每日扫盲(四):java之Netty原理和使用
转自:https://www.jdon.com/concurrent/netty.html
Netty是一个高性能 事件驱动的异步的非堵塞的IO(NIO)框架,用于建立TCP等底层的连接,基于Netty可以建立高性能的Http服务器。支持HTTP、 WebSocket 、Protobuf、 Binary TCP |和UDP,Netty已经被很多高性能项目作为其Socket底层基础,如HornetQ Infinispan Vert.x
Play Framework Finangle和 Cassandra。其竞争对手是:Apache MINA和 Grizzly。
传统堵塞的IO读取如下:
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("input.bin");
int byte = is.read(); // 当前线程等待结果到达直至错误
而使用NIO如下:
while (true) {
selector.select(); // 从多个通道请求事件
Iterator it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
SelectorKey key = (SelectionKey) it.next();
handleKey(key);
it.remove();
}
}
堵塞与非堵塞原理
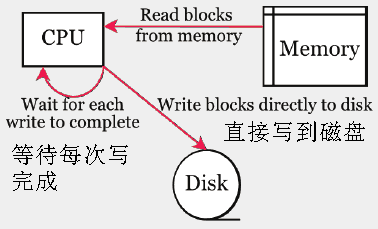
传统硬件的堵塞如下,从内存中读取数据,然后写到磁盘,而CPU一直等到磁盘写完成,磁盘的写操作是慢的,这段时间CPU被堵塞不能发挥效率。
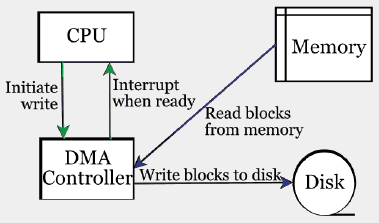
使用非堵塞的DMA如下图:CPU只是发出写操作这样的指令,做一些初始化工作,DMA具体执行,从内存中读取数据,然后写到磁盘,当完成写后发出一个中断事件给CPU。这段时间CPU是空闲的,可以做别的事情。这个原理称为Zero.copy零拷贝。
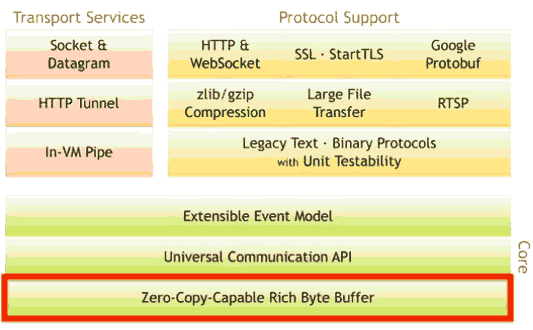
Netty底层基于上述Java NIO的零拷贝原理实现:
比较
- Tomcat是一个Web服务器,它是采取一个请求一个线程,当有1000客户端时,会耗费很多内存。通常一个线程将花费 256kb到1mb的stack空间。
- Node.js是一个线程服务于所有请求,在错误处理上有限制
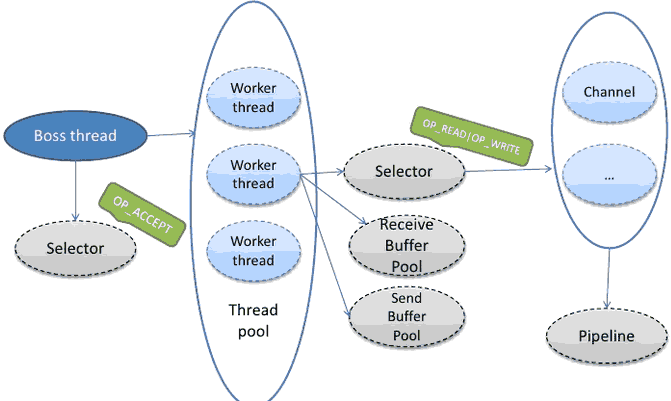
- Netty是一个线程服务于很多请求,如下图,当从Java NIO获得一个Selector事件,将激活通道Channel。
演示
Netty的使用代码如下:
Channel channel = ...
ChannelFuture cf = channel.write(data);
cf.addListener(
new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if(!future.isSuccess() {
future.cause().printStacktrace();
...
}
...
}
});
...
cf.sync();
通过引入观察者监听,当有数据时,将自动激活监听者中的代码运行。
我们使用Netty建立一个服务器代码:
public class EchoServer {
private final int port;
public EchoServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void run() throws Exception {
// Configure the server.
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 100)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO)).childHandler(newChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(
// new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO),
new EchoServerHandler());
}
});
// Start the server.
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync();
// Wait until the server socket is closed.
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
// Shut down all event loops to terminate all threads.
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
这段代码调用:在9999端口启动
new EchoServer(9999).run();
我们需要完成的代码是EchoServerHandler:
public class EchoServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(EchoServerHandler.class.getName());
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ctx.write(msg);
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.flush();
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
// Close the connection when an exception is raised.
logger.log(Level.WARNING, "Unexpected exception from downstream.", cause);
ctx.close();
}
}
原理
一个Netty服务器的原理如下:
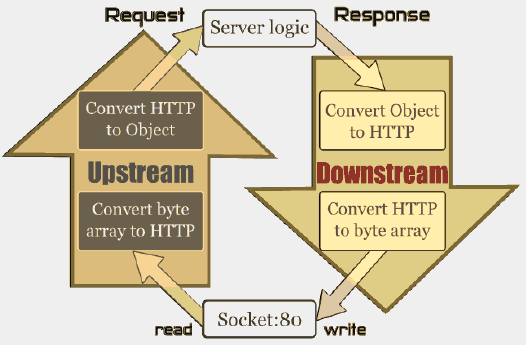
图中每次请求的读取是通过UpStream来实现,然后激活我们的服务逻辑如EchoServerHandler,而服务器向外写数据,也就是响应是通过DownStream实现的。每个通道Channel包含一对UpStream和DownStream,以及我们的handlers(EchoServerHandler),如下图,这些都是通过channel pipeline封装起来的,数据流在管道里流动,每个Socket对应一个ChannelPipeline。
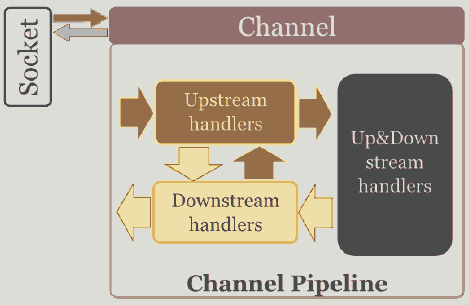
CHANNELPIPELINE是关键,它类似Unix的管道,有以下作用:
- 为每个Channel 保留 ChannelHandlers ,如EchoServerHandler
- 所有的事件都要通过它
- 不断地修改:类似unix的SH管道: echo "Netty is shit...." | sed -e 's/is /is the /'
- 一个Channel对应一个 ChannelPipeline
- 包含协议编码解码 安全验证SSL/TLS和应用逻辑
客户端代码
前面我们演示了服务器端代码,下面是客户端代码:
public class EchoClient {
private final String host;
private final int port;
private final int firstMessageSize;
public EchoClient(String host, int port, int firstMessageSize) {
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
this.firstMessageSize = firstMessageSize;
}
public void run() throws Exception {
// Configure the client.
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class).option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true).handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(
// new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO),
new EchoClientHandler(firstMessageSize));
}
});
// Start the client.
ChannelFuture f = b.connect(host, port).sync();
// Wait until the connection is closed.
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
// Shut down the event loop to terminate all threads.
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
客户端的应用逻辑EchoClientHandler:
public class EchoClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(EchoClientHandler.class.getName());
private final ByteBuf firstMessage;
/**
* Creates a client-side handler.
*/
public EchoClientHandler(int firstMessageSize) {
if (firstMessageSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("firstMessageSize: " + firstMessageSize);
}
firstMessage = Unpooled.buffer(firstMessageSize);
for (int i = 0; i < firstMessage.capacity(); i++) {
firstMessage.writeByte((byte) i);
}
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
ctx.writeAndFlush(firstMessage);
System.out.print("active");
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ctx.write(msg);
System.out.print("read");
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.flush();
System.out.print("readok");
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
// Close the connection when an exception is raised.
logger.log(Level.WARNING, "Unexpected exception from downstream.", cause);
ctx.close();
}
}
最新文章
- Android 7.1 - App Shortcuts
- GoLang几种读文件方式的比较
- SQL基础(2)-约束
- 判断 ACdream 1202 Integer in C++
- Java Garbage Collection/垃圾收集 策略查看
- SQL SERVER 清空日志
- Fuel 5.1安装openstack I版本号环境
- C#仪器数据文件解析-RTF文件
- Mysql 查询重复的记录
- .NET开发中基础问题,CODE First AND DB First(大牛自动忽略,小白可以看一下)
- jvm 常用参数
- MYSQL主从复制制作配置方案
- 【HTML5】HTML5中video元素事件详解(实时监测当前播放时间)
- nginx配置框架问题
- Android ScrollView和ListView联用,且ListView可以下拉刷新和上拉加载
- 自学Zabbix7.1 IT services
- WPS 2019 How To Create New Sheets For Each Row In Excel?
- 处理jquery的ajax请求session过期跳转到登录页面
- readv与writev
- Knowledge Tracing -- 基于贝叶斯的学生知识点追踪(BKT)