各种排序算法实现(JAVA)
2024-10-19 16:46:04
转载: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42453117/article/details/100036347
Exer010Sort01BubbleSortV1
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 本代码的知识点:
* 冒泡排序
* 它重复地访问过要排序的数列,一次比较两个元素,如果他们的顺序错误就把他们交换过来
*/
public class Exer010Sort01BubbleSortV1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[] = {3, 44, 38, 5, 47, 15, 36, 26, 27, 2, 46, 4, 19, 50, 48};
//记录比较次数
int count = 0;
//i=0,第一轮比较
for (int i = 0; i < a.length - 1; i++) {
//第一轮,两两比较
for (int j = 0; j < a.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (a[j] > a[j + 1]) {
int temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = temp;
}
count++;
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));//[2, 3, 4, 5, 15, 19, 26, 27, 36, 38, 44, 46, 47, 48, 50]
System.out.println("一共比较了:" + count + "次");//一共比较了:105次
}
}
Exer010Sort01BubbleSortV2
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 本代码的知识点:
* 优化,减少排序次数
*/
public class Exer010Sort01BubbleSortV2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[] = {3, 44, 38, 5, 47, 15, 36, 26, 27, 2, 46, 4, 19, 50, 48};
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length - 1; i++) {
boolean flag = true;
for (int j = 0; j < a.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (a[j] > a[j + 1]) {
int temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = temp;
flag = false;
}
count++;
}
if (flag) {
break;
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));// [2, 3, 4, 5, 15, 19, 26, 27, 36, 38, 44, 46, 47, 48, 50]
System.out.println("一共比较了:" + count + "次");//一共比较了:95次
}
}
Exer010Sort02SelectSort
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 本代码的知识点:
* 选择排序
* 先定义一个记录最小元素的下标,然后循环一次后面的,找到最小的元素,最后将他放到前面排序好的序列。
*/
public class Exer010Sort02SelectSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[] = {3, 44, 38, 5, 47, 15, 36, 26, 27, 2, 46, 4, 19, 50, 48};
for (int i = 0; i < a.length - 1; i++) {
int index = i;//标记第一个为待比较的数
for (int j = i + 1; j < a.length; j++) { //然后从后面遍历与第一个数比较
if (a[j] < a[index]) { //如果小,就交换最小值
index = j;//保存最小元素的下标
}
}
//找到最小值后,将最小的值放到第一的位置,进行下一遍循环
int temp = a[index];
a[index] = a[i];
a[i] = temp;
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));//[2, 3, 4, 5, 15, 19, 26, 27, 36, 38, 44, 46, 47, 48, 50]
}
}
Exer010Sort03InsertSort
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 本代码的知识点:
* 插入排序
* 定义一个待插入的数,再定义一个待插入数的前一个数的下标,然后拿待插入数与前面的数组一一比较,最后交换。
*/
public class Exer010Sort03InsertSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[] = {3, 44, 38, 5, 47, 15, 36, 26, 27, 2, 46, 4, 19, 50, 48};
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { //长度不减1,是因为要留多一个位置方便插入数
//定义待插入的数
int insertValue = a[i];
//找到待插入数的前一个数的下标
int insertIndex = i - 1;
while (insertIndex >= 0 && insertValue < a[insertIndex]) {//拿a[i]与a[i-1]的前面数组比较
a[insertIndex + 1] = a[insertIndex];
insertIndex--;
}
a[insertIndex + 1] = insertValue;
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));//[2, 3, 4, 5, 15, 19, 26, 27, 36, 38, 44, 46, 47, 48, 50]
}
}
Exer010Sort04ShellSort
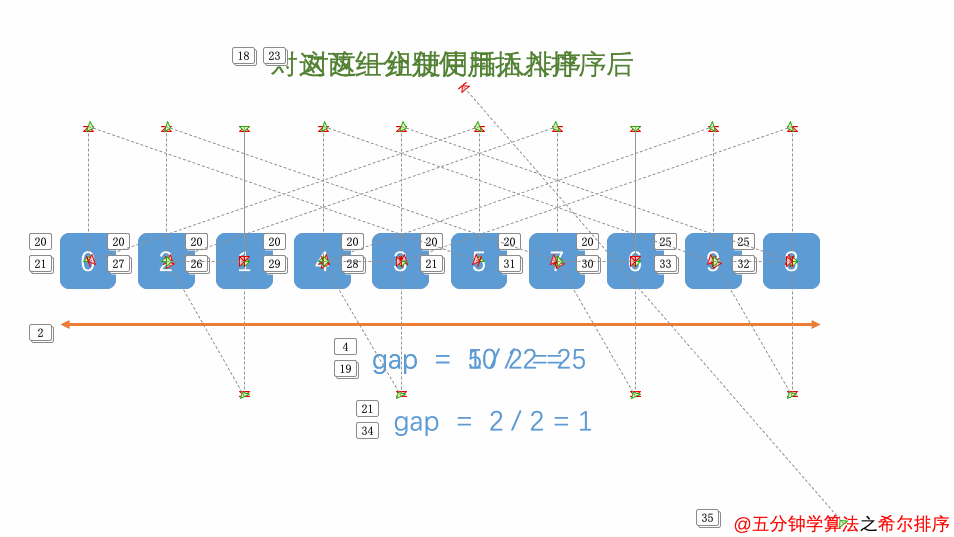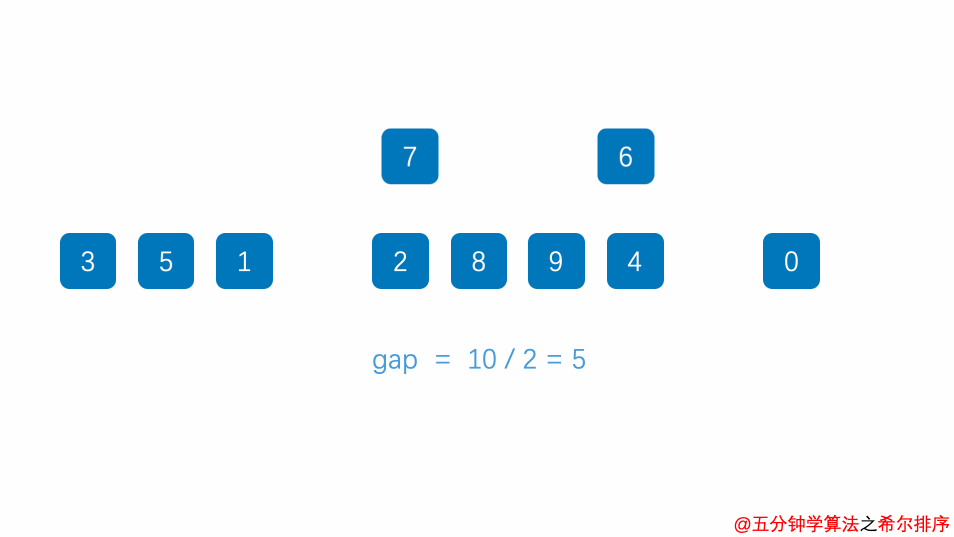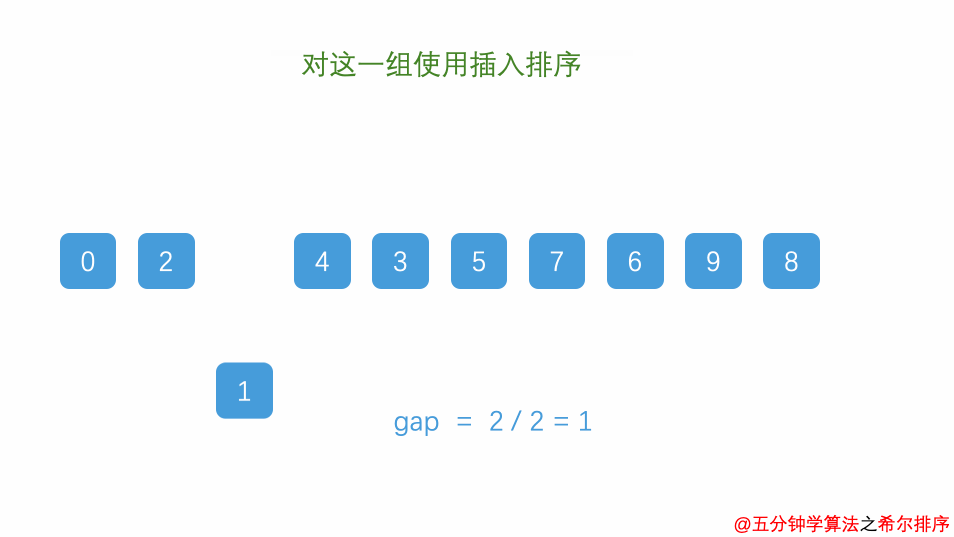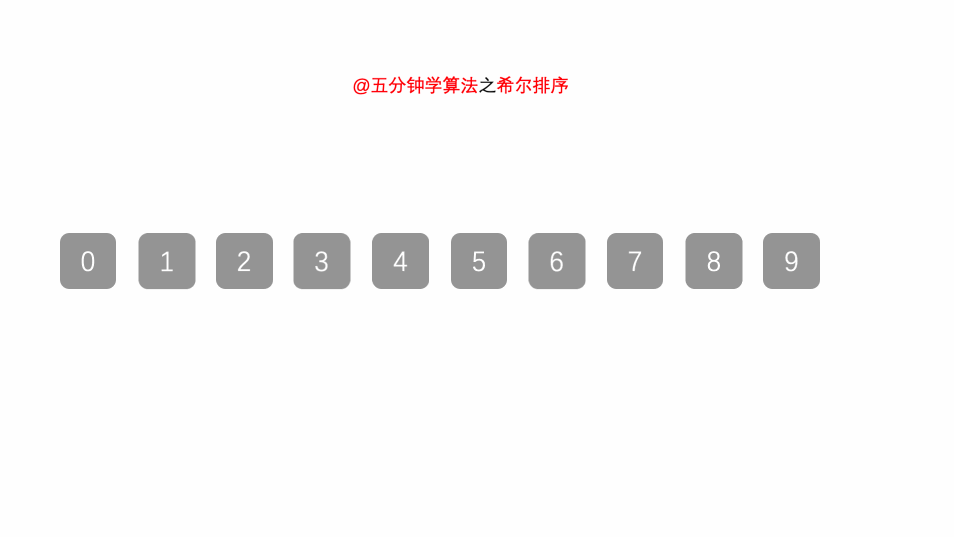
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 本代码的知识点:
* 希尔排序
* 插入排序的升级
*/
public class Exer010Sort04ShellSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[] = {3, 44, 38, 5, 47, 15, 36, 26, 27, 2, 46, 4, 19, 50, 48};
int count = 0;//比较次数
for (int gap = a.length / 2; gap > 0; gap = gap / 2) {
//将整个数组分为若干个子数组
for (int i = gap; i < a.length; i++) {
//遍历各组的元素
for (int j = i - gap; j >= 0; j = j - gap) {
//交换元素
if (a[j] > a[j + gap]) {
int temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + gap];
a[j + gap] = temp;
count++;
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(count);//16
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));//[2, 3, 4, 5, 15, 19, 26, 27, 36, 38, 44, 46, 47, 48, 50]
}
}
Exer010Sort05QuickSort
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 本代码的知识点:
* 快速排序
*/
public class Exer010Sort05QuickSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//int a[]={50,1,12,2};
int a[]={3,44,38,5,47,15,36,26,27,2,46,4,19,50,48};
quicksort(a,0,a.length-1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
private static void quicksort(int[] a, int low, int high) {
int i,j;
if (low>high) {
return;
}
i=low;
j=high;
int temp=a[low];//基准位,low=length时,会报异常,java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 4 ,所以必须在if判断后面,就跳出方法。
while(i<j){
//先从右边开始往左递减,找到比temp小的值才停止
while ( temp<=a[j] && i<j) {
j--;
}
//再看左边开始往右递增,找到比temp大的值才停止
while ( temp>=a[i] && i<j) {
i++;
}
//满足 i<j 就交换,继续循环while(i<j)
if (i<j) {
int t=a[i];
a[i]=a[j];
a[j]=t;
}
}
//最后将基准位跟 a[i]与a[j]相等的位置,进行交换,此时i=j
a[low]=a[i];
a[i]=temp;
//左递归
quicksort(a, low, j-1);
//右递归
quicksort(a, j+1, high);
}
}
Exer010Sort06MergeSort
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 本代码的知识点:
* 合并排序
*/
public class Exer010Sort06MergeSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[] = {3, 44, 38, 5, 47, 15, 36, 26, 27, 2, 46, 4, 19, 50, 48};
//int a[]={5,2,4,7,1,3,2,2};
int temp[] = new int[a.length];
mergesort(a, 0, a.length - 1, temp);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
private static void mergesort(int[] a, int left, int right, int[] temp) {
//分解
if (left < right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
//向左递归进行分解
mergesort(a, left, mid, temp);
//向右递归进行分解
mergesort(a, mid + 1, right, temp);
//每分解一次便合并一次
merge(a, left, right, mid, temp);
}
}
private static void merge(int[] a, int left, int right, int mid, int[] temp) {
int i = left; //初始i,左边有序序列的初始索引
int j = mid + 1;//初始化j,右边有序序列的初始索引(右边有序序列的初始位置即中间位置的后一位置)
int t = 0;//指向temp数组的当前索引,初始为0
//先把左右两边的数据(已经有序)按规则填充到temp数组
//直到左右两边的有序序列,有一边处理完成为止
while (i <= mid && j <= right) {
//如果左边有序序列的当前元素小于或等于右边的有序序列的当前元素,就将左边的元素填充到temp数组中
if (a[i] <= a[j]) {
temp[t] = a[i];
t++;//索引向后移
i++;//i后移
} else {
//反之,将右边有序序列的当前元素填充到temp数组中
temp[t] = a[j];
t++;//索引向后移
j++;//j后移
}
}
//把剩余数据的一边的元素填充到temp中
while (i <= mid) {
//此时说明左边序列还有剩余元素
//全部填充到temp数组
temp[t] = a[i];
t++;
i++;
}
while (j <= right) {
//此时说明左边序列还有剩余元素
//全部填充到temp数组
temp[t] = a[j];
t++;
j++;
}
//将temp数组的元素复制到原数组
t = 0;
int tempLeft = left;
while (tempLeft <= right) {
a[tempLeft] = temp[t];
t++;
tempLeft++;
}
}
}
Exer010Sort07HeapSort
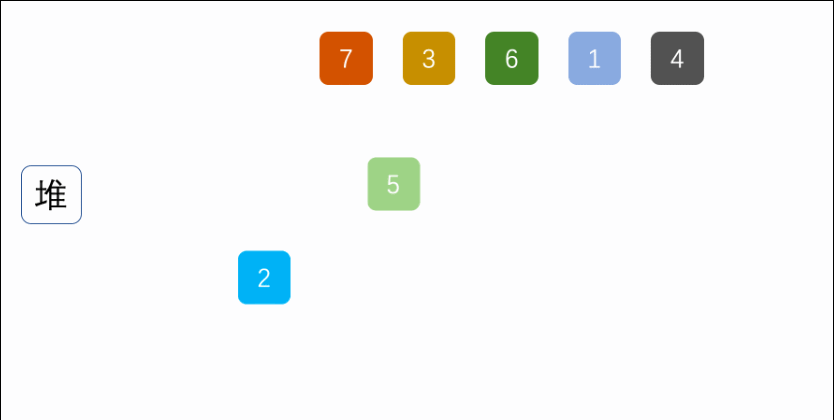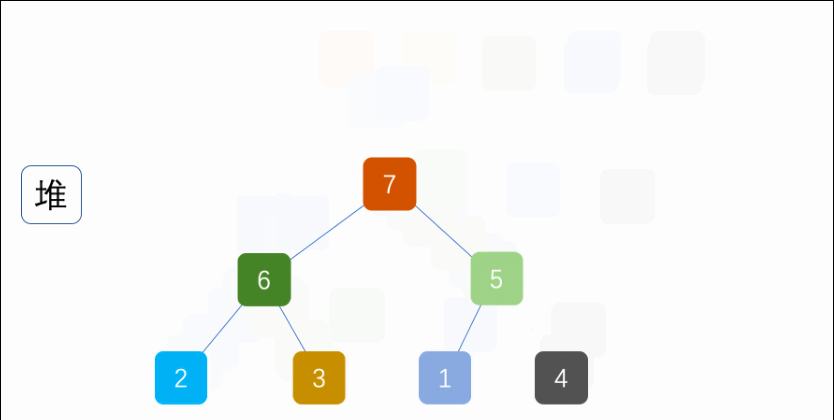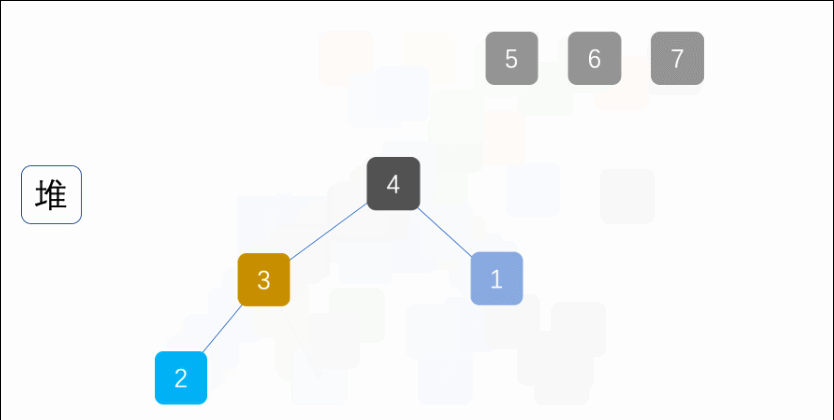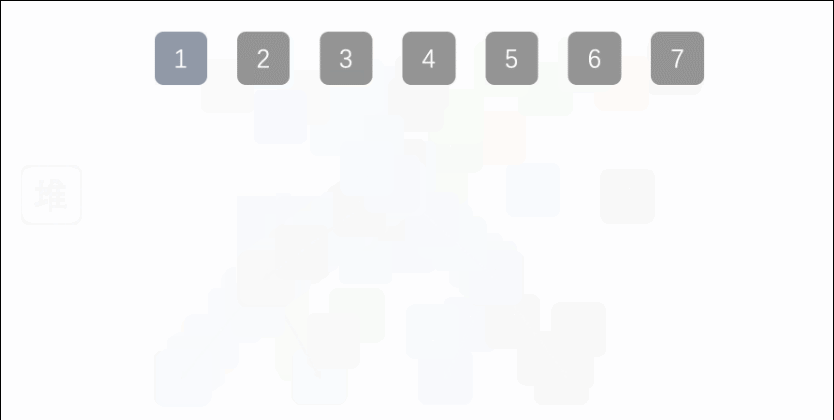
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 本代码的知识点:
* 堆排序
*/
public class Exer010Sort07HeapSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[] = {3, 44, 38, 5, 47, 15, 36, 26, 27, 2, 46, 4, 19, 50, 48};
sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
public static void sort(int[] arr) {
int length = arr.length;
//构建堆
buildHeap(arr, length);
for (int i = length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
//将堆顶元素与末位元素调换
int temp = arr[0];
arr[0] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
//数组长度-1 隐藏堆尾元素
length--;
//将堆顶元素下沉 目的是将最大的元素浮到堆顶来
sink(arr, 0, length);
}
}
private static void buildHeap(int[] arr, int length) {
for (int i = length / 2; i >= 0; i--) {
sink(arr, i, length);
}
}
private static void sink(int[] arr, int index, int length) {
int leftChild = 2 * index + 1;//左子节点下标
int rightChild = 2 * index + 2;//右子节点下标
int present = index;//要调整的节点下标
//下沉左边
if (leftChild < length && arr[leftChild] > arr[present]) {
present = leftChild;
}
//下沉右边
if (rightChild < length && arr[rightChild] > arr[present]) {
present = rightChild;
}
//如果下标不相等 证明调换过了
if (present != index) {
//交换值
int temp = arr[index];
arr[index] = arr[present];
arr[present] = temp;
//继续下沉
sink(arr, present, length);
}
}
}
Exer010Sort08CountSort
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 本代码的知识点:
* 计数排序
*/
public class Exer010Sort08CountSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = { 4, 2, 2, 8, 3, 3, 1 };
// 找到数组中最大的值 ---> max:8
int max = findMaxElement(array);
int[] sortedArr = countingSort(array, max + 1);
System.out.println("计数排序后的数组: " + Arrays.toString(sortedArr));
}
private static int findMaxElement(int[] array) {
int max = array[0];
for (int val : array) {
if (val > max) {
max = val;
}
}
return max;
}
private static int[] countingSort(int[] array, int range) { //range:8+1
int[] output = new int[array.length];
int[] count = new int[range];
//初始化: count1数组
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
count[array[i]]++;
}
//计数: count2数组,累加次数后的,这里用count2区分
for (int i = 1; i < range; i++) {
count[i] = count[i] + count[i - 1];
}
//排序:最后数组
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
output[count[array[i]] - 1] = array[i];
count[array[i]]--;
}
return output;
}
}
Exer010Sort09BucketSort
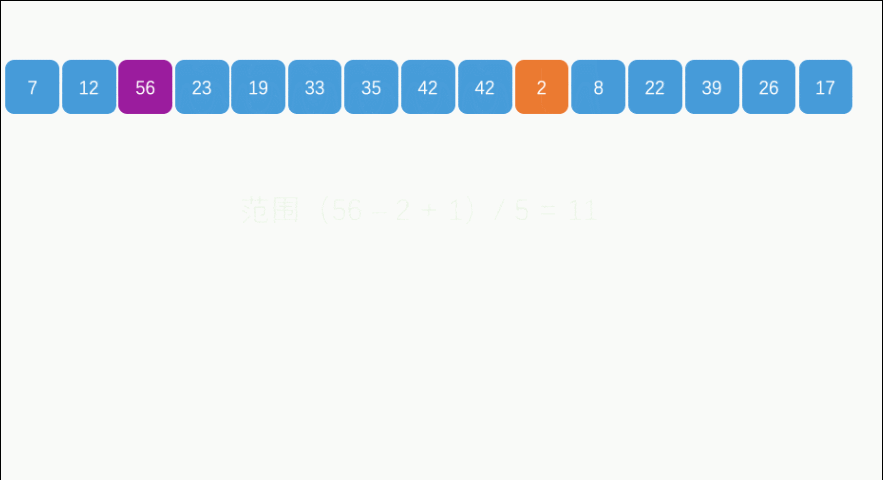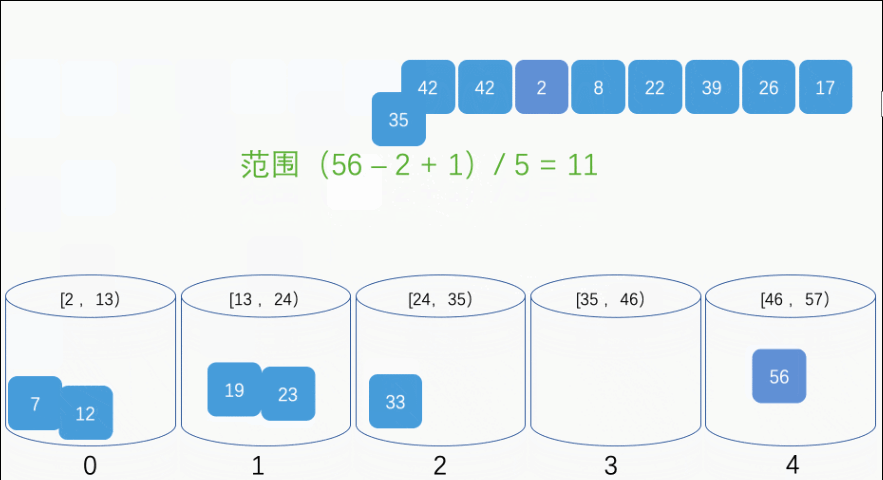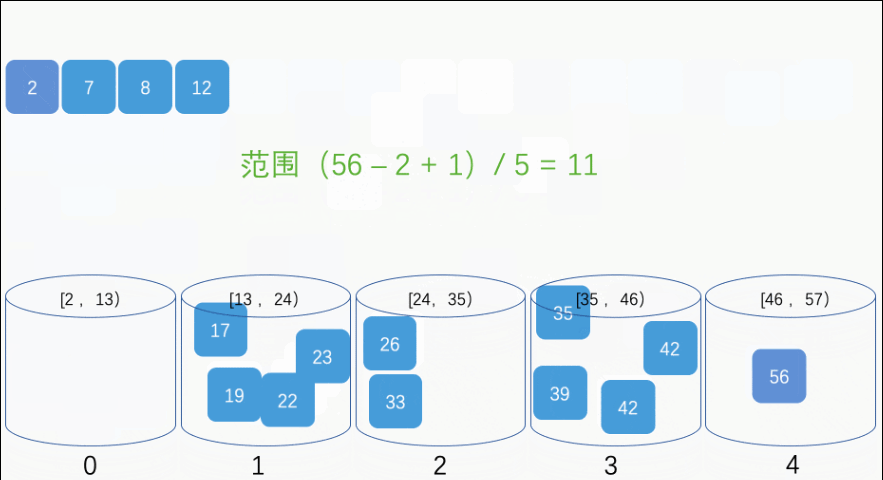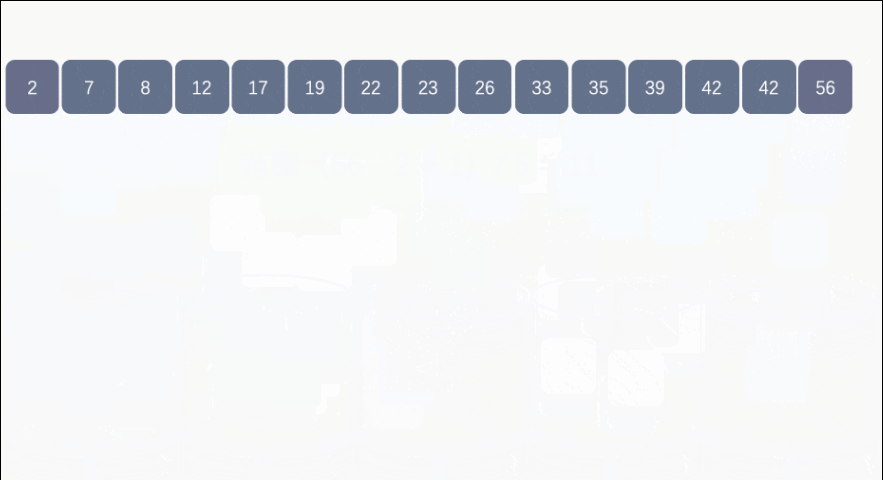
import java.util.*;
/**
* 本代码的知识点:
* 桶排序
*/
public class Exer010Sort09BucketSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 输入元素均在 [0, 10) 这个区间内
float[] arr = new float[]{0.12f, 2.2f, 8.8f, 7.6f, 7.2f, 6.3f, 9.0f, 1.6f, 5.6f, 2.4f};
bucketSort(arr);
printArray(arr);
}
public static void bucketSort(float[] arr) {
// 新建一个桶的集合
ArrayList<LinkedList<Float>> buckets = new ArrayList<LinkedList<Float>>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// 新建一个桶,并将其添加到桶的集合中去。
// 由于桶内元素会频繁的插入,所以选择 LinkedList 作为桶的数据结构
buckets.add(new LinkedList<Float>());
}
// 将输入数据全部放入桶中并完成排序
for (float data : arr) {
int index = getBucketIndex(data);
insertSort(buckets.get(index), data);
}
// 将桶中元素全部取出来并放入 arr 中输出
int index = 0;
for (LinkedList<Float> bucket : buckets) {
for (Float data : bucket) {
arr[index++] = data;
}
}
}
/**
* 计算得到输入元素应该放到哪个桶内
*/
public static int getBucketIndex(float data) {
// 这里例子写的比较简单,仅使用浮点数的整数部分作为其桶的索引值
// 实际开发中需要根据场景具体设计
return (int) data;
}
/**
* 我们选择插入排序作为桶内元素排序的方法 每当有一个新元素到来时,我们都调用该方法将其插入到恰当的位置
*/
public static void insertSort(List<Float> bucket, float data) {
ListIterator<Float> it = bucket.listIterator();
boolean insertFlag = true;
while (it.hasNext()) {
if (data <= it.next()) {
it.previous(); // 把迭代器的位置偏移回上一个位置
it.add(data); // 把数据插入到迭代器的当前位置
insertFlag = false;
break;
}
}
if (insertFlag) {
bucket.add(data); // 否则把数据插入到链表末端
}
}
public static void printArray(float[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + ", ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
Exer010Sort10RaixSort
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 本代码的知识点:
* 基数排序
*/
public class Exer010Sort10RaixSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 53, 3, 542, 748, 14, 214 };
// 得到数组中最大的数
int max = arr[0];// 假设第一个数就是数组中的最大数
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
// 得到最大数是几位数
// 通过拼接一个空串将其变为字符串进而求得字符串的长度,即为位数
int maxLength = (max + "").length();
// 定义一个二维数组,模拟桶,每个桶就是一个一维数组
// 为了防止放入数据的时候桶溢出,我们应该尽量将桶的容量设置得大一些
int[][] bucket = new int[10][arr.length];
// 记录每个桶中实际存放的元素个数
// 定义一个一维数组来记录每个桶中每次放入的元素个数
int[] bucketElementCounts = new int[10];
// 通过变量n帮助取出元素位数上的数
for (int i = 0, n = 1; i < maxLength; i++, n *= 10) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
// 针对每个元素的位数进行处理
int digitOfElement = arr[j] / n % 10;
// 将元素放入对应的桶中
// bucketElementCounts[digitOfElement]就是桶中的元素个数,初始为0,放在第一位
bucket[digitOfElement][bucketElementCounts[digitOfElement]] = arr[j];
// 将桶中的元素个数++
// 这样接下来的元素就可以排在前面的元素后面
bucketElementCounts[digitOfElement]++;
}
// 按照桶的顺序取出数据并放回原数组
int index = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < bucket.length; k++) {
// 如果桶中有数据,才取出放回原数组
if (bucketElementCounts[k] != 0) {
// 说明桶中有数据,对该桶进行遍历
for (int l = 0; l < bucketElementCounts[k]; l++) {
// 取出元素放回原数组
arr[index++] = bucket[k][l];
}
}
// 每轮处理后,需要将每个bucketElementCounts[k]置0
bucketElementCounts[k] = 0;
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));//[3, 14, 53, 214, 542, 748]
}
}
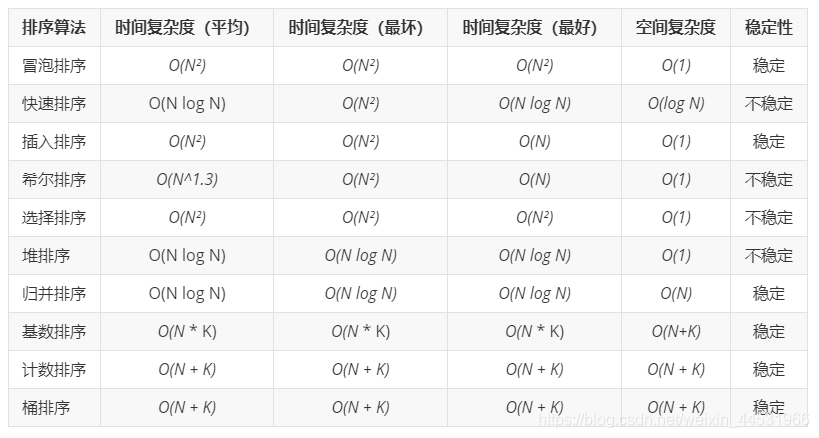
复杂度
最新文章
- spring的路径通配符
- FreeMarker标签与使用
- HQL的语言
- 通达OA 免狗迁移到公网 的另类解决办法
- Visual Studio 2015 预览版 - 支持跨平台开发Android/iOS应用程序(内置安卓模拟器)
- IOS 单例模式的学习
- SFTP上传下载(C#)
- MEF初体验之五:Lazy Exports
- java 方法学习
- Android ViewDragHelper完全解析 自定义ViewGroup神器
- KoaHub.JS基于Node.js开发的mysql的node.js驱动程序代码
- VS2013各版本激活密钥
- Google Android Studio Kotlin 开发环境配置
- Java代理和动态代理
- JavaScript Html页面加载完成三种写法
- Node.js 进程平滑离场剖析
- DUMP101 企业级电商FE
- vue 线上不支持put方法
- Mycat - 高可用与负载均衡实现,满满的干货!
- cocos2d内存管理,类的生命周期