CH10 泛型算法
概述
大多数算法都定义在algorithm头文件中。
Note:算法永远不会执行容器操作
泛型算法本身不会执行容器的操作,而是通过迭代器来访问、修改等操作
10.1
题目要求读取数据存入vector,并实现用户可以查找的值出现在vector中的次数,所以可以考虑用户查找文件中某个数出现的次数,所以可以考虑文件操作
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
ifstream infile(argv[]);
if (!infile)
cerr << "can not open the file!" << endl;
vector <int> iv;
int num;
while (infile >> num)
iv.push_back(num);
cout << "please enter the number you want to find" << endl;
int val;
cin >> val;
cout << "the count number " << val << " is :" << count(iv.begin(), iv.end(), val) << endl; system("pause");
return ;
}
10.2
同上,只是,程序区别大小写
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <list>
#include <string>
#include <fstream> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char*argv[])
{
ifstream infile(argv[]);
if (!infile)
{
cerr << "can not open the file,please check" << endl;
return -;
}
list<string>sl;
string words;
while (infile >> words)
sl.push_back(words);
string word;
cout << "please enter the word you want to count" << endl;
cin >> word;
cout <<"the number of "<<word<<" is :"<< count(sl.begin(), sl.end(), word) << endl; }
只读算法
对于只读算法,通常最好使用cbegin()和cend(),但是如果用算法返回的迭代器来改变元素的值,就需要使用begin()和end()的结果作为参数
那些只接受一个单一迭代器来表示第二个序列的算法,都家丁第二个序列至少与第一个序列一样长。
10.3
accumulate(iv.begin(),iv.end(),0)
10.4
accumulate()将第三个参数作为求和的起点,序列中的元素的类型与第三个参数类型匹配,这里第三个是int型,所以前两个会被转换为int型。
写容器算法
一些算法从两个序列中读取元素。构成这两个序列的元素可以来自于不同类型的容器。例如,第一个序列可能保存于一个vector,而第二个可能保存于一个list、deque,内置数组或其他容器中。而且,两个序列中元素的类型也不要求严格匹配。
算法不检查写操作
fill_n(vec.begin(), vec.size(), );//将所有元素重置为0
back_insert:接受一个容器的引用,返回一个与该容器绑定的插入迭代器,当通过此迭代器赋值时,赋值运算符会调用push_back将一个具有给定值的元素添加到容器中
vector<int> vec;
auto it = back_insert(vec);//通过它赋值会将元素添加到vector中
*it = ;//vec 中现在有一个元素42
copy算法:向目的位置的迭代器指向的输出序列中元素写入数据,接受三个迭代器,一对输入范围,第三个目的序列其实位置。
//使用copy实现内置数组的拷贝
int a1[] = { ,,,,,,,,, };
int a2[sizeof(a1) / sizeof(*a1)];//a2与a1大小相同
auto ret = copy(a1, begin(), a1.end(), a2);//使用copy将a1内容拷贝给a2,ret指向拷贝到
//a2的尾元素之后的位置
重排容器元素的算法
sort:接受一对迭代器,表示排序的范围, 按字典顺序排序
unique 重排输入范围,使得每个单词只出现一次
插入迭代器
插入迭代器(insert iterator)迭代器适配器,接受一个容器,生成一个迭代器,该迭代器使用容器操作箱给定容器添加元素。有3个创建插入迭代器的模板:
back_inserter:在类型为T的容器末尾添加元素,创建一个使用push_back的迭代器
front_inserter :容器头部插入元素,创建一个使用push_front的迭代器
inserter:创建一个insert的迭代器,该函数接受两个参数,第二个参数是一个指向容器的迭代器,元素被插入到给定迭代器表示的元素之前
当调用inserter(c,iter)时,c是绑定的容器,得到一个迭代器,使用它时,会将元素插入到iter原来所指向的元素之前的位置。如果it是由inserter生成的迭代器,则下面的语句
*it = val;
效果与下面代码一样
it = c.insert(it, val);
++it;
front_inserter生成的迭代器的行为与inserter生成迭代器不同,front_inserter总是插入到容器的第一个元素之前。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator> using namespace std; int main()
{
vector<int> iv1 = { ,,,, };
vector<int>iv2;
vector<int>iv3;
vector<int> iv4 = { , };
copy(iv1.cbegin(), iv1.cend(), back_inserter(iv2));
for (auto it : iv2)
cout << it << " ";
cout << endl;
copy(iv1.cbegin(), iv1.cend(), inserter(iv4, iv4.begin()));
for (auto it : iv4)
cout << it << " ";
cout << endl; copy(iv1.cbegin(), iv1.cend(), inserter(iv3, iv3.begin()));
for (auto it : iv3)
cout << it << " ";
cout << endl;
list<int> il1 = { ,,,, };
list<int>il2;
list<int>il3;
copy(il1.cbegin(), il1.cend(), front_inserter(il2));
for (auto it : il2)
cout << it << " ";
cout << endl;
copy(il1.cbegin(), il1.cend(), inserter(il3, il3.begin()));
for (auto it : il3)
cout << it << " ";
cout << endl;
system("pause");
return ;
}
iostream 迭代器
iostream类型不是容器,标准库定义了可用于这些IO类型对象的迭代器
istream_iterator :读取输入流,
ostream_iterator: 想一个输出流写数据
创建一个流迭代器时,必须指定迭代器将要读写的数据的类型。一个istream_iterator使用>>读取流,所以istream_iterator要读取的数据类型必须定义了输入运算符>>.
istream_iterator<int> int_it(cin);//从cin读取int
istream_iterator<int> int_eof;//默认初始化迭代器,初始化为尾后迭代器
ifstream infile("a_file");
istream_iterator<string> str_it(infile);//使用istream_iterator从a_file读取数据
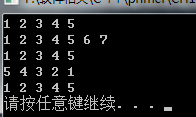
下面是一个使用istream_iterator从cin读取数据存入vector 的例子
istream_iterator<int> in_iter(cin);
istream_iterator<int>eof;
vector<int>vec;
while (in_iter != eof)
vec.push_back(*in_iter++);
测试结果
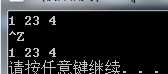
使用迭代器范围更为简洁
vector<int>vec(in_iter, eof);
测试结果
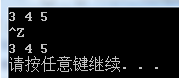
使用算法操作流迭代器
使用一对istream_iterator 调用accumulate:
istream_iterator<int> in_iter(cin);
istream_iterator<int>eof;
cout << accumulate(in_iter, eof, ) << endl;
此调用会计算从标准输入读取的值的和。
ostream_iterator操作
可以对任何具有输出运算符<<的类型定义ostream_iterator。当创建一个ostream_iterator时,可以提供第二个参数。
ostream_iterator<T>out(os);//out将类型为T的值写到输出流os中
ostream_iterator<T>out(os, d);//out将类型为T的值写到输出流os中,每个值后面都输出一个d,d指向一个
//空字符串结尾的字符数组
使用ostream_iterator输出序列
ostream_iterator<int> out_iter(cout, " ");
for (auto e : vec)
*out_iter++ = e;//赋值语句将元素写入到cout
cout << endl;
当向out_iter赋值时,可以忽略解引用和递增运算,即,循环可以写成下面这样
for (auto e : vec)
out_iter = e;//赋值语句将元素写入到cout
cout << endl;
但是推荐第一种形式,流迭代器的使用和其它迭代器的使用保持一致
//调用copy打印,比循环更简洁
copy(vec.begin(), vec.end(), out_iter);
cout << endl;
10.29
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <iterator>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std; int main(int argc, char*argv[])
{
ifstream infile(argv[]);
if (!infile)
{
cerr << "can not open the file" << endl;
return -;
}
istream_iterator<string>str_in_iter(infile);//从输入文件流infile读取数据
istream_iterator<string>eof;
vector<string>svec(str_in_iter, eof);
ostream_iterator<string>str_out_iter(cout, " ");
for (auto e : svec)
*str_out_iter++ = e; cout << endl; system("pause");
return ;
}
测试结果
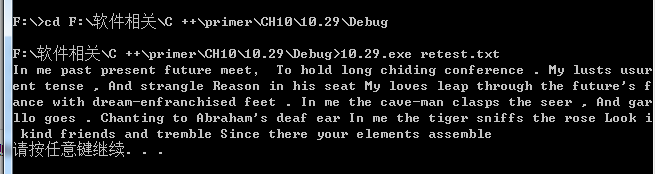
10.30 10.31
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator> using namespace std; int main()
{
istream_iterator<int> in_it(cin);
istream_iterator<int> eof;
vector<int>iv;
while (in_it != eof)
iv.push_back(*in_it++);
sort(iv.begin(), iv.end()); ostream_iterator<int>out_it(cout, " ");
copy(iv.begin(), iv.end(), out_it);
cout << endl;
//10.31
unique_copy(iv.begin(), iv.end(), out_it);
system("pause");
return ;
}
10.33
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <fstream> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char*argv[])
{
if (argc != )
cerr << " the number of files is not correct" << endl;
ifstream infile(argv[]);
if (!infile)
{
cerr << "can not open the file " << endl;
return -;
} ofstream odd_out(argv[]);
if (!odd_out)
cerr << "can not open the file or the file does not exist" << endl;
ofstream even_out(argv[]);
if(!even_out)
cerr << "can not open the file or the file does not exist" << endl; istream_iterator<int> in_iter(infile);
istream_iterator<int> eof;
/*ostream_iterator<int>out_iter_odd(cout, " ");
ostream_iterator<int>out_iter_even(cout, " ");*/
ostream_iterator<int>out_iter_odd(odd_out, " ");
ostream_iterator<int>out_iter_even(even_out, " ");
while (in_iter != eof)
{
if (*in_iter % )
*out_iter_odd++ = *in_iter;
else
out_iter_even++ = *in_iter;
in_iter++;
} system("pause");
return ;
}
最新文章
- 【JQ+锚标记实现点击页面回到顶部】
- Django补充及初识Ajax
- Xcode 7如何 免费 真机调试iOS应用
- HTML5 Web 客户端五种离线存储方式汇总
- Linux laptop-mode 电池供电时鼠标间歇失灵问题解决
- EF环境搭建碰到的问题
- java反射基本使用操作
- oVirt-engine项目UI结构
- PHP 开发社区微信服务号实战图解
- -- Warning: Skipping the data of table mysql.event. Specify the --events option explicitly.
- java的nio之:java的nio系列教程之概述
- 简单修改 MySQL 的 root 账号密码
- 【转】类中如何引用server.MapPath()
- AndroidSDK无法下载API包的解决方法
- [cc150] 括号问题
- hdoj 2044一只小蜜蜂...【斐波那契变形】
- mnist数据集转换bmp图片
- openstack、kvm CentOS升级内核
- Ormlite自定义db的位置和自动更新问题
- 为什么 as sysdba着陆方法oracle数据库,为什么刚刚输入username和password我们都可以登录?