第09课:【实战】Redis网络通信模块源码分析(2)
侦听 fd 与客户端 fd 是如何挂载到 EPFD 上去的
同样的方式,要把一个 fd 挂载到 EPFD 上去,需要调用系统 API epoll_ctl ,搜索一下这个函数名。在文件 ae_epoll.c 中我们找到 aeApiAddEvent 函数:
static int aeApiAddEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, int mask) {
aeApiState *state = eventLoop->apidata;
struct epoll_event ee = {0}; /* avoid valgrind warning */
/* If the fd was already monitored for some event, we need a MOD
* operation. Otherwise we need an ADD operation. */
int op = eventLoop->events[fd].mask == AE_NONE ?
EPOLL_CTL_ADD : EPOLL_CTL_MOD;
ee.events = 0;
mask |= eventLoop->events[fd].mask; /* Merge old events */
if (mask & AE_READABLE) ee.events |= EPOLLIN;
if (mask & AE_WRITABLE) ee.events |= EPOLLOUT;
ee.data.fd = fd;
if (epoll_ctl(state->epfd,op,fd,&ee) == -1) return -1;
return 0;
}
当把一个 fd 绑定到 EPFD 上去的时候,先从 eventLoop( aeEventLoop类型 )中寻找是否存在已关注的事件类型,如果已经有了,说明使用 epoll_ctl 是更改已绑定的 fd 事件类型( EPOLL_CTL_MOD ),否则就是添加 fd 到 EPFD 上。
在 aeApiAddEvent 加个断点,再重启下 redis-server 。触发断点后的调用堆栈如下:
#0 aeCreateFileEvent (eventLoop=0x7ffff083a0a0, fd=15, mask=mask@entry=1, proc=0x437f50 <acceptTcpHandler>, clientData=clientData@entry=0x0) at ae.c:145
#1 0x000000000042f83b in initServer () at server.c:1927
#2 0x0000000000423803 in main (argc=<optimized out>, argv=0x7fffffffe588) at server.c:3857
同样在 initServer 函数中,结合上文分析的侦听 fd 的创建过程,去掉无关代码,抽出这个函数的主脉络得到如下伪代码:
void initServer(void) {
//记录程序进程 ID
server.pid = getpid();
//创建程序的 aeEventLoop 对象和 epfd 对象
server.el = aeCreateEventLoop(server.maxclients+CONFIG_FDSET_INCR);
//创建侦听 fd
listenToPort(server.port,server.ipfd,&server.ipfd_count) == C_ERR)
//将侦听 fd 设置为非阻塞的
anetNonBlock(NULL,server.sofd);
//创建 Redis 的定时器,用于执行定时任务 cron
/* Create the timer callback, this is our way to process many background
* operations incrementally, like clients timeout, eviction of unaccessed
* expired keys and so forth. */
aeCreateTimeEvent(server.el, 1, serverCron, NULL, NULL) == AE_ERR
//将侦听 fd 绑定到 epfd 上去
/* Create an event handler for accepting new connections in TCP and Unix
* domain sockets. */
aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, server.ipfd[j], AE_READABLE, acceptTcpHandler,NULL) == AE_ERR
//创建一个管道,用于在需要时去唤醒 epoll_wait 挂起的整个 EventLoop
/* Register a readable event for the pipe used to awake the event loop
* when a blocked client in a module needs attention. */
aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, server.module_blocked_pipe[0], AE_READABLE, moduleBlockedClientPipeReadable,NULL) == AE_ERR)
}
注意:这里所说的“主脉络”是指我们关心的网络通信的主脉络,不代表这个函数中其他代码就不是主要的。
如何验证这个断点处挂载到 EPFD 上的 fd 就是侦听 fd 呢?很简单,创建侦听 fd 时,用 GDB 记录下这个 fd 的值。例如,当我的电脑某次运行时,侦听 fd 的值是 15 。如下图( 调试工具用的是 CGDB ):
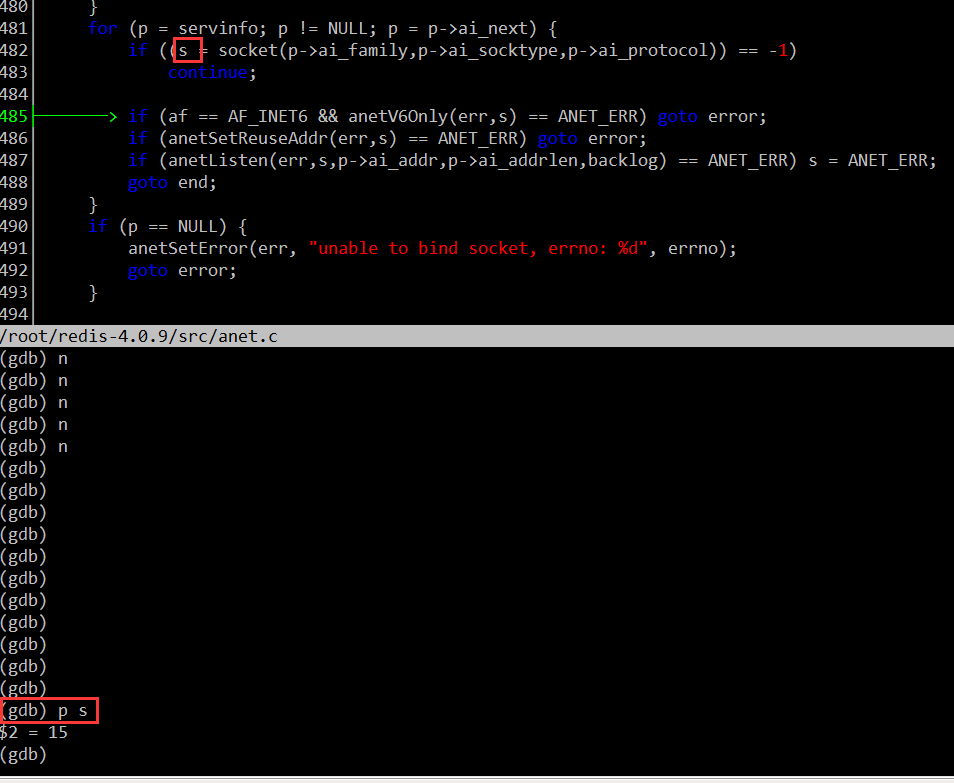
然后在运行程序至绑定 fd 的地方,确认一下绑定到 EPFD 上的 fd 值:

这里的 fd 值也是 15 ,说明绑定的 fd 是侦听 fd 。当然在绑定侦听 fd 时,同时也指定了只关注可读事件,并设置事件回调函数为 acceptTcpHandler 。对于侦听 fd ,一般只要关注可读事件就可以了,当触发可读事件,说明有新的连接到来。
aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, server.ipfd[j], AE_READABLE, acceptTcpHandler,NULL) == AE_ERR
acceptTcpHandler 函数定义如下( 位于文件 networking.c 中 ):
void acceptTcpHandler(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {
int cport, cfd, max = MAX_ACCEPTS_PER_CALL;
char cip[NET_IP_STR_LEN];
UNUSED(el);
UNUSED(mask);
UNUSED(privdata);
while(max--) {
cfd = anetTcpAccept(server.neterr, fd, cip, sizeof(cip), &cport);
if (cfd == ANET_ERR) {
if (errno != EWOULDBLOCK)
serverLog(LL_WARNING,
"Accepting client connection: %s", server.neterr);
return;
}
serverLog(LL_VERBOSE,"Accepted %s:%d", cip, cport);
acceptCommonHandler(cfd,0,cip);
}
}
anetTcpAccept 函数中调用的就是我们上面说的 anetGenericAccept 函数了。
int anetTcpAccept(char *err, int s, char *ip, size_t ip_len, int *port) {
int fd;
struct sockaddr_storage sa;
socklen_t salen = sizeof(sa);
if ((fd = anetGenericAccept(err,s,(struct sockaddr*)&sa,&salen)) == -1)
return ANET_ERR;
if (sa.ss_family == AF_INET) {
struct sockaddr_in *s = (struct sockaddr_in *)&sa;
if (ip) inet_ntop(AF_INET,(void*)&(s->sin_addr),ip,ip_len);
if (port) *port = ntohs(s->sin_port);
} else {
struct sockaddr_in6 *s = (struct sockaddr_in6 *)&sa;
if (ip) inet_ntop(AF_INET6,(void*)&(s->sin6_addr),ip,ip_len);
if (port) *port = ntohs(s->sin6_port);
}
return fd;
}
至此,这段流程总算连起来了,在 acceptTcpHandler 上加个断点,然后重新运行一下 redis-server ,再开个 redis-cli 去连接 redis-server 。看看是否能触发该断点,如果能触发该断点,说明我们的分析是正确的。
经验证,确实触发了该断点。
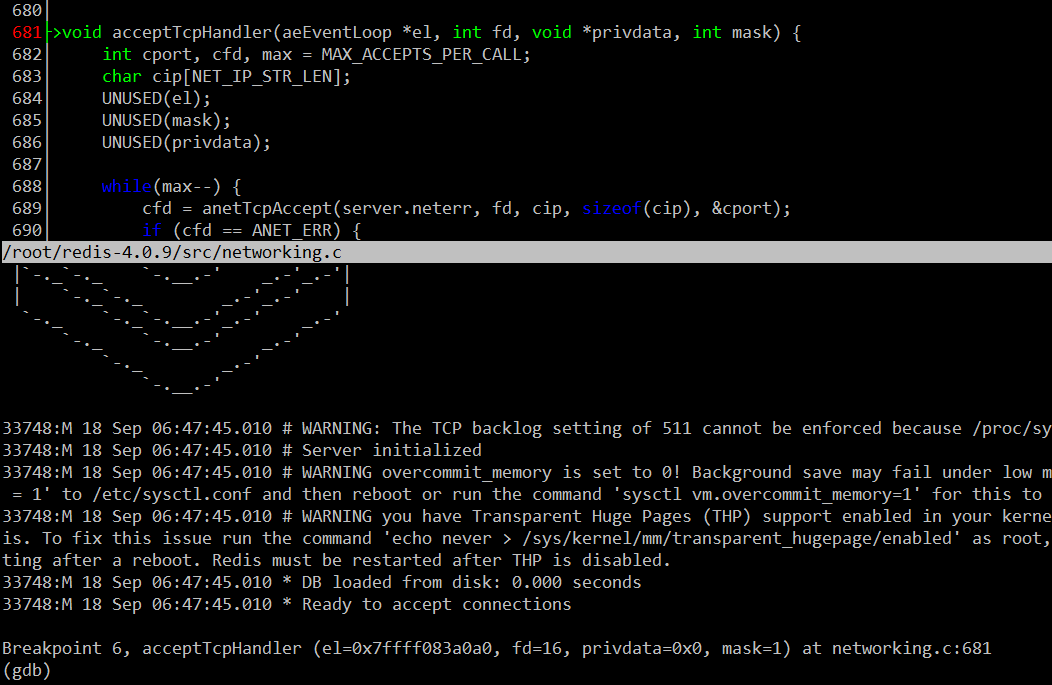
在 acceptTcpHandler 中成功接受新连接后,产生客户端 fd ,然后调用 acceptCommonHandler 函数,在该函数中调用 createClient 函数,在 createClient 函数中先将客户端 fd 设置成非阻塞的,然后将该 fd 关联到 EPFD 上去,同时记录到整个程序的 aeEventLoop 对象上。
client *createClient(int fd) {
//将客户端 fd 设置成非阻塞的
anetNonBlock(NULL,fd);
//启用 tcp NoDelay 选项
anetEnableTcpNoDelay(NULL,fd);
//根据配置,决定是否启动 tcpkeepalive 选项
if (server.tcpkeepalive)
anetKeepAlive(NULL,fd,server.tcpkeepalive);
//将客户端 fd 绑定到 epfd,同时记录到 aeEventLoop 上,关注的事件为 AE_READABLE,回调函数为
//readQueryFromClient
aeCreateFileEvent(server.el,fd,AE_READABLE, readQueryFromClient, c) == AE_ERR
return c;
}
如何处理 fd 可读事件
客户端 fd 触发可读事件后,回调函数是 readQueryFromClient 。该函数实现如下( 位于 networking.c 文件中):
void readQueryFromClient(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {
client *c = (client*) privdata;
int nread, readlen;
size_t qblen;
UNUSED(el);
UNUSED(mask);
readlen = PROTO_IOBUF_LEN;
/* If this is a multi bulk request, and we are processing a bulk reply
* that is large enough, try to maximize the probability that the query
* buffer contains exactly the SDS string representing the object, even
* at the risk of requiring more read(2) calls. This way the function
* processMultiBulkBuffer() can avoid copying buffers to create the
* Redis Object representing the argument. */
if (c->reqtype == PROTO_REQ_MULTIBULK && c->multibulklen && c->bulklen != -1
&& c->bulklen >= PROTO_MBULK_BIG_ARG)
{
int remaining = (unsigned)(c->bulklen+2)-sdslen(c->querybuf);
if (remaining < readlen) readlen = remaining;
}
qblen = sdslen(c->querybuf);
if (c->querybuf_peak < qblen) c->querybuf_peak = qblen;
c->querybuf = sdsMakeRoomFor(c->querybuf, readlen);
nread = read(fd, c->querybuf+qblen, readlen);
if (nread == -1) {
if (errno == EAGAIN) {
return;
} else {
serverLog(LL_VERBOSE, "Reading from client: %s",strerror(errno));
freeClient(c);
return;
}
} else if (nread == 0) {
serverLog(LL_VERBOSE, "Client closed connection");
freeClient(c);
return;
} else if (c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) {
/* Append the query buffer to the pending (not applied) buffer
* of the master. We'll use this buffer later in order to have a
* copy of the string applied by the last command executed. */
c->pending_querybuf = sdscatlen(c->pending_querybuf,
c->querybuf+qblen,nread);
}
sdsIncrLen(c->querybuf,nread);
c->lastinteraction = server.unixtime;
if (c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) c->read_reploff += nread;
server.stat_net_input_bytes += nread;
if (sdslen(c->querybuf) > server.client_max_querybuf_len) {
sds ci = catClientInfoString(sdsempty(),c), bytes = sdsempty();
bytes = sdscatrepr(bytes,c->querybuf,64);
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Closing client that reached max query buffer length: %s (qbuf initial bytes: %s)", ci, bytes);
sdsfree(ci);
sdsfree(bytes);
freeClient(c);
return;
}
/* Time to process the buffer. If the client is a master we need to
* compute the difference between the applied offset before and after
* processing the buffer, to understand how much of the replication stream
* was actually applied to the master state: this quantity, and its
* corresponding part of the replication stream, will be propagated to
* the sub-slaves and to the replication backlog. */
if (!(c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER)) {
processInputBuffer(c);
} else {
size_t prev_offset = c->reploff;
processInputBuffer(c);
size_t applied = c->reploff - prev_offset;
if (applied) {
replicationFeedSlavesFromMasterStream(server.slaves,
c->pending_querybuf, applied);
sdsrange(c->pending_querybuf,applied,-1);
}
}
}
给这个函数加个断点,然后重新运行下 redis-server ,再启动一个客户端,然后尝试给服务器发送一个命令“set hello world”。但是在我们实际调试的时候会发现。只要 redis-cli 一连接成功,GDB 就触发该断点,此时并没有发送我们预想的命令。我们单步调试 readQueryFromClient 函数,将收到的数据打印出来,得到如下字符串:
(gdb) p c->querybuf
$8 = (sds) 0x7ffff09b8685 "*1\r\n$7\r\nCOMMAND\r\n"
c → querybuf 是什么呢?这里 c 的类型是 client 结构体,它是上文中连接接收成功后产生的新客户端 fd 绑定回调函数时产生的、并传递给 readQueryFromClient 函数的参数。我们可以在 server.h 中找到它的定义:
* With multiplexing we need to take per-client state.
* Clients are taken in a linked list. */
typedef struct client {
uint64_t id; /* Client incremental unique ID. */
int fd; /* Client socket. */
redisDb *db; /* Pointer to currently SELECTed DB. */
robj *name; /* As set by CLIENT SETNAME. */
sds querybuf; /* Buffer we use to accumulate client queries. */
//省略掉部分字段
} client;
client 实际上是存储每个客户端连接信息的对象,其 fd 字段就是当前连接的 fd,querybuf 字段就是当前连接的接收缓冲区,也就是说每个新客户端连接都会产生这样一个对象。从 fd 上收取数据后就存储在这个 querybuf 字段中。
我们贴一下完整的 createClient 函数的代码:
client *createClient(int fd) {
client *c = zmalloc(sizeof(client));
/* passing -1 as fd it is possible to create a non connected client.
* This is useful since all the commands needs to be executed
* in the context of a client. When commands are executed in other
* contexts (for instance a Lua script) we need a non connected client. */
if (fd != -1) {
anetNonBlock(NULL,fd);
anetEnableTcpNoDelay(NULL,fd);
if (server.tcpkeepalive)
anetKeepAlive(NULL,fd,server.tcpkeepalive);
if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el,fd,AE_READABLE,
readQueryFromClient, c) == AE_ERR)
{
close(fd);
zfree(c);
return NULL;
}
}
selectDb(c,0);
uint64_t client_id;
atomicGetIncr(server.next_client_id,client_id,1);
c->id = client_id;
c->fd = fd;
c->name = NULL;
c->bufpos = 0;
c->querybuf = sdsempty();
c->pending_querybuf = sdsempty();
c->querybuf_peak = 0;
c->reqtype = 0;
c->argc = 0;
c->argv = NULL;
c->cmd = c->lastcmd = NULL;
c->multibulklen = 0;
c->bulklen = -1;
c->sentlen = 0;
c->flags = 0;
c->ctime = c->lastinteraction = server.unixtime;
c->authenticated = 0;
c->replstate = REPL_STATE_NONE;
c->repl_put_online_on_ack = 0;
c->reploff = 0;
c->read_reploff = 0;
c->repl_ack_off = 0;
c->repl_ack_time = 0;
c->slave_listening_port = 0;
c->slave_ip[0] = '\0';
c->slave_capa = SLAVE_CAPA_NONE;
c->reply = listCreate();
c->reply_bytes = 0;
c->obuf_soft_limit_reached_time = 0;
listSetFreeMethod(c->reply,freeClientReplyValue);
listSetDupMethod(c->reply,dupClientReplyValue);
c->btype = BLOCKED_NONE;
c->bpop.timeout = 0;
c->bpop.keys = dictCreate(&objectKeyPointerValueDictType,NULL);
c->bpop.target = NULL;
c->bpop.numreplicas = 0;
c->bpop.reploffset = 0;
c->woff = 0;
c->watched_keys = listCreate();
c->pubsub_channels = dictCreate(&objectKeyPointerValueDictType,NULL);
c->pubsub_patterns = listCreate();
c->peerid = NULL;
listSetFreeMethod(c->pubsub_patterns,decrRefCountVoid);
listSetMatchMethod(c->pubsub_patterns,listMatchObjects);
if (fd != -1) listAddNodeTail(server.clients,c);
initClientMultiState(c);
return c;
}
最新文章
- C++虚函数和函数指针一起使用
- PHP 使用 debug_print_backtrace() 或 debug_backtrace() 打印栈轨迹
- Git实现从本地添加项目到远程仓库
- linux下socket编程-进程间通信
- 墨菲定律-Murphy's Law (转载)
- PHP正则表达式之定界符和原子介绍
- js实现未知宽高的元素在指定元素中垂直水平居中
- mac下搭建react-native环境
- lib-flexible 结合 WKWebView 的样式错乱解决方法
- ARM学习笔记4——加载存储指令
- Java synchronized 详解
- Layer 中自定义属性的动画
- 【Owin 学习系列】2. Owin Startup 类解析
- 常见的Linux操作系统推荐
- oc __weak和__strong的区别
- Pytorch 细节记录
- 【IT笔试面试题整理】判断链表是否存在环路,并找出回路起点
- 《LINUX内核设计与实现》第一、二章学习总结
- Html学习笔记3
- 10 款基于 jQuery 的切换效果插件推荐