HillCrest Sensor HAL
1. 抽象定义
Google为Sensor提供了统一的HAL接口,不同的硬件厂商需要根据该接口来实现并完成具体的硬件抽象层,Android中Sensor的HAL接口定义在:hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/sensors.h,
其中定义了几个数据类型:
- sensor_t - 包含传感器相关信息
- sensors_module_t - 传感器硬件模块类型
- sensors_event_t - 传感器事件
- sensors_poll_device_t - 传感器抽象设备类型
HAL实现必须完成下面的函数接口:
- get_sensors_list - 返回所有传感器的列表
- activate - 启动或停止传感器
- batch - 设置传感器的参数,如采样率和最大报告延迟
- setDelay - 仅用于 1.0 版本的 HAL,设置指定传感器的采样率
- flush - 刷写指定传感器的 FIFO 并在完成后报告刷写完成事件
- poll - 返回可用的传感器事件
1.1 sensor type
sensor type的定义如下:
[sensors-base.h]
enum {
SENSOR_TYPE_META_DATA = 0,
SENSOR_TYPE_ACCELEROMETER = 1,
SENSOR_TYPE_MAGNETIC_FIELD = 2,
SENSOR_TYPE_ORIENTATION = 3,
SENSOR_TYPE_GYROSCOPE = 4,
SENSOR_TYPE_LIGHT = 5,
SENSOR_TYPE_PRESSURE = 6,
SENSOR_TYPE_TEMPERATURE = 7,
SENSOR_TYPE_PROXIMITY = 8,
SENSOR_TYPE_GRAVITY = 9,
...
}
#define SENSOR_STRING_TYPE_ACCELEROMETER "android.sensor.accelerometer"
#define SENSOR_STRING_TYPE_MAGNETIC_FIELD "android.sensor.magnetic_field"
#define SENSOR_STRING_TYPE_ORIENTATION "android.sensor.orientation"
#define SENSOR_STRING_TYPE_GYROSCOPE "android.sensor.gyroscope"
#define SENSOR_STRING_TYPE_LIGHT "android.sensor.light"
#define SENSOR_STRING_TYPE_PRESSURE "android.sensor.pressure"
#define SENSOR_STRING_TYPE_TEMPERATURE "android.sensor.temperature"
#define SENSOR_STRING_TYPE_PROXIMITY "android.sensor.proximity"
1.2 sensor_t
sensor_t 的定义如下
[sensors.h]
struct sensor_t {
/* Name of this sensor.
* All sensors of the same "type" must have a different "name".
*/
const char* name;
/* vendor of the hardware part */
const char* vendor;
/* version of the hardware part + driver. The value of this field
* must increase when the driver is updated in a way that changes the
* output of this sensor. This is important for fused sensors when the
* fusion algorithm is updated.
*/
int version;
/* handle that identifies this sensors. This handle is used to reference
* this sensor throughout the HAL API.
*/
int handle;
/* this sensor's type. */
int type; //sensor type
/* maximum range of this sensor's value in SI units */
float maxRange;
/* smallest difference between two values reported by this sensor */
float resolution;
/* rough estimate of this sensor's power consumption in mA */
float power;
/* this value depends on the reporting mode:
*
* continuous: minimum sample period allowed in microseconds
* on-change : 0
* one-shot :-1
* special : 0, unless otherwise noted
*/
int32_t minDelay;
/* number of events reserved for this sensor in the batch mode FIFO.
* If there is a dedicated FIFO for this sensor, then this is the
* size of this FIFO. If the FIFO is shared with other sensors,
* this is the size reserved for that sensor and it can be zero.
*/
uint32_t fifoReservedEventCount;
/* maximum number of events of this sensor that could be batched.
* This is especially relevant when the FIFO is shared between
* several sensors; this value is then set to the size of that FIFO.
*/
uint32_t fifoMaxEventCount;
/* type of this sensor as a string.
*
* If type is OEM specific or sensor manufacturer specific type
* (>=SENSOR_TYPE_DEVICE_PRIVATE_BASE), this string must be defined with reserved domain of
* vendor/OEM as a prefix, e.g. com.google.glass.onheaddetector
*
* For sensors of Android defined types, Android framework will override this value. It is ok to
* leave it pointing to an empty string.
*/
const char* stringType;
/* permission required to see this sensor, register to it and receive data.
* Set to "" if no permission is required. Some sensor types like the
* heart rate monitor have a mandatory require_permission.
* For sensors that always require a specific permission, like the heart
* rate monitor, the android framework might overwrite this string
* automatically.
*/
const char* requiredPermission;
/* This value is defined only for continuous mode and on-change sensors. It is the delay between
* two sensor events corresponding to the lowest frequency that this sensor supports. When lower
* frequencies are requested through batch()/setDelay() the events will be generated at this
* frequency instead. It can be used by the framework or applications to estimate when the batch
* FIFO may be full.
*
* NOTE: 1) period_ns is in nanoseconds where as maxDelay/minDelay are in microseconds.
* continuous, on-change: maximum sampling period allowed in microseconds.
* one-shot, special : 0
* 2) maxDelay should always fit within a 32 bit signed integer. It is declared as 64 bit
* on 64 bit architectures only for binary compatibility reasons.
* Availability: SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_3
*/
#ifdef __LP64__
int64_t maxDelay;
#else
int32_t maxDelay;
#endif
/* Flags for sensor. See SENSOR_FLAG_* above. Only the least significant 32 bits are used here.
* It is declared as 64 bit on 64 bit architectures only for binary compatibility reasons.
* Availability: SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_3
*/
#ifdef __LP64__
uint64_t flags;
#else
uint32_t flags;
#endif
/* reserved fields, must be zero */
void* reserved[2];
};
1.3 sensor_module_t
该结构体实际上是对标准硬件模块hw_module_t的一个扩展,增加一个get_sensor_list函数,用于获取传感器的列表,以及set_operation_mode设置为相关的mode;
struct sensors_module_t {
struct hw_module_t common;
/**
* Enumerate all available sensors. The list is returned in "list".
* return number of sensors in the list
*/
int (*get_sensors_list)(struct sensors_module_t* module,
struct sensor_t const** list);
/**
* Place the module in a specific mode. The following modes are defined
*
* 0 - Normal operation. Default state of the module.
* 1 - Loopback mode. Data is injected for the supported
* sensors by the sensor service in this mode.
* return 0 on success
* -EINVAL if requested mode is not supported
* -EPERM if operation is not allowed
*/
int (*set_operation_mode)(unsigned int mode);
};
1.4 sensors_poll_device_t
sensors_poll_device_t 定义了以下方法
[sensors.h]
struct sensors_poll_device_t {
struct hw_device_t common;
int (*activate)(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev,
int sensor_handle, int enabled);
int (*setDelay)(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev,
int sensor_handle, int64_t sampling_period_ns);
int (*poll)(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev,
sensors_event_t* data, int count);
};
2. 抽象方法
2.1 get_sensors_list
sensors_module_t 是用于为传感器创建 Android 硬件模块的类型。HAL 的实现必须定义一个该类型的对象 HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM,以提供 get_sensors_list 函数。
[HAL.cpp]
struct sensors_module_t HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
.common = {
.tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
#ifdef SENSORS_MODULE_API_VERSION_0_1
.module_api_version = SENSORS_MODULE_API_VERSION_0_1,
#else
.module_api_version = 0,
#endif
.hal_api_version = 0,
.id = SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
.name = "Freespace SensorHub Sensor Module",
.author = "Hillcrest Labs, Inc.",
.methods = &sensors_module_methods,
.dso = 0,
.reserved = {},
},
.get_sensors_list = get_sensors_list
};
get_sensors_list 提供由 HAL 实现的传感器列表,该函数返回列表中的传感器数量。
调用单例模式实例化,然后调用对应方法获取传感器列表,返回对应的 sensor_t 结构体数组指针。
static int get_sensors_list(struct sensors_module_t* module,
struct sensor_t const** list) {
if (getContext()) {
return getContext()->getSensorList(list);
}
return 0;
}
static Context * getContext() {
if (context_) {
return context_;
}
if (!HAL_ENABLED) {
return NULL;
}
context_ = new Context();
#ifdef ENABLE_SOURCE_OBSERVER
if (OBS_ENABLED) {
hubServer_ = new HubServer(*context_, true);
}
#endif
return context_;
}
2.2 open method
打开 sensor 的实例化对象, 并填充 hw_device_t
static struct hw_module_methods_t sensors_module_methods = {
.open = open_sensors
};
struct hcrest_sensors_device_t {
#ifdef SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_1
struct sensors_poll_device_1 base; // must be first
#else
struct sensors_poll_device_t base; // must be first
#endif
unsigned int magic;
void * context;
};
static hcrest_sensors_device_t hwdevice_;
static bool open_ = false;
static int open_sensors(const struct hw_module_t* module, const char* name,
struct hw_device_t** device) {
LOGI("Freespace SensorHub HAL open");
LOGD(" open from: %s", name);
LOGI(" version: " FS_SENSORHUB_HAL_VERSION);
if (open_) {
LOGE("Already open, refusing open_sensors");
return -EBUSY;
}
int rc;
*device = NULL;
Context * context = getContext();
if (context) {
hwdevice_.base.common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG;
#if defined(SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_3)
hwdevice_.base.common.version = SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_3;
#elif defined(SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_2)
hwdevice_.base.common.version = SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_2;
#elif defined(SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_1)
hwdevice_.base.common.version = SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_1;
#elif defined(SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_0)
hwdevice_.base.common.version = SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_0;
#else
hwdevice_.base.common.version = 0;
#endif
hwdevice_.base.common.module = const_cast<hw_module_t*>(module);
hwdevice_.base.common.close = ctx_close;
hwdevice_.base.activate = ctx_activate;
hwdevice_.base.setDelay = ctx_setDelay;
hwdevice_.base.poll = ctx_poll;
#ifdef SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_1
hwdevice_.base.batch = ctx_batch;
hwdevice_.base.flush = ctx_flush;
#endif
hwdevice_.magic = HCREST_MAGIC;
hwdevice_.context = context;
rc = context->open();
#ifdef ENABLE_SOURCE_OBSERVER
if (rc == 0 && OBS_ENABLED) {
LOGI("Initializing source server");
if ((rc = hubServer_->init())) {
LOGE("Failed initializing server");
freeContext();
}
}
#endif
if (!rc) {
*device = &hwdevice_.base.common;
}
} else {
// Dummy context
*device = NULL;
rc = 0;
LOGD(">>> Dummy Sensors <<<");
}
LOGD("Freespace SensorHub HAL open = %s, device=%p ", rc ? strerror(-rc) : "Success", *device);
return rc;
}
先看下 context->open() , 打开挂在 SensorHub 上的所有 sensor,并设置 hcrest_sensors_device_t
[Context.cpp]
int Context::open() {
int rc;
quit_ = false;
#ifdef CONTROL_INTERFACE
rc = ctrlIface_.init(this);
if (rc < 0) {
return rc;
}
#endif
if ((rc = hub_.probe())) {
return rc;
}
#ifdef EXTENSION_LIB
if ((rc = external_sensors_init(*this))) {
LOGW("Error from external_sensors_init() = %d; %s", rc, strerror(rc));
}
#endif
return 0;
}
SensorHub::probe() 继续调用基类的 probe, SensorHubDevice::probe 到这里浅尝辄止。
[SensorHub.cpp]
int SensorHub::probe() {
AutoLock _l(configLock_);
AutoLock _ll(pollLock_);
int rc = SensorHubDevice::probe();
if (rc < 0) {
return rc;
}
rc = frsDirector_.probe();
if (rc < 0) {
return rc;
}
ctx_.addFd(normal_.getFd(), POLLIN | POLLHUP | POLLERR, this);
if ((rc = initSensorsLocked())) {
return rc;
}
// switch to non-blocking
open_ = true;
return 0;
}
2.3 activate、setDelay、poll
[HAL.cpp]
static int ctx_activate(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev, int handle, int enabled) {
return toContext(dev)->activate(handle, enabled);
}
static int ctx_setDelay(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev, int handle, int64_t ns) {
return toContext(dev)->setDelay(handle, ns);
}
static int ctx_poll(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev, sensors_event_t* data, int count) {
return toContext(dev)->pollEvents(data, count);
}
#ifdef SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_1
static int ctx_batch(struct sensors_poll_device_1 *dev, int sensor_handle, int flags,
int64_t sampling_period_ns,
int64_t max_report_latency_ns) {
return toContext(dev)->batch(sensor_handle, flags, sampling_period_ns, max_report_latency_ns);
}
static int ctx_flush(struct sensors_poll_device_1 *dev, int sensor_handle) {
return toContext(dev)->flush(sensor_handle);
}
#endif
- activate 激活或禁用传感器
int (*activate)(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev, int sensor_handle, int enabled);
如果 enabled 为 1 且传感器已激活,则该函数是空操作且操作成功。
如果 enabled 为 0 且传感器已禁用,则该函数是空操作且操作成功。
如果操作成功了,则该函数返回 0;否则返回表示错误的负数。
- poll 机制来轮询读取数据
int (*poll)(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev, sensors_event_t* data, int count);
- batch 设置传感器的参数(包括采样率和最大报告延迟)
int (*batch)( struct sensors_poll_device_1* dev, int sensor_handle, int flags, int64_t sampling_period_ns, int64_t max_report_latency_ns);
- flush 将刷新完成事件添加到指定传感器的硬件 FIFO末尾并刷新 FIFO
int (*flush)(struct sensors_poll_device_t* dev, int sensor_handle);
Sensor HAL的简单流程可以按照下面来理解:
当设备启动时,调用 get_sensors_list。
当传感器激活时,则先使用请求的参数调用 batch 函数,然后调用 activate(..., enable=1)。
当激活状态下的传感器的请求特性发生变化时,会调用 batch 函数。
可以随时调用 flush,甚至在未激活的传感器上也可以调用(在这种情况下,该函数必须返回 -EINVAL)
当传感器禁用时,将调用 activate(..., enable=0)。
在进行上述调用的同时,会反复调用 poll 函数来请求数据。甚至在没有传感器激活的情况下,也可以调用 poll。
3. 框架流程
当前方案AP并未直接对接 SensorHUB,而是将 SensorHUB 挂载在一颗 MCU 上,AP与MCU通过USB相连接,进行数据传输。
基本框架如下图所示:
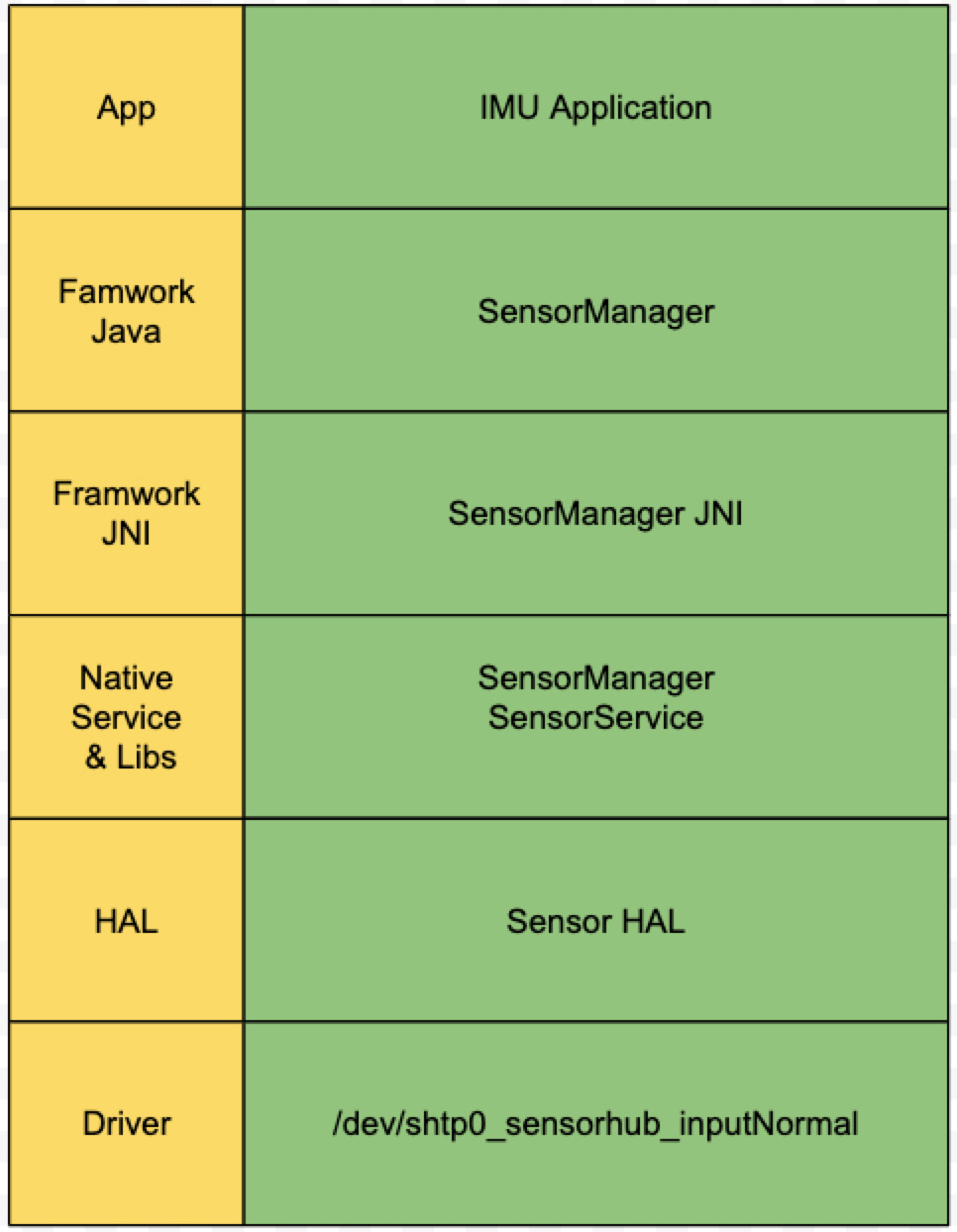
IMU App
App 通过正常的 SDK 接口访问 Sensor 服务,获取 Sensor 数据。Framewrok Java
SensorManager 提供了 Java 层 Sensor 的接口,并通过 JNI 和 Native SensorManager 通信。
代码位于frameworks/base/core/java/android/hardware/SensorManage.javaFramework JNI
提供机制,供 SensorManager 和 Native SensorManager 通信。
代码位于frameworks/base/core/jni/android_hardware_SensorManager.cppNative Service & Libs
SensorManager 属于 NativeLibs,为 JNI 提供接口,获取 SensorService 的服务,从而获取 SensorEvent;
代码位于frameworks/native/libs/sensor/SensorManager.cpp
SensorService 属于 NativeService,向 SensorManager 注册服务,和 Sensor HAL 进行交互,控制 sensor 和获取 SensorEvent。
代码位于frameworks/native/services/sensorservice/SensorService.cppHAL
SensorHub HAL,向上为 Native SensorService 提供接口,向下和 Driver 进行交互。Driver
创建虚拟设备节点,并提供接口供 HAL 层获取 SensorEvent 和控制 Sensor。
4. 问题分析
问题现象:
IMU sensordump App 无法获取 Accelerometer Sensor 数据
初步分析:
通过 dumpsys sensorservice 获取相关信息,发现 Client 0 中 Accelerometer 的状态是 First flush pending, 并不是 active 的状态。
2 active connections
Connection Number: 0
Operating Mode: NORMAL
org.cvpcs.android.sensordump.ASensor | WakeLockRefCount 0 | uid 10056 | cache size 0 | max cache size 984
Rokid Glasses Accelerometer 0x00000001 | status: First flush pending | pending flush events 0
events recvd: 0 | sent 0 | cache 0 | dropped 0 | total_acks_needed 0 | total_acks_recvd 0
Connection Number: 1
Operating Mode: NORMAL
com.android.server.policy.WindowOrientationListener | WakeLockRefCount 0 | uid 1000 | cache size 0 | max cache size 984
Rokid Glasses Accelerometer 0x00000001 | status: active | pending flush events 0
events recvd: 3976 | sent 3971 | cache 5 | dropped 0 | total_acks_needed 0 | total_acks_recvd 0
根据 log 定位 sensorservice 代码的位置,确定 mFirstFlushPending 标志被设置为 true
[SensorEventConnection.cpp]
void SensorService::SensorEventConnection::dump(String8& result) {
Mutex::Autolock _l(mConnectionLock);
result.appendFormat("\tOperating Mode: %s\n",mDataInjectionMode ? "DATA_INJECTION" : "NORMAL");
result.appendFormat("\t %s | WakeLockRefCount %d | uid %d | cache size %d | "
"max cache size %d\n", mPackageName.string(), mWakeLockRefCount, mUid, mCacheSize,
mMaxCacheSize);
for (size_t i = 0; i < mSensorInfo.size(); ++i) {
const FlushInfo& flushInfo = mSensorInfo.valueAt(i);
result.appendFormat("\t %s 0x%08x | status: %s | pending flush events %d \n",
mService->getSensorName(mSensorInfo.keyAt(i)).string(),
mSensorInfo.keyAt(i),
flushInfo.mFirstFlushPending ? "First flush pending" :
"active",
flushInfo.mPendingFlushEventsToSend);
这个标志在构造函数初始化列表中被初始化为 false,那么这个标志是在哪里被修改的呢?
SensorEventConnection 类提供了 setFirstFlushPending 方法去设置这个标志,
[SensorEventConnection.cpp]
void SensorService::SensorEventConnection::setFirstFlushPending(int32_t handle,
bool value) {
Mutex::Autolock _l(mConnectionLock);
ssize_t index = mSensorInfo.indexOfKey(handle);
if (index >= 0) {
FlushInfo& flushInfo = mSensorInfo.editValueAt(index);
flushInfo.mFirstFlushPending = value;
}
}
而这个方法在类 SensorService 的 enable 方法中被调用。
[SensorService.cpp]
status_t SensorService::enable(const sp<SensorEventConnection>& connection,
int handle, nsecs_t samplingPeriodNs, nsecs_t maxBatchReportLatencyNs, int reservedFlags,
const String16& opPackageName) {
...
if (err == NO_ERROR &&
sensor->getSensor().getReportingMode() == AREPORTING_MODE_CONTINUOUS &&
rec->getNumConnections() > 1) {
connection->setFirstFlushPending(handle, true);
status_t err_flush = sensor->flush(connection.get(), handle);
// Flush may return error if the underlying h/w sensor uses an older HAL.
if (err_flush == NO_ERROR) {
rec->addPendingFlushConnection(connection.get());
} else {
connection->setFirstFlushPending(handle, false);
}
}
...
}
参考前面的 Sensor HAL 的流程分析,对比 enable 方法中的流程,先执行 batch 设置采样时间等参数,然后调用 flush 刷新 FIFO,最后调用 activcate 激活传感器。
SensorService 继承于 Thread, 复写方法 threadLoop,不断的从 Sensor HAL 中读取数据
[SensorService.cpp]
bool SensorService::threadLoop() {
ALOGD("nuSensorService thread starting...");
// each virtual sensor could generate an event per "real" event, that's why we need to size
// numEventMax much smaller than MAX_RECEIVE_BUFFER_EVENT_COUNT. in practice, this is too
// aggressive, but guaranteed to be enough.
const size_t vcount = mSensors.getVirtualSensors().size();
const size_t minBufferSize = SensorEventQueue::MAX_RECEIVE_BUFFER_EVENT_COUNT;
const size_t numEventMax = minBufferSize / (1 + vcount);
SensorDevice& device(SensorDevice::getInstance());
const int halVersion = device.getHalDeviceVersion();
do {
ssize_t count = device.poll(mSensorEventBuffer, numEventMax);
if (count < 0) {
ALOGE("sensor poll failed (%s)", strerror(-count));
break;
}
// Reset sensors_event_t.flags to zero for all events in the buffer.
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
mSensorEventBuffer[i].flags = 0;
}
在读取完数据后,它会向所有连接的 Client 发送 SensorEvents
[SensorService.cpp]
// Send our events to clients. Check the state of wake lock for each client and release the
// lock if none of the clients need it.
bool needsWakeLock = false;
size_t numConnections = activeConnections.size();
for (size_t i=0 ; i < numConnections; ++i) {
if (activeConnections[i] != 0) {
activeConnections[i]->sendEvents(mSensorEventBuffer, count, mSensorEventScratch,
mMapFlushEventsToConnections);
needsWakeLock |= activeConnections[i]->needsWakeLock();
// If the connection has one-shot sensors, it may be cleaned up after first trigger.
// Early check for one-shot sensors.
if (activeConnections[i]->hasOneShotSensors()) {
cleanupAutoDisabledSensorLocked(activeConnections[i], mSensorEventBuffer,
count);
}
}
}
在 SendEvents 的方法中,判断获取的数据流中类型是否存在 SENSOR_TYPE_META_DATA ,如果有且 flushInfo.mFirstFlushPending == true,设置该标志为 false,然后接收到的数据才能被送到 Client。
[SensorEventConnection.cpp]
status_t SensorService::SensorEventConnection::sendEvents(
sensors_event_t const* buffer, size_t numEvents,
sensors_event_t* scratch,
wp<const SensorEventConnection> const * mapFlushEventsToConnections) {
...
if (scratch) {
size_t i=0;
while (i<numEvents) {
int32_t sensor_handle = buffer[i].sensor;
if (buffer[i].type == SENSOR_TYPE_META_DATA) {
ALOGD_IF(DEBUG_CONNECTIONS, "flush complete event sensor==%d ",
buffer[i].meta_data.sensor);
// Setting sensor_handle to the correct sensor to ensure the sensor events per
// connection are filtered correctly. buffer[i].sensor is zero for meta_data
// events.
sensor_handle = buffer[i].meta_data.sensor;
}
ssize_t index = mSensorInfo.indexOfKey(sensor_handle);
// Check if this connection has registered for this sensor. If not continue to the
// next sensor_event.
if (index < 0) {
++i;
continue;
}
FlushInfo& flushInfo = mSensorInfo.editValueAt(index);
// Check if there is a pending flush_complete event for this sensor on this connection.
if (buffer[i].type == SENSOR_TYPE_META_DATA && flushInfo.mFirstFlushPending == true &&
mapFlushEventsToConnections[i] == this) {
flushInfo.mFirstFlushPending = false;
ALOGD_IF(DEBUG_CONNECTIONS, "First flush event for sensor==%d ",
buffer[i].meta_data.sensor);
++i;
continue;
}
...
}
...
}
...
// NOTE: ASensorEvent and sensors_event_t are the same type.
ssize_t size = SensorEventQueue::write(mChannel,
reinterpret_cast<ASensorEvent const*>(scratch), count);
...
}
到这里问题的原因基本可以定位了,结合 libsensors log 确定 SensorHUB HAL 没有上报 SENSOR_TYPE_META_DATA 类型的数据到 SensorService,导致数据无法发送到对应的 Client。
这里追查了代码,发现 SENSOR_TYPE_META_DATA 类型的数据的上报流程不能正常工作,因为 SensorHUB HAL 适配当前方案时,移除了部分代码。在修改了这部分流程后,顺利解决了这一问题。
2 active connections
Connection Number: 0
Operating Mode: NORMAL
org.cvpcs.android.sensordump.ASensor | WakeLockRefCount 0 | uid 10056 | cache size 0 | max cache size 984
Rokid Glasses Accelerometer 0x00000001 | status: active | pending flush events 0
events recvd: 6168 | sent 4353 | cache 1815 | dropped 0 | total_acks_needed 0 | total_acks_recvd 0
Connection Number: 1
Operating Mode: NORMAL
com.android.server.policy.WindowOrientationListener | WakeLockRefCount 0 | uid 1000 | cache size 0 | max cache size 984
Rokid Glasses Accelerometer 0x00000001 | status: active | pending flush events 0
events recvd: 589106 | sent 588481 | cache 625 | dropped 0 | total_acks_needed 0 | total_acks_recvd 0
0 direct connections
最新文章
- Git原理及常用操作命令总结
- 用 string 进行插入、替代、查找输出下标等操作
- 后台设置gridview不换行
- 【HDU】4035 Maze
- 完全图解scrollLeft,scrollWidth,clientWidth,offsetWidth 获取相对途径,滚动图片(网上找的,未经试验,但觉得比较好)
- 小数量宽带用户的福音,Panabit 云计费easyradius 接口隆重发布,PA宽带计费系统
- Arbitrage(bellman_ford)
- XML引入多scheme文件约束简单示例
- 你需要知道的三个 CSS3技巧(转)
- SQLServer2005 常用语法大全
- windowsphone中获取手机位置信息
- hdu2102(bfs)
- 【leetcode】LRU
- PHP学习笔记----IIS7下安装配置php环境
- Activiti工作流(一)之基本操作介绍
- UEP-添加表格
- Can't connect to X11 window server using ':1.0' as the value of the DISPLAY variable.
- JavaScript 对象属性底层原理
- y7000笔记本 darknet-yolo安装与测试(Ubuntu18.04+Cuda9.0+Cudnn7.1)
- 【学亮IT手记】Java 8新特性实例介绍