OVS-DPDK 流表查询详解
2024-09-08 12:47:15
一图胜千言:

flow和miniflow
在介绍之前先说一些概念:里面有两个结构很重要,一个是flow一个是miniflow这里介绍一下他们的数据结构和构造函数。
flow:
flow的特点是8字节对齐的,存储报文相关字段和其他原数据,用于匹配流表,数据包含四个层次:
- metadata: 入端口号,寄存器等信息
- l2: 源目的mac,vlan和mpls等信息
- l3: ipv4/ipv6源目的ip,ttl等信息
- l4: 源目的端口号,icmp code和type等信息。
flow的坏处就是占用了很大的字节,并且有很多字段都是0,在2.8版本中flow的大小是672字节。
miniflow
miniflow是flow的压缩版,因为flow占用字节很大,比如可以支持ARP,IP等报文,填充了arp字段,icmp报文就是空的了,浪费了很多信息。过程中用到hash作为key,也是根据miniflow计算hash值,不是用的flow。
struct miniflow {
struct flowmap map;
};
struct flowmap {
map_t bits[FLOWMAP_UNITS];
};
miniflow其包含两部分内容:
- struct flowmap map;是bit数组,使用其中的bit表示flow中哪个8字节存在有效数据,flow中占多少个8字节,那么就需要map中多个个bit,并且按照64bit向上取整。
- 第二部分是有效数据,有效数据动态分配,根据struct flowmap map;中1bit数个数进行分配,大小为bit数*8字节,该部分直接跟在map后面。该部分存储在netdev_flow_key结构中的buf数组。
miniflow数据结构:
//flow是8字节对齐的,除8得到flow中包含8字节的个数
#define FLOW_U64S (sizeof(struct flow) / sizeof(uint64_t)) //map大小为8字节,MAP_T_BITS 为64位
typedef unsigned long long map_t;
#define MAP_T_BITS (sizeof(map_t) * CHAR_BIT) //每位表示一个u64,FLOWMAP_UNITS 表示最少需要几个64位
#define FLOWMAP_UNITS DIV_ROUND_UP(FLOW_U64S, MAP_T_BITS) struct flowmap {
map_t bits[FLOWMAP_UNITS];
}; struct miniflow {
struct flowmap map;
/* Followed by:
* uint64_t values[n];
* where 'n' is miniflow_n_values(miniflow). */
}; struct netdev_flow_key {
uint32_t hash;
uint32_t len;
struct miniflow mf; // bits
uint64_t buf[FLOW_MAX_PACKET_U64S]; // 就是上边所说的value
}; // 有些字段是互斥的
#define FLOW_MAX_PACKET_U64S (FLOW_U64S \
/* Unused in datapath */ - FLOW_U64_SIZE(regs) \
- FLOW_U64_SIZE(metadata) \
/* L2.5/3 */ - FLOW_U64_SIZE(nw_src) /* incl. nw_dst */ \
- FLOW_U64_SIZE(mpls_lse) \
/* L4 */ - FLOW_U64_SIZE(tp_src) \
)
miniflow优点:
- 使用miniflow可以节省内存
- 如果只想遍历flow中的非0字段时,使用miniflow找到对应的非0字段,可以节省时间
flow->miniflow函数:miniflow_extract()
void
miniflow_extract(struct dp_packet *packet, struct miniflow *dst)
{
...
// 初始化赋值有两个关键,一个是这个values: return (uint64_t *)(mf + 1);
// 就是上边说的
uint64_t *values = miniflow_values(dst);
struct mf_ctx mf = { FLOWMAP_EMPTY_INITIALIZER, values,
values + FLOW_U64S };
...
if (md->skb_priority || md->pkt_mark) {
miniflow_push_uint32(mf, skb_priority, md->skb_priority);
miniflow_push_uint32(mf, pkt_mark, md->pkt_mark);
}
miniflow_push_be16(mf, dl_type, dl_type);
miniflow_pad_to_64(mf, dl_type);
... // 去取网络层信息,从这里可以看出,ovs暂时只支持IP,IPV6,ARP,RARP报文
if (OVS_LIKELY(dl_type == htons(ETH_TYPE_IP))){...}
else if
... // 提取传输层,从这里可以看出,ovs暂时支持传输层协议有TCP,UDP,SCTP,ICMP,ICMPV6
if (OVS_LIKELY(nw_proto == IPPROTO_TCP)){...}
else if
...
miniflow_push_uint32()
在上面将value保存到miniflow时,用到了几个辅助函数,比如下面的miniflow_push_uint32用来将一个32位的值保存到miniflow中FIELD对应的位置。其首先调用offsetof获取field在flow中的偏移字节数,因为flow是8字节对齐的,所以一个四字节的成员变量要么位于8字节的起始位置,要么位于8字节的中间位置,即对8取模值肯定为0或者4,再调用miniflow_push_uint32_保存到对应的位置,并设置map中对应的bit为1。
#define miniflow_push_uint32(MF, FIELD, VALUE) \
miniflow_push_uint32_(MF, offsetof(struct flow, FIELD), VALUE) #define miniflow_push_uint32_(MF, OFS, VALUE) \
{ \
MINIFLOW_ASSERT(MF.data < MF.end); \
\
//成员变量位于起始位置,需要调用miniflow_set_map设置对应的bit为1
if ((OFS) % 8 == 0) { \
miniflow_set_map(MF, OFS / 8); \
*(uint32_t *)MF.data = VALUE; \
} else if ((OFS) % 8 == 4) { \
//成员变量不在起始位置,要判断此变量所在的bit为1
miniflow_assert_in_map(MF, OFS / 8); \
*((uint32_t *)MF.data + 1) = VALUE; \
MF.data++; \
} \
}
miniflow->flow函数:miniflow_expand()
/* Initializes 'dst' as a copy of 'src'. */
void
miniflow_expand(const struct miniflow *src, struct flow *dst)
{
memset(dst, 0, sizeof *dst);
flow_union_with_miniflow(dst, src);
} /* Perform a bitwise OR of miniflow 'src' flow data with the equivalent
* fields in 'dst', storing the result in 'dst'. */
static inline void
flow_union_with_miniflow(struct flow *dst, const struct miniflow *src)
{
flow_union_with_miniflow_subset(dst, src, src->map);
} static inline void
flow_union_with_miniflow_subset(struct flow *dst, const struct miniflow *src,
struct flowmap subset)
{
uint64_t *dst_u64 = (uint64_t *) dst;
const uint64_t *p = miniflow_get_values(src);
map_t map;
//遍历所有的map
FLOWMAP_FOR_EACH_MAP (map, subset) {
size_t idx;
//遍历map中所有的非0bit
MAP_FOR_EACH_INDEX(idx, map) {
dst_u64[idx] |= *p++;
}
dst_u64 += MAP_T_BITS;
}
}
流表查询过程
概要
该部分入口在lib/dpif-netdev.c,就是最开始的那个图。
查询的缓存分为两层:一个是DFC,一个是dpcls,相当于microflow和megaflow,DFC由两部分组成,DFC(datapath flow cache):EMC(Exact match cache)+SMC(Signature match cache),另一部分就是dpcls(datapath classifer)。
SMC默认关闭:bool smc_enable = smap_get_bool(other_config, "smc-enable", false);
函数执行流程(不包含SMC的):
入口在dp_netdev_input__()
static void
dp_netdev_input__(struct dp_netdev_pmd_thread *pmd,
struct dp_packet_batch *packets,
bool md_is_valid, odp_port_t port_no)
{
#if !defined(__CHECKER__) && !defined(_WIN32)
const size_t PKT_ARRAY_SIZE = dp_packet_batch_size(packets);
#else
/* Sparse or MSVC doesn't like variable length array. */
enum { PKT_ARRAY_SIZE = NETDEV_MAX_BURST };
#endif
OVS_ALIGNED_VAR(CACHE_LINE_SIZE)
struct netdev_flow_key keys[PKT_ARRAY_SIZE];
struct netdev_flow_key *missed_keys[PKT_ARRAY_SIZE];
struct packet_batch_per_flow batches[PKT_ARRAY_SIZE];
size_t n_batches;
struct dp_packet_flow_map flow_map[PKT_ARRAY_SIZE];
uint8_t index_map[PKT_ARRAY_SIZE];
size_t n_flows, i; odp_port_t in_port; n_batches = 0;
// 1. dfc_processing之后会把miss的放到packets里
// 找到的可能已经batched了,或者放到flow_map里了
// flow_map里是未bathed的,可能直接是*flow或者是NULL,是NULL再去下一层cache查
dfc_processing(pmd, packets, keys, missed_keys, batches, &n_batches,
flow_map, &n_flows, index_map, md_is_valid, port_no); // 2. 如果有miss的,再去找fast-path,也就是查dpcls
if (!dp_packet_batch_is_empty(packets)) {
in_port = packets->packets[0]->md.in_port.odp_port;
fast_path_processing(pmd, packets, missed_keys,
flow_map, index_map, in_port);
} /* Batch rest of packets which are in flow map. */
for (i = 0; i < n_flows; i++) {
struct dp_packet_flow_map *map = &flow_map[i]; if (OVS_UNLIKELY(!map->flow)) {
continue;
}
dp_netdev_queue_batches(map->packet, map->flow, map->tcp_flags,
batches, &n_batches);
} for (i = 0; i < n_batches; i++) {
batches[i].flow->batch = NULL;
} // 执行每个packet的action
for (i = 0; i < n_batches; i++) {
packet_batch_per_flow_execute(&batches[i], pmd);
}
}
1. DFC查询:dfc_processing()
static inline size_t
dfc_processing(struct dp_netdev_pmd_thread *pmd,
struct dp_packet_batch *packets_,
struct netdev_flow_key *keys,
struct netdev_flow_key **missed_keys,
struct packet_batch_per_flow batches[], size_t *n_batches,
struct dp_packet_flow_map *flow_map,
size_t *n_flows, uint8_t *index_map,
bool md_is_valid, odp_port_t port_no)
{
struct netdev_flow_key *key = &keys[0];
size_t n_missed = 0, n_emc_hit = 0;
struct dfc_cache *cache = &pmd->flow_cache;
struct dp_packet *packet;
size_t cnt = dp_packet_batch_size(packets_);
// emc的插入概率,如果为0,表示不开启emc
uint32_t cur_min = pmd->ctx.emc_insert_min;
int i;
uint16_t tcp_flags;
bool smc_enable_db;
// 记录未batched的个数
size_t map_cnt = 0;
// 这个变量用于保序
bool batch_enable = true;
// 获取smc是否开启参数
atomic_read_relaxed(&pmd->dp->smc_enable_db, &smc_enable_db);
pmd_perf_update_counter(&pmd->perf_stats,
md_is_valid ? PMD_STAT_RECIRC : PMD_STAT_RECV,
cnt); do_dfc_hook(pmd, packets_, batches, n_batches);
cnt = dp_packet_batch_size(packets_); // 逐个对dp_packet_batch中的每一个packet进行处理
DP_PACKET_BATCH_REFILL_FOR_EACH (i, cnt, packet, packets_) {
struct dp_netdev_flow *flow;
// 若packet包长小于以太头的长度直接丢包
if (OVS_UNLIKELY(dp_packet_size(packet) < ETH_HEADER_LEN)) {
dp_packet_delete(packet);
COVERAGE_INC(datapath_drop_rx_invalid_packet);
continue;
}
// 对数据手工预取可减少读取延迟,从而提高性能
if (i != cnt - 1) {
struct dp_packet **packets = packets_->packets;
/* Prefetch next packet data and metadata. */
OVS_PREFETCH(dp_packet_data(packets[i+1]));
pkt_metadata_prefetch_init(&packets[i+1]->md);
} // 初始化metadata首先将pkt_metadata中flow_in_port前的字节全部设为0
// 将in_port.odp_port设为port_no, tunnel.ipv6_dst设为in6addr_any
if (!md_is_valid) {
pkt_metadata_init(&packet->md, port_no);
}
// 报文转化为miniflow, 上文有讲
miniflow_extract(packet, &key->mf);
key->len = 0; /* Not computed yet. */
// 计算当前报文miniflow的hash值
key->hash =
(md_is_valid == false)
? dpif_netdev_packet_get_rss_hash_orig_pkt(packet, &key->mf)
: dpif_netdev_packet_get_rss_hash(packet, &key->mf); // 根据key->hash,emc_entry alive,miniflow 3个条件得到dp_netdev_flow
// cur_min = 0,表示不可能插入,后面有讲什么时候才会插入EMC
flow = (cur_min != 0) ? emc_lookup(&cache->emc_cache, key) : NULL; if (OVS_LIKELY(flow)) {
tcp_flags = miniflow_get_tcp_flags(&key->mf);
n_emc_hit++; // 命中次数+1
// 为了保证报文的顺序,所有的packet对应的flow都用flow_map存储
// flow_map里面就是packet数量对应的(packet,flow,tcp_flag)
// 最后会把这些在dp_netdev_input__里重新把顺序合并一下
if (OVS_LIKELY(batch_enable)) {
// 把查到的flow加到batches里第n_batches个batch里
dp_netdev_queue_batches(packet, flow, tcp_flags, batches,
n_batches);
} else { packet_enqueue_to_flow_map(packet, flow, tcp_flags,
flow_map, map_cnt++);
}
} else {
// 这些数据结构用于smc查询时的记录
// 没查到把packet放到packets_里,从下标0再开始放
// 最后packets_都是未查到的
dp_packet_batch_refill(packets_, packet, i);
index_map[n_missed] = map_cnt;
flow_map[map_cnt++].flow = NULL;
missed_keys[n_missed] = key;
key = &keys[++n_missed];
batch_enable = false; // 之后的都是未batched的
}
}
*n_flows = map_cnt; pmd_perf_update_counter(&pmd->perf_stats, PMD_STAT_EXACT_HIT, n_emc_hit);
// 如果没有开启smc,直接返回了
if (!smc_enable_db) {
return dp_packet_batch_size(packets_);
} smc_lookup_batch(pmd, keys, missed_keys, packets_,
n_missed, flow_map, index_map); return dp_packet_batch_size(packets_);
}
1.1 emc查询:emc_lookup()
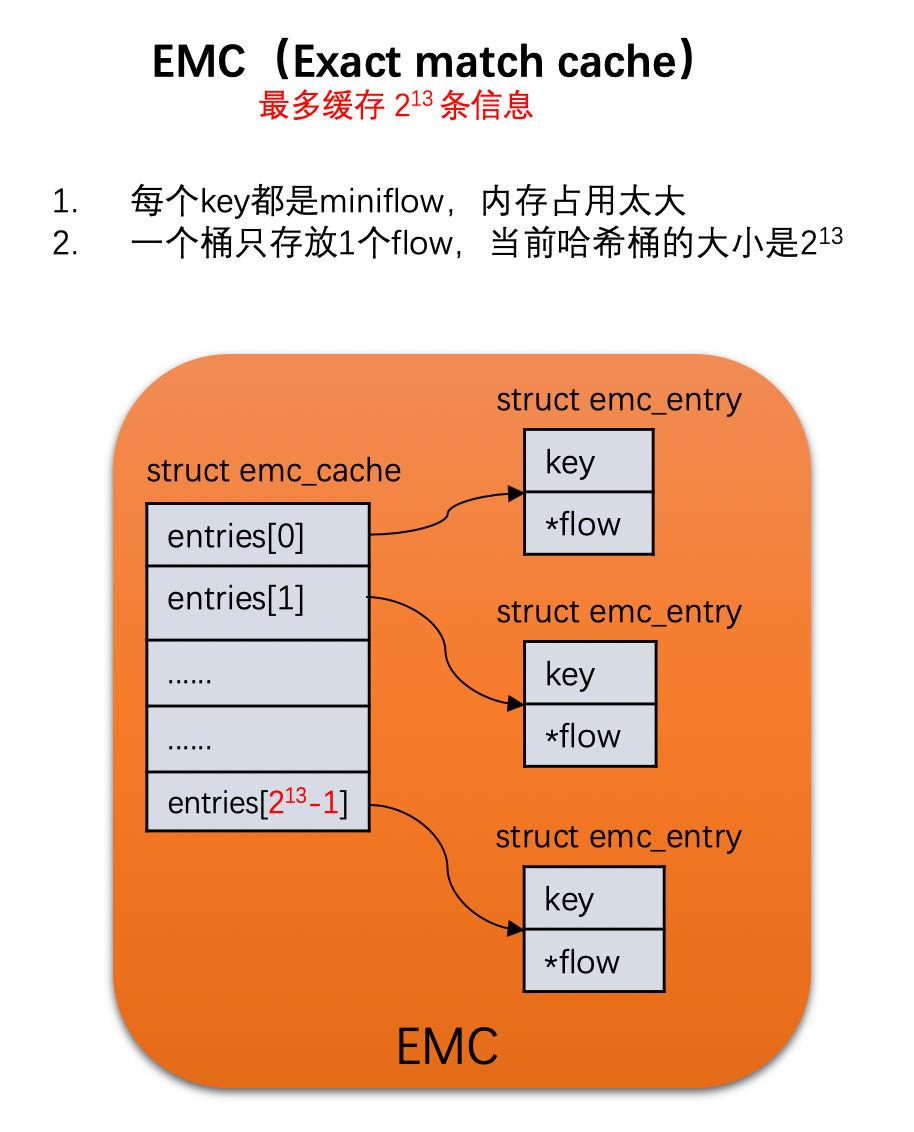
static inline struct dp_netdev_flow *
emc_lookup(struct emc_cache *cache, const struct netdev_flow_key *key)
{
struct emc_entry *current_entry;
// 这里说一下,一个hash分配两个桶,长度为13位,cache桶的大小为1<<13
// struct emc_cache {
// struct emc_entry entries[EM_FLOW_HASH_ENTRIES];
// int sweep_idx; /* For emc_cache_slow_sweep(). */
// };
EMC_FOR_EACH_POS_WITH_HASH (cache, current_entry, key->hash) {
if (current_entry->key.hash == key->hash
&& emc_entry_alive(current_entry)
&& emc_flow_key_equal_mf(¤t_entry->key, &key->mf)) {
/* We found the entry with the 'key->mf' miniflow */
return current_entry->flow;
}
}
return NULL;
} #define EM_FLOW_HASH_SHIFT 13
#define EM_FLOW_HASH_ENTRIES (1u << EM_FLOW_HASH_SHIFT)
#define EM_FLOW_HASH_MASK (EM_FLOW_HASH_ENTRIES - 1)
#define EM_FLOW_HASH_SEGS 2
#define EMC_FOR_EACH_POS_WITH_HASH(EMC, CURRENT_ENTRY, HASH) \
for (uint32_t i__ = 0, srch_hash__ = (HASH); \
(CURRENT_ENTRY) = &(EMC)->entries[srch_hash__ & EM_FLOW_HASH_MASK], \
i__ < EM_FLOW_HASH_SEGS; \
i__++, srch_hash__ >>= EM_FLOW_HASH_SHIFT) // 比较miniflow是否相同
static inline bool
emc_flow_key_equal_mf(const struct netdev_flow_key *key,
const struct miniflow *mf)
{
return !memcmp(&key->mf, mf, key->len);
}
EMC查询函数执行:
1.2 smc查询:smc_lookup_batch()
static inline void
smc_lookup_batch(struct dp_netdev_pmd_thread *pmd,
struct netdev_flow_key *keys,
struct netdev_flow_key **missed_keys,
struct dp_packet_batch *packets_,
const int cnt,
struct dp_packet_flow_map *flow_map,
uint8_t *index_map)
{
int i;
struct dp_packet *packet;
size_t n_smc_hit = 0, n_missed = 0;
struct dfc_cache *cache = &pmd->flow_cache;
struct smc_cache *smc_cache = &cache->smc_cache;
const struct cmap_node *flow_node;
int recv_idx;
uint16_t tcp_flags; /* Prefetch buckets for all packets */
for (i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
OVS_PREFETCH(&smc_cache->buckets[keys[i].hash & SMC_MASK]);
} DP_PACKET_BATCH_REFILL_FOR_EACH (i, cnt, packet, packets_) {
struct dp_netdev_flow *flow = NULL;
// 找到hash相同的flow链表的头节点
flow_node = smc_entry_get(pmd, keys[i].hash);
bool hit = false;
/* Get the original order of this packet in received batch. */
recv_idx = index_map[i]; if (OVS_LIKELY(flow_node != NULL)) {
// 遍历一下看看哪一个是相同的,这个通过offsetof找到存放该cmap结构体的首地址
// dp_netdev_flow里面的首地址就是,
CMAP_NODE_FOR_EACH (flow, node, flow_node) {
/* Since we dont have per-port megaflow to check the port
* number, we need to verify that the input ports match. */
if (OVS_LIKELY(dpcls_rule_matches_key(&flow->cr, &keys[i]) &&
flow->flow.in_port.odp_port == packet->md.in_port.odp_port)) {
tcp_flags = miniflow_get_tcp_flags(&keys[i].mf);
keys[i].len =
netdev_flow_key_size(miniflow_n_values(&keys[i].mf));
if (emc_probabilistic_insert(pmd, &keys[i], flow)) {
if (flow->status == OFFLOAD_NONE) {
queue_netdev_flow_put(pmd->dp->dp_flow_offload, \
pmd->dp->class, \
flow, NULL, DP_NETDEV_FLOW_OFFLOAD_OP_ADD);
}
}
packet_enqueue_to_flow_map(packet, flow, tcp_flags,
flow_map, recv_idx);
n_smc_hit++;
hit = true;
break;
}
}
if (hit) {
continue;
}
}
// SMC也miss了,和之前一样,把miss的放packets_里,从0开始放
dp_packet_batch_refill(packets_, packet, i);
index_map[n_missed] = recv_idx;
missed_keys[n_missed++] = &keys[i];
} pmd_perf_update_counter(&pmd->perf_stats, PMD_STAT_SMC_HIT, n_smc_hit);
}
查找hash相同的链表头:smc_entry_get()
static inline const struct cmap_node *
smc_entry_get(struct dp_netdev_pmd_thread *pmd, const uint32_t hash)
{
struct smc_cache *cache = &(pmd->flow_cache).smc_cache;
// smc_cache桶的大小是(1<<18),SMC_MASK=(1<<18)- 1
// 先通过后hash的后18位定位到桶
struct smc_bucket *bucket = &cache->buckets[hash & SMC_MASK];
// 一个桶有4个16位的sig,存key->hash前16位,正好是64位
// 遍历4个元素看那个匹配,获得匹配后的cmap的下标
uint16_t sig = hash >> 16;
uint16_t index = UINT16_MAX; for (int i = 0; i < SMC_ENTRY_PER_BUCKET; i++) {
if (bucket->sig[i] == sig) {
index = bucket->flow_idx[i];
break;
}
}
// 通过index找到在dpcls里的桶位置
if (index != UINT16_MAX) {
return cmap_find_by_index(&pmd->flow_table, index);
}
return NULL;
}
1.3 更新emc:emc_probabilistic_insert()
命中SMC后,插入回上一层cache(EMC)里:emc_probabilistic_insert()
插入EMC的条件:
默认插入流表的概率是1%,可以通过ovs-vsctl set Open_vSwitch . other_config:emc-insert-prob=10 设置概率,表示平均10条流表有1条插入,当为0时禁用EMC,当为1的时候,百分百插入。设置后会在代码里设置emc_insert_min字段为uint_max/10,插入的时候生成一个uint_random(),如果随机数小于emc_insert_min才会插入。
static inline bool
emc_probabilistic_insert(struct dp_netdev_pmd_thread *pmd,
const struct netdev_flow_key *key,
struct dp_netdev_flow *flow)
{
/* Insert an entry into the EMC based on probability value 'min'. By
* default the value is UINT32_MAX / 100 which yields an insertion
* probability of 1/100 ie. 1% */
uint32_t min = pmd->ctx.emc_insert_min;
if (min && random_uint32() <= min) {
emc_insert(&(pmd->flow_cache).emc_cache, key, flow);
return true;
}
return false;
}
emc_insert同样有我在内核查询里的问题,如果cache里没有该miniflow,会找一个hash值小的entry,覆盖这个entry,那如果有一个hash很大的flow被插入了,但是这个flow之后就没用过了,那岂不是这个entry就浪费了,不会被用到。
找到了合适的emc_entry。则将报文对应的netdev_dev_flow key信息存储到该表项中。而对于这个表项,原有的emc_entry.flow有可能还有指向一条旧的流表,需要将这条流表的引用计数减1,如果减1后达到0,则释放该流表空间。同时更新emc_entry.flow重新指向新的流表。到此为止,EMC表项更新完毕。
static inline void
emc_insert(struct emc_cache *cache, const struct netdev_flow_key *key,
struct dp_netdev_flow *flow)
{
struct emc_entry *to_be_replaced = NULL;
struct emc_entry *current_entry; EMC_FOR_EACH_POS_WITH_HASH(cache, current_entry, key->hash) {
if (netdev_flow_key_equal(¤t_entry->key, key)) {
/* We found the entry with the 'mf' miniflow */
emc_change_entry(current_entry, flow, NULL);
return;
}
/* Replacement policy: put the flow in an empty (not alive) entry, or
* in the first entry where it can be */ if (!to_be_replaced
|| (emc_entry_alive(to_be_replaced)
&& !emc_entry_alive(current_entry))
|| current_entry->key.hash < to_be_replaced->key.hash) {
// 这个黄色判断就是我迷惑的地方
to_be_replaced = current_entry;
}
}
/* We didn't find the miniflow in the cache.
* The 'to_be_replaced' entry is where the new flow will be stored */
emc_change_entry(to_be_replaced, flow, key);
}
1.4 EMC的轮训更新
在pmd_thread_main()里面:
if (lc++ > 1024) {
lc = 0;
coverage_try_clear();
// 这里的optimize是排序一下TSS
dp_netdev_pmd_try_optimize(pmd, poll_list, poll_cnt);
dp_netdev_pmd_hook_idle_run(pmd);
#ifdef ENABLE_EMC
if (!ovsrcu_try_quiesce()) {
emc_cache_slow_sweep(pmd->dp, &((pmd->flow_cache).emc_cache));
}
#else
ovsrcu_try_quiesce();
#endif
for (i = 0; i < poll_cnt; i++) {
uint64_t current_seq =
netdev_get_change_seq(poll_list[i].rxq->port->netdev);
if (poll_list[i].change_seq != current_seq) {
poll_list[i].change_seq = current_seq;
poll_list[i].rxq_enabled =
netdev_rxq_enabled(poll_list[i].rxq->rx);
}
}
}
1.5 承上启下:OVS的TSS算法
dpcls是megaflow的查询过程,使用TSS算法,是个很老的算法了,看源码之前,先讲一下ovs里面的TSS,之前内核已经讲过,但是没有讲OVS里做的优化,下边再说一次,然后建议再去看一下这个有很多图的博客OVS-DPDK Datapath Classifier,这样之后对整个dpcls流程就有所了解了。
TSS算法原理
OVS 在内核态使用了元组空间搜索算法(Tuple Space Search,简称 TSS)进行流表查找,元组空间搜索算法的核心思想是,把所有规则按照每个字段的前缀长度进行组合,并划分为不同的元组中,然后在这些元组集合中进行哈希查找。我们举例说明,假设现有 10 条规则以及 3 个匹配字段,每个匹配字段长度均为 4:
我们将每条规则各匹配字段的前缀长度提取出来,按照前缀长度进行组合,并根据前缀长度组合进行分组:
我们将每个前缀长度组合称为 元组,每个元组对应于哈希表的一个桶,同一前缀长度组合内的所有规则放置在同一个哈希桶内:
10 条规则被划分为 4 个元组,因此最多只需要四次查找,就可以找到对应的规则。
算法优缺点
为什么OVS选择TSS,而不选择其他查找算法?论文给出了以下三点解释:
(1)在虚拟化数据中心环境下,流的添加删除比较频繁,TSS支持高效的、常数时间的表项更新; (2)TSS支持任意匹配域的组合; (3)TSS存储空间随着流的数量线性增长,空间复杂度为 O(N),N 为规则数目。
元组空间搜索算法的缺点是,由于基于哈希表实现,因此查找的时间复杂度不能确定。当所有规则各个字段的前缀长度组合数目过多时,查找性能会大大降低,最坏情况下需要查找所有规则。
OVS里做的排序优化
查找的过程需要从前向后遍历所有元组,命中了就不用往后查了。OVS给每个元组加了一个命中次数,命中次数越多,元组这个链表越靠前,这样就可以减少了查表次数。
2. dpcls查询
2.1 dpcls相关数据结构
// 线程安全的
#define OVSRCU_TYPE(TYPE) struct { ATOMIC(TYPE) p; } struct cmap {
OVSRCU_TYPE(struct cmap_impl *) impl;
}; /* The implementation of a concurrent hash map. */
struct cmap_impl {
// 补齐64字节
PADDED_MEMBERS_CACHELINE_MARKER(CACHE_LINE_SIZE, cacheline0,
unsigned int n; /* Number of in-use elements. */
unsigned int max_n; /* Max elements before enlarging. */
unsigned int min_n; /* Min elements before shrinking. */
uint32_t mask; /* Number of 'buckets', minus one. */
uint32_t basis; /* Basis for rehashing client's
hash values. */
);
PADDED_MEMBERS_CACHELINE_MARKER(CACHE_LINE_SIZE, cacheline1,
struct cmap_bucket buckets[1];
);
}; struct cmap_bucket {
/* Padding to make cmap_bucket exactly one cache line long. */
PADDED_MEMBERS(CACHE_LINE_SIZE,
// 锁机制,读和写都会+1,读的时候等到变成偶数再去读,保证安全
atomic_uint32_t counter;
// 桶中的每个槽用(hashs[i], nodes[i])元组来表示
uint32_t hashes[CMAP_K];
struct cmap_node nodes[CMAP_K];
);
};
struct cmap_node {
OVSRCU_TYPE(struct cmap_node *) next; /* Next node with same hash. */
}; /* 二级匹配表.每个报文接收端口对应一个 */
struct dpcls {
struct cmap_node node; /* 链表节点 */
odp_port_t in_port; /* 报文接收端口 */
struct cmap subtables_map; // 管理下边subtables的索引,用于遍历
struct pvector subtables; // 上文TSS算法所说的元组表
}
struct pvector {
// 指向具体子表信息
OVSRCU_TYPE(struct pvector_impl *) impl;
// 平时,temp都是为NULL.只有当pvector扩充时,temp才用来临时缓存数据.
// 待排好序后,再拷贝到impl中,temp再置NULL
struct pvector_impl *temp;
}; // 相当于vector<pvector_entry>
struct pvector_impl {
size_t size; /* Number of entries in the vector */
size_t allocated; /* Number allocted entries */
/* 初始化的时候只有4个元素.后续可能会扩充 */
struct pvector_entry vector[];
}
struct pvector_entry {
// pvector_impl中的vector是按照priority从小到大排序的
// pmd_thread_main里会把priority赋值为hit_cnt,然后排序
int priority;
/* 实际指向了struct dpcls_subtable结构 */
void *ptr;
}
// 子表信息
struct dpcls_subtable {
/* The fields are only used by writers. */
struct cmap_node cmap_node OVS_GUARDED; /* Within dpcls 'subtables_map'. */ struct cmap rules; // 该表的bucket内容
uint32_t hit_cnt; // 命中该子表的次数 // 下边是mask的miniflow前两个的bits里1的个数
uint8_t mf_bits_set_unit0;
uint8_t mf_bits_set_unit1;
// 根据mf_bits_set_unit01选择最合适的查找算法
dpcls_subtable_lookup_func lookup_func; /* Caches the masks to match a packet to, reducing runtime calculations. */
uint64_t *mf_masks; // 由下边的mask->mf->bits[01]得来的,
struct netdev_flow_key mask; // 该表的掩码信息
}; 关于上边的mf_masks与mask,举个例子
mf_bits_set_unit0 = 4, mf_bits_set_unit1 = 0
netdev_flow_key.mf.bits[0] = 111010 (2进制)
mf_masks = [1, 111, 1111, 11111] (2进制)
三个图对应他们的关系,链表三用于遍历的,查找过程中并不会通过链表三方式搜索。查找的时候走的就是链表二的流程。
2.2 dpcls查询入口:fast_path_processing->dpcls_lookup()
static bool
dpcls_lookup(struct dpcls *cls, const struct netdev_flow_key *keys[],
struct dpcls_rule **rules, const size_t cnt,
int *num_lookups_p)
{
#define MAP_BITS (sizeof(uint32_t) * CHAR_BIT)
BUILD_ASSERT_DECL(MAP_BITS >= NETDEV_MAX_BURST); struct dpcls_subtable *subtable;
uint32_t keys_map = TYPE_MAXIMUM(uint32_t); /* Set all bits. */ if (cnt != MAP_BITS) {
/*keys_map中置1位数为包的总数,并且第i位对应第i个包*/
keys_map >>= MAP_BITS - cnt; /* Clear extra bits. */
}
memset(rules, 0, cnt * sizeof *rules); int lookups_match = 0, subtable_pos = 1;
uint32_t found_map; PVECTOR_FOR_EACH (subtable, &cls->subtables) {
// 查找函数,对应下边的lookup_generic()
found_map = subtable->lookup_func(subtable, keys_map, keys, rules); uint32_t pkts_matched = count_1bits(found_map);
// 搜索的子表个数,加上的是当前这几个key找了多少个表
lookups_match += pkts_matched * subtable_pos; keys_map &= ~found_map;
if (!keys_map) {
if (num_lookups_p) {
*num_lookups_p = lookups_match;
}
// 全找到了
return true;
}
subtable_pos++;
} if (num_lookups_p) {
*num_lookups_p = lookups_match;
}
// 没有全找到
return false;
}
lookup_generic()
ovs-dpdk里面有avx512-gather.c,使用avx512优化了look_up,整体逻辑还是一样的,这里只说dpif-netdev-lookup-generic
入口在这里,往下走,传进去subtable有效字段有多大
static uint32_t
dpcls_subtable_lookup_generic(struct dpcls_subtable *subtable,
uint32_t keys_map,
const struct netdev_flow_key *keys[],
struct dpcls_rule **rules)
{
return lookup_generic_impl(subtable, keys_map, keys, rules,
subtable->mf_bits_set_unit0,
subtable->mf_bits_set_unit1);
} static inline uint32_t ALWAYS_INLINE
lookup_generic_impl(struct dpcls_subtable *subtable, // 当前的subtable
uint32_t keys_map, // miss_bit_map
const struct netdev_flow_key *keys[], // miss_key
struct dpcls_rule **rules, // save hit_rule
const uint32_t bit_count_u0,
const uint32_t bit_count_u1)
{
// 有几个包
const uint32_t n_pkts = count_1bits(keys_map);
ovs_assert(NETDEV_MAX_BURST >= n_pkts);
uint32_t hashes[NETDEV_MAX_BURST]; // 根据mask字段的大小开空间
const uint32_t bit_count_total = bit_count_u0 + bit_count_u1;
// 一个batch最大是NETDEV_MAX_BURST
const uint32_t block_count_required = bit_count_total * NETDEV_MAX_BURST;
uint64_t *mf_masks = subtable->mf_masks;
int i; // 申请存储一个batch报文信息的数组,存放
uint64_t *blocks_scratch = get_blocks_scratch(block_count_required); // 获得每个key与当前表的mask“与运算”的结果
ULLONG_FOR_EACH_1 (i, keys_map) {
netdev_flow_key_flatten(keys[i],
&subtable->mask, // 该表的掩码信息
mf_masks, // 由subtable->mask处理后的mask
&blocks_scratch[i * bit_count_total],
bit_count_u0,
bit_count_u1);
} // 算出来每一个key在该subtable里的hash值,该hash值由“mask字节数,key和mask与运算结果”得出
ULLONG_FOR_EACH_1 (i, keys_map) {
uint64_t *block_ptr = &blocks_scratch[i * bit_count_total];
uint32_t hash = hash_add_words64(0, block_ptr, bit_count_total);
hashes[i] = hash_finish(hash, bit_count_total * 8);
} uint32_t found_map;
const struct cmap_node *nodes[NETDEV_MAX_BURST]; // 找到每个key在该subtable里的cmap,并且返回每个key有没有被找到,第i位是1则找到
found_map = cmap_find_batch(&subtable->rules, keys_map, hashes, nodes); ULLONG_FOR_EACH_1 (i, found_map) {
struct dpcls_rule *rule;
// 可能不同的rule有相同的hash,看那个是匹配的
CMAP_NODE_FOR_EACH (rule, cmap_node, nodes[i]) {
const uint32_t cidx = i * bit_count_total;
/*rule->mask & keys[i]的值与rule->flow相比较*/
uint32_t match = netdev_rule_matches_key(rule, bit_count_total,
&blocks_scratch[cidx]);
if (OVS_LIKELY(match)) {
rules[i] = rule;
subtable->hit_cnt++;
goto next;
}
}
ULLONG_SET0(found_map, i); /* Did not match. */
next:
; /* Keep Sparse happy. */
}
return found_map;
}
掩码运算netdev_flow_key_flatten()
// 这个函数对应dpif-netdev.c里面的dpcls_flow_key_gen_masks()
static inline void
netdev_flow_key_flatten(const struct netdev_flow_key *key, // 要查找的miss_key
const struct netdev_flow_key *mask,
const uint64_t *mf_masks,
uint64_t *blocks_scratch,
const uint32_t u0_count,
const uint32_t u1_count)
{
/* Load mask from subtable, mask with packet mf, popcount to get idx. */
const uint64_t *pkt_blocks = miniflow_get_values(&key->mf);
const uint64_t *tbl_blocks = miniflow_get_values(&mask->mf); // 获取miss_key和mask的miniflow /* Packet miniflow bits to be masked by pre-calculated mf_masks. */
const uint64_t pkt_bits_u0 = key->mf.map.bits[0];
const uint32_t pkt_bits_u0_pop = count_1bits(pkt_bits_u0);
const uint64_t pkt_bits_u1 = key->mf.map.bits[1]; // 这个函数就是把miss_key与subtable的掩码进行&运算
// 会运算出该mask在意字段结果,放到blocks_scratch里
netdev_flow_key_flatten_unit(&pkt_blocks[0], // key-mf的数据段
&tbl_blocks[0], // mask->mf的数据段
&mf_masks[0], // mask->mf->bits得来mask
&blocks_scratch[0], // 存放的地址
pkt_bits_u0, // key->mf里的bits[0]
u0_count); // mask->mf->bits[0]里1的个数 netdev_flow_key_flatten_unit(&pkt_blocks[pkt_bits_u0_pop], // 上边bits[0]的已经算过了,从bits[1]开始算
&tbl_blocks[u0_count],
&mf_masks[u0_count],
&blocks_scratch[u0_count],
pkt_bits_u1,
u1_count);
} static inline void
netdev_flow_key_flatten_unit(const uint64_t *pkt_blocks, // key-mf的数据段
const uint64_t *tbl_blocks, // mask->mf里的数据段
const uint64_t *mf_masks, // mask->mf->bits得来mask
uint64_t *blocks_scratch, // 存放到这里
const uint64_t pkt_mf_bits, // key->mf里的bits[01]
const uint32_t count) // mask->mf->bits[0]里1的个数
{ // 说一下意思,这个我们流程就是用key和subtable的mask与运算,肯定只需要与运算mask里
// 不为0的字段,其他的mask不关心,然后这个操作就是为了得到key对应字段是key->mf的第几位,
// 比如mask的bits[0]=11111, key的bits[0] = 10100, mask里的第3个1在key里面是第1个
// 这一位与的结果就是tbl_blocks[2]&pkt_blocks[0], 也就是怎么找到key里的下标0
// 就看key当前位之前有几个1就行了。这里这样做的1010111,
// 蓝色1之前有count_1bits(1010111 & 0001111) = 3 // 对上边的mask举个例子 count = 4;
// mask->mf->bits[0] = 111010 (2进制)
// mf_masks = [1, 111, 1111, 11111] (2进制);
// pkt_mf_bits = 010100
// blocks_scratch = [0,0,0,0,pkt_blocks[1]&tbl_blocks[4],0]
uint32_t i;
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
// 拿i=2举例
uint64_t mf_mask = mf_masks[i]; // mf_mask = 001111
uint64_t idx_bits = mf_mask & pkt_mf_bits; // idx_bits = 000100
const uint32_t pkt_idx = count_1bits(idx_bits); // pkt_idx = 1 uint64_t pkt_has_mf_bit = (mf_mask + 1) & pkt_mf_bits; // pkt_has_mf_bit = 010000
// 是否求掩码:mask当前位对应的key的字段,如果key在当前位是0,下边算掩码就会变成0
uint64_t no_bit = ((!pkt_has_mf_bit) > 0) - 1; // 2^64 - 1 // mask里第i个字段与运算key对应的字段
blocks_scratch[i] = pkt_blocks[pkt_idx] & tbl_blocks[i] & no_bit; //
}
}
key对应的cmap:cmap_find_batch()
unsigned long
cmap_find_batch(const struct cmap *cmap, unsigned long map,
uint32_t hashes[], const struct cmap_node *nodes[])
{
const struct cmap_impl *impl = cmap_get_impl(cmap);
unsigned long result = map;
int i;
// 每一位就是一个包,一字节8个包
uint32_t h1s[sizeof map * CHAR_BIT];
const struct cmap_bucket *b1s[sizeof map * CHAR_BIT];
const struct cmap_bucket *b2s[sizeof map * CHAR_BIT];
uint32_t c1s[sizeof map * CHAR_BIT]; // 每个impl里桶的数量为impl->mask+1
// 为什么mask是桶的个数减1:因为下标从0开始,找下表的时候直接(hash & impl->mask)就行了 // 至于为什么开两个?因为buckets存放的方法也是一个值对应两个hash
// 第一次hash1 = rehash(impl->basis, hash), 找buckets[hash1 & impl->mask], 遍历里面CMAP_K个元素
// 第二次hash2 = other_hash(hash1), 找buckets[hash2 & impl->mask], 遍历里面CMAP_K个元素 /* Compute hashes and prefetch 1st buckets. */
ULLONG_FOR_EACH_1(i, map) {
h1s[i] = rehash(impl, hashes[i]);
b1s[i] = &impl->buckets[h1s[i] & impl->mask];
OVS_PREFETCH(b1s[i]);
}
/* Lookups, Round 1. Only look up at the first bucket. */
ULLONG_FOR_EACH_1(i, map) {
uint32_t c1;
const struct cmap_bucket *b1 = b1s[i];
const struct cmap_node *node; do {
c1 = read_even_counter(b1);
// 找一下这个cmap_bucket里面有没有相同hash的
node = cmap_find_in_bucket(b1, hashes[i]);
} while (OVS_UNLIKELY(counter_changed(b1, c1))); if (!node) {
/* Not found (yet); Prefetch the 2nd bucket. */
b2s[i] = &impl->buckets[other_hash(h1s[i]) & impl->mask];
OVS_PREFETCH(b2s[i]);
c1s[i] = c1; /* We may need to check this after Round 2. */
continue;
}
/* Found. */
ULLONG_SET0(map, i); /* Ignore this on round 2. */
OVS_PREFETCH(node);
nodes[i] = node;
}
/* Round 2. Look into the 2nd bucket, if needed. */
ULLONG_FOR_EACH_1(i, map) {
uint32_t c2;
const struct cmap_bucket *b2 = b2s[i];
const struct cmap_node *node; do {
c2 = read_even_counter(b2);
node = cmap_find_in_bucket(b2, hashes[i]);
} while (OVS_UNLIKELY(counter_changed(b2, c2))); if (!node) {
// 可能被修改了,
if (OVS_UNLIKELY(counter_changed(b1s[i], c1s[i]))) {
node = cmap_find__(b1s[i], b2s[i], hashes[i]);
if (node) {
goto found;
}
}
/* Not found. */
ULLONG_SET0(result, i); /* Fix the result. */
continue;
}
found:
OVS_PREFETCH(node);
nodes[i] = node;
}
return result;
}
2.3 fast_path_processing()
static inline void
fast_path_processing(struct dp_netdev_pmd_thread *pmd,
struct dp_packet_batch *packets_,
struct netdev_flow_key **keys,
struct dp_packet_flow_map *flow_map,
uint8_t *index_map,
odp_port_t in_port)
{
const size_t cnt = dp_packet_batch_size(packets_);
#if !defined(__CHECKER__) && !defined(_WIN32)
const size_t PKT_ARRAY_SIZE = cnt;
#else
/* Sparse or MSVC doesn't like variable length array. */
enum { PKT_ARRAY_SIZE = NETDEV_MAX_BURST };
#endif
struct dp_packet *packet;
struct dpcls *cls;
struct dpcls_rule *rules[PKT_ARRAY_SIZE];
struct dp_netdev *dp = pmd->dp;
int upcall_ok_cnt = 0, upcall_fail_cnt = 0;
int lookup_cnt = 0, add_lookup_cnt;
bool any_miss; for (size_t i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
/* Key length is needed in all the cases, hash computed on demand. */
keys[i]->len = netdev_flow_key_size(miniflow_n_values(&keys[i]->mf));
}
/* Get the classifier for the in_port */
// 找到端口对应的dpcls结构,每个port有自己的dpcls,因为每个port收到的报文会更相似
cls = dp_netdev_pmd_lookup_dpcls(pmd, in_port);
if (OVS_LIKELY(cls)) {
// 调用dpcls_lookup进行匹配
any_miss = !dpcls_lookup(cls, (const struct netdev_flow_key **)keys,
rules, cnt, &lookup_cnt);
} else {
any_miss = true;
memset(rules, 0, sizeof(rules));
}
// 如果有miss的,则需要进行openflow流表查询
if (OVS_UNLIKELY(any_miss) && !fat_rwlock_tryrdlock(&dp->upcall_rwlock)) {
uint64_t actions_stub[512 / 8], slow_stub[512 / 8];
struct ofpbuf actions, put_actions; ofpbuf_use_stub(&actions, actions_stub, sizeof actions_stub);
ofpbuf_use_stub(&put_actions, slow_stub, sizeof slow_stub); DP_PACKET_BATCH_FOR_EACH (i, packet, packets_) {
struct dp_netdev_flow *netdev_flow; if (OVS_LIKELY(rules[i])) {
continue;
}
// 此时可能已经更新了,在进入upcall之前如果再查一次,如果能够查到,会比upcall消耗的少得多
netdev_flow = dp_netdev_pmd_lookup_flow(pmd, keys[i],
&add_lookup_cnt);
if (netdev_flow) {
lookup_cnt += add_lookup_cnt;
rules[i] = &netdev_flow->cr;
continue;
}
// 第一级和第二级流表查找失败后,就要查找第三级流表了,即openflow流表,这也称为upcall调用。
// 在普通ovs下是通过netlink实现的,在ovs+dpdk下,直接在pmd线程中调用upcall_cb即可。
// 开始查找openflow流表。如果查找openflow流表成功并需要下发到dpcls时,需要判断是否超出最大流表限制
int error = handle_packet_upcall(pmd, packet, keys[i],
&actions, &put_actions); if (OVS_UNLIKELY(error)) {
upcall_fail_cnt++;
} else {
upcall_ok_cnt++;
}
} ofpbuf_uninit(&actions);
ofpbuf_uninit(&put_actions);
fat_rwlock_unlock(&dp->upcall_rwlock);
} else if (OVS_UNLIKELY(any_miss)) {
DP_PACKET_BATCH_FOR_EACH (i, packet, packets_) {
if (OVS_UNLIKELY(!rules[i])) {
dp_packet_delete(packet);
COVERAGE_INC(datapath_drop_lock_error);
upcall_fail_cnt++;
}
}
} DP_PACKET_BATCH_FOR_EACH (i, packet, packets_) {
struct dp_netdev_flow *flow;
/* Get the original order of this packet in received batch. */
int recv_idx = index_map[i];
uint16_t tcp_flags; if (OVS_UNLIKELY(!rules[i])) {
continue;
} flow = dp_netdev_flow_cast(rules[i]); bool hook_cached = false;
if (pmd->cached_hook && \
pmd->cached_hook_pmd && \
pmd->cached_hook->hook_flow_miss) {
hook_cached = pmd->cached_hook->hook_flow_miss(pmd->cached_hook_pmd, packet, flow);
} if (!hook_cached) {
bool smc_enable_db;
atomic_read_relaxed(&pmd->dp->smc_enable_db, &smc_enable_db);
// 查找到了packet,如果开启了smc,更新smc
if (smc_enable_db) {
uint32_t hash = dp_netdev_flow_hash(&flow->ufid);
smc_insert(pmd, keys[i], hash);
}
// 查到了packet,看是否写会更新上一层cache(EMC)
if (emc_probabilistic_insert(pmd, keys[i], flow)) {
if (flow->status == OFFLOAD_NONE) {
queue_netdev_flow_put(pmd->dp->dp_flow_offload, \
pmd->dp->class, \
flow, NULL, DP_NETDEV_FLOW_OFFLOAD_OP_ADD);
}
}
}
/* Add these packets into the flow map in the same order
* as received.
*/
tcp_flags = miniflow_get_tcp_flags(&keys[i]->mf);
packet_enqueue_to_flow_map(packet, flow, tcp_flags,
flow_map, recv_idx);
}
// 更新各个信息
pmd_perf_update_counter(&pmd->perf_stats, PMD_STAT_MASKED_HIT,
cnt - upcall_ok_cnt - upcall_fail_cnt);
pmd_perf_update_counter(&pmd->perf_stats, PMD_STAT_MASKED_LOOKUP,
lookup_cnt);
pmd_perf_update_counter(&pmd->perf_stats, PMD_STAT_MISS,
upcall_ok_cnt);
pmd_perf_update_counter(&pmd->perf_stats, PMD_STAT_LOST,
upcall_fail_cnt);
}
2.4 smc更新smc_insert()
static inline void
smc_insert(struct dp_netdev_pmd_thread *pmd,
const struct netdev_flow_key *key,
uint32_t hash)
{
struct smc_cache *smc_cache = &(pmd->flow_cache).smc_cache;
struct smc_bucket *bucket = &smc_cache->buckets[key->hash & SMC_MASK];
uint16_t index;
uint32_t cmap_index;
int i; //布谷鸟算法
cmap_index = cmap_find_index(&pmd->flow_table, hash);
index = (cmap_index >= UINT16_MAX) ? UINT16_MAX : (uint16_t)cmap_index; /* If the index is larger than SMC can handle (uint16_t), we don't
* insert */
if (index == UINT16_MAX) {
//表明找到了
return;
} /* If an entry with same signature already exists, update the index */
uint16_t sig = key->hash >> 16;
for (i = 0; i < SMC_ENTRY_PER_BUCKET; i++) {
if (bucket->sig[i] == sig) {
bucket->flow_idx[i] = index;
return;
}
}
/* If there is an empty entry, occupy it. */
for (i = 0; i < SMC_ENTRY_PER_BUCKET; i++) {
if (bucket->flow_idx[i] == UINT16_MAX) {
bucket->sig[i] = sig;
bucket->flow_idx[i] = index;
return;
}
}
/* Otherwise, pick a random entry. */
i = random_uint32() % SMC_ENTRY_PER_BUCKET;
bucket->sig[i] = sig;
bucket->flow_idx[i] = index;
}
3. upcall到openflow查找,然后更新dpcls
这里就不讲具体代码了,讲一下大概:到openflow查找后会更新dpcls,执行dp_netdev_flow_add() --> dpcls_insert() --> dpcls_find_subtable() --> cmap_insert()
dpcls_find_subtable():
找一下是否存在相同mask的subtable,存在返回这个subtable,不存在就创建一个subtable,创建的时候会调用dpcls_create_subtable,里面有个dpcls_subtable_get_best_impl会根据mask的miniflow的bits[0]和bits[1]选择的查找算法。
cmap_insert里hash算法用的就是布谷鸟hash,hash两次,插入的核心代码:
static bool
cmap_try_insert(struct cmap_impl *impl, struct cmap_node *node, uint32_t hash)
{
uint32_t h1 = rehash(impl, hash);
uint32_t h2 = other_hash(h1);
// hash两次找到两个桶
struct cmap_bucket *b1 = &impl->buckets[h1 & impl->mask];
struct cmap_bucket *b2 = &impl->buckets[h2 & impl->mask]; // 插入规则:
// 1.是否有相同hash的node,就插到对应链上
// 2.没有相同hash,就看有没有空的node
// 3.都不行就通过bfs,看能否让b1,b2空出来一个,把这个放进去
// 都不行就插入失败
return (OVS_UNLIKELY(cmap_insert_dup(node, hash, b1) ||
cmap_insert_dup(node, hash, b2)) ||
OVS_LIKELY(cmap_insert_bucket(node, hash, b1) ||
cmap_insert_bucket(node, hash, b2)) ||
cmap_insert_bfs(impl, node, hash, b1, b2));
}
参考博客:
OVS-DPDK Datapath Classifier :这个是理论上的流程,看完就知道这个算法流程了
ovs分类器 flow和miniflow :很重要的结构体miniflow
OVS-DPDK DataPath Classifier反向设计 :这个有很多详细的解释,但不怎么流畅
最新文章
- c#多态性
- C# 访问数据库
- LeetCode 26 Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array
- SqlServer 笔记一 某表中每个月的产品数量(DATENAME() 与 DATEPART()、YEAR())
- Vuejs注意点
- 细谈WEB标准
- JavaScript ---属性
- Jquery 前端模版
- C#中Attribute介绍
- Why am I getting an error converting a Foo** → const Foo**?
- C#中如何正确的操作字符串?
- http://www.cnbc.com/2016/07/12/tensions-in-south-china-sea-to-persist-even-after-court-ruling.html
- 把zlog封装成模块,隐藏zlog
- NET Core 中的依赖注入
- Java——值传递与引用传递
- 洛谷P3959 宝藏
- Scrapy实战篇(五)之爬取历史天气数据
- Mongodb 基础 数据导入导出和用户管理
- Airtest Project的探索和使用
- WTForms组件