataSource != null) {
// Reset DataSource holder.
configTimeDataSourceHolder.remove();
}
}
} /**
* Execute schema update script, determined by the Configuration object
* used for creating the SessionFactory. A replacement for Hibernate's
* SchemaUpdate class, for automatically executing schema update scripts
* on application startup. Can also be invoked manually.
* <p>Fetch the LocalSessionFactoryBean itself rather than the exposed
* SessionFactory to be able to invoke this method, e.g. via
* {@code LocalSessionFactoryBean lsfb = (LocalSessionFactoryBean) ctx.getBean("&mySessionFactory");}.
* <p>Uses the SessionFactory that this bean generates for accessing a
* JDBC connection to perform the script.
* @throws DataAccessException in case of script execution errors
* @see #setSchemaUpdate
* @see org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration#generateSchemaUpdateScript
* @see org.hibernate.tool.hbm2ddl.SchemaUpdate
*/
public void updateDatabaseSchema() throws DataAccessException {
logger.info("Updating database schema for Hibernate SessionFactory");
DataSource dataSource = getDataSource();
if (dataSource != null) {
// Make given DataSource available for the schema update.
configTimeDataSourceHolder.set(dataSource);
}
try {
SessionFactory sessionFactory = getSessionFactory();
final Dialect dialect = ((SessionFactoryImplementor) sessionFactory).getDialect();
HibernateTemplate hibernateTemplate = new HibernateTemplate(sessionFactory);
hibernateTemplate.setFlushMode(HibernateTemplate.FLUSH_NEVER);
hibernateTemplate.execute(
new HibernateCallback<Object>() {
@Override
public Object doInHibernate(Session session) throws HibernateException, SQLException {
Connection con = session.connection();
DatabaseMetadata metadata = new DatabaseMetadata(con, dialect);
String[] sql = getConfiguration().generateSchemaUpdateScript(dialect, metadata);
executeSchemaScript(con, sql);
return null;
}
}
);
}
finally {
if (dataSource != null) {
configTimeDataSourceHolder.remove();
}
}
} /**
* Execute schema creation script, determined by the Configuration object
* used for creating the SessionFactory. A replacement for Hibernate's
* SchemaValidator class, to be invoked after application startup.
* <p>Fetch the LocalSessionFactoryBean itself rather than the exposed
* SessionFactory to be able to invoke this method, e.g. via
* {@code LocalSessionFactoryBean lsfb = (LocalSessionFactoryBean) ctx.getBean("&mySessionFactory");}.
* <p>Uses the SessionFactory that this bean generates for accessing a
* JDBC connection to perform the script.
* @throws DataAccessException in case of script execution errors
* @see org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration#validateSchema
* @see org.hibernate.tool.hbm2ddl.SchemaValidator
*/
public void validateDatabaseSchema() throws DataAccessException {
logger.info("Validating database schema for Hibernate SessionFactory");
DataSource dataSource = getDataSource();
if (dataSource != null) {
// Make given DataSource available for the schema update.
configTimeDataSourceHolder.set(dataSource);
}
try {
SessionFactory sessionFactory = getSessionFactory();
final Dialect dialect = ((SessionFactoryImplementor) sessionFactory).getDialect();
HibernateTemplate hibernateTemplate = new HibernateTemplate(sessionFactory);
hibernateTemplate.setFlushMode(HibernateTemplate.FLUSH_NEVER);
hibernateTemplate.execute(
new HibernateCallback<Object>() {
@Override
public Object doInHibernate(Session session) throws HibernateException, SQLException {
Connection con = session.connection();
DatabaseMetadata metadata = new DatabaseMetadata(con, dialect, false);
getConfiguration().validateSchema(dialect, metadata);
return null;
}
}
);
}
finally {
if (dataSource != null) {
configTimeDataSourceHolder.remove();
}
}
} /**
* Execute schema drop script, determined by the Configuration object
* used for creating the SessionFactory. A replacement for Hibernate's
* SchemaExport class, to be invoked on application setup.
* <p>Fetch the LocalSessionFactoryBean itself rather than the exposed
* SessionFactory to be able to invoke this method, e.g. via
* {@code LocalSessionFactoryBean lsfb = (LocalSessionFactoryBean) ctx.getBean("&mySessionFactory");}.
* <p>Uses the SessionFactory that this bean generates for accessing a
* JDBC connection to perform the script.
* @throws org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException in case of script execution errors
* @see org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration#generateDropSchemaScript
* @see org.hibernate.tool.hbm2ddl.SchemaExport#drop
*/
public void dropDatabaseSchema() throws DataAccessException {
logger.info("Dropping database schema for Hibernate SessionFactory");
SessionFactory sessionFactory = getSessionFactory();
final Dialect dialect = ((SessionFactoryImplementor) sessionFactory).getDialect();
HibernateTemplate hibernateTemplate = new HibernateTemplate(sessionFactory);
hibernateTemplate.execute(
new HibernateCallback<Object>() {
@Override
public Object doInHibernate(Session session) throws HibernateException, SQLException {
Connection con = session.connection();
String[] sql = getConfiguration().generateDropSchemaScript(dialect);
executeSchemaScript(con, sql);
return null;
}
}
);
} /**
* Execute schema creation script, determined by the Configuration object
* used for creating the SessionFactory. A replacement for Hibernate's
* SchemaExport class, to be invoked on application setup.
* <p>Fetch the LocalSessionFactoryBean itself rather than the exposed
* SessionFactory to be able to invoke this method, e.g. via
* {@code LocalSessionFactoryBean lsfb = (LocalSessionFactoryBean) ctx.getBean("&mySessionFactory");}.
* <p>Uses the SessionFactory that this bean generates for accessing a
* JDBC connection to perform the script.
* @throws DataAccessException in case of script execution errors
* @see org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration#generateSchemaCreationScript
* @see org.hibernate.tool.hbm2ddl.SchemaExport#create
*/
public void createDatabaseSchema() throws DataAccessException {
logger.info("Creating database schema for Hibernate SessionFactory");
DataSource dataSource = getDataSource();
if (dataSource != null) {
// Make given DataSource available for the schema update.
configTimeDataSourceHolder.set(dataSource);
}
try {
SessionFactory sessionFactory = getSessionFactory();
final Dialect dialect = ((SessionFactoryImplementor) sessionFactory).getDialect();
HibernateTemplate hibernateTemplate = new HibernateTemplate(sessionFactory);
hibernateTemplate.execute(
new HibernateCallback<Object>() {
@Override
public Object doInHibernate(Session session) throws HibernateException, SQLException {
Connection con = session.connection();
String[] sql = getConfiguration().generateSchemaCreationScript(dialect);
executeSchemaScript(con, sql);
return null;
}
}
);
}
finally {
if (dataSource != null) {
configTimeDataSourceHolder.remove();
}
}
} /**
* Execute the given schema script on the given JDBC Connection.
* <p>Note that the default implementation will log unsuccessful statements
* and continue to execute. Override the {@code executeSchemaStatement}
* method to treat failures differently.
* @param con the JDBC Connection to execute the script on
* @param sql the SQL statements to execute
* @throws SQLException if thrown by JDBC methods
* @see #executeSchemaStatement
*/
protected void executeSchemaScript(Connection con, String[] sql) throws SQLException {
if (sql != null && sql.length > 0) {
boolean oldAutoCommit = con.getAutoCommit();
if (!oldAutoCommit) {
con.setAutoCommit(true);
}
try {
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
try {
for (String sqlStmt : sql) {
executeSchemaStatement(stmt, sqlStmt);
}
}
finally {
JdbcUtils.closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
finally {
if (!oldAutoCommit) {
con.setAutoCommit(false);
}
}
}
} /**
* Execute the given schema SQL on the given JDBC Statement.
* <p>Note that the default implementation will log unsuccessful statements
* and continue to execute. Override this method to treat failures differently.
* @param stmt the JDBC Statement to execute the SQL on
* @param sql the SQL statement to execute
* @throws SQLException if thrown by JDBC methods (and considered fatal)
*/
protected void executeSchemaStatement(Statement stmt, String sql) throws SQLException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Executing schema statement: " + sql);
}
try {
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
}
catch (SQLException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Unsuccessful schema statement: " + sql, ex);
}
}
} }
配置Hibernate的局部事务管理器HibernateTransactionManager,HibernateTransactionManager的源码是:
/*
* Copyright 2002-2014 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.orm.hibernate3; import java.sql.Connection;
import javax.sql.DataSource; import org.hibernate.ConnectionReleaseMode;
import org.hibernate.FlushMode;
import org.hibernate.HibernateException;
import org.hibernate.Interceptor;
import org.hibernate.JDBCException;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.exception.GenericJDBCException;
import org.hibernate.impl.SessionImpl; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException;
import org.springframework.dao.DataAccessResourceFailureException;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.ConnectionHolder;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceUtils;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.JdbcTransactionObjectSupport;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy;
import org.springframework.jdbc.support.SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator;
import org.springframework.jdbc.support.SQLExceptionTranslator;
import org.springframework.transaction.CannotCreateTransactionException;
import org.springframework.transaction.IllegalTransactionStateException;
import org.springframework.transaction.InvalidIsolationLevelException;
import org.springframework.transaction.TransactionDefinition;
import org.springframework.transaction.TransactionSystemException;
import org.springframework.transaction.support.AbstractPlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.support.DefaultTransactionStatus;
import org.springframework.transaction.support.ResourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionSynchronizationManager; /**
* {@link org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager}
* implementation for a single Hibernate {@link org.hibernate.SessionFactory}.
* Binds a Hibernate Session from the specified factory to the thread, potentially
* allowing for one thread-bound Session per factory. {@link SessionFactoryUtils}
* and {@link HibernateTemplate} are aware of thread-bound Sessions and participate
* in such transactions automatically. Using either of those or going through
* {@code SessionFactory.getCurrentSession()} is required for Hibernate
* access code that needs to support this transaction handling mechanism.
*
* <p>Supports custom isolation levels, and timeouts that get applied as
* Hibernate transaction timeouts.
*
* <p>This transaction manager is appropriate for applications that use a single
* Hibernate SessionFactory for transactional data access, but it also supports
* direct DataSource access within a transaction (i.e. plain JDBC code working
* with the same DataSource). This allows for mixing services which access Hibernate
* and services which use plain JDBC (without being aware of Hibernate)!
* Application code needs to stick to the same simple Connection lookup pattern as
* with {@link org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager}
* (i.e. {@link org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceUtils#getConnection}
* or going through a
* {@link org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy}).
*
* <p>Note: To be able to register a DataSource's Connection for plain JDBC code,
* this instance needs to be aware of the DataSource ({@link #setDataSource}).
* The given DataSource should obviously match the one used by the given
* SessionFactory. To achieve this, configure both to the same JNDI DataSource,
* or preferably create the SessionFactory with {@link LocalSessionFactoryBean} and
* a local DataSource (which will be autodetected by this transaction manager).
*
* <p>JTA (usually through {@link org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager})
* is necessary for accessing multiple transactional resources within the same
* transaction. The DataSource that Hibernate uses needs to be JTA-enabled in
* such a scenario (see container setup). Normally, JTA setup for Hibernate is
* somewhat container-specific due to the JTA TransactionManager lookup, required
* for proper transactional handling of the SessionFactory-level read-write cache.
*
* <p>Fortunately, there is an easier way with Spring: {@link SessionFactoryUtils}
* (and thus {@link HibernateTemplate}) registers synchronizations with Spring's
* {@link org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionSynchronizationManager}
* (as used by {@link org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager}),
* for proper after-completion callbacks. Therefore, as long as Spring's
* JtaTransactionManager drives the JTA transactions, Hibernate does not require
* any special configuration for proper JTA participation. Note that there are
* special restrictions with EJB CMT and restrictive JTA subsystems: See
* {@link org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager}'s javadoc for details.
*
* <p>This transaction manager supports nested transactions via JDBC 3.0 Savepoints.
* The {@link #setNestedTransactionAllowed} "nestedTransactionAllowed"} flag defaults
* to "false", though, as nested transactions will just apply to the JDBC Connection,
* not to the Hibernate Session and its cached entity objects and related context.
* You can manually set the flag to "true" if you want to use nested transactions
* for JDBC access code which participates in Hibernate transactions (provided that
* your JDBC driver supports Savepoints). <i>Note that Hibernate itself does not
* support nested transactions! Hence, do not expect Hibernate access code to
* semantically participate in a nested transaction.</i>
*
* <p>Requires Hibernate 3.6.x, as of Spring 4.0.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 1.2
* @see #setSessionFactory
* @see #setDataSource
* @see LocalSessionFactoryBean
* @see SessionFactoryUtils#getSession
* @see SessionFactoryUtils#applyTransactionTimeout
* @see SessionFactoryUtils#releaseSession
* @see HibernateTemplate
* @see org.hibernate.SessionFactory#getCurrentSession()
* @see org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceUtils#getConnection
* @see org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceUtils#applyTransactionTimeout
* @see org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceUtils#releaseConnection
* @see org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate
* @see org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager
* @see org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager
* @deprecated as of Spring 4.3, in favor of Hibernate 4.x/5.x
*/
@Deprecated
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class HibernateTransactionManager extends AbstractPlatformTransactionManager
implements ResourceTransactionManager, BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean { private SessionFactory sessionFactory; private DataSource dataSource; private boolean autodetectDataSource = true; private boolean prepareConnection = true; private boolean hibernateManagedSession = false; private boolean earlyFlushBeforeCommit = false; private Object entityInterceptor; private SQLExceptionTranslator jdbcExceptionTranslator; private SQLExceptionTranslator defaultJdbcExceptionTranslator; /**
* Just needed for entityInterceptorBeanName.
* @see #setEntityInterceptorBeanName
*/
private BeanFactory beanFactory; /**
* Create a new HibernateTransactionManager instance.
* A SessionFactory has to be set to be able to use it.
* @see #setSessionFactory
*/
public HibernateTransactionManager() {
} /**
* Create a new HibernateTransactionManager instance.
* @param sessionFactory SessionFactory to manage transactions for
*/
public HibernateTransactionManager(SessionFactory sessionFactory) {
this.sessionFactory = sessionFactory;
afterPropertiesSet();
} /**
* Set the SessionFactory that this instance should manage transactions for.
*/
public void setSessionFactory(SessionFactory sessionFactory) {
this.sessionFactory = sessionFactory;
} /**
* Return the SessionFactory that this instance should manage transactions for.
*/
public SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
return this.sessionFactory;
} /**
* Set the JDBC DataSource that this instance should manage transactions for.
* The DataSource should match the one used by the Hibernate SessionFactory:
* for example, you could specify the same JNDI DataSource for both.
* <p>If the SessionFactory was configured with LocalDataSourceConnectionProvider,
* i.e. by Spring's LocalSessionFactoryBean with a specified "dataSource",
* the DataSource will be auto-detected: You can still explicitly specify the
* DataSource, but you don't need to in this case.
* <p>A transactional JDBC Connection for this DataSource will be provided to
* application code accessing this DataSource directly via DataSourceUtils
* or JdbcTemplate. The Connection will be taken from the Hibernate Session.
* <p>The DataSource specified here should be the target DataSource to manage
* transactions for, not a TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy. Only data access
* code may work with TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy, while the transaction
* manager needs to work on the underlying target DataSource. If there's
* nevertheless a TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy passed in, it will be
* unwrapped to extract its target DataSource.
* @see #setAutodetectDataSource
* @see LocalDataSourceConnectionProvider
* @see LocalSessionFactoryBean#setDataSource
* @see org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy
* @see org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceUtils
* @see org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate
*/
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
if (dataSource instanceof TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy) {
// If we got a TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy, we need to perform transactions
// for its underlying target DataSource, else data access code won't see
// properly exposed transactions (i.e. transactions for the target DataSource).
this.dataSource = ((TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy) dataSource).getTargetDataSource();
}
else {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
} /**
* Return the JDBC DataSource that this instance manages transactions for.
*/
public DataSource getDataSource() {
return this.dataSource;
} /**
* Set whether to autodetect a JDBC DataSource used by the Hibernate SessionFactory,
* if set via LocalSessionFactoryBean's {@code setDataSource}. Default is "true".
* <p>Can be turned off to deliberately ignore an available DataSource, in order
* to not expose Hibernate transactions as JDBC transactions for that DataSource.
* @see #setDataSource
* @see LocalSessionFactoryBean#setDataSource
*/
public void setAutodetectDataSource(boolean autodetectDataSource) {
this.autodetectDataSource = autodetectDataSource;
} /**
* Set whether to prepare the underlying JDBC Connection of a transactional
* Hibernate Session, that is, whether to apply a transaction-specific
* isolation level and/or the transaction's read-only flag to the underlying
* JDBC Connection.
* <p>Default is "true". If you turn this flag off, the transaction manager
* will not support per-transaction isolation levels anymore. It will not
* call {@code Connection.setReadOnly(true)} for read-only transactions
* anymore either. If this flag is turned off, no cleanup of a JDBC Connection
* is required after a transaction, since no Connection settings will get modified.
* @see java.sql.Connection#setTransactionIsolation
* @see java.sql.Connection#setReadOnly
*/
public void setPrepareConnection(boolean prepareConnection) {
this.prepareConnection = prepareConnection;
} /**
* Set whether to operate on a Hibernate-managed Session instead of a
* Spring-managed Session, that is, whether to obtain the Session through
* Hibernate's {@link org.hibernate.SessionFactory#getCurrentSession()}
* instead of {@link org.hibernate.SessionFactory#openSession()} (with a Spring
* {@link org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionSynchronizationManager}
* check preceding it).
* <p>Default is "false", i.e. using a Spring-managed Session: taking the current
* thread-bound Session if available (e.g. in an Open-Session-in-View scenario),
* creating a new Session for the current transaction otherwise.
* <p>Switch this flag to "true" in order to enforce use of a Hibernate-managed Session.
* Note that this requires {@link org.hibernate.SessionFactory#getCurrentSession()}
* to always return a proper Session when called for a Spring-managed transaction;
* transaction begin will fail if the {@code getCurrentSession()} call fails.
* <p>This mode will typically be used in combination with a custom Hibernate
* {@link org.hibernate.context.CurrentSessionContext} implementation that stores
* Sessions in a place other than Spring's TransactionSynchronizationManager.
* It may also be used in combination with Spring's Open-Session-in-View support
* (using Spring's default {@link SpringSessionContext}), in which case it subtly
* differs from the Spring-managed Session mode: The pre-bound Session will <i>not</i>
* receive a {@code clear()} call (on rollback) or a {@code disconnect()}
* call (on transaction completion) in such a scenario; this is rather left up
* to a custom CurrentSessionContext implementation (if desired).
*/
public void setHibernateManagedSession(boolean hibernateManagedSession) {
this.hibernateManagedSession = hibernateManagedSession;
} /**
* Set whether to perform an early flush before proceeding with a commit.
* <p>Default is "false", performing an implicit flush as part of the actual
* commit step. Switch this to "true" in order to enforce an explicit early
* flush right <i>before</i> the actual commit step.
* <p>An early flush happens before the before-commit synchronization phase,
* making flushed state visible to {@code beforeCommit} callbacks of registered
* {@link org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionSynchronization}
* objects. Such explicit flush behavior is consistent with Spring-driven
* flushing in a JTA transaction environment, so may also get enforced for
* consistency with JTA transaction behavior.
* @see #prepareForCommit
*/
public void setEarlyFlushBeforeCommit(boolean earlyFlushBeforeCommit) {
this.earlyFlushBeforeCommit = earlyFlushBeforeCommit;
} /**
* Set the bean name of a Hibernate entity interceptor that allows to inspect
* and change property values before writing to and reading from the database.
* Will get applied to any new Session created by this transaction manager.
* <p>Requires the bean factory to be known, to be able to resolve the bean
* name to an interceptor instance on session creation. Typically used for
* prototype interceptors, i.e. a new interceptor instance per session.
* <p>Can also be used for shared interceptor instances, but it is recommended
* to set the interceptor reference directly in such a scenario.
* @param entityInterceptorBeanName the name of the entity interceptor in
* the bean factory
* @see #setBeanFactory
* @see #setEntityInterceptor
*/
public void setEntityInterceptorBeanName(String entityInterceptorBeanName) {
this.entityInterceptor = entityInterceptorBeanName;
} /**
* Set a Hibernate entity interceptor that allows to inspect and change
* property values before writing to and reading from the database.
* Will get applied to any new Session created by this transaction manager.
* <p>Such an interceptor can either be set at the SessionFactory level,
* i.e. on LocalSessionFactoryBean, or at the Session level, i.e. on
* HibernateTemplate, HibernateInterceptor, and HibernateTransactionManager.
* It's preferable to set it on LocalSessionFactoryBean or HibernateTransactionManager
* to avoid repeated configuration and guarantee consistent behavior in transactions.
* @see LocalSessionFactoryBean#setEntityInterceptor
* @see HibernateTemplate#setEntityInterceptor
* @see HibernateInterceptor#setEntityInterceptor
*/
public void setEntityInterceptor(Interceptor entityInterceptor) {
this.entityInterceptor = entityInterceptor;
} /**
* Return the current Hibernate entity interceptor, or {@code null} if none.
* Resolves an entity interceptor bean name via the bean factory,
* if necessary.
* @throws IllegalStateException if bean name specified but no bean factory set
* @throws BeansException if bean name resolution via the bean factory failed
* @see #setEntityInterceptor
* @see #setEntityInterceptorBeanName
* @see #setBeanFactory
*/
public Interceptor getEntityInterceptor() throws IllegalStateException, BeansException {
if (this.entityInterceptor instanceof Interceptor) {
return (Interceptor) entityInterceptor;
}
else if (this.entityInterceptor instanceof String) {
if (this.beanFactory == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot get entity interceptor via bean name if no bean factory set");
}
String beanName = (String) this.entityInterceptor;
return this.beanFactory.getBean(beanName, Interceptor.class);
}
else {
return null;
}
} /**
* Set the JDBC exception translator for this transaction manager.
* <p>Applied to any SQLException root cause of a Hibernate JDBCException that
* is thrown on flush, overriding Hibernate's default SQLException translation
* (which is based on Hibernate's Dialect for a specific target database).
* @param jdbcExceptionTranslator the exception translator
* @see java.sql.SQLException
* @see org.hibernate.JDBCException
* @see org.springframework.jdbc.support.SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator
* @see org.springframework.jdbc.support.SQLStateSQLExceptionTranslator
*/
public void setJdbcExceptionTranslator(SQLExceptionTranslator jdbcExceptionTranslator) {
this.jdbcExceptionTranslator = jdbcExceptionTranslator;
} /**
* Return the JDBC exception translator for this transaction manager, if any.
*/
public SQLExceptionTranslator getJdbcExceptionTranslator() {
return this.jdbcExceptionTranslator;
} /**
* The bean factory just needs to be known for resolving entity interceptor
* bean names. It does not need to be set for any other mode of operation.
* @see #setEntityInterceptorBeanName
*/
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
} @Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
if (getSessionFactory() == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Property 'sessionFactory' is required");
}
if (this.entityInterceptor instanceof String && this.beanFactory == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Property 'beanFactory' is required for 'entityInterceptorBeanName'");
} // Check for SessionFactory's DataSource.
if (this.autodetectDataSource && getDataSource() == null) {
DataSource sfds = SessionFactoryUtils.getDataSource(getSessionFactory());
if (sfds != null) {
// Use the SessionFactory's DataSource for exposing transactions to JDBC code.
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Using DataSource [" + sfds +
"] of Hibernate SessionFactory for HibernateTransactionManager");
}
setDataSource(sfds);
}
}
} @Override
public Object getResourceFactory() {
return getSessionFactory();
} @Override
protected Object doGetTransaction() {
HibernateTransactionObject txObject = new HibernateTransactionObject();
txObject.setSavepointAllowed(isNestedTransactionAllowed()); SessionHolder sessionHolder =
(SessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(getSessionFactory());
if (sessionHolder != null) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Found thread-bound Session [" +
SessionFactoryUtils.toString(sessionHolder.getSession()) + "] for Hibernate transaction");
}
txObject.setSessionHolder(sessionHolder);
}
else if (this.hibernateManagedSession) {
try {
Session session = getSessionFactory().getCurrentSession();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Found Hibernate-managed Session [" +
SessionFactoryUtils.toString(session) + "] for Spring-managed transaction");
}
txObject.setExistingSession(session);
}
catch (HibernateException ex) {
throw new DataAccessResourceFailureException(
"Could not obtain Hibernate-managed Session for Spring-managed transaction", ex);
}
} if (getDataSource() != null) {
ConnectionHolder conHolder = (ConnectionHolder)
TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(getDataSource());
txObject.setConnectionHolder(conHolder);
} return txObject;
} @Override
protected boolean isExistingTransaction(Object transaction) {
HibernateTransactionObject txObject = (HibernateTransactionObject) transaction;
return (txObject.hasSpringManagedTransaction() ||
(this.hibernateManagedSession && txObject.hasHibernateManagedTransaction()));
} @Override
protected void doBegin(Object transaction, TransactionDefinition definition) {
HibernateTransactionObject txObject = (HibernateTransactionObject) transaction; if (txObject.hasConnectionHolder() && !txObject.getConnectionHolder().isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"Pre-bound JDBC Connection found! HibernateTransactionManager does not support " +
"running within DataSourceTransactionManager if told to manage the DataSource itself. " +
"It is recommended to use a single HibernateTransactionManager for all transactions " +
"on a single DataSource, no matter whether Hibernate or JDBC access.");
} Session session = null; try {
if (txObject.getSessionHolder() == null || txObject.getSessionHolder().isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) {
Interceptor entityInterceptor = getEntityInterceptor();
Session newSession = (entityInterceptor != null ?
getSessionFactory().openSession(entityInterceptor) : getSessionFactory().openSession());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Opened new Session [" + SessionFactoryUtils.toString(newSession) +
"] for Hibernate transaction");
}
txObject.setSession(newSession);
} session = txObject.getSessionHolder().getSession(); if (this.prepareConnection && isSameConnectionForEntireSession(session)) {
// We're allowed to change the transaction settings of the JDBC Connection.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(
"Preparing JDBC Connection of Hibernate Session [" + SessionFactoryUtils.toString(session) + "]");
}
Connection con = session.connection();
Integer previousIsolationLevel = DataSourceUtils.prepareConnectionForTransaction(con, definition);
txObject.setPreviousIsolationLevel(previousIsolationLevel);
}
else {
// Not allowed to change the transaction settings of the JDBC Connection.
if (definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT) {
// We should set a specific isolation level but are not allowed to...
throw new InvalidIsolationLevelException(
"HibernateTransactionManager is not allowed to support custom isolation levels: " +
"make sure that its 'prepareConnection' flag is on (the default) and that the " +
"Hibernate connection release mode is set to 'on_close' (SpringTransactionFactory's default). " +
"Make sure that your LocalSessionFactoryBean actually uses SpringTransactionFactory: Your " +
"Hibernate properties should *not* include a 'hibernate.transaction.factory_class' property!");
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(
"Not preparing JDBC Connection of Hibernate Session [" + SessionFactoryUtils.toString(session) + "]");
}
} if (definition.isReadOnly() && txObject.isNewSession()) {
// Just set to MANUAL in case of a new Session for this transaction.
session.setFlushMode(FlushMode.MANUAL);
} if (!definition.isReadOnly() && !txObject.isNewSession()) {
// We need AUTO or COMMIT for a non-read-only transaction.
FlushMode flushMode = session.getFlushMode();
if (flushMode.lessThan(FlushMode.COMMIT)) {
session.setFlushMode(FlushMode.AUTO);
txObject.getSessionHolder().setPreviousFlushMode(flushMode);
}
} Transaction hibTx; // Register transaction timeout.
int timeout = determineTimeout(definition);
if (timeout != TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
// Use Hibernate's own transaction timeout mechanism on Hibernate 3.1+
// Applies to all statements, also to inserts, updates and deletes!
hibTx = session.getTransaction();
hibTx.setTimeout(timeout);
hibTx.begin();
}
else {
// Open a plain Hibernate transaction without specified timeout.
hibTx = session.beginTransaction();
} // Add the Hibernate transaction to the session holder.
txObject.getSessionHolder().setTransaction(hibTx); // Register the Hibernate Session's JDBC Connection for the DataSource, if set.
if (getDataSource() != null) {
Connection con = session.connection();
ConnectionHolder conHolder = new ConnectionHolder(con);
if (timeout != TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
conHolder.setTimeoutInSeconds(timeout);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Exposing Hibernate transaction as JDBC transaction [" + con + "]");
}
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(getDataSource(), conHolder);
txObject.setConnectionHolder(conHolder);
} // Bind the session holder to the thread.
if (txObject.isNewSessionHolder()) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(getSessionFactory(), txObject.getSessionHolder());
}
txObject.getSessionHolder().setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txObject.isNewSession()) {
try {
if (session.getTransaction().isActive()) {
session.getTransaction().rollback();
}
}
catch (Throwable ex2) {
logger.debug("Could not rollback Session after failed transaction begin", ex);
}
finally {
SessionFactoryUtils.closeSession(session);
txObject.setSessionHolder(null);
}
}
throw new CannotCreateTransactionException("Could not open Hibernate Session for transaction", ex);
}
} @Override
protected Object doSuspend(Object transaction) {
HibernateTransactionObject txObject = (HibernateTransactionObject) transaction;
txObject.setSessionHolder(null);
SessionHolder sessionHolder =
(SessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResource(getSessionFactory());
txObject.setConnectionHolder(null);
ConnectionHolder connectionHolder = null;
if (getDataSource() != null) {
connectionHolder = (ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResource(getDataSource());
}
return new SuspendedResourcesHolder(sessionHolder, connectionHolder);
} @Override
protected void doResume(Object transaction, Object suspendedResources) {
SuspendedResourcesHolder resourcesHolder = (SuspendedResourcesHolder) suspendedResources;
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.hasResource(getSessionFactory())) {
// From non-transactional code running in active transaction synchronization
// -> can be safely removed, will be closed on transaction completion.
TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResource(getSessionFactory());
}
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(getSessionFactory(), resourcesHolder.getSessionHolder());
if (getDataSource() != null) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(getDataSource(), resourcesHolder.getConnectionHolder());
}
} @Override
protected void prepareForCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
if (this.earlyFlushBeforeCommit && status.isNewTransaction()) {
HibernateTransactionObject txObject = (HibernateTransactionObject) status.getTransaction();
Session session = txObject.getSessionHolder().getSession();
if (!session.getFlushMode().lessThan(FlushMode.COMMIT)) {
logger.debug("Performing an early flush for Hibernate transaction");
try {
session.flush();
}
catch (HibernateException ex) {
throw convertHibernateAccessException(ex);
}
finally {
session.setFlushMode(FlushMode.MANUAL);
}
}
}
} @Override
protected void doCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
HibernateTransactionObject txObject = (HibernateTransactionObject) status.getTransaction();
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Committing Hibernate transaction on Session [" +
SessionFactoryUtils.toString(txObject.getSessionHolder().getSession()) + "]");
}
try {
txObject.getSessionHolder().getTransaction().commit();
}
catch (org.hibernate.TransactionException ex) {
// assumably from commit call to the underlying JDBC connection
throw new TransactionSystemException("Could not commit Hibernate transaction", ex);
}
catch (HibernateException ex) {
// assumably failed to flush changes to database
throw convertHibernateAccessException(ex);
}
} @Override
protected void doRollback(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
HibernateTransactionObject txObject = (HibernateTransactionObject) status.getTransaction();
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Rolling back Hibernate transaction on Session [" +
SessionFactoryUtils.toString(txObject.getSessionHolder().getSession()) + "]");
}
try {
txObject.getSessionHolder().getTransaction().rollback();
}
catch (org.hibernate.TransactionException ex) {
throw new TransactionSystemException("Could not roll back Hibernate transaction", ex);
}
catch (HibernateException ex) {
// Shouldn't really happen, as a rollback doesn't cause a flush.
throw convertHibernateAccessException(ex);
}
finally {
if (!txObject.isNewSession() && !this.hibernateManagedSession) {
// Clear all pending inserts/updates/deletes in the Session.
// Necessary for pre-bound Sessions, to avoid inconsistent state.
txObject.getSessionHolder().getSession().clear();
}
}
} @Override
protected void doSetRollbackOnly(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
HibernateTransactionObject txObject = (HibernateTransactionObject) status.getTransaction();
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Setting Hibernate transaction on Session [" +
SessionFactoryUtils.toString(txObject.getSessionHolder().getSession()) + "] rollback-only");
}
txObject.setRollbackOnly();
} @Override
protected void doCleanupAfterCompletion(Object transaction) {
HibernateTransactionObject txObject = (HibernateTransactionObject) transaction; // Remove the session holder from the thread.
if (txObject.isNewSessionHolder()) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResource(getSessionFactory());
} // Remove the JDBC connection holder from the thread, if exposed.
if (getDataSource() != null) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResource(getDataSource());
} Session session = txObject.getSessionHolder().getSession();
if (this.prepareConnection && session.isConnected() && isSameConnectionForEntireSession(session)) {
// We're running with connection release mode "on_close": We're able to reset
// the isolation level and/or read-only flag of the JDBC Connection here.
// Else, we need to rely on the connection pool to perform proper cleanup.
try {
Connection con = session.connection();
DataSourceUtils.resetConnectionAfterTransaction(con, txObject.getPreviousIsolationLevel());
}
catch (HibernateException ex) {
logger.debug("Could not access JDBC Connection of Hibernate Session", ex);
}
} if (txObject.isNewSession()) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Closing Hibernate Session [" + SessionFactoryUtils.toString(session) +
"] after transaction");
}
SessionFactoryUtils.closeSessionOrRegisterDeferredClose(session, getSessionFactory());
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Not closing pre-bound Hibernate Session [" +
SessionFactoryUtils.toString(session) + "] after transaction");
}
if (txObject.getSessionHolder().getPreviousFlushMode() != null) {
session.setFlushMode(txObject.getSessionHolder().getPreviousFlushMode());
}
if (!this.hibernateManagedSession) {
session.disconnect();
}
}
txObject.getSessionHolder().clear();
} /**
* Return whether the given Hibernate Session will always hold the same
* JDBC Connection. This is used to check whether the transaction manager
* can safely prepare and clean up the JDBC Connection used for a transaction.
* <p>Default implementation checks the Session's connection release mode
* to be "on_close". Unfortunately, this requires casting to SessionImpl,
* as of Hibernate 3.1. If that cast doesn't work, we'll simply assume
* we're safe and return {@code true}.
* @param session the Hibernate Session to check
* @see org.hibernate.impl.SessionImpl#getConnectionReleaseMode()
* @see org.hibernate.ConnectionReleaseMode#ON_CLOSE
*/
protected boolean isSameConnectionForEntireSession(Session session) {
if (!(session instanceof SessionImpl)) {
// The best we can do is to assume we're safe.
return true;
}
ConnectionReleaseMode releaseMode = ((SessionImpl) session).getConnectionReleaseMode();
return ConnectionReleaseMode.ON_CLOSE.equals(releaseMode);
} /**
* Convert the given HibernateException to an appropriate exception
* from the {@code org.springframework.dao} hierarchy.
* <p>Will automatically apply a specified SQLExceptionTranslator to a
* Hibernate JDBCException, else rely on Hibernate's default translation.
* @param ex HibernateException that occurred
* @return a corresponding DataAccessException
* @see SessionFactoryUtils#convertHibernateAccessException
* @see #setJdbcExceptionTranslator
*/
protected DataAccessException convertHibernateAccessException(HibernateException ex) {
if (getJdbcExceptionTranslator() != null && ex instanceof JDBCException) {
return convertJdbcAccessException((JDBCException) ex, getJdbcExceptionTranslator());
}
else if (GenericJDBCException.class == ex.getClass()) {
return convertJdbcAccessException((GenericJDBCException) ex, getDefaultJdbcExceptionTranslator());
}
return SessionFactoryUtils.convertHibernateAccessException(ex);
} /**
* Convert the given Hibernate JDBCException to an appropriate exception
* from the {@code org.springframework.dao} hierarchy, using the
* given SQLExceptionTranslator.
* @param ex Hibernate JDBCException that occurred
* @param translator the SQLExceptionTranslator to use
* @return a corresponding DataAccessException
*/
protected DataAccessException convertJdbcAccessException(JDBCException ex, SQLExceptionTranslator translator) {
return translator.translate("Hibernate flushing: " + ex.getMessage(), ex.getSQL(), ex.getSQLException());
} /**
* Obtain a default SQLExceptionTranslator, lazily creating it if necessary.
* <p>Creates a default
* {@link org.springframework.jdbc.support.SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator}
* for the SessionFactory's underlying DataSource.
*/
protected synchronized SQLExceptionTranslator getDefaultJdbcExceptionTranslator() {
if (this.defaultJdbcExceptionTranslator == null) {
if (getDataSource() != null) {
this.defaultJdbcExceptionTranslator = new SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator(getDataSource());
}
else {
this.defaultJdbcExceptionTranslator = SessionFactoryUtils.newJdbcExceptionTranslator(getSessionFactory());
}
}
return this.defaultJdbcExceptionTranslator;
} /**
* Hibernate transaction object, representing a SessionHolder.
* Used as transaction object by HibernateTransactionManager.
*/
private class HibernateTransactionObject extends JdbcTransactionObjectSupport { private SessionHolder sessionHolder; private boolean newSessionHolder; private boolean newSession; public void setSession(Session session) {
this.sessionHolder = new SessionHolder(session);
this.newSessionHolder = true;
this.newSession = true;
} public void setExistingSession(Session session) {
this.sessionHolder = new SessionHolder(session);
this.newSessionHolder = true;
this.newSession = false;
} public void setSessionHolder(SessionHolder sessionHolder) {
this.sessionHolder = sessionHolder;
this.newSessionHolder = false;
this.newSession = false;
} public SessionHolder getSessionHolder() {
return this.sessionHolder;
} public boolean isNewSessionHolder() {
return this.newSessionHolder;
} public boolean isNewSession() {
return this.newSession;
} public boolean hasSpringManagedTransaction() {
return (this.sessionHolder != null && this.sessionHolder.getTransaction() != null);
} public boolean hasHibernateManagedTransaction() {
return (this.sessionHolder != null && this.sessionHolder.getSession().getTransaction().isActive());
} public void setRollbackOnly() {
this.sessionHolder.setRollbackOnly();
if (hasConnectionHolder()) {
getConnectionHolder().setRollbackOnly();
}
} @Override
public boolean isRollbackOnly() {
return this.sessionHolder.isRollbackOnly() ||
(hasConnectionHolder() && getConnectionHolder().isRollbackOnly());
} @Override
public void flush() {
try {
this.sessionHolder.getSession().flush();
}
catch (HibernateException ex) {
throw convertHibernateAccessException(ex);
}
}
} /**
* Holder for suspended resources.
* Used internally by {@code doSuspend} and {@code doResume}.
*/
private static class SuspendedResourcesHolder { private final SessionHolder sessionHolder; private final ConnectionHolder connectionHolder; private SuspendedResourcesHolder(SessionHolder sessionHolder, ConnectionHolder conHolder) {
this.sessionHolder = sessionHolder;
this.connectionHolder = conHolder;
} private SessionHolder getSessionHolder() {
return this.sessionHolder;
} private ConnectionHolder getConnectionHolder() {
return this.connectionHolder;
}
} }
找不到LocalSessionFactoryBean的hibernateProperties那就去找LocalSessionFactoryBean的父类AbstractSessionFactoryBean,AbstractSessionFactoryBean的源码:
/*
* Copyright 2002-2012 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.orm.hibernate3; import javax.sql.DataSource; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.hibernate.HibernateException;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean; /**
* Abstract {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean} that creates
* a Hibernate {@link org.hibernate.SessionFactory} within a Spring application
* context, providing general infrastructure not related to Hibernate's
* specific configuration API.
*
* <p>This class implements the
* {@link org.springframework.dao.support.PersistenceExceptionTranslator}
* interface, as autodetected by Spring's
* {@link org.springframework.dao.annotation.PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor},
* for AOP-based translation of native exceptions to Spring DataAccessExceptions.
* Hence, the presence of e.g. LocalSessionFactoryBean automatically enables
* a PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor to translate Hibernate exceptions.
*
* <p>This class mainly serves as common base class for {@link LocalSessionFactoryBean}.
* For details on typical SessionFactory setup, see the LocalSessionFactoryBean javadoc.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 2.0
* @see #setExposeTransactionAwareSessionFactory
* @see org.hibernate.SessionFactory#getCurrentSession()
* @see org.springframework.dao.annotation.PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor
* @deprecated as of Spring 4.3, in favor of Hibernate 4.x/5.x
*/
@Deprecated
public abstract class AbstractSessionFactoryBean extends HibernateExceptionTranslator
implements FactoryBean<SessionFactory>, InitializingBean, DisposableBean { /** Logger available to subclasses */
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass()); private DataSource dataSource; private boolean useTransactionAwareDataSource = false; private boolean exposeTransactionAwareSessionFactory = true; private SessionFactory sessionFactory; /**
* Set the DataSource to be used by the SessionFactory.
* If set, this will override corresponding settings in Hibernate properties.
* <p>If this is set, the Hibernate settings should not define
* a connection provider to avoid meaningless double configuration.
* <p>If using HibernateTransactionManager as transaction strategy, consider
* proxying your target DataSource with a LazyConnectionDataSourceProxy.
* This defers fetching of an actual JDBC Connection until the first JDBC
* Statement gets executed, even within JDBC transactions (as performed by
* HibernateTransactionManager). Such lazy fetching is particularly beneficial
* for read-only operations, in particular if the chances of resolving the
* result in the second-level cache are high.
* <p>As JTA and transactional JNDI DataSources already provide lazy enlistment
* of JDBC Connections, LazyConnectionDataSourceProxy does not add value with
* JTA (i.e. Spring's JtaTransactionManager) as transaction strategy.
* @see #setUseTransactionAwareDataSource
* @see HibernateTransactionManager
* @see org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager
* @see org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.LazyConnectionDataSourceProxy
*/
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
} /**
* Return the DataSource to be used by the SessionFactory.
*/
public DataSource getDataSource() {
return this.dataSource;
} /**
* Set whether to use a transaction-aware DataSource for the SessionFactory,
* i.e. whether to automatically wrap the passed-in DataSource with Spring's
* TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy.
* <p>Default is "false": LocalSessionFactoryBean is usually used with Spring's
* HibernateTransactionManager or JtaTransactionManager, both of which work nicely
* on a plain JDBC DataSource. Hibernate Sessions and their JDBC Connections are
* fully managed by the Hibernate/JTA transaction infrastructure in such a scenario.
* <p>If you switch this flag to "true", Spring's Hibernate access will be able to
* <i>participate in JDBC-based transactions managed outside of Hibernate</i>
* (for example, by Spring's DataSourceTransactionManager). This can be convenient
* if you need a different local transaction strategy for another O/R mapping tool,
* for example, but still want Hibernate access to join into those transactions.
* <p>A further benefit of this option is that <i>plain Sessions opened directly
* via the SessionFactory</i>, outside of Spring's Hibernate support, will still
* participate in active Spring-managed transactions. However, consider using
* Hibernate's {@code getCurrentSession()} method instead (see javadoc of
* "exposeTransactionAwareSessionFactory" property).
* <p><b>WARNING:</b> When using a transaction-aware JDBC DataSource in combination
* with OpenSessionInViewFilter/Interceptor, whether participating in JTA or
* external JDBC-based transactions, it is strongly recommended to set Hibernate's
* Connection release mode to "after_transaction" or "after_statement", which
* guarantees proper Connection handling in such a scenario. In contrast to that,
* HibernateTransactionManager generally requires release mode "on_close".
* <p>Note: If you want to use Hibernate's Connection release mode "after_statement"
* with a DataSource specified on this LocalSessionFactoryBean (for example, a
* JTA-aware DataSource fetched from JNDI), switch this setting to "true".
* Otherwise, the ConnectionProvider used underneath will vote against aggressive
* release and thus silently switch to release mode "after_transaction".
* @see #setDataSource
* @see #setExposeTransactionAwareSessionFactory
* @see org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy
* @see org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager
* @see org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.OpenSessionInViewFilter
* @see org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.OpenSessionInViewInterceptor
* @see HibernateTransactionManager
* @see org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager
*/
public void setUseTransactionAwareDataSource(boolean useTransactionAwareDataSource) {
this.useTransactionAwareDataSource = useTransactionAwareDataSource;
} /**
* Return whether to use a transaction-aware DataSource for the SessionFactory.
*/
protected boolean isUseTransactionAwareDataSource() {
return this.useTransactionAwareDataSource;
} /**
* Set whether to expose a transaction-aware current Session from the
* SessionFactory's {@code getCurrentSession()} method, returning the
* Session that's associated with the current Spring-managed transaction, if any.
* <p>Default is "true", letting data access code work with the plain
* Hibernate SessionFactory and its {@code getCurrentSession()} method,
* while still being able to participate in current Spring-managed transactions:
* with any transaction management strategy, either local or JTA / EJB CMT,
* and any transaction synchronization mechanism, either Spring or JTA.
* Furthermore, {@code getCurrentSession()} will also seamlessly work with
* a request-scoped Session managed by OpenSessionInViewFilter/Interceptor.
* <p>Turn this flag off to expose the plain Hibernate SessionFactory with
* Hibernate's default {@code getCurrentSession()} behavior, supporting
* plain JTA synchronization only. Alternatively, simply override the
* corresponding Hibernate property "hibernate.current_session_context_class".
* @see SpringSessionContext
* @see org.hibernate.SessionFactory#getCurrentSession()
* @see org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager
* @see HibernateTransactionManager
* @see org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.OpenSessionInViewFilter
* @see org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.OpenSessionInViewInterceptor
*/
public void setExposeTransactionAwareSessionFactory(boolean exposeTransactionAwareSessionFactory) {
this.exposeTransactionAwareSessionFactory = exposeTransactionAwareSessionFactory;
} /**
* Return whether to expose a transaction-aware proxy for the SessionFactory.
*/
protected boolean isExposeTransactionAwareSessionFactory() {
return this.exposeTransactionAwareSessionFactory;
} /**
* Build and expose the SessionFactory.
* @see #buildSessionFactory()
* @see #wrapSessionFactoryIfNecessary
*/
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
SessionFactory rawSf = buildSessionFactory();
this.sessionFactory = wrapSessionFactoryIfNecessary(rawSf);
afterSessionFactoryCreation();
} /**
* Wrap the given SessionFactory with a proxy, if demanded.
* <p>The default implementation simply returns the given SessionFactory as-is.
* Subclasses may override this to implement transaction awareness through
* a SessionFactory proxy, for example.
* @param rawSf the raw SessionFactory as built by {@link #buildSessionFactory()}
* @return the SessionFactory reference to expose
* @see #buildSessionFactory()
*/
protected SessionFactory wrapSessionFactoryIfNecessary(SessionFactory rawSf) {
return rawSf;
} /**
* Return the exposed SessionFactory.
* Will throw an exception if not initialized yet.
* @return the SessionFactory (never {@code null})
* @throws IllegalStateException if the SessionFactory has not been initialized yet
*/
protected final SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
if (this.sessionFactory == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("SessionFactory not initialized yet");
}
return this.sessionFactory;
} /**
* Close the SessionFactory on bean factory shutdown.
*/
@Override
public void destroy() throws HibernateException {
logger.info("Closing Hibernate SessionFactory");
try {
beforeSessionFactoryDestruction();
}
finally {
this.sessionFactory.close();
}
} /**
* Return the singleton SessionFactory.
*/
@Override
public SessionFactory getObject() {
return this.sessionFactory;
} @Override
public Class<? extends SessionFactory> getObjectType() {
return (this.sessionFactory != null ? this.sessionFactory.getClass() : SessionFactory.class);
} @Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
} /**
* Build the underlying Hibernate SessionFactory.
* @return the raw SessionFactory (potentially to be wrapped with a
* transaction-aware proxy before it is exposed to the application)
* @throws Exception in case of initialization failure
*/
protected abstract SessionFactory buildSessionFactory() throws Exception; /**
* Hook that allows post-processing after the SessionFactory has been
* successfully created. The SessionFactory is already available through
* {@code getSessionFactory()} at this point.
* <p>This implementation is empty.
* @throws Exception in case of initialization failure
* @see #getSessionFactory()
*/
protected void afterSessionFactoryCreation() throws Exception {
} /**
* Hook that allows shutdown processing before the SessionFactory
* will be closed. The SessionFactory is still available through
* {@code getSessionFactory()} at this point.
* <p>This implementation is empty.
* @see #getSessionFactory()
*/
protected void beforeSessionFactoryDestruction() {
} }
可以看到C3P0数据源com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource的父类是com.mchange.v2.c3p0.AbstractComboPooledDataSource,com.mchange.v2.c3p0.AbstractComboPooledDataSource的父类是com.mchange.v2.c3p0.impl.AbstractPoolBackedDataSource,com.mchange.v2.c3p0.AbstractComboPooledDataSource和com.mchange.v2.c3p0.impl.AbstractPoolBackedDataSource都实现了
 com.mchange.v2.c3p0.PooledDataSource接口,而接口com.mchange.v2.c3p0.PooledDataSource的父类是javax.sql.DataSource。
com.mchange.v2.c3p0.PooledDataSource接口,而接口com.mchange.v2.c3p0.PooledDataSource的父类是javax.sql.DataSource。
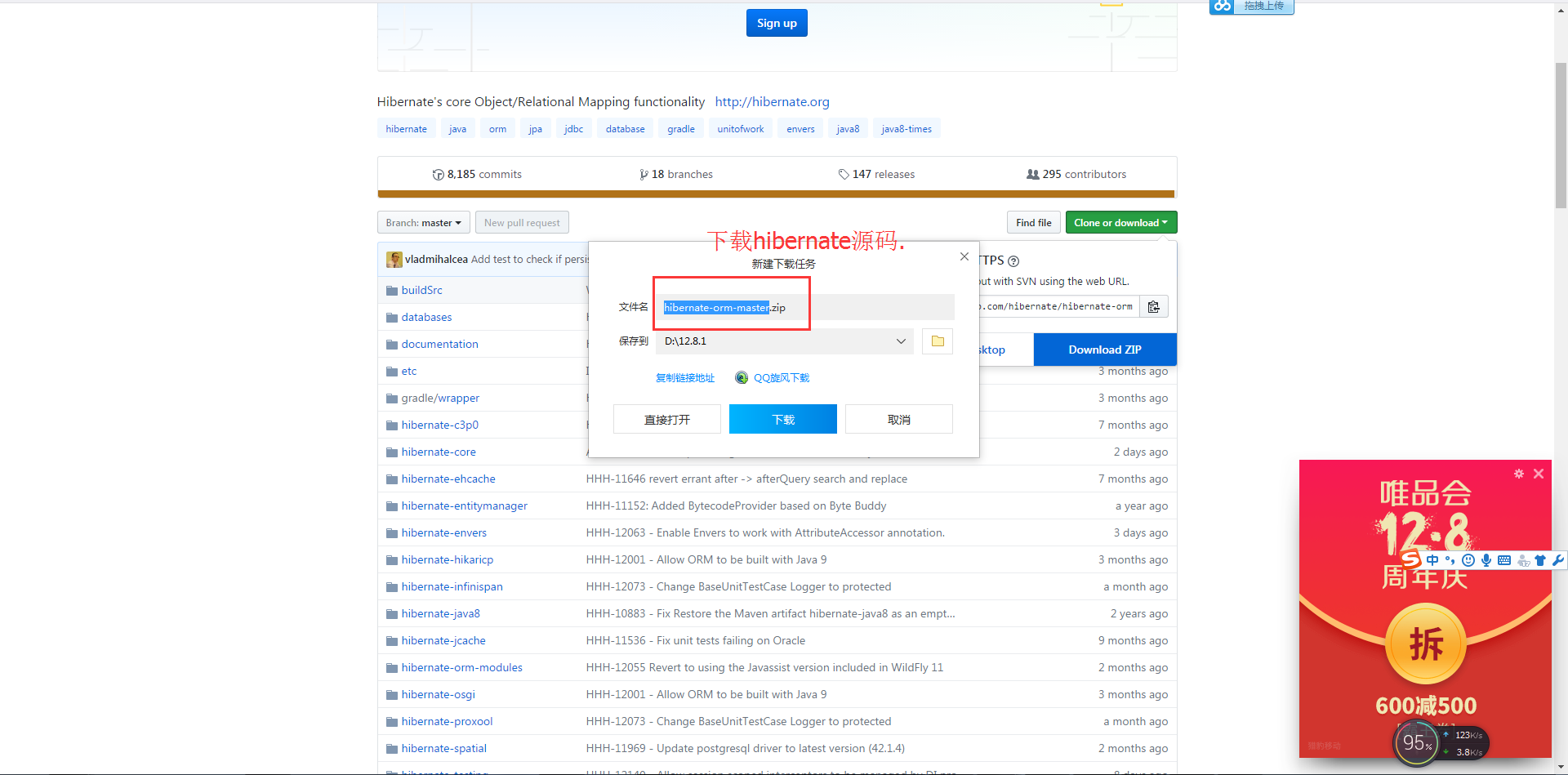
SessionFactory源码在hibernate3源码包中的位置:D:\12.8.1\hibernate-orm-master\hibernate-orm-master\hibernate-core\src\main\java\org\hibernate\SessionFactory.java
SessionFactory的源码:
/*
* Hibernate, Relational Persistence for Idiomatic Java
*
* License: GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL), version 2.1 or later.
* See the lgpl.txt file in the root directory or <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl-2.1.html>.
*/
package org.hibernate; import java.io.Serializable;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.naming.Referenceable;
import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory; import org.hibernate.boot.spi.SessionFactoryOptions;
import org.hibernate.engine.spi.FilterDefinition;
import org.hibernate.jpa.HibernateEntityManagerFactory;
import org.hibernate.metadata.ClassMetadata;
import org.hibernate.metadata.CollectionMetadata;
import org.hibernate.stat.Statistics; /**
* The main contract here is the creation of {@link Session} instances. Usually
* an application has a single {@link SessionFactory} instance and threads
* servicing client requests obtain {@link Session} instances from this factory.
* <p/>
* The internal state of a {@link SessionFactory} is immutable. Once it is created
* this internal state is set. This internal state includes all of the metadata
* about Object/Relational Mapping.
* <p/>
* Implementors <strong>must</strong> be threadsafe.
*
* @see org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration
*
* @author Gavin King
* @author Steve Ebersole
*/
public interface SessionFactory extends EntityManagerFactory, HibernateEntityManagerFactory, Referenceable, Serializable, java.io.Closeable {
/**
* Get the special options used to build the factory.
*
* @return The special options used to build the factory.
*/
SessionFactoryOptions getSessionFactoryOptions(); /**
* Obtain a {@link Session} builder.
*
* @return The session builder
*/
SessionBuilder withOptions(); /**
* Open a {@link Session}.
* <p/>
* JDBC {@link Connection connection(s} will be obtained from the
* configured {@link org.hibernate.engine.jdbc.connections.spi.ConnectionProvider} as needed
* to perform requested work.
*
* @return The created session.
*
* @throws HibernateException Indicates a problem opening the session; pretty rare here.
*/
Session openSession() throws HibernateException; /**
* Obtains the current session. The definition of what exactly "current"
* means controlled by the {@link org.hibernate.context.spi.CurrentSessionContext} impl configured
* for use.
* <p/>
* Note that for backwards compatibility, if a {@link org.hibernate.context.spi.CurrentSessionContext}
* is not configured but JTA is configured this will default to the {@link org.hibernate.context.internal.JTASessionContext}
* impl.
*
* @return The current session.
*
* @throws HibernateException Indicates an issue locating a suitable current session.
*/
Session getCurrentSession() throws HibernateException; /**
* Obtain a {@link StatelessSession} builder.
*
* @return The stateless session builder
*/
StatelessSessionBuilder withStatelessOptions(); /**
* Open a new stateless session.
*
* @return The created stateless session.
*/
StatelessSession openStatelessSession(); /**
* Open a new stateless session, utilizing the specified JDBC
* {@link Connection}.
*
* @param connection Connection provided by the application.
*
* @return The created stateless session.
*/
StatelessSession openStatelessSession(Connection connection); /**
* Retrieve the statistics fopr this factory.
*
* @return The statistics.
*/
Statistics getStatistics(); /**
* Destroy this <tt>SessionFactory</tt> and release all resources (caches,
* connection pools, etc).
* <p/>
* It is the responsibility of the application to ensure that there are no
* open {@link Session sessions} before calling this method as the impact
* on those {@link Session sessions} is indeterminate.
* <p/>
* No-ops if already {@link #isClosed closed}.
*
* @throws HibernateException Indicates an issue closing the factory.
*/
void close() throws HibernateException; /**
* Is this factory already closed?
*
* @return True if this factory is already closed; false otherwise.
*/
boolean isClosed(); /**
* Obtain direct access to the underlying cache regions.
*
* @return The direct cache access API.
*/
@Override
Cache getCache(); /**
* Obtain a set of the names of all filters defined on this SessionFactory.
*
* @return The set of filter names.
*/
Set getDefinedFilterNames(); /**
* Obtain the definition of a filter by name.
*
* @param filterName The name of the filter for which to obtain the definition.
* @return The filter definition.
* @throws HibernateException If no filter defined with the given name.
*/
FilterDefinition getFilterDefinition(String filterName) throws HibernateException; /**
* Determine if this session factory contains a fetch profile definition
* registered under the given name.
*
* @param name The name to check
* @return True if there is such a fetch profile; false otherwise.
*/
boolean containsFetchProfileDefinition(String name); /**
* Retrieve this factory's {@link TypeHelper}.
*
* @return The factory's {@link TypeHelper}
*/
TypeHelper getTypeHelper(); // ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// Deprecations /**
* Retrieve the {@link ClassMetadata} associated with the given entity class.
*
* @param entityClass The entity class
*
* @return The metadata associated with the given entity; may be null if no such
* entity was mapped.
*
* @throws HibernateException Generally null is returned instead of throwing.
*
* @deprecated Use the descriptors from {@link #getMetamodel()} instead
*/
@Deprecated
ClassMetadata getClassMetadata(Class entityClass); /**
* Retrieve the {@link ClassMetadata} associated with the given entity class.
*
* @param entityName The entity class
*
* @return The metadata associated with the given entity; may be null if no such
* entity was mapped.
*
* @throws HibernateException Generally null is returned instead of throwing.
* @since 3.0
*
* @deprecated Use the descriptors from {@link #getMetamodel()} instead
*/
@Deprecated
ClassMetadata getClassMetadata(String entityName); /**
* Get the {@link CollectionMetadata} associated with the named collection role.
*
* @param roleName The collection role (in form [owning-entity-name].[collection-property-name]).
*
* @return The metadata associated with the given collection; may be null if no such
* collection was mapped.
*
* @throws HibernateException Generally null is returned instead of throwing.
*
* @deprecated Use the descriptors from {@link #getMetamodel()} instead
*/
@Deprecated
CollectionMetadata getCollectionMetadata(String roleName); /**
* Retrieve the {@link ClassMetadata} for all mapped entities.
*
* @return A map containing all {@link ClassMetadata} keyed by the
* corresponding {@link String} entity-name.
*
* @throws HibernateException Generally empty map is returned instead of throwing.
*
* @since 3.0 changed key from {@link Class} to {@link String}.
*
* @deprecated Use the descriptors from {@link #getMetamodel()} instead
*/
@Deprecated
Map<String,ClassMetadata> getAllClassMetadata(); /**
* Get the {@link CollectionMetadata} for all mapped collections.
*
* @return a map from <tt>String</tt> to <tt>CollectionMetadata</tt>
*
* @throws HibernateException Generally empty map is returned instead of throwing.
*
* @deprecated Use the descriptors from {@link #getMetamodel()} instead
*/
@Deprecated
Map getAllCollectionMetadata();
}
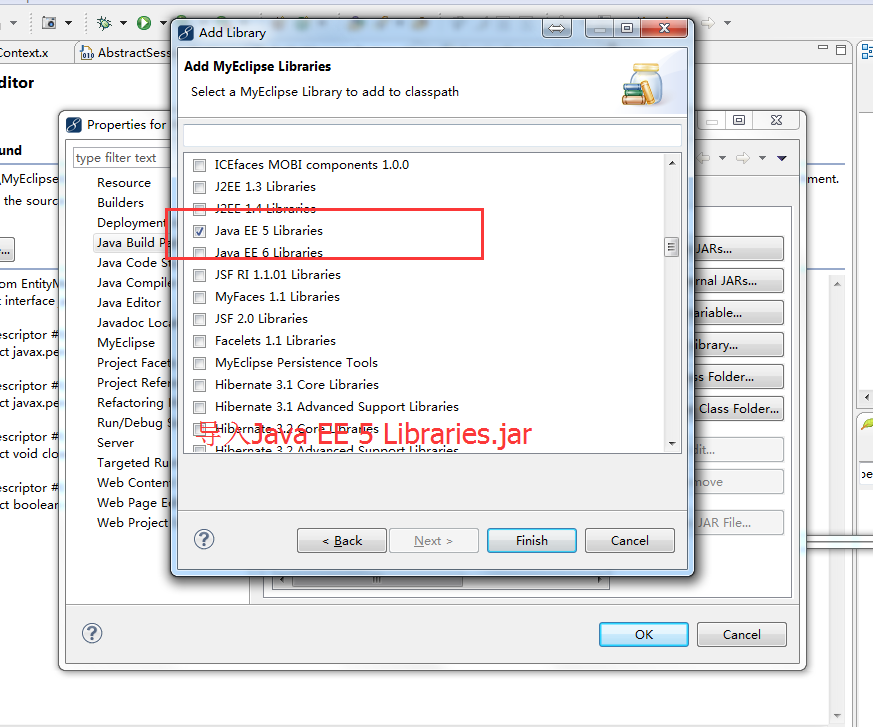
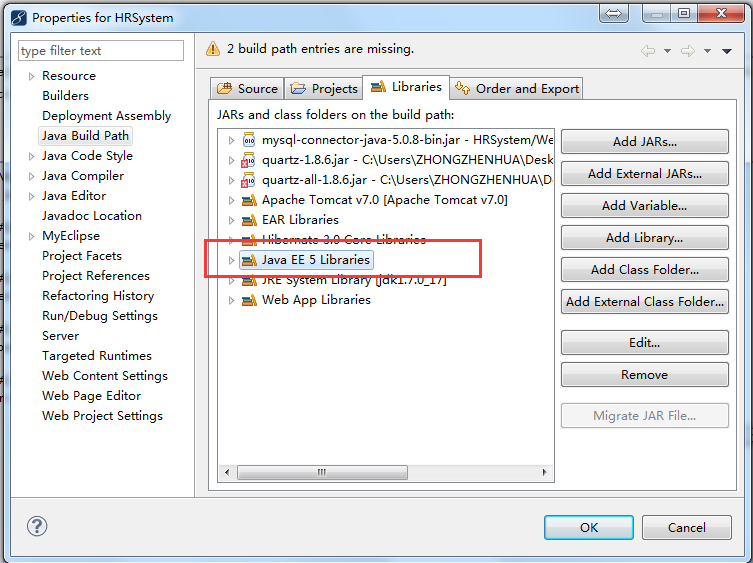 HibernateEntityManagerFactory的源码在hibernate3源码包hibernate-orm-master中的位置:D:\12.8.1\hibernate-orm-master\hibernate-orm-master\hibernate-core\src\main\java\org\hibernate\ejb\HibernateEntityManagerFactory.java和D:\12.8.1\hibernate-orm-master\hibernate-orm-master\hibernate-core\src\main\java\org\hibernate\jpa\HibernateEntityManagerFactory.java
HibernateEntityManagerFactory的源码在hibernate3源码包hibernate-orm-master中的位置:D:\12.8.1\hibernate-orm-master\hibernate-orm-master\hibernate-core\src\main\java\org\hibernate\ejb\HibernateEntityManagerFactory.java和D:\12.8.1\hibernate-orm-master\hibernate-orm-master\hibernate-core\src\main\java\org\hibernate\jpa\HibernateEntityManagerFactory.java

EntityManagerFactoryImpl的源码在hibernate3源码包hibernate-orm-stable中的位置:D:\12.8.1\hibernate-orm-stable\hibernate-entitymanager\src\main\java\org\hibernate\ejb\EntityManagerImpl.java
不用查LocalSessionFactoryBean的源码查的那么辛苦了,在Hibernate发布包hibernate-distribution-3.6.0.Final-dist的project\etc路径下,提供了一个hibernate.properties文件。该文件详细列出了Hibernate配置文件的所有属性。下面列出hibernate.properties文件里面的MySQL配置段,使用该配置段就可以快速配置Hibernate与MySQL数据库的连接。
hibernate.properties文件里面可以配置MySQL数据库的方言
## MySQL #hibernate.dialect org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
#hibernate.dialect org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLInnoDBDialect
#hibernate.dialect org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLMyISAMDialect
#hibernate.connection.driver_class com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
#hibernate.connection.url jdbc:mysql:///test
#hibernate.connection.username gavin
#hibernate.connection.password
hibernate.properties文件里面可以配置自动模式导出SQL脚本,
## auto schema export #hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto create-drop
#hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto create
#hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto update
#hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto validate
hibernate.properties文件里面还可以配置是否在后台打印SQL语句
#hibernate.show_sql true
hibernate.properties文件里面还可以配置是否在后台格式化打印SQL语句
hibernate.format_sql true
重新生成一下实体类对应的
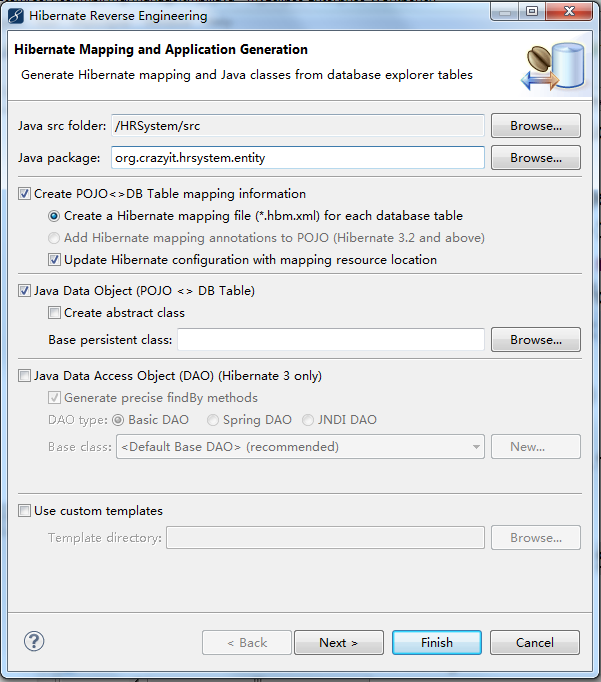

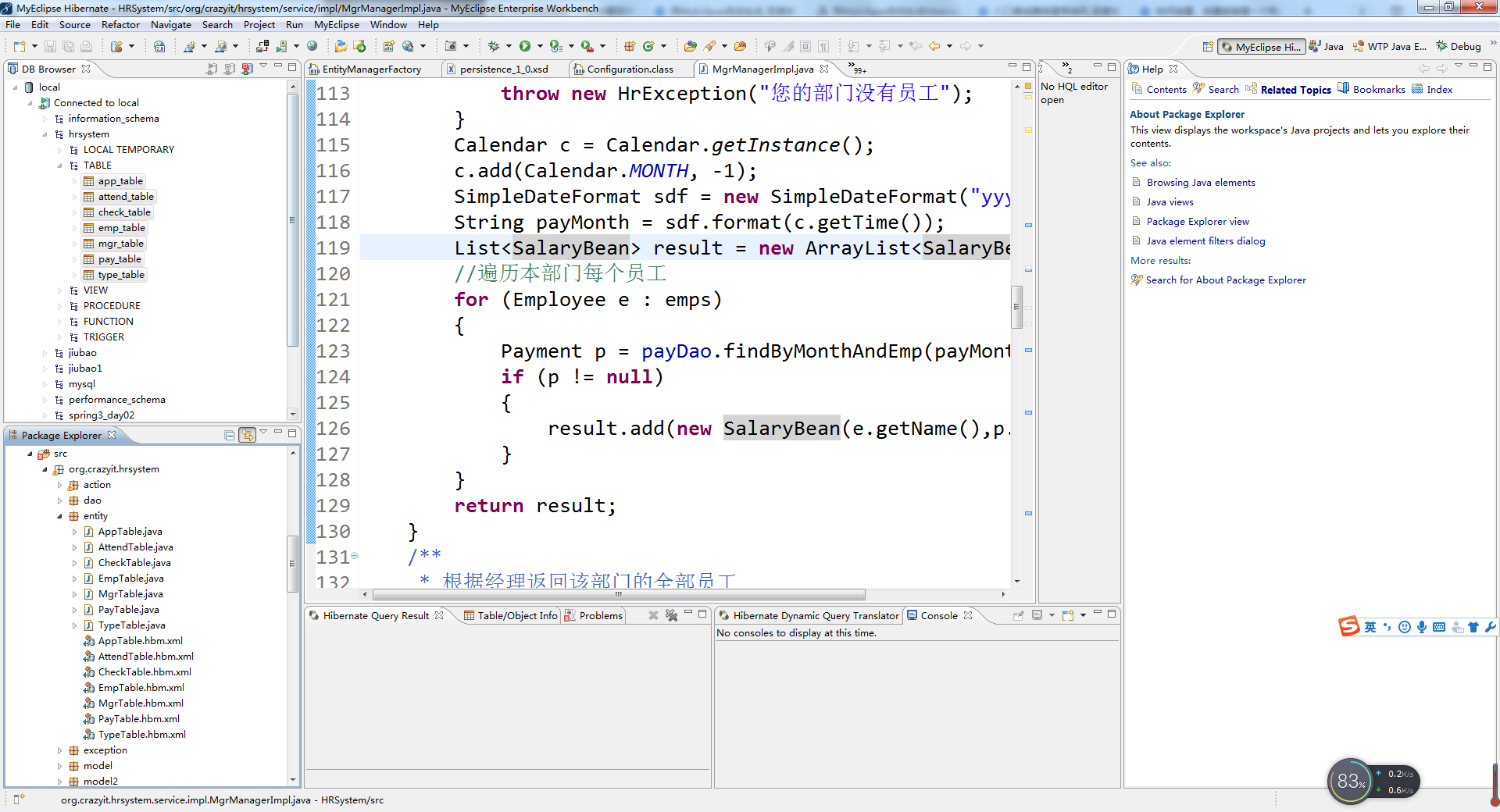

- commons-logging.jar (59.4 KB)
- 下载次数: 692
- commons-logging-1.1.jar (51.6 KB)
- 下载次数: 1537
导入aspectjweaver.jar试试
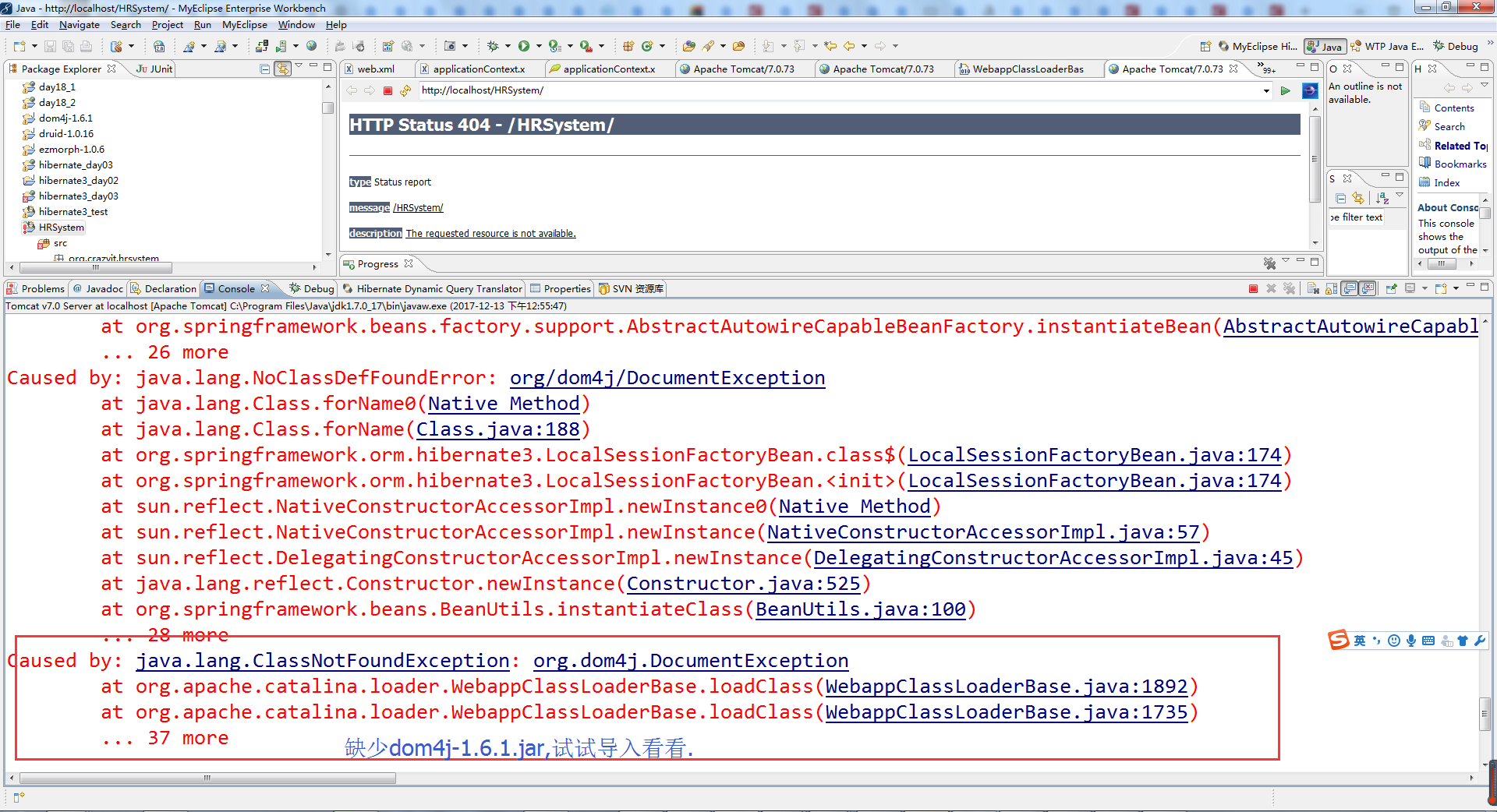

提示缺少jar包,应该导入commons-collections.jar
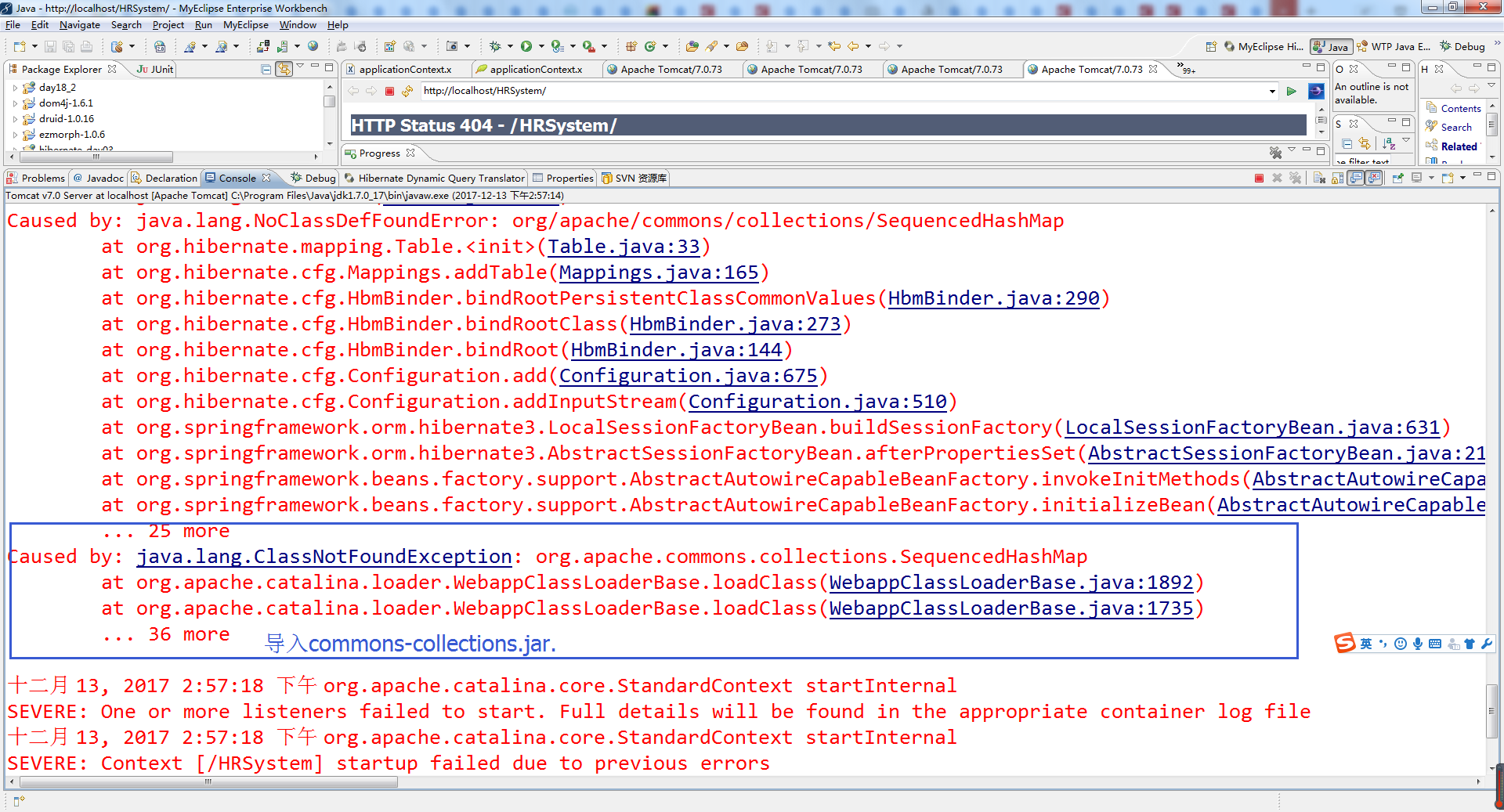
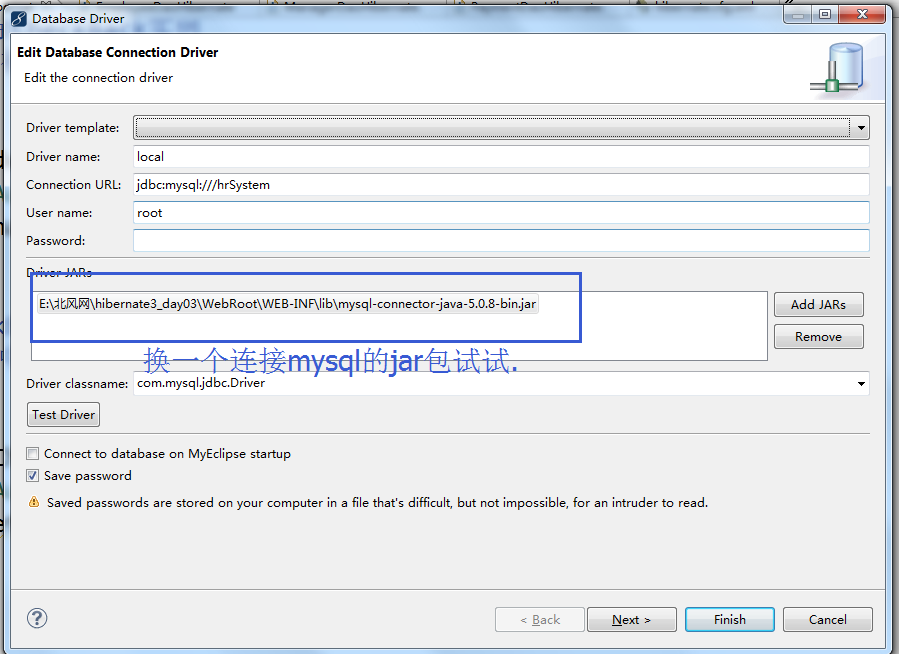
试用ermaster,支持逆向工程(从数据库导入生成ER图)
- Eclipse安装此插件的地址是:http://ermaster.sourceforge.net/update-site/

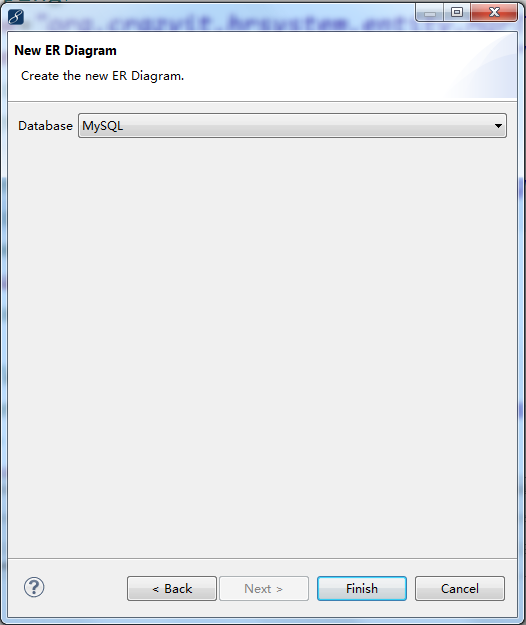
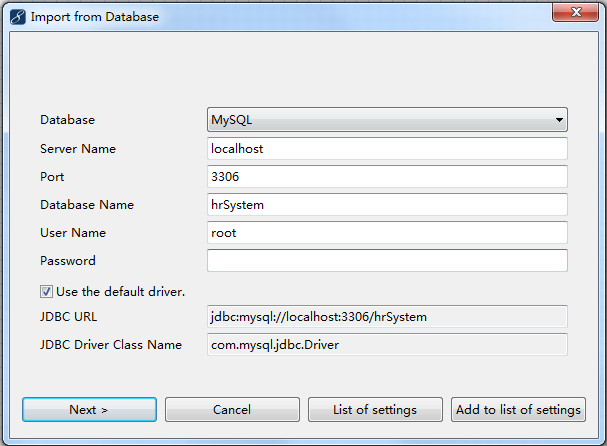
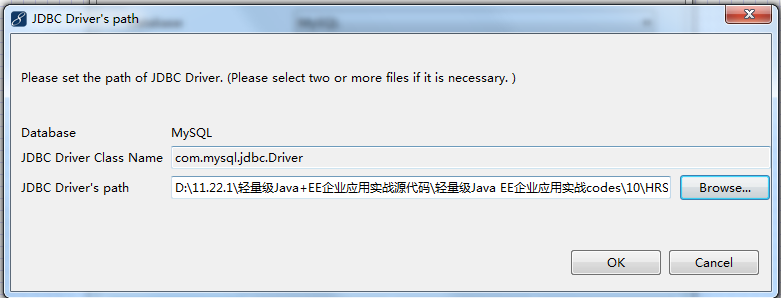


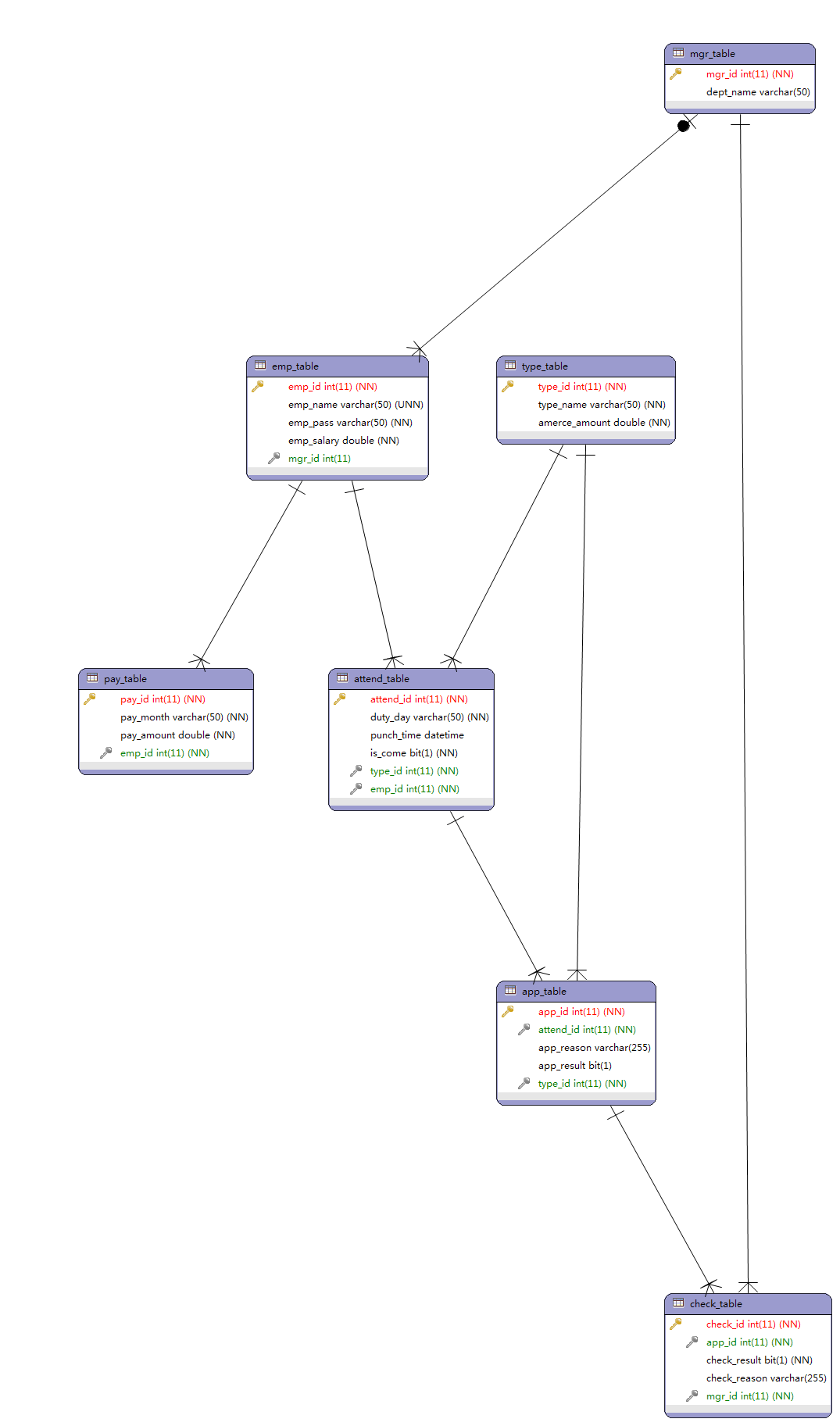
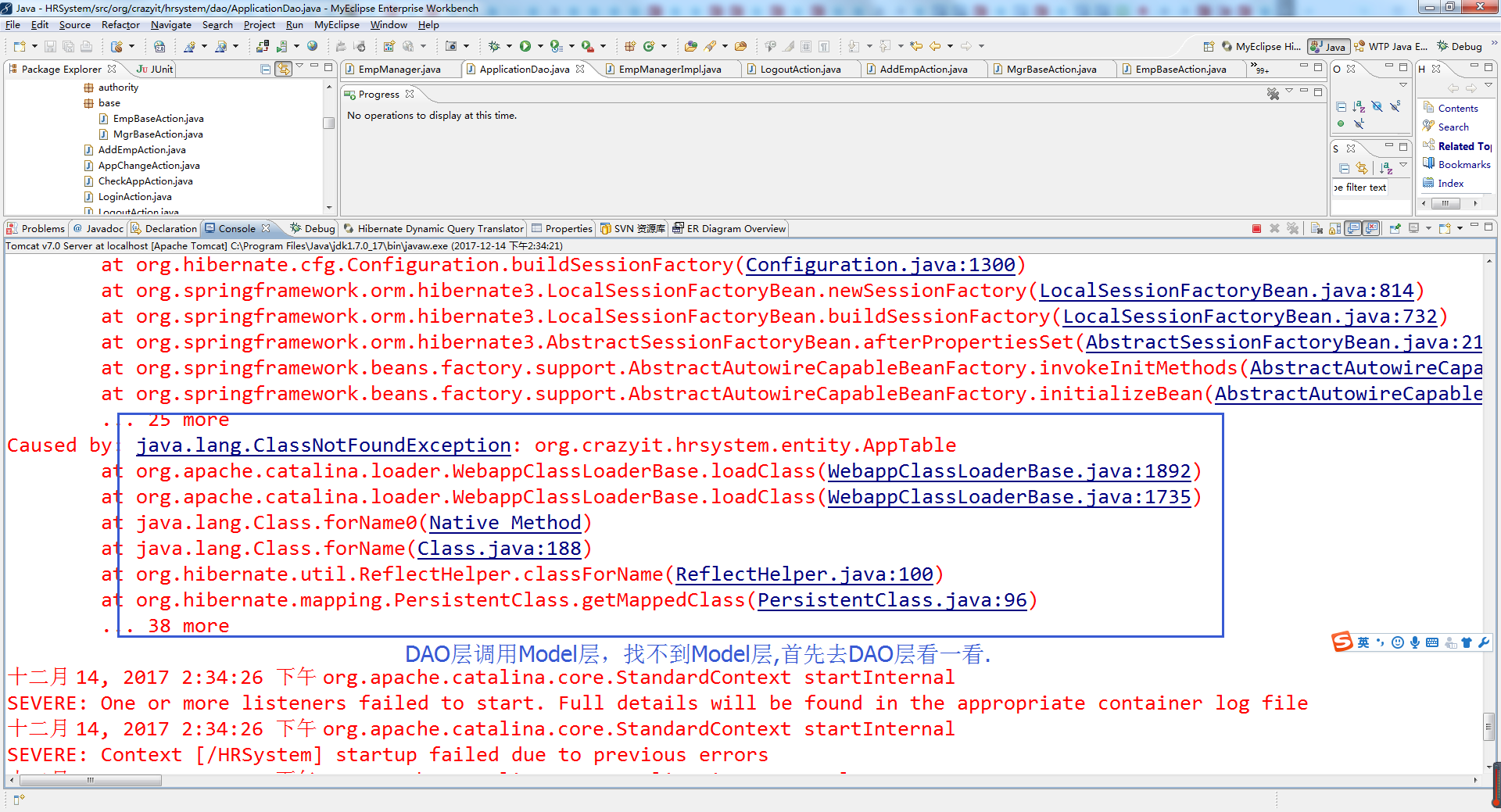
最新文章
- JavaScript常见的五种数组去重的方式
- PhoneGap初试!
- 轻松自动化---selenium-webdriver(python) (二)
- 使用UISegmentedControl的一个注意事项
- bootstrap-11
- qt下调用win32api 修改分辨率
- 【CodeForces 624C】Graph and String
- [BZOJ3786]星系探索
- 【crunch bang】程序中文化
- Android AVD创建及设置中各参数详解
- 洛谷P1519 穿越栅栏 Overfencing
- eclipse 插件
- win7、xp下Meclipse SVN用户名修改
- struct内存对齐
- CC++初学者编程教程(15) 基于cocos2dx的安卓打包环境
- Android Realm数据库使用指南
- 201521123103 《Java学习笔记》 第六周学习总结
- 基于python的统计公报关键数据爬取
- matlab 写文件
- 从锅炉工到AI专家(10)