《Unix/Linux系统编程》第九周学习笔记
2024-10-21 23:14:05
《Unix/Linux系统编程》第九周学习笔记
信号和中断
- 中断”是从I/O设备或协处理器发送到CPU的外部请求,它将CPU从正常执行转移 到中断处理。与发送给CPU的中断请求一样,“信号”是发送给进程的请求,将进程从正常执行转移到中断处理。
- 进程:一个“进程”就是一系列活动。广义的 “进程”包括:从事日常事务的人。在用户模式或内核模式下运行的Unix/Linux进程。执行机器指令的CPU。
- 中断是发送给“进程”的事件,它将“进程”从正常活动转移到其他活动,称为“中断处理”。“进程”可在完成“中断”处理后恢复正常活动。
根据来源,中断可分为三类:
- 来自硬件的中断;
- 来自其他人的中断;
- 自己造成的中断。
按照紧急程度,中断可分为以下几类:
- 不可屏蔽(NMI);
- 可屏蔽。
进程中断
- 这类中断是发送给进程的中断。当某进程正在执行时,可能会收到来自3个不同来源的中断:
- 来自硬件的中断:终端、间隔定时器的“Ctrl+C”组合键等。
- 来自其他进程的中断:kill(pid,SIG#), death_of_child等。
- 自己造成的中断:除以0、无效地址等。
- 每个进程中断都被转换为一个唯一ID号,发送给进程。与多种类的人员中断不同,我们始终可限制在一个进程中的中断的数量。
- Unix/Linux中的进程中断称为信号,编号为1到31。
- 进程的PROC结构体中有对应每个信号的动作函数,进程可在收到信号后执行该动作函数。
- 与人员类似,进程也可屏蔽某些类型的信号,以推迟处理。必要时,进程还可能会修改信号动作函数。
硬件中断:
- 这类中断是发送给处理器或CPU的信号。它们也有三个可能的来源:
- 来自硬件的中断:定时器、I/O设备等.
- 来自其他处理器的中断:FFP. DMA、多处理器系统中的其他CPU。
- 自己造成的中断:除以0、保护错误、INT指令。
- 毎个中断都有唯一的中断向量号。动作函数是中断向量表中的中断处理程序。
进程的陷阱错误
- 进程可能会自己造成中断。这些中断是由被CPU识别为异常的错误引起的,例如除以0、无效地址、非法指令、越权等。
- 当进程遇到异常时,它会陷入操作系统内核,将陷阱原因转换为信号编号,并将信号发送给自己。如果在用户模式下发生异常,则进程的默认操作是终止,并使用一个可选的内存转储进行调试。
信号处理
#define SIGHUP 1
#define SIGINT 2
#define SIGQUIT 3
#define SIGILL 4
#define SIGTRAP 5
#define SIGABRT 6
#define SIGIOT 6
#define SIGBUS 7
#define SIGFPE 8
#define SIGKILL 9
#define SIGUSR1 10
#define SIGSEGV 11
#define SIGUSR2 12
#define SIGPIPE 13
#define SIGALRM 14
#define SIGTERM 15
#define SIGSTKFLT 16
#define SIGCHLD 17
#define SIGCONT 18
#define SIGSTOP 19
#define SIGTSTP 20
#dpfine STGTTTN 21
#define SIGTTOU 22
#define SIGURG 23
#define SIGXCPU 24
#define SIGXFSZ 25
#define SIGVTALRM 26
#define SIGPROF 27
#define SIGWINCH 28
#define SIGPOLL 29
#define SIGPWR 30
#define SIGSYS 31
Unix/Linux信号示例
按“Ctrl+C”组合键通常会导致当前运行的进程终止。原因如下:
- “Ctr1+C”组合键会生成一个键盘硬件中断。键盘中断处理程序将“Ctrl+C”组合键转换为SIGINT(2)信号,发送给终端上的所有进程,并唤醒等待键盘输人的进程。在内核模式下,每个进程都要检查和处理未完成的信号。进程对大多数信号的默认操作是调用内核的kexit(exitValue)函数来终止。在Linux中,exitValue的低位字节是导致进程终止的信号编号。
用户可使用nohup a.out 命令在后台运行一个程序。即使在用户退出后,进程仍将继续运行。
- nobup命令会使sh像往常一样复刻子进程来执行程序,但是子进程会忽略SIGHuP(1)信号。当用户退出时,sh会向与终端有关的所有进程发送一个SIGHUP信号。后台进程在接收到这一信号后,会忽略它并继续运行。为防止后台进程使用终端进行I/O,后台进程通常会断开与终端的连接(通过将其文件描述符0、1、2重定向到/dev/null),使其完全不受任何面向终端信号的影响。
用户可以使用sh命令killpid(orkill-s9pia)杀死该进程。方法如下。
- 执行杀死的进程向pid标识的目标进程发送一个SIGTERM ( 15 )信号,请求它死亡。目标进程将会遵从请求并终止。如果进程选择忽略SIGTERM信号,它可能拒绝死亡。
实践
sigaction
#include <stdio.h>
#include <signal.h>
void sig_catch(int signo){
if(signo == SIGINT){
printf("catch you SIGINT: %d\n",signo);
}else if(signo == SIGQUIT){
printf("catch you SIGQUIT: %d\n",signo);
}
return ;
}
int main(){
struct sigaction act,oldact;
act.sa_handler = sig_catch;
sigemptyset(&(act.sa_mask));
act.sa_flags = 0;
int ret = sigaction(SIGINT,&act,&oldact);
ret = sigaction(SIGQUIT,&act,&oldact);
signal(SIGINT,sig_catch);
while(1);
return 0;
}

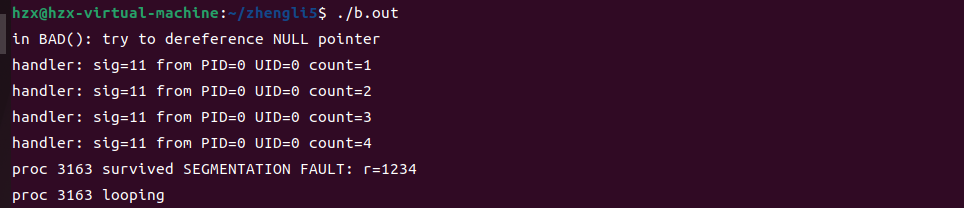
segfault.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <setjmp.h>
#include <string.h>
jmp_buf env;
int count = 0;
void handler(int sig, siginfo_t *siginfo, void *context)
{
printf("handler: sig=%d from PID=%d UID=%d count=%d\n",
sig, siginfo->si_pid, siginfo->si_uid, ++count);
if (count >= 4) // let it occur up to 4 times
longjmp(env, 1234);
}
int BAD()
{
int *ip = 0;
printf("in BAD(): try to dereference NULL pointer\n");
*ip = 123; // dereference a NULL pointer
printf("should not see this line\n");
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int r;
struct sigaction act;
memset(&act, 0, sizeof(act));
act.sa_sigaction = &handler;
act.sa_flags = SA_SIGINFO;
sigaction(SIGSEGV, &act, NULL);
if ((r = setjmp(env)) == 0)
BAD();
else
printf("proc %d survived SEGMENTATION FAULT: r=%d\n", getpid(), r);
printf("proc %d looping\n", getpid());
while (1);
}
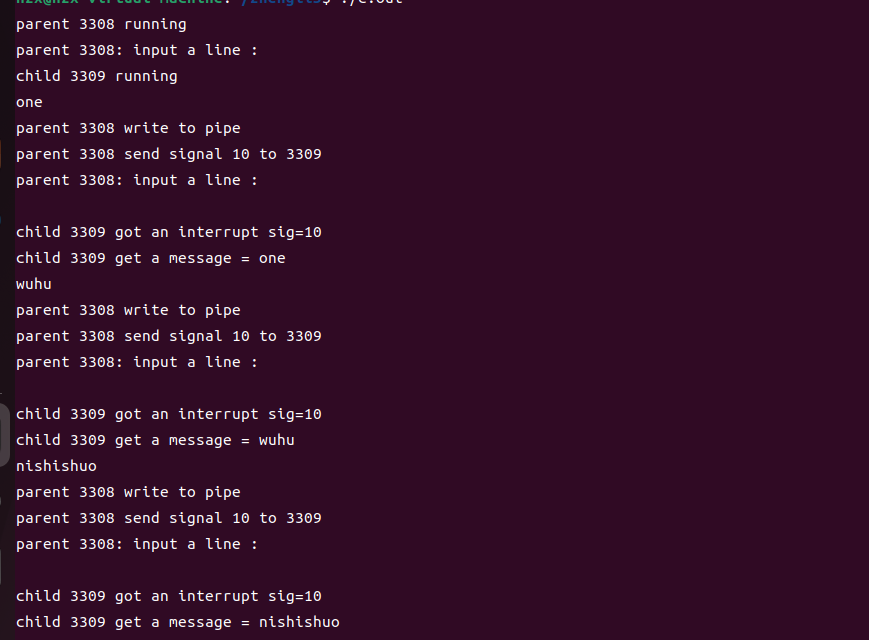
ipc
#include <stdio.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define LEN 64
int ppipe[2]; // pipe descriptors
int pid; // child pid
char line[LEN];
int parent()
{
printf("parent %d running\n", getpid());
close(ppipe[0]); // parent = pipe writer
while(1){
printf("parent %d: input a line : \n", getpid());
fgets(line, LEN, stdin);
line[strlen(line)-1] = 0; // kill \n at end
printf("parent %d write to pipe\n", getpid());
write(ppipe[1], line, LEN); // write to pipe
printf("parent %d send signal 10 to %d\n", getpid(), pid);
kill(pid, SIGUSR1); // send signal to child process
}
}
void chandler(int sig)
{
printf("\nchild %d got an interrupt sig=%d\n", getpid(), sig);
read(ppipe[0], line, LEN); // read pipe
printf("child %d get a message = %s\n", getpid(), line);
}
int child()
{
char msg[LEN];
int parent = getppid();
printf("child %d running\n", getpid());
close(ppipe[1]); // child is pipe reader
signal(SIGUSR1, chandler); // install signal catcher
while(1);
}
int main()
{
pipe(ppipe); // create a pipe
pid = fork(); // fork a child process
if (pid) // parent
parent();
else
child();
}
问题及解决
- 进程之间的通信是靠什么,如果是子父进程之间的关系
- 参考博客(https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45396618/article/details/119464178)
最新文章
- eclipse tomcat 集成
- Java JDK 环境变量配置
- poj3693
- html5 请求的URL转成 OC可用属性字符串显示
- Zepto Code Rush 2014 A. Feed with Candy
- ffmpeg常用命令
- Angularjs,WebAPI 搭建一个简易权限管理系统 —— Angularjs名词与概念(一)
- UVA 11916 Emoogle Grid(同余模)
- javascript类继承系列四(组合继承)
- CodeForces 591B
- haproxy 看到的是https,后台是http的原因
- openwrt固件支持3G和4G上网卡
- Zend Studio配合Xdebug调试
- BZOJ 1046: [HAOI2007]上升序列【贪心+二分状态+dp+递归】
- golang的GET请求(类似于PHP的CURL)
- web语义化之SEO和ARIA
- foxit pdf强制页面视图所有情况都为'合适宽度'
- Pandas系列(八)-筛选工具介绍
- linux xfs的一次io异常导致的crash
- [编译] 3、在Linux下搭建51单片机的开发烧写环境(makefile版)