java线程池的使用学习
1. 线程池的创建
线程池的创建使用ThreadPoolExecutor类,有利于编码时更好的明确线程池运行规则。
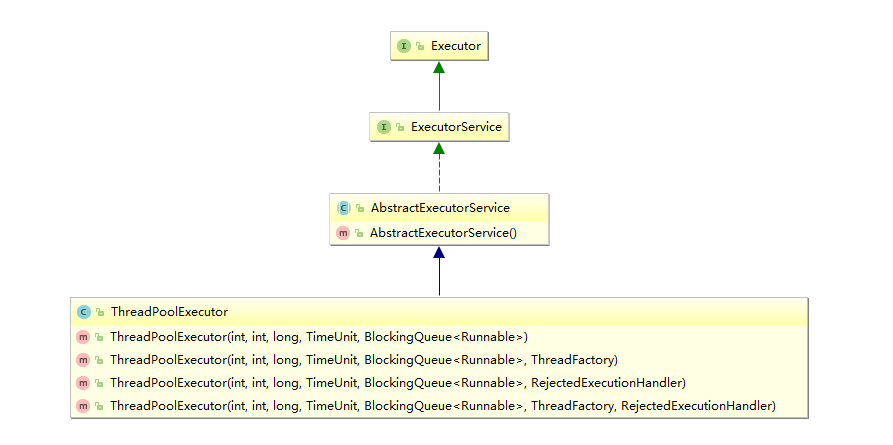
//构造函数
/**
* Creates a new {@code ThreadPoolExecutor} with the given initial
* parameters.
*
* @param corePoolSize the number of threads to keep in the pool, even
* if they are idle, unless {@code allowCoreThreadTimeOut} is set
* @param maximumPoolSize the maximum number of threads to allow in the
* pool
* @param keepAliveTime when the number of threads is greater than
* the core, this is the maximum time that excess idle threads
* will wait for new tasks before terminating.
* @param unit the time unit for the {@code keepAliveTime} argument
* @param workQueue the queue to use for holding tasks before they are
* executed. This queue will hold only the {@code Runnable}
* tasks submitted by the {@code execute} method.
* @param threadFactory the factory to use when the executor
* creates a new thread
* @param handler the handler to use when execution is blocked
* because the thread bounds and queue capacities are reached
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if one of the following holds:<br>
* {@code corePoolSize < 0}<br>
* {@code keepAliveTime < 0}<br>
* {@code maximumPoolSize <= 0}<br>
* {@code maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize}
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code workQueue}
* or {@code threadFactory} or {@code handler} is null
*/
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}
参数含义
(1) 核心线程数corePoolSize: 保持在池中的线程数
(2) 最大线程数maximumPoolSize
(3) 保活时间keepAliveTime: 线程数大于corePoolSize,闲置线程最大空闲时间
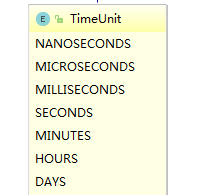
(4) 时间单位unit
(5) 阻塞队列workQueue
java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue主要实现类有:
- ArrayBlockingQueue: 数组结构有界阻塞队列,FIFO排序。其构造函数必须设置队列长度。
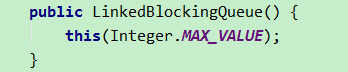
- LinkedBlockingQueue:链表结构有界阻塞队列,FIFO排序。队列默认最大长度为Integer.MAX_VALUE,故可能会堆积大量请求,导致OOM。
- PriorityBlockingQueue:支持优先级排序的无界阻塞队列。默认自然顺序排列,可以通过比较器comparator指定排序规则。
- DelayQueue:支持延时获取元素的无界阻塞队列。队列使用PriorityQueue实现。
(6) 线程创建接口threadFactory
- 默认使用Executors.defaultThreadFactory()。
- 可以自定义ThreadFactory实现或使用第三方实现,方便指定有意义的线程名称。
import com.google.common.util.concurrent.ThreadFactoryBuilder;
...
ThreadFactory namedThreadFactory = new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("my-pool-%d").build();
public class MyThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
private final AtomicInteger threadNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final String namePrefix;
MyThreadFactory(String namePrefix) {
this.namePrefix = namePrefix+"-";
}
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread( r,namePrefix + threadNumber.getAndIncrement());
if (t.isDaemon()) {
t.setDaemon(true);
}
if (t.getPriority() != Thread.NORM_PRIORITY) {
t.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
}
return t;
}
}
(7) 饱和策略handler
- ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy():终止策略(默认) , 抛出java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionException异常。
- ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy(): 重试添加当前的任务,他会自动重复调用execute()方法。
- ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy(): 抛弃下一个即将被执行的任务,然后尝试重新提交新的任务。最好不和优先级队列一起使用,因为它会抛弃优先级最高的任务。
- ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy(): 抛弃策略, 抛弃当前任务。
2. 线程池的运行规则
execute添加任务到线程池:
一个任务通过execute(Runnable)方法被添加到线程池。任务是一个 Runnable类型的对象,任务的执行方法就是 Runnable类型对象的run()方法。
线程池运行规则:
当一个任务通过execute(Runnable)方法添加到线程池时:
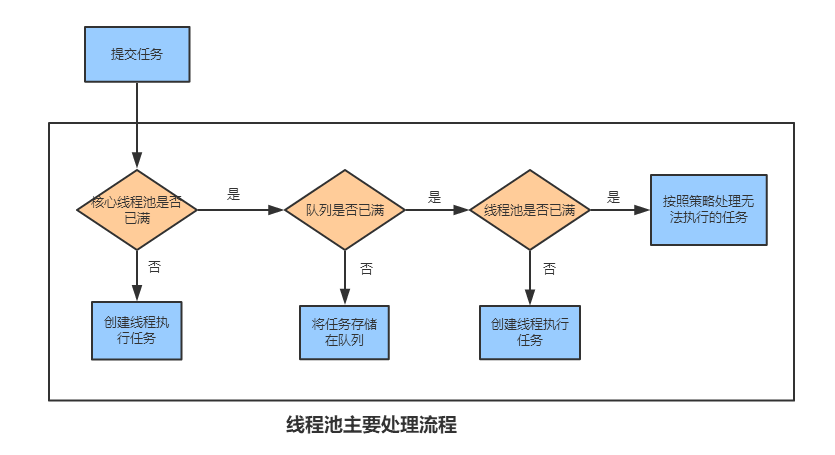
如果此时线程池中的数量小于corePoolSize,即使线程池中的线程都处于空闲状态,也要创建新的线程来处理被添加的任务。
如果此时线程池中的数量等于 corePoolSize,但是缓冲队列 workQueue未满,那么任务被放入缓冲队列。
如果此时线程池中的数量大于corePoolSize,缓冲队列workQueue满,并且线程池中的数量小于maximumPoolSize,建新的线程来处理被添加的任务。
如果此时线程池中的数量大于corePoolSize,缓冲队列workQueue满,并且线程池中的数量等于maximumPoolSize,那么通过 handler所指定的策略来处理此任务。
也就是:处理任务的优先级为:
核心线程corePoolSize - > 任务队列workQueue - > 最大线程maximumPoolSize
如果三者都满了,使用handler策略处理该任务。
- 当线程池中的线程数量大于 corePoolSize时,如果某线程空闲时间超过keepAliveTime,线程将被终止。这样,线程池可以动态的调整池中的线程数。
// execute方法源码实现(jdk1.8)
public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
/*
* Proceed in 3 steps:
*
* 1. If fewer than corePoolSize threads are running, try to
* start a new thread with the given command as its first
* task. The call to addWorker atomically checks runState and
* workerCount, and so prevents false alarms that would add
* threads when it shouldn't, by returning false.
*
* 2. If a task can be successfully queued, then we still need
* to double-check whether we should have added a thread
* (because existing ones died since last checking) or that
* the pool shut down since entry into this method. So we
* recheck state and if necessary roll back the enqueuing if
* stopped, or start a new thread if there are none.
*
* 3. If we cannot queue task, then we try to add a new
* thread. If it fails, we know we are shut down or saturated
* and so reject the task.
*/
int c = ctl.get();
if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) {
if (addWorker(command, true))
return;
c = ctl.get();
}
if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) {
int recheck = ctl.get();
if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command))
reject(command);
else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0)
addWorker(null, false);
}
else if (!addWorker(command, false))
reject(command);
}
3. 线程池的关闭
通过调用线程池的shutdown或shutdownNow方法来关闭线程池。
- shutdown:将线程池的状态设置成SHUTDOWN状态,然后interrupt空闲线程。
- shutdownNow:线程池的状态设置成STOP,然后尝试interrupt所有线程,包括正在运行的。
关于线程池状态,源码中的注释比较清晰:

再看一下源代码:
// 在关闭中,之前提交的任务会被执行(包含正在执行的,在阻塞队列中的),但新任务会被拒绝。
public void shutdown() {
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
checkShutdownAccess();
// 状态设置为shutdown
advanceRunState(SHUTDOWN);
// interrupt空闲线程
interruptIdleWorkers();
onShutdown(); // hook for ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
// 尝试终止线程池
tryTerminate();
}
其中,interruptIdleWorkers()方法往下调用了interruptIdleWorkers(), 这里w.tryLock()比较关键。
中断之前需要先tryLock()获取worker锁,正在运行的worker tryLock()失败(runWorker()方法会先对worker上锁),故正在运行的worker不能中断。

// 尝试停止所有正在执行的任务,停止对等待任务的处理,并返回正在等待被执行的任务列表
public List<Runnable> shutdownNow() {
List<Runnable> tasks;
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
checkShutdownAccess();
// 状态设置为STOP
advanceRunState(STOP);
// 停止所有线程 interruptWorkers逻辑简单些,循环对所有worker调用interruptIfStarted().(interrupt所有线程)
interruptWorkers();
tasks = drainQueue();
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
tryTerminate();
return tasks;
}
4. 线程池的使用场合
(1)单个任务处理的时间比较短;
(2)需要处理的任务数量大;
5. 线程池大小的设置
可根据计算任务类型估算线程池设置大小:
cpu密集型:可采用Runtime.avaliableProcesses()+1个线程;
IO密集型:由于阻塞操作多,可使用更多的线程,如2倍cpu核数。
6 实现举例
场景: ftp服务器收到文件后,触发相关搬移/处理操作。
public class FtpEventHandler extends DefaultFtplet {
@Override
public FtpletResult onUploadEnd(FtpSession session, FtpRequest request)
throws FtpException, IOException {
// 获取文件名
String fileName = request.getArgument();
Integer index = fileName.lastIndexOf("/");
String realFileName = fileName.substring(index + 1);
index = realFileName.lastIndexOf("\\");
realFileName = realFileName.substring(index + 1);
// **处理文件**
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 50, 10,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(3));
threadPool.execute(new fileSenderThread(realFileName));
return FtpletResult.DEFAULT;
}
}
Spring也提供了ThreadPoolTaskExecutor
<!--spring.xml配置示例-->
<bean id="gkTaskExecutor" class="org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor">
<property name="allowCoreThreadTimeOut" value="true"/>
<property name="corePoolSize" value="10"/>
<property name="maxPoolSize" value="50"/>
<property name="queueCapacity" value="3"/>
<property name="keepAliveSeconds" value="10"/>
<property name="rejectedExecutionHandler"
value="#{new java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$CallerRunsPolicy()}"/>
<property name="threadNamePrefix" value="gkTaskExecutor"/>
</bean>
//java代码中注入bean
@Autowired
@Qualifier("gkTaskExecutor")
private ThreadPoolTaskExecutor gkTaskExecutor;
end.
最新文章
- AutoMapper的介绍与使用(一)
- FFmpeg数据结构:AVPacket解析
- myql Connect
- python中list作为全局变量无需global声明的原因
- html5zero 网站模板 影片素材
- thinkPHP 中去除URL中的index.php
- Hadoop学习记录(1)|伪分布安装
- delphi 保存 和 打开 TREE VIEW的节点已经展开的状态
- iOS 百度地图监听地图状态
- A Statistical View of Deep Learning (III): Memory and Kernels
- linux网络编程:使用单进程实现多客户端通信
- java-框架-索引
- 爬虫_电影天堂 热映电影(xpath)
- spring boot集成ehcache 2.x 用于hibernate二级缓存
- 通过清华大学镜像下载Android源码并编译源码
- 八大排序算法之七—堆排序(Heap Sort)
- [转]Vue.js 入门教程
- Chapter 3 Phenomenon——9
- Callable 和 Runnable 的区别
- linux下,MySQL默认的数据文档存储目录为/var/lib/mysql。