A. New Building for SIS Codeforce
The building consists of n towers, h floors each, where the towers are labeled from 1 to n, the floors are labeled from 1 to h. There is a passage between any two adjacent towers (two towers i and i + 1 for all i: 1 ≤ i ≤ n - 1) on every floor x, where a ≤ x ≤ b. It takes exactly one minute to walk between any two adjacent floors of a tower, as well as between any two adjacent towers, provided that there is a passage on that floor. It is not permitted to leave the building.
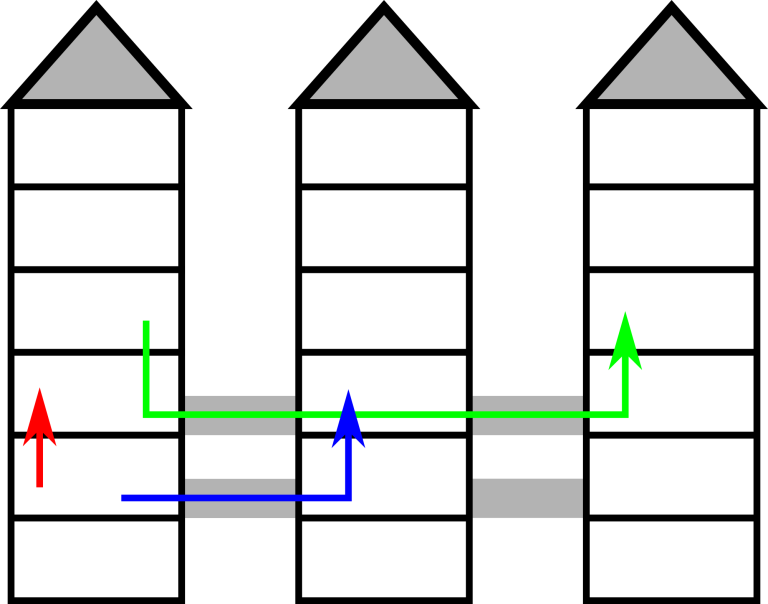
The picture illustrates the first example.
You have given k pairs of locations (ta, fa), (tb, fb): floor fa of tower ta and floor fb of tower tb. For each pair you need to determine the minimum walking time between these locations.
The first line of the input contains following integers:
- n: the number of towers in the building (1 ≤ n ≤ 108),
- h: the number of floors in each tower (1 ≤ h ≤ 108),
- a and b: the lowest and highest floor where it's possible to move between adjacent towers (1 ≤ a ≤ b ≤ h),
- k: total number of queries (1 ≤ k ≤ 104).
Next k lines contain description of the queries. Each description consists of four integers ta, fa, tb, fb (1 ≤ ta, tb ≤ n, 1 ≤ fa, fb ≤ h). This corresponds to a query to find the minimum travel time between fa-th floor of the ta-th tower and fb-th floor of the tb-th tower.
For each query print a single integer: the minimum walking time between the locations in minutes.
3 6 2 3 3
1 2 1 3
1 4 3 4
1 2 2 3
1
4
2
一道特别简单的题
题意:从一个塔的某一层到另一个塔的某一层,需要的最短时间。条件:每上下一层都要一秒,每从一个塔去临近的塔需要一秒,每个塔去临近的塔只有a-b层有通道去。
思路:分类讨论一下。
1、当出发地和目的地是同一个塔:abs(fa-fb)
2.1、当出发地和目的地不同塔:但是有一个在有通道范围内,或者两者都不在范围内但一个<=a一个>=b:abs(ta-tb)+abs(fa-fb)
2.2、当出发和目的地楼层都<=a:abs(ta-tb)+abs(fa-a)+abs(fb-a)
2.3、当出发地和目的地楼层都>=b:abs(ta-tb)+abs(fa-b)+abs(fb-b)
此人的思维:https://blog.csdn.net/miranda_ymz/article/details/81603271
但是我不喜欢此人的代码。
if(ta==tb)
cout<<abs(fa-fb)<<endl;
这是第一部分“当出发地和目的地是同一个塔”
else
{
if(fa>=b&&fb>=b)
cout<<abs(ta-tb)+(fb-b)+(fa-b)<<endl;
else if(fa<=a&&fb<=a)
cout<<abs(ta-tb)+(a-fa)+(a-fb)<<endl;
else
cout<<abs(ta-tb)+abs(fa-fb)<<endl;
}
这是第二部分,你只需要控制先判断同在b之上和同在a之下,剩余的就是一个大于b或者小于a,另一个在a和b之间。(不用那么多的判断)
上代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n,h,a,b,k;
cin>>n>>h>>a>>b>>k;
while(k--)
{
int ta,tb,fa,fb;
cin>>ta>>fa>>tb>>fb;
if(ta==tb)
cout<<abs(fa-fb)<<endl;
else
{
if(fa>=b&&fb>=b)
cout<<abs(ta-tb)+(fb-b)+(fa-b)<<endl;
else if(fa<=a&&fb<=a)
cout<<abs(ta-tb)+(a-fa)+(a-fb)<<endl;
else
cout<<abs(ta-tb)+abs(fa-fb)<<endl;
}
}
return ;
}
最新文章
- 数据结构算法C语言实现(八)--- 3.2栈的应用举例:迷宫求解与表达式求值
- js动画 无缝轮播 进度条 文字页面展示 div弹窗遮罩效果
- SpringMVC+spring-security+sitemesh+hibernate+freemarker整合-转
- [SQL]sql语句中charindex的用法
- HDU 2845 Beans (DP)
- PHP搭建OAuth2.0
- google 论文
- USB枚举详细过程剖析(转)
- sublime test3 使用技巧
- ES6是什么
- vue 初始化data中的数据
- Spark在Windows下的环境搭建(转)
- Atcoder Regular-074 Writeup
- Tesseract-OCR 3.05 多过语言文字识别(运行程序+中英日韩语言包)
- [HDU4123]Bob’s Race
- Qt 自学QGraphicsItem要点 积累
- Python 使用 Postfix 发送邮件
- [转]The NTLM Authentication Protocol and Security Support Provider
- ZT 设计模式六大原则(5):迪米特法则
- Oracle数据库的归档模式(archivelog mode)