源码分析(5)-ArrayList、Vector和LinkedList(JDK1.8)
2024-09-04 03:43:18
一、概述
1、线程安全:ArrayList和LinkedList非线程安全的、Vector线程安全的。
2、底层数据结构:ArrayList和Vector底层数据结构是数组;LinkedList双向链表。
3、时间复杂度是否受插入和删除元素位置影响:ArrayList和Vector受影响,add(E e)方法时间复杂度O(1)和add(int index, E element)方法时间复杂度O(n-index);LinkedList受影响,add(E e)方法时间复杂度O(1)和add(int index, E element)方法时间复杂度O(n)。
4、是否支持随机访问:ArrayList和Vector支持;LinkedList不支持。
5、内存空间占用:ArrayList和Vector空间浪费主要体现在在list列表的结尾会预留一定的容量空间;LinkedList空间花费则体现在每一个元素都需要消耗更多的空间(因为要存放直接后继和直接前驱以及数据)。
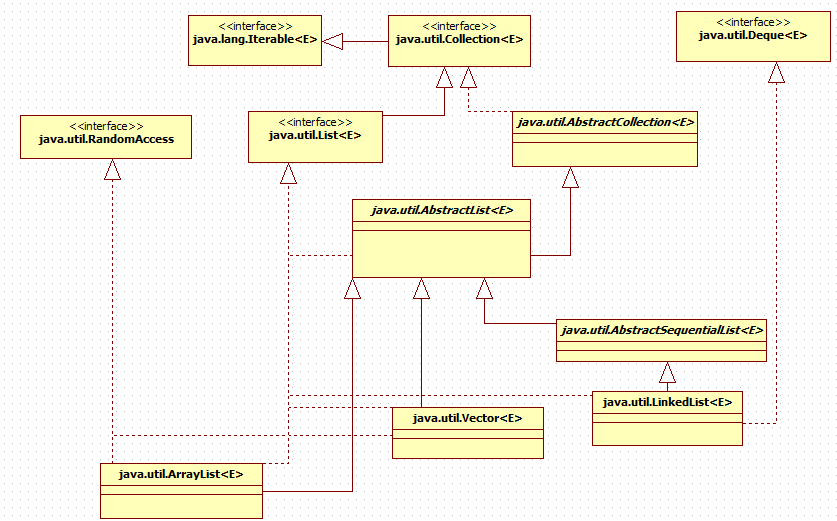
二、集合UML类图
ArrayList和LinkedList继承和实现相同,LinkedList实现java.util.Deque<E>接口和继承java.util.AbstractSequentialList<E>抽象类。
三、ArrayList源码分析
1、重要成员变量
//数组,存储数据
transient Object[] elementData;
//数组长度
private int size;
//数组结构变更次数
protected transient int modCount = 0;
2、插入
//添加元素
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1);//确认容量足够
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
} private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
//计算容量
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);//初始化容量10,返回初始容量和需要最小容量选择最大值
}
return minCapacity;
}
//
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)//最小需要容量大于数组长度,进行扩容
grow(minCapacity);
}
//扩容
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);扩容1.5倍
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)//扩容后容量和需要的最小容量
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);//设置最大容量
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);//复制数组
}
//指定位置添加数组
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index);//复制插入数组
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
3、删除
//删除元素
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved);数组复制,index位置以后的元素前移1个位置
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
四、Vector源码分析
成员方法和ArrayList相似,不同之处在于方法都是synchronized同步锁修饰。
1、重要成员变量
//数组,存储数据和ArrayList相同
protected Object[] elementData;
//数组长度,等同于ArrayList的size
protected int elementCount;
//扩容量
protected int capacityIncrement;
2、插入
//添加元素
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);//确保容量
elementData[elementCount++] = e;//尾部添加元素
return true;
}
//
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);//扩容
}
//
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ? capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);//默认扩容2倍
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);//复制数组
}
五、LinkedList源码分析
1、重要成员变量
//双向链表节点长度
transient int size = 0;
//头结点
transient Node<E> first;
//尾结点
transient Node<E> last;
2、数据结构
private static class Node<E> {
E item;//数据
Node<E> next;//下一个节点
Node<E> prev;//前一个节点
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
3、插入
//插入到头部
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
//
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node<E> f = first;//头结点
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)//头结点为空
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;//原头结点的前一个节点指向新节点
size++;
modCount++;
}
//尾部添加节点
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
//
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;//尾结点
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)//尾结点为空,此时头尾节点都是空
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;//尾结点执行新节点
size++;
modCount++;
}
//插入节点默认在尾部添加
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
//指定位置添加节点
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index); if (index == size)
linkLast(element);//尾部添加节点
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
//
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
//
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index); if (index < (size >> 1)) {//插入位置小于0.5*size,正向遍历
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)//查询待插入位置节点
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)//逆向遍历
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
4、删除
//删除指定位置元素
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));//遍历查询index位置元素
}
//
E unlink(Node<E> x) {//删除数据
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev; if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
} if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
} x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
其他方法不再讲解。
最新文章
- [Spring]支持注解的Spring调度器
- ichart.js绘制虚线 ,平均分虚线
- GitHub详解(GitHub for Windows)
- 【转】 TCP协议中的三次握手和四次挥手(图解)
- 标签视图控制器UITabBarController
- 【BZOJ】【1037】【ZJOI2008】生日聚会party
- 南阳理工ACM975--关于521
- CentOS 6.5系统上安装MySQL数据库
- MySQL学习笔记(三)—索引
- An explicit value for the identity column in table can only be specified when a column list is used and IDENTITY_INSERT is ON
- 黏包现象之TCP
- Bitmap那些事之内存占用计算和加载注意事项
- Javascript数组系列二之迭代方法1
- wstngfw 初始化的一些配置
- Fabric实例
- MongoDB修改与聚合二
- 大数据之superset
- 在WPF中实现平滑滚动
- HDU 1501 Zipper(DFS)
- linux centos7 erlang rabbitmq安装