老徐和阿珍的故事:Runnable和Callable有什么不同?
人物背景:
老徐,男,本名徐福贵,从事Java相关研发工作多年,职场老油条,摸鱼小能手,虽然岁数不大但长的比较着急,人称老徐。据说之前炒某币败光了所有家产,甚至现在还有欠债。
阿珍,女,本名陈家珍,刚刚入职不久的实习生,虽然是职场菜鸟但聪明好学。据说是学校的四大校花之一,追求她的人从旺角排到了铜锣湾,不过至今还单身。
阿珍探出头看了看老徐的屏幕,全部都是绿色的曲线图,好奇地问:“老徐,你看的这是什么?”老徐看的太入神,转过头才发现阿珍,尬尴地笑了笑说:“我就是看看最近的行情。”老徐立马切换了窗口。
阿珍没在意又继续问到:“Runnable和Callable两个接口我总搞混,这个到底有什么不同?”
面对阿珍的灵魂拷问,老徐淡定自若地说:“Runnable是用于提供多线程任务支持的核心接口,Callable是在Java 1.5中添加的Runnable的改进版本。”
“在聊它们不同之前,我们先分别了解一下两个接口。”老徐一边说着,一边打开了源码:
Runnable接口
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
public abstract void run();
}
Runnable接口是一个函数式接口,它只有一个run()方法,不接受任何参数,也不返回任何值。由于方法签名没有指定throws子句,因此无法进一步传播已检查的异常。它适用于我们不使用线程执行结果的情况,例如,异步打印日志:
package one.more;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class LoggingTask implements Runnable {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LoggingTask.class);
private String name;
public LoggingTask(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
logger.info("{}说:你好!", this.name);
}
}
在上面例中,根据name参数把信息记录在日志文件中,没有返回值。我们可以通过Thread启动,比如:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "万猫学社";
Thread thread = new Thread(new LoggingTask(name));
thread.start();;
}
我们也可以通过ExecutorService启动,比如:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "万猫学社";
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
executorService.execute(new LoggingTask(name));
executorService.shutdown();
}
Callable接口
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Callable<V> {
V call() throws Exception;
}
Callable接口也是一个函数式接口,它只有一个call()方法,不接受任何参数,返回一个泛型值V,在方法签名上包含throws Exception子句,因此我们可以很容易地进一步传播已检查异常。它适用于我们使用线程执行结果的情况,例如,异步计算阶乘:
package one.more;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
public class FactorialTask implements Callable<Integer> {
private int n;
public FactorialTask(int n) {
this.n = n;
}
@Override
public Integer call() throws IllegalArgumentException {
int fact = 1;
if (n < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("必须大于等于零");
}
for (int i = n; i > 1; i--) {
fact = fact * i;
}
return fact;
}
}
在上面例中,根据n参数计算它的阶乘,并可以返回计算结结果。我们只能通过ExecutorService启动,比如:
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
Future<Integer> future = executorService.submit(new FactorialTask(5));
System.out.println(future.get());
executorService.shutdown();
}
call()方法的结果可以通过Future对象获取到,如果在调用Future对象的get()方法时,call()方法出现了异常,异常会被继续传递,比如:
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
Future<Integer> future = executorService.submit(new FactorialTask(-1));
System.out.println(future.get());
executorService.shutdown();
}
抛出如下异常:
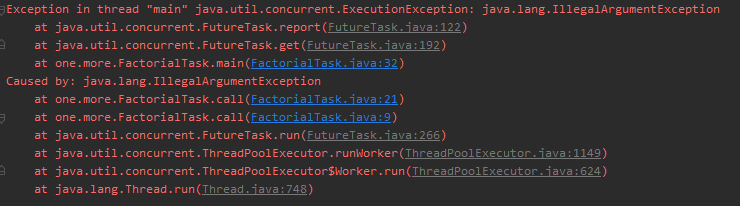
老徐回头看看了阿珍,说:“这回你知道有什么不同了吧!”阿珍一头雾水地说:“信息量有点大呀,可以给我总结一下吗?”“当然可以。”老徐回答。
总结
Runnable和Callable的不同:
- Callable的任务执行后可返回值,Runnable的任务不能返回值。
- Callable只可以通过
ExecutorService启动,Runnable可以通过Thread和ExecutorService启动。 - Callable的call()方法可以传播已检查异常,Runnable的run()方法不可以。
最后,谢谢你这么帅,还给我点赞和关注。
微信公众号:万猫学社
微信扫描二维码
关注后回复「电子书」
获取12本Java必读技术书籍

最新文章
- 深入浅出Mybatis系列(八)---mapper映射文件配置之select、resultMap
- Jquery的multifile使用随记
- apache开启虚拟主机localhost无法访问
- C++引用(References)
- cocos2d粒子效果
- ios中view的生命周期
- leetcode修炼之路——83. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
- 【RN6752】模拟高清AHD芯片或成为车机新标配
- 你绝不能错过的效率神器 —— Alfred
- Codeforces__Raising Bacteria
- Jquery之isPlainObject源码分析
- C#几个经常用到的字符串的截取
- C#匿名类型和动态解析减少定义传输类模板
- Android Studio 之 注释模板
- UVA1160 X-Plosives
- s21day12 python笔记
- Stream基础知识
- max virtual memory areas vm.max_map_count [65530] is too low, increase to at least [262144]
- [转]Phantomjs实现获取网页快照并生成缩略图
- jQuery----each()方法