点云3D 目标检测
点云
点云是雷达采集到的信息.
关于点云基本介绍参考https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/22581673
ros中的点云消息结构:http://docs.ros.org/jade/api/sensor_msgs/html/msg/PointCloud2.html
# This message holds a collection of N-dimensional points, which may
# contain additional information such as normals, intensity, etc. The
# point data is stored as a binary blob, its layout described by the
# contents of the "fields" array.
# The point cloud data may be organized 2d (image-like) or 1d
# (unordered). Point clouds organized as 2d images may be produced by
# camera depth sensors such as stereo or time-of-flight.
# Time of sensor data acquisition, and the coordinate frame ID (for 3d
# points).
Header header
# 2D structure of the point cloud. If the cloud is unordered, height is
# 1 and width is the length of the point cloud.
uint32 height
uint32 width
# Describes the channels and their layout in the binary data blob.
PointField[] fields
bool is_bigendian # Is this data bigendian?
uint32 point_step # Length of a point in bytes
uint32 row_step # Length of a row in bytes
uint8[] data # Actual point data, size is (row_step*height)
bool is_dense # True if there are no invalid points
PointField结构:http://docs.ros.org/melodic/api/sensor_msgs/html/msg/PointField.html
# This message holds the description of one point entry in the
# PointCloud2 message format.
uint8 INT8 = 1
uint8 UINT8 = 2
uint8 INT16 = 3
uint8 UINT16 = 4
uint8 INT32 = 5
uint8 UINT32 = 6
uint8 FLOAT32 = 7
uint8 FLOAT64 = 8
string name # Name of field
uint32 offset # Offset from start of point struct
uint8 datatype # Datatype enumeration, see above
uint32 count # How many elements in the field
点云消息数据存储在PointCloud2.data中.
示例:
header: // 点云的头信息
seq: 963 //
stamp: // 时间戳
secs: 1541143772
nsecs: 912011000
frame_id: "/camera_init"
height: 1 // If the cloud is unordered, height is 1 如果cloud 是无序的 height 是 1
width: 852578 //点云的长度
fields: // sensor_msgs/PointField[] fields
-
name: "x"
offset: 0
datatype: 7 // uint8 INT8 = 1
// uint8 UINT8 = 2
// uint8 INT16 = 3
// uint8 UINT16 = 4
// uint8 INT32 = 5
// uint8 UINT32 = 6
// uint8 FLOAT32 = 7
// uint8 FLOAT64 = 8
count: 1
-
name: "y"
offset: 4
datatype: 7
count: 1
-
name: "z"
offset: 8
datatype: 7
count: 1
-
name: "intensity"
offset: 16
datatype: 7
count: 1
is_bigendian: False
point_step: 32 // Length of a point in bytes 一个点占的字节数
row_step: 27282496 // Length of a row in bytes 一行的长度占用的字节数
data: [ .......................................................... ] // Actual point data, size is (row_step*height)
is_dense: True // 没有非法数据点
datatype=7对应的类型为PointField.FLOAT32,size为4.x/y/z的偏移都是正常的.为什么intensity的offset变成了16而不是12呢?ros在包装PointCloud2的时候可能在PointField之间添加了一些额外信息,这点我们在处理的时候要注意一下.同理还有Point与Point之间也可能有额外的信息.
点云rosbag转numpy
参考https://gist.github.com/bigsnarfdude/eeb156dc7b4caca69f5b31037da54708
我们想将PointCloud2格式的msg转换为numpy的矩阵格式.即转换成m行n列,每一列即为x,y,z,intensity...
首先我们希望对msg.data做反序列化处理,即
def msg_to_arr(msg):
arr = np.fromstring(msg.data, dtype_list)
现在问题变成了如何从点云的datatype转到numpy的datatype
DUMMY_FIELD_PREFIX = '__'
# mappings between PointField types and numpy types
type_mappings = [(PointField.INT8, np.dtype('int8')), (PointField.UINT8, np.dtype('uint8')), (PointField.INT16, np.dtype('int16')),
(PointField.UINT16, np.dtype('uint16')), (PointField.INT32, np.dtype('int32')), (PointField.UINT32, np.dtype('uint32')),
(PointField.FLOAT32, np.dtype('float32')), (PointField.FLOAT64, np.dtype('float64'))]
pftype_to_nptype = dict(type_mappings)
nptype_to_pftype = dict((nptype, pftype) for pftype, nptype in type_mappings)
# sizes (in bytes) of PointField types
pftype_sizes = {PointField.INT8: 1, PointField.UINT8: 1, PointField.INT16: 2, PointField.UINT16: 2,
PointField.INT32: 4, PointField.UINT32: 4, PointField.FLOAT32: 4, PointField.FLOAT64: 8}
def fields_to_dtype(fields, point_step):
'''
Convert a list of PointFields to a numpy record datatype.
'''
offset = 0
np_dtype_list = []
for f in fields:
while offset < f.offset:
# might be extra padding between fields
np_dtype_list.append(('%s%d' % (DUMMY_FIELD_PREFIX, offset), np.uint8))
offset += 1
dtype = pftype_to_nptype[f.datatype]
if f.count != 1:
dtype = np.dtype((dtype, f.count))
np_dtype_list.append((f.name, dtype))
offset += pftype_sizes[f.datatype] * f.count
# might be extra padding between points
while offset < point_step:
np_dtype_list.append(('%s%d' % (DUMMY_FIELD_PREFIX, offset), np.uint8))
offset += 1
return np_dtype_list
代码逻辑很清楚,pftype_to_nptype和nptype_to_pftype定义了点云消息中数据结构和numpy中数据结构的映射关系.
唯一需要注意的就是前面提到过的ros在包装PointCloud2的时候可能在PointField之间添加了一些额外信息,这点我们在处理的时候要注意一下.同理还有Point与Point之间也可能有额外的信息. 代码里的
while offset < f.offset:
# might be extra padding between fields
np_dtype_list.append(('%s%d' % (DUMMY_FIELD_PREFIX, offset), np.uint8))
offset += 1
# might be extra padding between points
while offset < point_step:
np_dtype_list.append(('%s%d' % (DUMMY_FIELD_PREFIX, offset), np.uint8))
offset += 1
就是为了处理上述问题.
复现点云检测模型SqueezeSeg检测点云数据
https://blog.csdn.net/AdamShan/article/details/83544089
原文用的py2.7,复现的时候遇到了很多问题
- conda activate env2.7
- pip install tensorflow
- pip install easydict
- pip install joblib
直接运行squeezeseg_ros_node.py的时候会报如下错误.
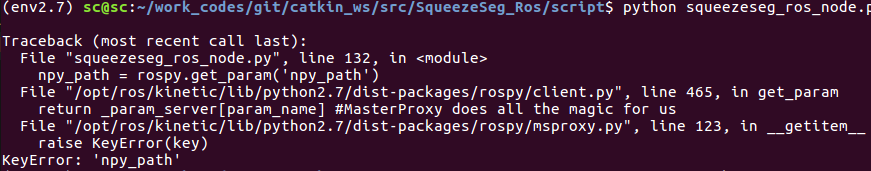
错误代码的意思是出错于读launch文件.
npy_path = rospy.get_param('npy_path')
这一句会读launch文件中的配置.
在执行了roslaunch squeezeseg_ros squeeze_seg_ros.launch之后,会报错
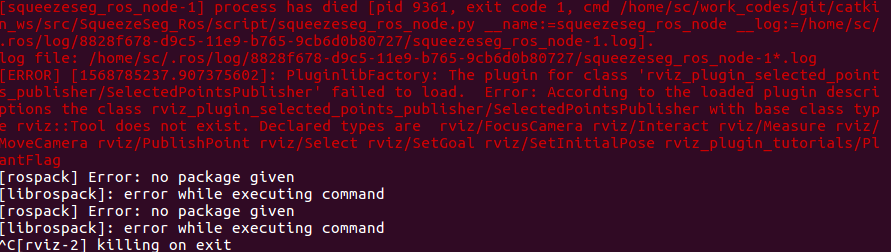
这之后再执行python squeezeseg_ros_node.py就可以正常运行了.
最新文章
- C#网络编程——IPHostEntry
- 根据Excel的内容和word模板生成对应的word文档
- java坦克大战源码下载
- java判断字符串是否为数字或中文或字母
- JavaScript中this和$(this)之间的区别以及extend的使用
- fedora 配置
- 【GK101 谐波数据生成器】上位机软件升级(版本:1.1)
- OBJECT ARX 获取标注样式信息
- Android Dialogs(6)Dialog类使用示例:用系统theme和用自定义的theme
- div 块跟随 鼠标点击
- SQL Union和SQL Union All用法
- Android学习笔记(九)一个例子弄清Service与Activity通信
- (转载)php的类中可以不定义成员变量,直接在构造方法中使用并赋值吗?
- 13 java 设计模式--单例模式
- HTML5之新增标签用途及应用场景
- VB2012读取xml
- libevent安装后缺少libevent_openssl.so
- JavaSE 软件工程师 认证考试试卷3
- Nginx 配置TCP代理
- JDK8+Tomcat8配置https【转】