emqtt 1 (初初初初稿)
第一篇,先简单分析一下整个emqtt 的大致结构,包括两个部分:
1、message packet 类型
2、message 流向
message packet 类型
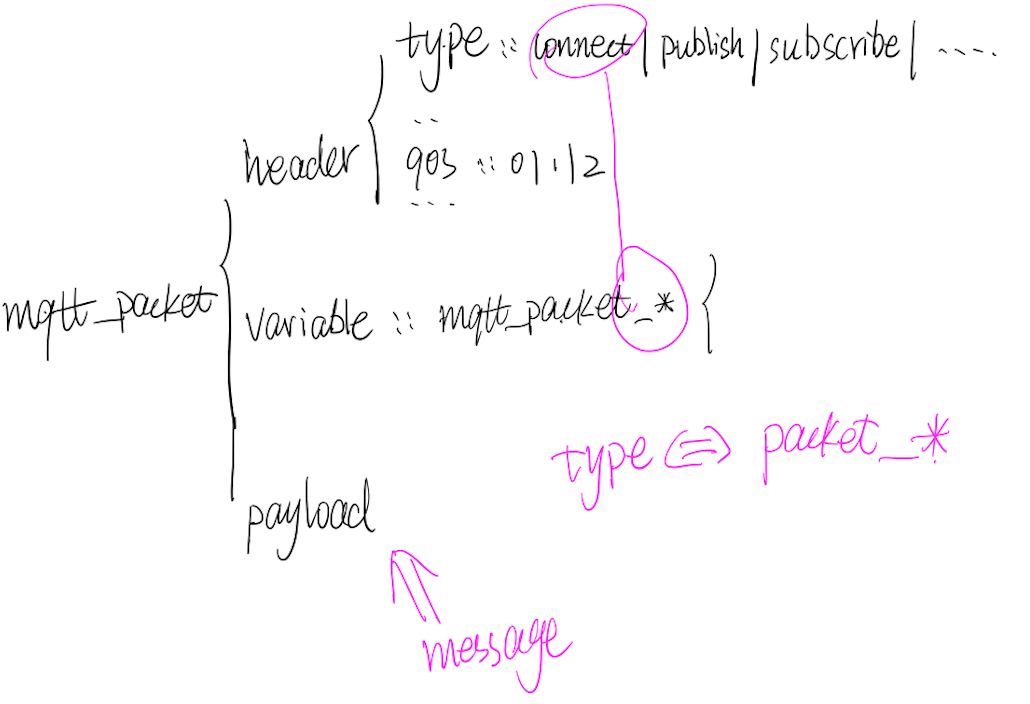
P1:mqtt_packet 的基本结构,其中header 中的type 与variable 的mqtt_packet_* 一一对应。
emqtt 的packet 定义如下:
-record(mqtt_packet,
{header :: #mqtt_packet_header{},
variable :: #mqtt_packet_connect{} | #mqtt_packet_connack{}
| #mqtt_packet_publish{} | #mqtt_packet_puback{}
| #mqtt_packet_subscribe{} | #mqtt_packet_suback{}
| #mqtt_packet_unsubscribe{} | #mqtt_packet_unsuback{}
| mqtt_packet_id() | undefined,
payload :: binary() | undefined }).
包括包头、包的类型、实际的数据消息。
在emqtt 中,message packet 的类型主要分为一下几类(这些类型,基本上定义在emqttd_protocol.hrl 文件中):
1、connect/connack

P2:connect packet的基本结构
用于客户端向server端建立链接以及server 端向client 确定链接。
-record(mqtt_packet_connect,
{client_id = <<>> :: mqtt_client_id(),
proto_ver = ?MQTT_PROTO_V311 :: mqtt_vsn(),
proto_name = <<"MQTT">> :: binary(),
will_retain = false :: boolean(),
will_qos = ?QOS_0 :: mqtt_qos(),
will_flag = false :: boolean(),
clean_sess = false :: boolean(),
keep_alive = 60 :: non_neg_integer(),
will_topic = undefined :: undefined | binary(),
will_msg = undefined :: undefined | binary(),
username = undefined :: undefined | binary(),
password = undefined :: undefined | binary()}). -record(mqtt_packet_connack,
{ack_flags = ?RESERVED :: 0 | 1,
return_code :: mqtt_connack() }).
其中,主要的几个字段,client_id、proto_ver、proto_name以及keep_alive。
client_id在username undefined的情况下,充当username的角色,是客户端的唯一标识,在接下来的session manage以及 subscription 管理中,具有非常重要的作用。
2、subscribe/suback
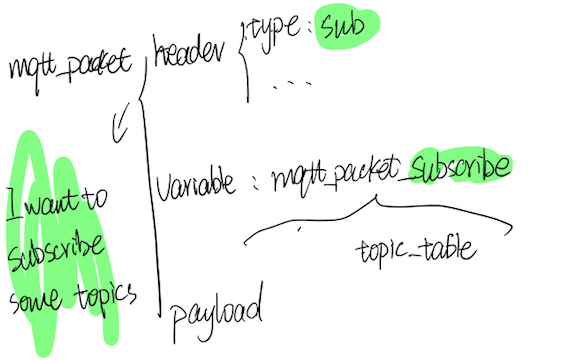
P3:subscribe packet的基本结构
用于处理客户端 subscribe 某个topic,已经server端向客户端的确认。
-record(mqtt_packet_subscribe,
{packet_id :: mqtt_packet_id(),
topic_table :: list({binary(), mqtt_qos()}) }).
-record(mqtt_packet_suback,
{packet_id :: mqtt_packet_id(),
qos_table :: list(mqtt_qos() | 128) }).
topic_table 字段表示的是所要subscribe的topic 以及对应的QoS。
3、unsubscribe/unsuback
subscribe的反向操作
4、publish/puback
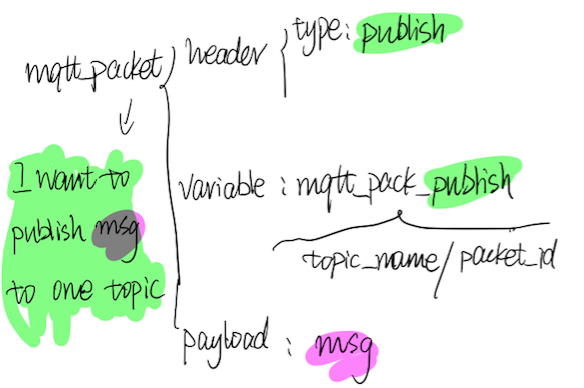
P4: publish packet的基本结构
-record(mqtt_packet_publish,
{topic_name :: binary(),
packet_id :: mqtt_packet_id() }). -record(mqtt_packet_puback,
{packet_id :: mqtt_packet_id() }).
topic_name指定了将要publish到的topic的名字。
在emqtt中,用Erlanger中record数据类型,定义了以上一种message packet的类型,而且,这些类型的packet的作用都显而易见。
message 流向
首先,mqtt是基于TCP协议的,因此,emqtt本身也是架构在TCP server上的service。其底层,基于esockd(主要借鉴RabbitMQ networking的实现)。socket controlling 进程的执行逻辑是emqttd_client module。emqttd_client module主要与esockd application 中的esockd_connection module 相关联,并存在必要的callback 关系。
由于socket controlling 进程的入口以及主要执行逻辑由emqttd_client module实现。
因此:
- message进入到server后,首先由emqttd_client module进行处理
进入到emqtt server的message,主要是二进制socket数据,想要转换成Erlang的内部数据结构,就必要进行必要的数据解析。
1、socket 数据包接收
handle_info({inet_async, _Sock, _Ref, {ok, Data}}, State) ->
Size = size(Data),
?LOG(debug, "RECV ~p", [Data], State),
emqttd_metrics:inc('bytes/received', Size),
received(Data, rate_limit(Size, State#client_state{await_recv = false}));
L2,L3,L4这三行代码主要用于调试和metric。
2、socket 数据包解析
socket 二进制数据包的解析,主要是由emqttd_parser module进行处理,包括二进制协议的解析以及socket 粘包的处理。
- message 由emqttd_parser module进行二进制数据协议的解析
解析成为mqtt_pakcet record 类型的数据结构。
3、mqtt packet 处理
emqtt中,mqtt packet的处理是由emqtt_protocol module完成,其入口函数为received/2:
%% A Client can only send the CONNECT Packet once over a Network Connection.
-spec(received(mqtt_packet(), proto_state()) -> {ok, proto_state()} | {error, any()}).
received(Packet = ?PACKET(?CONNECT), State = #proto_state{connected = false}) ->
process(Packet, State#proto_state{connected = true}); received(?PACKET(?CONNECT), State = #proto_state{connected = true}) ->
{error, protocol_bad_connect, State}; %% Received other packets when CONNECT not arrived.
received(_Packet, State = #proto_state{connected = false}) ->
{error, protocol_not_connected, State}; received(Packet = ?PACKET(_Type), State) ->
trace(recv, Packet, State),
case validate_packet(Packet) of
ok ->
process(Packet, State);
{error, Reason} ->
{error, Reason, State}
end.
前三个子函数,主要处理"是否已经login"相关的packet,而最后一个子函数则是在login 之后,处理正常的packet。
在emqttd_protocol module 中,由入口函数received 做简单的处理之后,则交由本module 中的process/2 函数进行处理,并最后交由后续的实际业务module 进行处理。
- mqtt packet 由emqttd_protocol module进行处理,并交由后续的module
综上,在emqtt中,message 基本的流向为:
- message进入到server后,首先由emqttd_client module进行处理
- message 由emqttd_parser module进行二进制数据协议的解析
- mqtt packet 由emqttd_protocol module进行处理,并交由后续的module
- 后续根据不同类型的packet,再做不同的处理
图示如下:
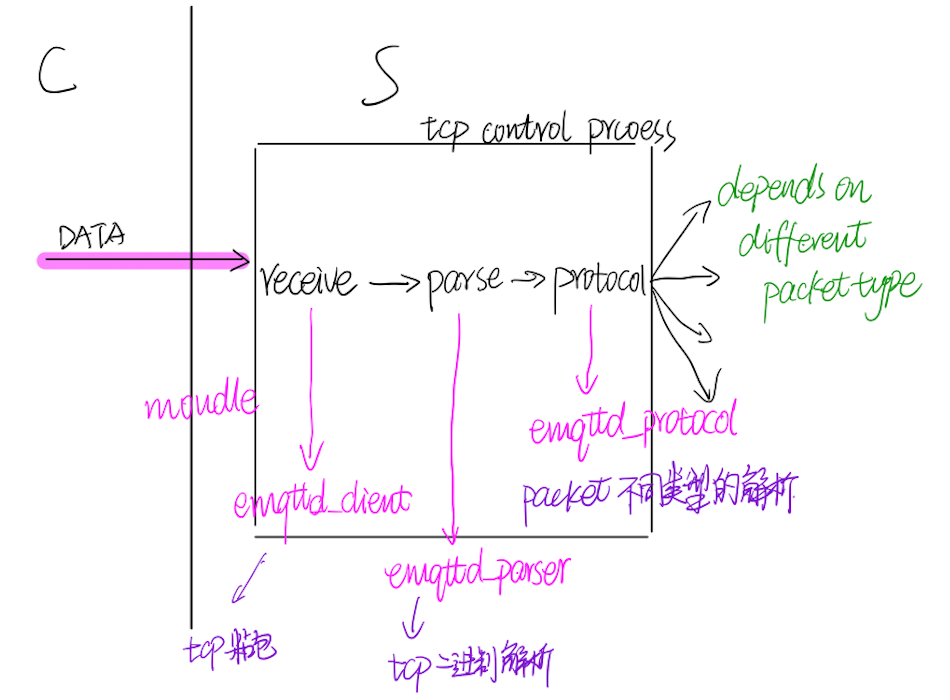
P5: message基本流向示意图
总结
需要?
最新文章
- 51nod1085(01背包)
- MyBatis知多少(10)应用程序数据库
- 字符串分割与存入List集合
- Java中类名与文件名的关系
- 实现IEnumberable接口和IEnumberator
- C/C++中static关键字详解-zz
- SVN “工作副本 “...” 已经锁定”的解决的方法
- in/exists not in/not exists null
- JVM优化
- 常见内部函数----Python
- Netty4具体解释二:开发第一个Netty应用程序
- github--hello,world(参考官网)
- laravel 对查询结果的二次筛选
- 招聘面试—关于Mysql的一点儿总结
- 简单的新手加法运算(基于Struts2)
- JS_高程3.基本概念(4)操作符
- IntelliJ IDE破解
- day_6.16网络编程
- Source Insight 如何将script等文件加入
- 【Java集合源代码剖析】ArrayList源代码剖析