cf div2 234 D
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Dima took up the biology of bacteria, as a result of his experiments, he invented k types of bacteria. Overall, there are n bacteria at his laboratory right now, and the number of bacteria of type i equals ci. For convenience, we will assume that all the bacteria are numbered from 1 to n. The bacteria of type ci are numbered from 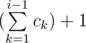 to
to 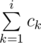 .
.
With the help of special equipment Dima can move energy from some bacteria into some other one. Of course, the use of such equipment is not free. Dima knows m ways to move energy from some bacteria to another one. The way with number i can be described with integers ui, vi and xi mean that this way allows moving energy from bacteria with number ui to bacteria with number vi or vice versa for xi dollars.
Dima's Chef (Inna) calls the type-distribution correct if there is a way (may be non-direct) to move energy from any bacteria of the particular type to any other bacteria of the same type (between any two bacteria of the same type) for zero cost.
As for correct type-distribution the cost of moving the energy depends only on the types of bacteria help Inna to determine is the type-distribution correct? If it is, print the matrix d with size k × k. Cell d[i][j] of this matrix must be equal to the minimal possible cost of energy-moving from bacteria with type i to bacteria with type j.
The first line contains three integers n, m, k (1 ≤ n ≤ 105; 0 ≤ m ≤ 105; 1 ≤ k ≤ 500). The next line contains k integers c1, c2, ..., ck (1 ≤ ci ≤ n). Each of the next m lines contains three integers ui, vi, xi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ 105; 0 ≤ xi ≤ 104). It is guaranteed that 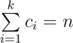 .
.
If Dima's type-distribution is correct, print string «Yes», and then k lines: in the i-th line print integers d[i][1], d[i][2], ..., d[i][k] (d[i][i] = 0). If there is no way to move energy from bacteria i to bacteria j appropriate d[i][j] must equal to -1. If the type-distribution isn't correct print «No».
4 4 2
1 3
2 3 0
3 4 0
2 4 1
2 1 2
Yes
0 2
2 0
3 1 2
2 1
1 2 0
Yes
0 -1
-1 0
3 2 2
2 1
1 2 0
2 3 1
Yes
0 1
1 0
3 0 2
1 2
No 好吧,cf第四道居然这么水,虽然死长死长的,每个类型中取一个点深搜只走权为0的路,然后判断能不能覆盖同类型的所有点即可判断,然后更新dis[i][j] ( 1<=i<= k, 1<=j<=k)的值,走一次floyd即可
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #define maxn 100005 int n,m,k;
int c[],first[maxn],next[ * maxn],v[ * maxn],x[ * maxn],dis[][],u1[ * maxn];
bool flag = ;
bool vis[maxn]; void addedge(int a,int b,int id) {
int e = first[a];
next[id] = e;
first[a] = id;
} void dfs(int u,int type) {
vis[u] = ;
//printf("u = %d type = %d\n",u,type);
for(int e = first[u]; e != -; e = next[e]) {
if(!vis[ v[e] ] && x[e] == ) {
dfs(v[e],type);
}
}
}
void solve() {
for(int i = ; i <= k; i++) {
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
dfs(c[i],i); for(int j = c[i - ] + ; j <= c[i]; j++) {
if(!vis[j]) {
flag = ;
//printf(" i = %d\n",i);
return;
}
} }
} void floyd() {
for(int p = ; p <= k; p++) {
for(int i = ; i <= k; i++) {
for(int j = ; j <= k; j++) {
if(dis[i][p] != - && dis[p][j] != -) {
dis[i][j] = dis[i][j] == - ? dis[i][p] + dis[p][j] :
min(dis[i][j],dis[i][p] + dis[p][j]);
}
}
}
}
}
void output() {
if(flag) {
printf("Yes\n"); for(int i = ; i < * m; i += ) {
int id1,id2;
id1 = lower_bound(c + ,c + k + ,u1[i]) - c;
id2 = lower_bound(c + ,c + k + ,v[i]) - c;
if(id1 == id2) continue;
dis[id1][id2] = dis[id2][id1] = dis[id1][id2] == - ?
x[i] : min(dis[id1][id2],x[i]);
} floyd(); for(int i = ; i <= k; i++) {
for(int j = ; j <= k; j++) {
printf("%d",dis[i][j]);
if(j != k) printf(" ");
}
printf("\n");
}
} else {
printf("No\n");
}
} int main() { freopen("sw.in","r",stdin); scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&k); for(int i = ; i <= k; i++) {
scanf("%d",&c[i]);
} for(int i = ; i <= k; i++) {
c[i] += c[i - ];
} for(int i = ; i <= k; i++) {
for(int j = ; j <= k; j++) {
if(i == j) dis[i][j] = ;
else dis[i][j] = -;
}
} for(int i = ; i <= n; i++) first[i] = -; for(int i = ; i < * m; i = i + ) {
int a,b,w;
scanf("%d%d%d",&u1[i],&v[i],&x[i]);
v[i + ] = u1[i];
u1[i + ] = v[i];
x[i + ] = x[i];
addedge(u1[i],v[i],i);
addedge(v[i],u1[i],i + );
} solve(); output(); return ; }
最新文章
- Adapter的封装之路
- Eclipse创建Android模拟器创建选项解释
- 集成IJKplayer视频直播框架
- chmod 和 chown 的用法
- dedecms SQL数据库连接信息注解(借鉴)
- (转载)mysql查询一天,查询一周,查询一个月的数据
- HTML5 音频视频
- 设计模式的征途—16.访问者(Visitor)模式
- gitlab一键安装+配置(备份+LADP认证)
- 使用c#对MongoDB进行查询(1)
- PHP实现单例模式和观察者模式
- 用PHPExcel导出导入Excel
- chromedriver与chrome版本映射表
- ES6 js中const,var,let区别 今天第一次遇到const定义的变量
- thinkphp 3.2 加载第三方库 第三方命名空间库
- 基于无锁队列和c++11的高性能线程池
- Hadoop概念学习系列之pagerank的友情链接(三十八)
- 使用CAS实现无锁的SkipList
- Knowing how all your components work together: distributed tracing with Zipkin
- (新)解决php版本ueditor中动态配置图片URL前缀(imageurlprefix)的方法
热门文章
- WPF:定制Checkbox样式,让“正确”绿得好看,让“错误”红的显眼
- 多路转接之poll和select
- C#设计模式之装饰者模式(Decorator Pattern)
- 如果选择构建ui界面方式,手写代码,xib和StoryBoard间的博弈
- Shade勒索病毒 中敲诈病毒解密 如 issbakev9_Data.MDF.id-A1E.f_tactics@aol.com.xtbl 解决方法
- 着色Test
- mui开发
- xml基础学习笔记01
- Codeforces Beta Round #69 (Div. 1 Only) C. Beavermuncher-0xFF 树上贪心
- Oracle Goldengate和Oracle Data Integrator的初步认识