Linux---who命令学习
who命令
获取正在登录系统的用户
使用Linux的who命令

第一个参数book代表用户名,第二个参数tty7代表终端名,第三个参数代表时间,第四个参数代表用户的登录地址。
阅读手册
使用命令读手册
$ man who
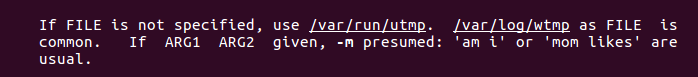
可以知道who这个命令从 /var/run/utmp 和 /var/log/wtmp 两个文件中获取数据,
再通过命令,查找关于 “utmp” 的信息
$ man -k utmp

-k的意思是根据关键字查找
$man 5 utmp
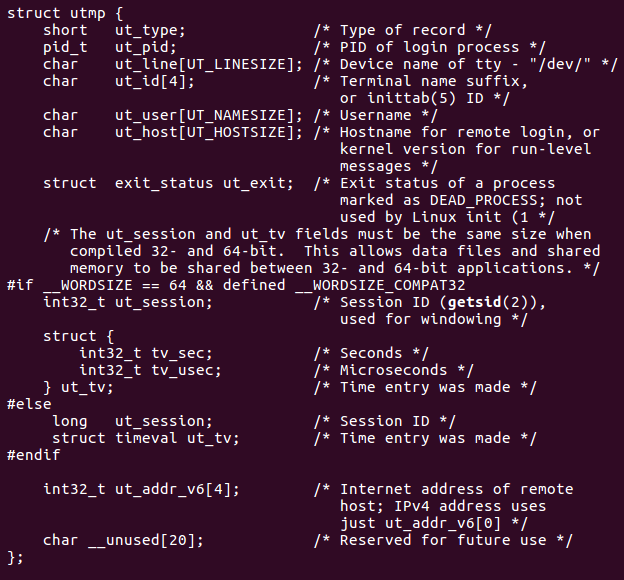
我们查询到一些关于utmp结构体中的元素,比如ut_user用户名字、ut_line用户设备、ut_time登录时间等。
who命令的工作流程
打开utmp
+----> 读取记录 ------ +
| |
+-------显示记录 |
关闭utmp <------ +
who命令的编写---版本1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <utmp.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h> void show_info(struct utmp *utbufp);
int main()
{
struct utmp current_record;
int utmp_fd;
int reclen = sizeof(current_record); utmp_fd = open(UTMP_FILE,O_RDONLY);
if(utmp_fd == -)
return -; while( read(utmp_fd, ¤t_record,reclen) == reclen )
show_info(¤t_record); close(utmp_fd);
return ;
} void show_info(struct utmp *utbufp)
{ printf("%-8.8s",utbufp->ut_name);
printf(" ");
printf("%-8.8s",utbufp->ut_line);
printf(" ");
printf("%101d",utbufp->ut_time);
printf(" ");
printf("(%s)",utbufp->ut_host);
printf(" ");
printf("\n");
}
输出结果:
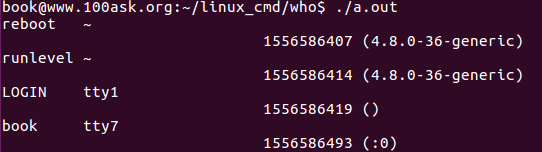
问题:
1. 有部分数据不是真实用户的。
2. 时间显示不对。
解决方法:
1.第一个问题
继续使用命令
$ man 5 utmp
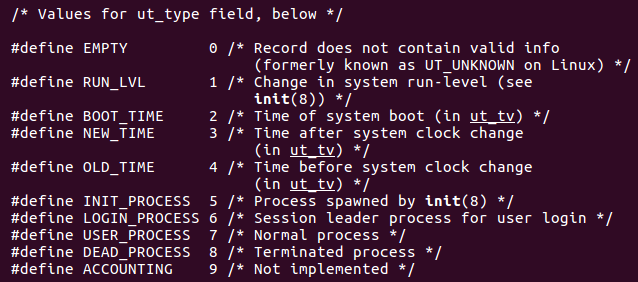
看到 ut_type中 USER_PROCESS表示的是已经登录的用户 ,那么第一个问题就解决了。
2.第二个问题
使用命令
$ man -k time | grep transform

看到ctime,使用命令查看ctime的使用方法
$ man 3 ctime

使用这个函数将 timeval转换成一个字符串并返回一个指针,那么第二个问题也解决了。
who命令的编写---版本2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <utmp.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h> void show_info(struct utmp *utbufp);
void show_time(long timeval);
int main()
{
struct utmp current_record;
int utmp_fd;
int reclen = sizeof(current_record); utmp_fd = open(UTMP_FILE,O_RDONLY);
if(utmp_fd == -)
return -; while( read(utmp_fd, ¤t_record,reclen) == reclen )
show_info(¤t_record); close(utmp_fd);
return ;
} void show_info(struct utmp *utbufp)
{
if(utbufp->ut_type != USER_PROCESS)
return; printf("%-8.8s",utbufp->ut_name);
printf(" ");
printf("%-8.8s",utbufp->ut_line);
printf(" ");
show_time(utbufp->ut_time);
printf(" ");
printf("(%s)",utbufp->ut_host);
printf("\n");
} void show_time(long timeval)
{
char *cp; cp = ctime(&timeval); printf("%12.12s",cp+); }
输出结果:

这样一个简单的who命令就完成了。
------------------------------于2019/5/5更新---------------------
改良who命令
在Linux---cp命令中,介绍了有关缓冲区和系统开销的知识,因此,我们可以改良自己编写的who命令。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <utmp.h> #define NRECS 16
#define NULLUT ((struct utmp*)NULL)
#define UTSIZE (sizeof(struct utmp)) static char utmpbuf[NRECS * UTSIZE];
static int num_recs;
static int cur_rec;
static int fd_utmp = -; struct utmp* utmp_next();
int utmp_reload();
int utmp_open(char *filename);
void utmp_close(); int utmp_open(char *filename)
{
fd_utmp = open(filename , O_RDONLY);
cur_rec = ;
num_recs = ;
return fd_utmp;
} struct utmp* utmp_next()
{
struct utmp* recp;
if(fd_utmp == -)
{
return NULLUT;
}
if(cur_rec == num_recs && utmp_reload() == )
{
return NULLUT;
} recp = (struct utmp*) &utmpbuf[cur_rec * UTSIZE];
cur_rec++;
return recp;
} int utmp_reload()
{
int aimt_read;
aimt_read = read(fd_utmp, utmpbuf, NRECS * UTSIZE);
num_recs = aimt_read / UTSIZE;
cur_rec = ;
return num_recs; } void utmp_close()
{
if(fd_utmp != -)
close(fd_utmp);
}
编写一个增大缓冲区的库,调用的次数减少到原来的1/16。这样程序能够在更短的时间内完成。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <utmp.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdlib.h> void show_info(struct utmp *utbufp);
void show_time(long timeval); #define SHOWHOST int main()
{
struct utmp* utbufp , *utmp_next();
if( utmp_open(UTMP_FILE) == -)
{
perror(UTMP_FILE);
exit();
} while( (utbufp = utmp_next()) != ((struct utmp *)NULL))
show_info(utbufp); utmp_close();
return ;
} void show_info(struct utmp *utbufp)
{
if(utbufp->ut_type != USER_PROCESS)
return; printf("%-8.8s",utbufp->ut_name);
printf(" ");
printf("%-8.8s",utbufp->ut_line);
printf(" ");
show_time(utbufp->ut_time);
printf(" ");
printf("(%s)",utbufp->ut_host);
printf("\n");
} void show_time(long timeval)
{
char *cp; cp = ctime(&timeval); printf("%12.12s",cp+); }
本篇笔记自拜读《 Unix/Linux编程实践教程》
我也推荐和我一样的初学者去拜读这本书,让你对linux有可下手的地方。
最新文章
- Dapper.Contrib:GetAsync<T> only supports an entity with a [Key] or an [ExplicitKey] property
- Android-socket服务端断重启后,android客户端自动重连
- Logistic回归小结
- JSP action elements - JavaBean
- linux之开发板与宿主机-GDB远程调试
- C#打开指定目录,并将焦点放在指定文件上。相对路径(程序起动的目录)
- 解决linux下oracle进入sqlplus环境中后退键显示^H、上下键无效与ctrl+l无法清屏等问题【weber出品必属精品】
- SQL 语句优化—— (二) 索引的利用
- C++ Primer 学习笔记_2_高速入口(继续)
- TCP协议和UDP协议下的socket
- 关于IE无法访问本机网络的问题
- appium-doctor
- 百度echart初用总结
- QMessageBox消息框
- bind this指针
- java 选择排序、冒泡排序、折半查找
- 【本周主题】第一期:JavaScript单线程与异步
- 浅析c#中==操作符和equals方法
- BZOJ3771 Triple 【NTT + 容斥】
- python 的输入和输出