C++ string类的学习
string类对于处理字符串的一些应用非常的方便,我个人感觉,string和字符数组const char *很像,而且又比字符数组用起来方便的多。
注意其删除,取子串,插入等函数里面都有一个重载版本是使用偏移量来操作的,注意其默认值是不同的,erase和substr里面的默认值是偏移量为0,个数是npos,如果只填写一个参数的话,会传给偏移量,那么将对该偏移量及之后的所有字符操作。如str.erase(5)将删除偏移量5开始的npos个字符,即删除str[5]及之后的所有字符。而insert有两个使用偏移量进行操作的重载函数,且都没有默认值,根据输入参数选择函数,如果写成str.insert(3,'c');那么将直接在str[3]的位置上插入1个c字符。
所以使用string的erase和substr操作的时候最好把两个参数写全了,且注意表示的不是偏移量区间(迭代器的版本才是区间),而是从某个偏移量开始的n个数,而使用insert的时候可以只写偏移量,也可以将偏移量和要插入的个数同时写出。
以上三种操作的所有重载函数如下:
删除
iterator erase(iterator first, iterator last);//删除[first,last)之间的所有字符,返回删除后迭代器的位置
iterator erase(iterator it);//删除it指向的字符,返回删除后迭代器的位置
string &erase(int pos = 0, int n = npos);//删除pos开始的n个字符,返回修改后的字符串
取子串
_Myt substr(size_type _Off = 0, size_type _Count = npos) const
插入
_Myt& insert(size_type _Off, const _Elem *_Ptr)
_Myt& insert(size_type _Off,size_type _Count, _Elem _Ch)
iterator insert(const_iterator _Where)
iterator insert(const_iterator _Where, _Elem _Ch)
void insert(const_iterator _Where, size_type _Count, _Elem _Ch)
void insert(const_iterator _Where, _It _First, _It _Last)
void _Insert(const_iterator _Where, _It _Count, _It _Ch,_Int_iterator_tag)
void _Insert(const_iterator _Where, _It _First, _It _Last,input_iterator_tag)
void insert(const_iterator _Where,const_pointer _First, const_pointer _Last)
void insert(const_iterator _Where,const_iterator _First, const_iterator _Last)
另外要注意string的下标访问不能过界,否则在运行的时候会报错
如下面这段程序
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str;
cin>>str;
int i=str.length()-;
if(str[++i]=='')
{
cout<<"hello";
}
return ;
}
由于str[++i]过界访问了,随便输入一段字符串就会出现下面的结果了
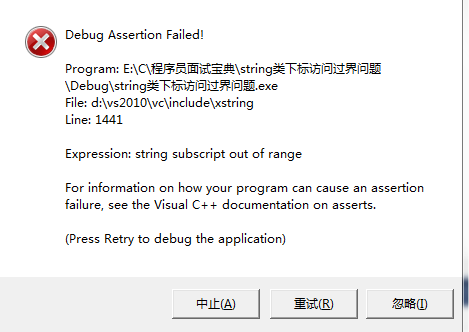
下面对比着标准的char * 函数学一些基本的string 操作
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string a="abcde";
string b="abcde";
string c="abde"; //strlen
int length=a.length();
//或者int length=a.size();也可以
cout<<length<<endl; //strcpy
string d=c;
cout<<d<<endl; //strcmp
if(a==b)
cout<<"ok"<<endl;
if(a<c)
cout<<"ok"<<endl;
if(b>c)
cout<<"ok"<<endl; //strcat
a=a+b;
cout<<a<<endl; //strstr
string e="abcdef";
int c_num=e.find('c');
cout<<"字符c的位置在"<<c_num<<endl;
string f="def";
int f_num=e.find(f);
cout<<"字符串f的位置在"<<f_num<<endl; //atoi
string num1="";
//先强制转换为const char *
//注意这里的const必不可少
const char * num_1=num1.c_str();
int num_int1=atoi(num_1);
cout<<num_int1<<endl; //itoa
int num_int2=;
char num_2[];
itoa(num_int2,num_2,);
string num2=num_2;
cout<<num2<<endl; //*******其他一些常用操作********//
//取子串
string g="abcd";
string h=g.substr(,);
cout<<"h is "<<h<<endl;
//删除
/*iterator erase(iterator first, iterator last);//删除[first,last)之间的所有字符,返回删除后迭代器的位置
iterator erase(iterator it);//删除it指向的字符,返回删除后迭代器的位置
string &erase(int pos = 0, int n = npos);//删除pos开始的n个字符,返回修改后的字符串*/
h=h.erase();
cout<<"erase h"<<h<<endl;
//判断是否为空
cout<<h.empty()<<endl; return ;
}
更加详细的操作如下:
string类的构造函数:
string(const char *s); //用c字符串s初始化
string(int n,char c); //用n个字符c初始化
此外,string类还支持默认构造函数和复制构造函数,如string s1;string s2="hello";都是正确的写法。当构造的string太长而无法表达时会抛出length_error异常 ;
string类的字符操作:
const char &operator[](int n)const;
const char &at(int n)const;
char &operator[](int n);
char &at(int n);
operator[]和at()均返回当前字符串中第n个字符的位置,但at函数提供范围检查,当越界时会抛出out_of_range异常,下标运算符[]不提供检查访问。
const char *data()const;//返回一个非null终止的c字符数组
const char *c_str()const;//返回一个以null终止的c字符串
int copy(char *s, int n, int pos = 0) const;//把当前串中以pos开始的n个字符拷贝到以s为起始位置的字符数组中,返回实际拷贝的数目
string的特性描述:
int capacity()const; //返回当前容量(即string中不必增加内存即可存放的元素个数)
int max_size()const; //返回string对象中可存放的最大字符串的长度
int size()const; //返回当前字符串的大小
int length()const; //返回当前字符串的长度
bool empty()const; //当前字符串是否为空
void resize(int len,char c);//把字符串当前大小置为len,并用字符c填充不足的部分
string类的输入输出操作:
string类重载运算符operator>>用于输入,同样重载运算符operator<<用于输出操作。
函数getline(istream &in,string &s);用于从输入流in中读取字符串到s中,以换行符'\n'分开。
string的赋值:
string &operator=(const string &s);//把字符串s赋给当前字符串
string &assign(const char *s);//用c类型字符串s赋值
string &assign(const char *s,int n);//用c字符串s开始的n个字符赋值
string &assign(const string &s);//把字符串s赋给当前字符串
string &assign(int n,char c);//用n个字符c赋值给当前字符串
string &assign(const string &s,int start,int n);//把字符串s中从start开始的n个字符赋给当前字符串
string &assign(const_iterator first,const_itertor last);//把first和last迭代器之间的部分赋给字符串
string的连接:
string &operator+=(const string &s);//把字符串s连接到当前字符串的结尾
string &append(const char *s); //把c类型字符串s连接到当前字符串结尾
string &append(const char *s,int n);//把c类型字符串s的前n个字符连接到当前字符串结尾
string &append(const string &s); //同operator+=()
string &append(const string &s,int pos,int n);//把字符串s中从pos开始的n个字符连接到当前字符串的结尾
string &append(int n,char c); //在当前字符串结尾添加n个字符c
string &append(const_iterator first,const_iterator last);//把迭代器first和last之间的部分连接到当前字符串的结尾
string的比较:
bool operator==(const string &s1,const string &s2)const;//比较两个字符串是否相等
运算符">","<",">=","<=","!="均被重载用于字符串的比较;
int compare(const string &s) const;//比较当前字符串和s的大小
int compare(int pos, int n,const string &s)const;//比较当前字符串从pos开始的n个字符组成的字符串与s的大小
int compare(int pos, int n,const string &s,int pos2,int n2)const;//比较当前字符串从pos开始的n个字符组成的字符串与s中
//pos2开始的n2个字符组成的字符串的大小
int compare(const char *s) const;
int compare(int pos, int n,const char *s) const;
int compare(int pos, int n,const char *s, int pos2) const;
compare函数在>时返回1,<时返回-1,==时返回0
string的子串:
string substr(int pos = 0,int n = npos) const;//返回pos开始的n个字符组成的字符串
string的交换:
void swap(string &s2); //交换当前字符串与s2的值
string类的查找函数:
int find(char c, int pos = 0) const;//从pos开始查找字符c在当前字符串的位置
int find(const char *s, int pos = 0) const;//从pos开始查找字符串s在当前串中的位置
int find(const char *s, int pos, int n) const;//从pos开始查找字符串s中前n个字符在当前串中的位置
int find(const string &s, int pos = 0) const;//从pos开始查找字符串s在当前串中的位置
//查找成功时返回所在位置,失败返回string::npos的值
int rfind(char c, int pos = npos) const;//从pos开始从后向前查找字符c在当前串中的位置
int rfind(const char *s, int pos = npos) const;
int rfind(const char *s, int pos, int n = npos) const;
int rfind(const string &s,int pos = npos) const;
//从pos开始从后向前查找字符串s中前n个字符组成的字符串在当前串中的位置,成功返回所在位置,失败时返回string::npos的值
int find_first_of(char c, int pos = 0) const;//从pos开始查找字符c第一次出现的位置
int find_first_of(const char *s, int pos = 0) const;
int find_first_of(const char *s, int pos, int n) const;
int find_first_of(const string &s,int pos = 0) const;
//从pos开始查找当前串中第一个在s的前n个字符组成的数组里的字符的位置。查找失败返回string::npos
int find_first_not_of(char c, int pos = 0) const;
int find_first_not_of(const char *s, int pos = 0) const;
int find_first_not_of(const char *s, int pos,int n) const;
int find_first_not_of(const string &s,int pos = 0) const;
//从当前串中查找第一个不在串s中的字符出现的位置,失败返回string::npos
int find_last_of(char c, int pos = npos) const;
int find_last_of(const char *s, int pos = npos) const;
int find_last_of(const char *s, int pos, int n = npos) const;
int find_last_of(const string &s,int pos = npos) const;
int find_last_not_of(char c, int pos = npos) const;
int find_last_not_of(const char *s, int pos = npos) const;
int find_last_not_of(const char *s, int pos, int n) const;
int find_last_not_of(const string &s,int pos = npos) const;
//find_last_of和find_last_not_of与find_first_of和find_first_not_of相似,只不过是从后向前查找
但是注意find_last_of从后往前查找字符串的时候返回的是字符串的最后一个字符的位置,而不是首字符的位置这个与rfind区分
string类的替换函数:
string &replace(int p0, int n0,const char *s);//删除从p0开始的n0个字符,然后在p0处插入串s
string &replace(int p0, int n0,const char *s, int n);//删除p0开始的n0个字符,然后在p0处插入字符串s的前n个字符
string &replace(int p0, int n0,const string &s);//删除从p0开始的n0个字符,然后在p0处插入串s
string &replace(int p0, int n0,const string &s, int pos, int n);//删除p0开始的n0个字符,然后在p0处插入串s中从pos开始的n个字符
string &replace(int p0, int n0,int n, char c);//删除p0开始的n0个字符,然后在p0处插入n个字符c
string &replace(iterator first0, iterator last0,const char *s);//把[first0,last0)之间的部分替换为字符串s
string &replace(iterator first0, iterator last0,const char *s, int n);//把[first0,last0)之间的部分替换为s的前n个字符
string &replace(iterator first0, iterator last0,const string &s);//把[first0,last0)之间的部分替换为串s
string &replace(iterator first0, iterator last0,int n, char c);//把[first0,last0)之间的部分替换为n个字符c
string &replace(iterator first0, iterator last0,const_iterator first, const_iterator last);//把[first0,last0)之间的部分替换成[first,last)之间的字符串
string类的插入函数:
string &insert(int p0, const char *s);
string &insert(int p0, const char *s, int n);
string &insert(int p0,const string &s);
string &insert(int p0,const string &s, int pos, int n);
//前4个函数在p0位置插入字符串s中pos开始的前n个字符
string &insert(int p0, int n, char c);//此函数在p0处插入n个字符c
iterator insert(iterator it, char c);//在it处插入字符c,返回插入后迭代器的位置
void insert(iterator it, const_iterator first, const_iterator last);//在it处插入[first,last)之间的字符
void insert(iterator it, int n, char c);//在it处插入n个字符c
string类的删除函数
iterator erase(iterator first, iterator last);//删除[first,last)之间的所有字符,返回删除后迭代器的位置
iterator erase(iterator it);//删除it指向的字符,返回删除后迭代器的位置
string &erase(int pos = 0, int n = npos);//删除pos开始的n个字符,返回修改后的字符串
string类的迭代器处理:
string类提供了向前和向后遍历的迭代器iterator,迭代器提供了访问各个字符的语法,类似于指针操作,迭代器不检查范围。
用string::iterator或string::const_iterator声明迭代器变量,const_iterator不允许改变迭代的内容。常用迭代器函数有:
const_iterator begin()const;
iterator begin(); //返回string的起始位置
const_iterator end()const;
iterator end(); //返回string的最后一个字符后面的位置
const_iterator rbegin()const;
iterator rbegin(); //返回string的最后一个字符的位置
const_iterator rend()const;
iterator rend(); //返回string第一个字符位置的前面
rbegin和rend用于从后向前的迭代访问,通过设置迭代器string::reverse_iterator,string::const_reverse_iterator实现
字符串流处理:
通过定义ostringstream和istringstream变量实现,#include <sstream>头文件中
例如:
string input("hello,this is a test");
istringstream is(input);
string s1,s2,s3,s4;
is>>s1>>s2>>s3>>s4;//s1="hello,this",s2="is",s3="a",s4="test"
ostringstream os;
os<<s1<<s2<<s3<<s4;
cout<<os.str();
最新文章
- GNURadio 使用问题
- Codeforces Round #341 Div.2 B. Wet Shark and Bishops
- XE3随笔21:系统默认语言与系统支持的语言列表
- 关于Hibernate的sequence diagram
- shell基本语法备忘
- ural 1572 Yekaterinozavodsk Great Well
- 【POJ2196】Specialized Four-Digit Numbers(暴力打表)
- 自动类型安全的.NET标准REST库refit
- 买房安全无忧 l 龙光集团与光大银行二手房资金监管战略合作!
- [Web]ORM模式的看法
- .gitconfig
- STM32的SWD调试进不了main函数
- mac 修改root密码
- Nginx详解二十六:Nginx架构篇之性能优化
- JavaScript——事件机制
- idea没有错误出现红色波浪线怎么去掉?
- 将 nginx 安装成 windows 的方法
- Linux常用命令--文件操作、权限设置
- 把配置和环境解耦 eliminate “works on my machine” problems when collaborating on code with co-workers docker架构与解决的问题
- qtjambi_ZC