从volatile说到i++的线程安全问题
简介
volatile关键字保证了在多线程环境下,被修饰的变量在别修改后会马上同步到主存,这样该线程对这个变量的修改就是对所有其他线程可见的,其他线程能够马上读到这个修改后值.
Thread的本地内存
- 每个Thread都拥有自己的线程存储空间
- Thread何时同步本地存储空间的数据到主存是不确定的
例子
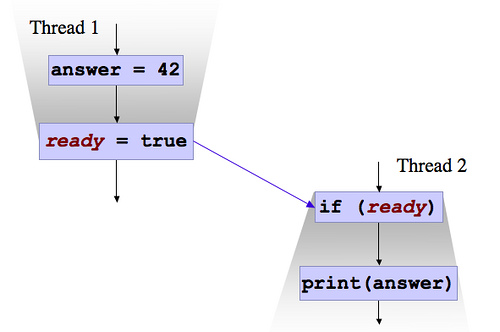
借用Google JEREMY MANSON 的解释,上图表示两个线程并发执行,而且代码顺序上为Thread1->Thread2
1. 不用 volatile
假如ready字段不使用volatile,那么Thread 1对ready做出的修改对于Thread2来说未必是可见的,是否可见是不确定的.假如此时thread1 ready泄露了(leak through)了,那么Thread 2可以看见ready为true,但是有可能answer的改变并没有泄露,则thread2有可能会输出 0 (answer=42对thread2并不可见)
2. 使用 volatile
使用volatile以后,做了如下事情
- 每次修改volatile变量都会同步到主存中
- 每次读取volatile变量的值都强制从主存读取最新的值(强制JVM不可优化volatile变量,如JVM优化后变量读取会使用cpu缓存而不从主存中读取)
- 线程 A 中写入 volatile 变量之前可见的变量, 在线程 B 中读取该 volatile 变量以后, 线程 B 对其他在 A 中的可见变量也可见. 换句话说, 写 volatile 类似于退出同步块, 而读取 volatile 类似于进入同步块
所以如果使用了volatile,那么Thread2读取到的值为read=>true,answer=>42,当然使用volatile的同时也会增加性能开销
注意
volatile并不能保证非源自性操作的多线程安全问题得到解决,volatile解决的是多线程间共享变量的可见性问题,而例如多线程的i++,++i,依然还是会存在多线程问题,它是无法解决了.如下:使用一个线程i++,另一个i--,最终得到的结果不为0
public class VolatileTest {
private static volatile int count = 0;
private static final int times = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public static void main(String[] args) {
long curTime = System.nanoTime();
Thread decThread = new DecThread();
decThread.start();
// 使用run()来运行结果为0,原因是单线程执行不会有线程安全问题
// new DecThread().run();
System.out.println("Start thread: " + Thread.currentThread() + " i++");
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
count++;
}
System.out.println("End thread: " + Thread.currentThread() + " i--");
// 等待decThread结束
while (decThread.isAlive());
long duration = System.nanoTime() - curTime;
System.out.println("Result: " + count);
System.out.format("Duration: %.2fs\n", duration / 1.0e9);
}
private static class DecThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Start thread: " + Thread.currentThread() + " i--");
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
count--;
}
System.out.println("End thread: " + Thread.currentThread() + " i--");
}
}
}
最后输出的结果是
Start thread: Thread[main,5,main] i++
Start thread: Thread[Thread-0,5,main] i--
End thread: Thread[main,5,main] i--
End thread: Thread[Thread-0,5,main] i--
Result: -460370604
Duration: 67.37s
原因是i++和++i并非原子操作,我们若查看字节码,会发现
void f1() { i++; }
的字节码如下
void f1();
Code:
0: aload_0
1: dup
2: getfield #2; //Field i:I
5: iconst_1
6: iadd
7: putfield #2; //Field i:I
10: return
可见i++执行了多部操作, 从变量i中读取读取i的值 -> 值+1 -> 将+1后的值写回i中,这样在多线程的时候执行情况就类似如下了
Thread1 Thread2
r1 = i; r3 = i;
r2 = r1 + 1; r4 = r3 + 1;
i = r2; i = r4;
这样会造成的问题就是 r1, r3读到的值都是 0, 最后两个线程都将 1 写入 i, 最后 i 等于 1, 但是却进行了两次自增操作
可知加了volatile和没加volatile都无法解决非原子操作的线程同步问题
线程同步问题的解决
Java提供了java.util.concurrent.atomic 包来提供线程安全的基本类型包装类,例子如下
package com.qunar.atomicinteger; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; /**
* @author zhenwei.liu created on 2013 13-9-2 下午10:18
* @version $Id$
*/
public class SafeTest { private static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0);
private static final int times = Integer.MAX_VALUE; public static void main(String[] args) { long curTime = System.nanoTime(); Thread decThread = new DecThread();
decThread.start(); // 使用run()来运行结果为0,原因是单线程执行不会有线程安全问题
// new DecThread().run(); System.out.println("Start thread: " + Thread.currentThread() + " i++"); for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
count.incrementAndGet();
} // 等待decThread结束
while (decThread.isAlive()); long duration = System.nanoTime() - curTime;
System.out.println("Result: " + count);
System.out.format("Duration: %.2f\n", duration / 1.0e9);
} private static class DecThread extends Thread { @Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Start thread: " + Thread.currentThread() + " i--");
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
count.decrementAndGet();
}
System.out.println("End thread: " + Thread.currentThread() + " i--");
}
}
}
输出
Start thread: Thread[main,5,main] i++
Start thread: Thread[Thread-0,5,main] i--
End thread: Thread[Thread-0,5,main] i--
Result: 0
Duration: 105.15
结论
- volatile解决了线程间共享变量的可见性问题
- 使用volatile会增加性能开销
- volatile并不能解决线程同步问题
- 解决i++或者++i这样的线程同步问题需要使用synchronized或者AtomicXX系列的包装类,同时也会增加性能开销
最新文章
- iPhone开发学习
- spring MVC 尝试传参json(应用部分)
- Cocos2d-Lua (练手) 微信打飞机
- 山东省滕州市木石镇化石沟村QQ群116528924
- ffmpeg-20160803-bin.7z
- UIWebView [web视图]
- WCF入门(二)-----实战开发
- 40个Java集合面试问题和答案【下】【转载】
- GAC的理解及其作用
- sBPM产品介绍
- PID算法
- SpringCloud(5)---Feign服务调用
- Spark Java API 计算 Levenshtein 距离
- MogoDB(6)--mongoDB高可用和4.0特性
- No input file specified.
- vue报错TypeError: Cannot read property '$createElement' of undefined
- supervisord 知识点
- ubuntu 下配置elasticSearch
- L3-014 周游世界 (30 分)
- Docker入门笔记(1)