C++ 双链表基本操作
2024-08-25 14:55:18
上一篇博客主要总结了单向链表,这次再总结一下双向链表.
1.概念
双向链表也叫双链表,是链表的一种,它的每个数据结点中都有两个指针,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱。所以,从双向链表中的任意一个结点开始,都可以很方便地访问它的前驱结点和后继结点。一般我们都构造双向循环链表。
结构图如下所示:
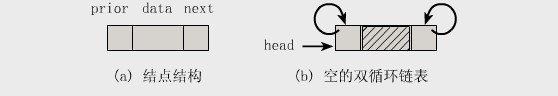
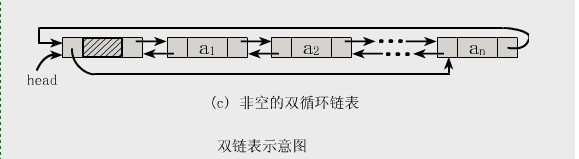
2.基本操作实例
DoubleList.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "DoubleList.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
DoubleList::DoubleList()
{
pDoubleListNode pDouList = NULL;
// 创建双链表
CreateDouList(pDouList);
PrintDouList(pDouList);
// 打印逆序链表
PrintDouReverseList(pDouList);
// 节点后插入节点
InsertNodeAfter(pDouList);
PrintDouList(pDouList);
// 节点前插入节点
InsertNodeBefore(pDouList);
PrintDouList(pDouList);
// 删除节点
DeleteNode(pDouList);
PrintDouList(pDouList);
// 删除链表
DeleteDouList(pDouList);
PrintDouList(pDouList);
system("PAUSE");
}
DoubleList::~DoubleList()
{
}
//创建双向链表
void DoubleList::CreateDouList(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
char x; // 定义成char型是用于输入'q'时可以退出,其实定义成int也能退出
pDoubleListNode p, s;
head = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
head->next = NULL;
head->prior = NULL; // 构造头结点p
p = head;
printf("\n输入双向链表的元素,每输入一个元素后按回车,输入q表示结束.\n");
fflush(stdin); //清空输入缓冲区
x = getchar();
while (x != 'q')
{
s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
s->data = x - ''; // 得到的是输入字符的ASCII码,减去30H就变成想要的数字
s->next = NULL;
s->prior = p;
p->next = s;
p = s;
fflush(stdin);
x = getchar();
}
if (x == 'q')
{
printf("双向链表构造完毕!\n");
}
}
//打印双向链表
void DoubleList::PrintDouList(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
pDoubleListNode p;
printf("\n打印出双向链表数据为:\n");
if (!IsDouListEmpty(head))
{
p = head->next;
while (p)
{
printf("%d\n", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
}
}
//逆序打印双向链表
void DoubleList::PrintDouReverseList(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
pDoubleListNode p;
printf("\n打印出逆序双向链表数据为:\n");
if (!IsDouListEmpty(head))
{
p = head->next;
while (p->next)
{
p = p->next;
}
while (p->prior)
{
printf("%d \n", p->data);
p = p->prior;
}
}
}
//求链表长度
int DoubleList::GetDouListLength(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
int length = ;
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("链表不存在,请先初始化!\n");
}
else
{
pDoubleListNode p = head->next;
while (p)
{
length++;
p = p->next;
}
}
return length;
}
//判断链表是否为空
bool DoubleList::IsDouListEmpty(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("链表不存在,请先初始化!\n");
return true;
}
else if (head->next == NULL)
{
printf("链表为空!\n");
return true;
} return false;
}
//把双向链表置空
void DoubleList::ClearDouList(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("链表不存在,请先初始化!\n");
}
else
{
pDoubleListNode p, q;
p = q = head->next; //是p、q指向第一个元素
head->next = NULL;
while (p) //逐个释放元素所占内存
{
p = p->next;
free(q);
q = p;
}
}
}
// 删除双向链表
void DoubleList::DeleteDouList(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
printf("\n删除双向链表\n");
ClearDouList(head);
free(head);
head = NULL;
}
// 在双向链表中第i个位置后面插入元素
void DoubleList::InsertNodeAfter(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
int data, pos;
pDoubleListNode p, s;
p = head;
int i = ;
printf("\n在双向链表中第i个位置后面插入元素\n");
printf("请输入要插入的元素和位置:\n");
scanf_s("%d%d", &data, &pos, );
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("链表不存在,请先初始化!\n");
}
else if (head->next == NULL)
{
printf("链表为空,插入第一个元素!\n");
s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
s->prior = NULL;
s->next = NULL;
head->next = s; // 将新结点插入head后
}
else if (pos< || pos>GetDouListLength(head) + )
{
printf("插入位置错误!\n");
}
else
{
while (i < pos)
{
p = p->next;
i++;
}
if (i == GetDouListLength(head)) //如果在最后一个元素后面插入data
{
s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
s->next = NULL;
s->prior = p;
p->next = s;
}
else
{
s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
s->next = p->next;
p->next->prior = s;
p->next = s;
s->prior = p;
}
}
}
// 在双向链表中第i个位置前面插入元素
void DoubleList::InsertNodeBefore(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
int data, pos;
pDoubleListNode p, s;
p = head;
int i = ;
printf("\n在双向链表中第i个位置前面插入元素\n");
printf("请输入要插入的元素和位置:\n");
scanf_s("%d%d", &data, &pos, );
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("链表不存在,请先初始化!\n");
}
else if (head->next == NULL)
{
printf("链表为空,插入第一个元素!\n");
s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
s->prior = NULL;
s->next = NULL;
head->next = s; // 将新结点插入head后
}
else if (pos< || pos>GetDouListLength(head) + )
{
printf("插入位置错误!\n");
}
else
{
while (i < pos)
{
p = p->next;
i++;
}
if (i == ) // 如果在第一个元素前面插入data
{
s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
head->next = s; // 将新结点插入head后
s->prior = head; // 新结点的前结点指向头结点
s->next = p; // 新结点的后结点指向原head的后结点
p->prior = s ; // 原第一个结点的前结点指向新结点
}
else
{
s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
s->prior = p->prior;
s->next = p;
p->prior->next = s;
p->prior = s;
}
}
}
//删除双向链表中的第i个元素
void DoubleList::DeleteNode(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
int pos;
int i = ;
pDoubleListNode p = head;
printf("\n在双向链表中删除第i个位置的元素\n");
printf("请输入要删除的位置:");
scanf_s("%d", &pos, ); if (IsDouListEmpty(head))
{
return;
}
else if (pos< || pos>GetDouListLength(head))
{
printf("删除的位置不存在!\n");
}
else
{
while (i < pos)
{
p = p->next;
i++;
}
if (i == GetDouListLength(head))
{
p->prior->next = NULL;
free(p);
}
else
{
p->prior->next = p->next;
p->next->prior = p->prior;
free(p);
}
}
}
DoubleList.h
#pragma once
typedef struct DoubleListNode
{
int data; //数据
struct DoubleListNode *prior; //前驱
struct DoubleListNode *next; //后继
}DoubleListNode, *pDoubleListNode;
class DoubleList
{
public:
DoubleList();
~DoubleList();
//初始化双向链表
void DoubleList::CreateDouList(pDoubleListNode &head);
//打印双向链表
void DoubleList::PrintDouList(pDoubleListNode &head);
//逆序打印双向链表
void DoubleList::PrintDouReverseList(pDoubleListNode &head);
//求链表长度
int DoubleList::GetDouListLength(pDoubleListNode &head);
//判断链表是否为空
bool DoubleList::IsDouListEmpty(pDoubleListNode &head);
//把双向链表置空
void DoubleList::ClearDouList(pDoubleListNode &head);
//删除双向链表
void DoubleList::DeleteDouList(pDoubleListNode &head);
//在双向链表中第i个位置后面插入元素m
void DoubleList::InsertNodeAfter(pDoubleListNode &head);
// 在双向链表中第i个位置前面插入元素
void DoubleList::InsertNodeBefore(pDoubleListNode &head);
//删除双向链表中的第i个元素
void DoubleList::DeleteNode(pDoubleListNode &head);
};
3.对链表插入节点的理解
例如在节点i前插入一个新的节点(即上面代码中的InsertNodeBefore函数):
链表结构体为:
typedef struct DoubleListNode
{
int data; // 数据
struct DoubleListNode *prior; // 前驱
struct DoubleListNode *next; // 后继
}DoubleListNode, *pDoubleListNode;
假设该链表由五个节点构成,分别为A,B,C,D,E
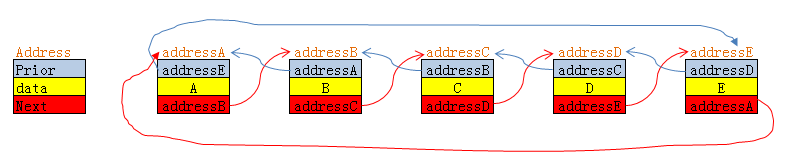
图中假设了A,B,C,D,E的地址分别为:addressA,addressB,addressC,addressD,addressE。
下面将分析链表的前插的例子:
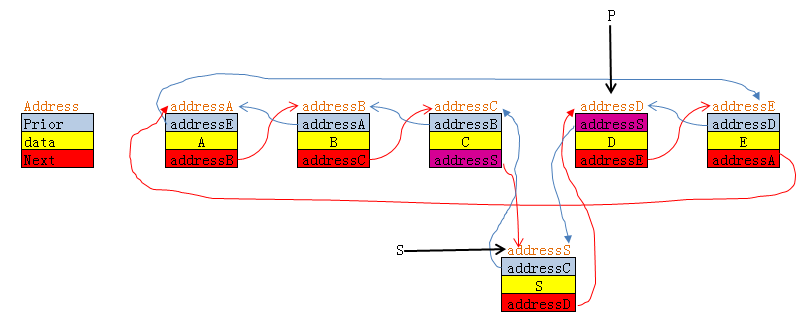
双链表的前插,下面这是在节点"D"前插入一个新的节点"S"的代码和分析
s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode)); // 申请一段内存空间,指针指向首地址为addressS
s->data = data; // 给节点S的数据赋值data
s->prior = p->prior; // p指向D节点, p->prior表示addressC,将它赋给s->prior,则s->prior里面的值是addressC,从而指向addressC这个地址即节点C,如下图S节点的蓝线
s->next = p; // p是addressD,将它赋给s->next,s->next中的值为addressD,也即s->next指向了D,如下图S节点的红线
p->prior->next = s; // p->prior 是addressC,即节点C,所以p->prior->next相当于没插入S之前的addressD,插入S后,将S的首地址即addressS赋给这个位置,所以此时,由C 到D的红线断裂,这个红线目标变成了S,如下图C节点的红线
p->prior = s; // 同理,p->prior也指向了S,即p->prior中addressC变成了addressS, D指向C的蓝线断裂。变成如下图D节点指向S节点的蓝线.
最新文章
- Oracle在线重定义DBMS_REDEFINITION 普通表—>分区表
- sublime3+quick3.5 完整使用教程
- 介绍四款windows下的神器
- sqlite数据库安装配置
- 16.2.2 Space Needed for keys
- HTC Vive开发笔记之手柄震动
- 【原】兼容IOS6以及旧版本的旋转处理方法,心得总结
- 在Function对象上扩展method方法
- android学习——Android Studio下创建menu布局文件
- Limiting To Select Only 5 Check Boxes Out Of Ten In Oracle Forms
- Android LogCat使用详解
- [转] linux之sed用法
- Ruby设计模式透析之 —— 适配器(Adapter)
- Java IO 过滤流 BufferedInput/OutputStream
- ###服务(Service)
- JSTL之forEach的使用详解(简单的技术说得很详细)
- require/exports 和 import/export 区别
- linux 基本操作
- 【Android开源库】美团等APP城市选择
- HDU5730