Area--->AreaRegistrationContext.MapRoute
文章引导
Area--->AreaRegister.RegisterAllArea()与Area区域的解析
引言:
学习本文建议先看下另一篇文章(Area--->AreaRegister.RegisterAllArea()与Area区域的解析),此篇文章着重解析AreaRegistrationContext.MapRoute函数。
一.先从MapRoute说起
接着上一篇文章的末尾进行阐述,上一篇文章的末尾为:

Area的注册过程的第一步先找到所有继承或实现AreaRegistration类的类并序列化之后保存进缓存文件。接着才是重头戏(MapRoute)进行路由注册。
在AreaRegistrationContext中同样存在同名的MapRoute函数。
public Route MapRoute(string name, string url, string[] namespaces)
{
return this.MapRoute(name, url, null, namespaces);
} public Route MapRoute(string name, string url, object defaults, object constraints)
{
return this.MapRoute(name, url, defaults, constraints, null);
} public Route MapRoute(string name, string url, object defaults, string[] namespaces)
{
return this.MapRoute(name, url, defaults, null, namespaces);
} public Route MapRoute(string name, string url, object defaults, object constraints, string[] namespaces)
{
if ((namespaces == null) && (this.Namespaces != null))
{
namespaces = this.Namespaces.ToArray<string>();
}
Route route1 = this.Routes.MapRoute(name, url, defaults, constraints, namespaces);
route1.DataTokens["area"] = this.AreaName;
bool flag = (namespaces == null) || (namespaces.Length == );
route1.DataTokens["UseNamespaceFallback"] = flag;
return route1;
}
在上部代码中可以看到,整个代码的核心最终还是引用的Routes.MapRoute进行路由的注册。
二.Routes.MapRoute
Routes就是一个RouteCollection,此处的Routes还需要追溯到上一篇文章

下面为AreaRegistrationContext的构造函数,通过构造函数完成This.Routes的初始化赋值。
public AreaRegistrationContext(string areaName, RouteCollection routes, object state)
{
this._namespaces = new HashSet<string>(StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(areaName))
{
throw System.Web.Mvc.Error.ParameterCannotBeNullOrEmpty("areaName");
}
if (routes == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("routes");
}
this.AreaName = areaName;
this.Routes = routes;
this.State = state;
}
我们接着来看Routes.MapRoute的代码
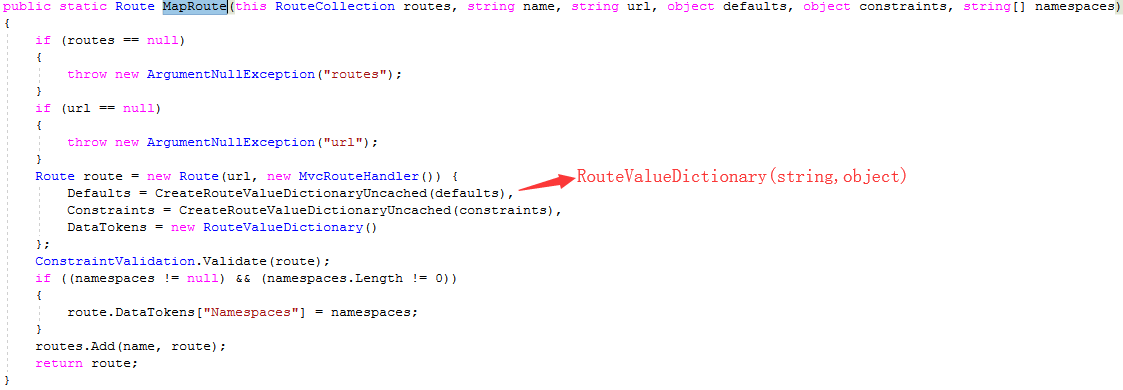
上面代码实例化一个Route并对属性进行赋值,其中Constraints和DataTokens值都一样,都是new RouteValueDictionary()。由于route.Constraints为空,则ConstraintValidation.Validate(route)不会运行函数内部代码。此扩展函数最后将信息Add进当前Routes,并返回路由信息route。
最后对Routes.DataTokens(RouteValueDictionary)添加信息,并返回Route。

三.总结
针对某个Area的路由映射是通过相应的AreaRegistration进行注册的,具体来说是在AreaRegistration的RegisterArea方法中调用AreaRegistrationContext对象的MapRoute方法进行注册的。如果在调用MapRoute方法中指定了表示命名空间的字符串,将自动作为注册的路由对象的命名空间,否则会将表示AreaRegistration所在命名空间的字符串加上"."后缀作为路由对象的命名空间。
这里说的路由对象的命名空间指的是通过Route对象的DataTokens属性表示的RouteValueDictionary对象中Key为Namespaces的字符串数组,而该字符串最终会转移到生成的RouteData的DataTokens中。
除此之外,在调用AareaRegistrationContext的MapRoute方法时,还会在注册Route对象DataTokens中添加一个Key为UseNamespaceFallback的条目表示是否采用后背命名空间 对Controller进行解析。如果注册对象具有命名控件(调用MapRoute方法时指定了命名空间或对应的AreaRegistration类型定义在某个命名空间中),该条目值为false。
在解析Controller类型过程中,会先通过RouteData包含的命名空间来解析Controller类型。如果Controller类型解析失败,则通过包含RouteData的DataTokens属性key为useNamespaceFallback值来判断是否使用后背命名空间来进行解析。如果为true,则通过当前ControllerBuilder的命名空间解析,如果失败则忽略命名空间直接采用类型名称进行匹配,否则直接抛出异常。
最新文章
- 从Bayesian角度浅析Batch Normalization
- Lex和Yacc入门
- XC通讯录
- UML 的基本组成
- bzoj3574[Hnoi2014]抄卡组
- zoj1074 To the Max
- RethinkDB创始人教你如何打造一个伟大的互联网产品
- 新建web project不自动生成web.xml解决方案
- editplus的设置
- How--to-deploy-smart-contracts-on
- spark2.2.1安装、pycharm连接spark配置
- bzoj 4660 Crazy Rabbit——LIS解决“相交”限制的思想
- Webhook是什么、怎么理解
- 5月23日——SPA单页面应用的原理
- TWebHttpRequest使用
- 第一篇,编译生成libcef_dll_wrapper
- php输出mysqli查询出来的结果
- 关于C++输出中文乱码的解决方案
- HF Reader
- python __slot__