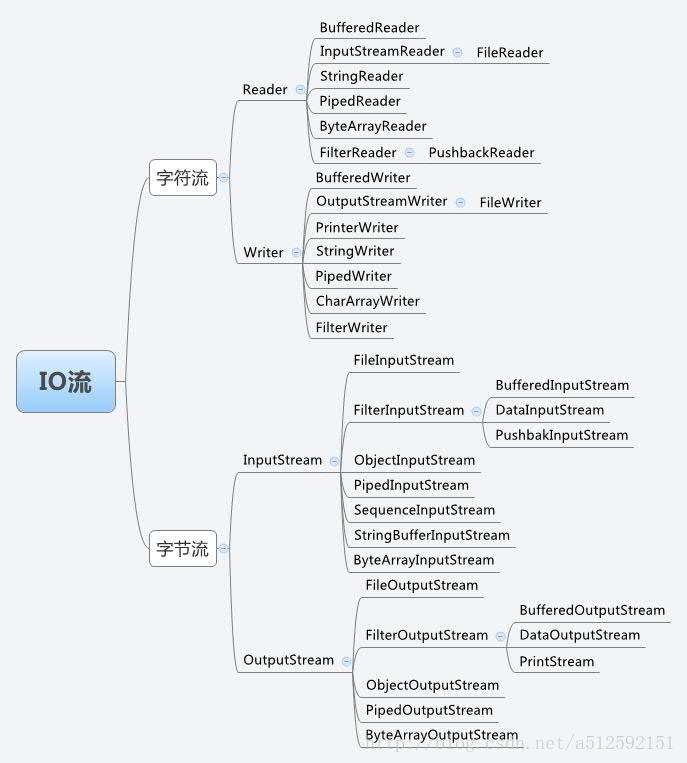
java从基础知识(九)I/O
java中的流可以从不同的角度进行分类
按流的方向:输入流、输出流(注意这里的输入(read)、输出是相对于程序而言的(writer),个人认为从读、写角度理解更为直观)
按处理数据单位:字节流、字符流(字节流为继承自InputStream和OutputStream的流,以字节(8位)为单位读写;字符流为继承自Reader和Writer的流,以字符(16位)为单位读写)
按实现功能:节点流、处理流(节点流直接与数据源相连读写;处理流在节点流的基础上,再套接一层以完成特定的读写功能)
一、File
1、File
public class FileTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String ps1 = File.pathSeparator;//与系统有关的路径分隔符(':'),为了方便,它被表示为一个字符串
char ps2 = File.pathSeparatorChar;//与系统有关的路径分隔符(':' 58)
String ps3 = File.separator ;//与系统有关的默认名称分隔符('/'),为了方便,它被表示为一个字符串
char ps4 = File.separatorChar ;//与系统有关的默认名称分隔符('/' 47)
File file = new File("/home/sunjf/a.txt");//通过将给定路径名字符串转换为抽象路径名来创建一个新 File 实例
File f = new File("/home/sunjf");
File f1 = new File(f, "a.txt");//根据 parent 抽象路径名和 child 路径名字符串创建一个新 File 实例
File f2 = new File("/home/sunjf", "c.txt");//根据 parent 路径名字符串和 child 路径名字符串创建一个新 File 实例
System.out.println("测试此抽象路径名表示的文件或目录是否存在 : " + file.exists());
System.out.println("测试应用程序是否可以读取此抽象路径名表示的文件 : " + file.canRead());
System.out.println("测试应用程序是否可以修改此抽象路径名表示的文件 : " + file.canWrite());
System.out.println("返回此抽象路径名父目录的路径名字符串;如果此路径名没有指定父目录,则返回 null : " + file.getParent());
System.out.println("返回由此抽象路径名表示的文件或目录的名称 : " + file.getName());
System.out.println("将此抽象路径名转换为一个路径名字符串 : " + file.getPath());
System.out.println("测试此抽象路径名表示的文件是否是一个目录 : " + file.isDirectory());
System.out.println("测试此抽象路径名表示的文件是否是一个标准文件 : " + file.isFile());
System.out.println("测试此抽象路径名指定的文件是否是一个隐藏文件 : " + file.isHidden());
System.out.println("测试此抽象路径名是否为绝对路径名 : " + file.isAbsolute());
System.out.println("返回此抽象路径名表示的文件最后一次被修改的时间 : " + file.lastModified());
System.out.println("返回由此抽象路径名表示的文件的长度 : " + file.length());
String[] pathStr = f.list();//返回一个字符串数组,这些字符串指定此抽象路径名表示的目录中的文件和目录
for(String s : pathStr) System.out.println("返回一个字符串数组,这些字符串指定此抽象路径名表示的目录中的文件和目录 " + s);
File[] fileArr = f.listFiles();
for(File index : fileArr) System.out.println("返回一个字符串数组,这些字符串指定此抽象路径名表示的目录中满足指定过滤器的文件和目录 " + index);
file.delete();//删除此抽象路径名表示的文件或目录
file.mkdir();//创建此抽象路径名指定的目录
//file.mkdirs();//创建此抽象路径名指定的目录,包括所有必需但不存在的父目录
//if (file.exists()) file.delete();
/*try {
file.createNewFile();//当且仅当不存在具有此抽象路径名指定名称的文件时,不可分地创建一个新的空文件
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}*/
}
}
二、字节流:OutputStream和InputStream
1、字节文件流:FileOutStream和FileInputStream
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("D:/a.txt");
try {
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);// 创建一个向指定 File 对象表示的文件中写入数据的文件输出流,会覆盖之前的数据
//FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:/a.txt");
//FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file, true);//不会覆盖之前数据
//FileOutputStream fos1 = new FileOutputStream("D:/a.txt", true);
//FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(fos1.getFD());//创建一个向指定文件描述符处写入数据的输出文件流,该文件描述符表示一个到文件系统中的某个实际文件的现有连接
System.out.println("返回与此流有关的文件描述符 : " + fos.getFD().getClass());
System.out.println("返回与此文件输出流有关的唯一 FileChannel 对象 : " + fos.getChannel().getClass());
char[] c = {'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', ' ', 'I', '/', 'O', '!', '\n'};
for (char ch : c) fos.write(ch);//将指定字节写入此文件输出流
byte[] b = {'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', ' ', 'I', '/', 'O', '!', '\n'};
fos.write(b);//将 b.length 个字节从指定 byte 数组写入此文件输出流中
fos.write(b, 6, 5);//将指定 byte 数组中从偏移量 off 开始的 len 个字节写入此文件输出流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
int index = 0;
while ((index = fis.read()) != -1) {//数据读出
System.out.print((char) index);
}
fos.close();//关闭写入流
fis.close();//关闭读出流
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2、字节缓存流:BufferOutputStream和BufferInputStream
继承自FilterOutputStream和FilterInputStream,实现了带缓冲的过滤流,它提供了缓冲机制,可以提高该I/O流的读取效率,在初始化时,除了要指定所连接的I/O流之外,还可以指定缓冲区的大小。在读写的同时对数据缓存,这样避免每次读写数据都要进行实际的物理读写操作,在用BufferdOutputStream输出时,数据先输入缓冲区,当缓冲区满的时再写入连接的输出流,可以调用flush()来清空缓冲区。
public class BufferStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("D:/a.txt");
try {
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
OutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file, true);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);//实例化需要通过OutputStream指定所连接的I/0流
byte[] b = {'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', ' ', 'I', '/', 'O', '!', '\n'};
bos.write(b);
bos.write(b);
bos.write(b);
bos.flush();//必须flush,write只是将数据写入缓存
InputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
int i = 0;
while ((i = bis.read()) != -1) System.out.print((char)i);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3、字节数据流:DataOutputStream和DataInputStream
数据输出流允许应用程序以适当方式将基本 Java 数据类型写入输出流中。然后,应用程序可以使用数据输入流将数据读入。需要注意的是输出流的写方法与输入流的读方法必须对应。
public class DateStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("/home/sunjf/a.txt");
try {
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
OutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(fos);
String str = "java流学习!";
//dos.writeUTF(str);//以与机器无关方式使用 UTF-8 修改版编码将一个字符串写入基础输出流
dos.writeLong(123l);//将一个 long 值以 8-byte 值形式写入基础输出流中,先写入高字节
dos.flush();
dos.close();
fos.close();
InputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(fis);
//System.out.println(dis.readUTF());
System.out.println(dis.readLong());//读取八个输入字节并返回一个 long 值
dis.close();
fis.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
4、字节对象流:ObjectOutputStream和ObjectInputStream
被读写的对象必须实现Serializable接口,及必须序列化。
public class ObjectStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("/home/sunjf/User.txt");
try {
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
OutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
User u = new User();
u.setUserName("java");
u.setAge(20);
oos.writeObject(u);
oos.close();
InputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
System.out.println(ois.readObject().toString());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class User implements Serializable {
private String userName;
private int age;
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return userName + " | " + age;
}
}
三、字符流:Writer和Reader
1、文件字符流:FileWriter和FileReader
使用字符流可以写入、读取汉字,如果用上面的字节流写入、读取得到的会是乱码。
public class WriterAndReaderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("/home/sunjf/a.txt");
try {
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
char[] c = {'你', '好', ',', '流', '!'};
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file);
//fw.write(c);//写入单个字符
//fw.write(c, 0, c.length);//将字符写入数组的某一部分
String str = "你好,流!";
fw.write(str, 0, str.length());//写入一部分字符串
fw.flush();//刷新该流的缓冲
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
int index = 0;
System.out.println("判断此流是否已经准备好用于读取 : " + fr.ready());
while ((index = fr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) index);//读取单个字符
//fr.skip('!');//跳过某些字符
}
fw.close();//关闭此流,但要先刷新它
fr.close();//关闭该流并释放与之关联的所有资源
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
2、缓存字符流:BufferWriter和BufferReader
除了多了缓存功能外,还可以按行读写数据。
public class BufferLineTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("D:/a.txt");
try {
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
Writer fw = new FileWriter(file, true);
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);//需要通过Writer指定连接的I/O流
String str = "你好,流!";
bw.write(str);
bw.newLine();//写入一个行分隔符
bw.write(str);
bw.newLine();
bw.write(str);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
Reader fr = new FileReader(file);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
String s = "";
while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) System.out.println(s);//读取一个文本行
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
四、总结
1、读取纯文本用Reader和Writer
2、按行读写用BufferWriter和BufferReader
3、数据流的读写方法必须对应
4、对象流的读写对象必须实现Serializable接口
5、处理流必须通过OutputStream和InputStream指定所链接的I/O流
最新文章
- Google Protocol Buffer开发环境搭建注意事项
- [转]快速构建App界面的框架(●'◡'●) -----SalutJs
- eclipse中新建javaweb项目,查看某些类的源码
- HTTP消息头
- 关于for,while与do while
- 2015-10-13 晴 tcp/ip卷1
- [Cocos2d-JS] 安卓机器的几个按钮
- AndroidApplication Fundamentals(Android应用基础)
- RequireJS学习笔记(转)
- ArcEngine 9.3 学习笔记(六):图层符号化(COlorRamp,MarkerSymbol,LineSymbol,FillSymbol,TextSymbol,3DChartSymbol,使用ServerStyle符号库,FeatureRender,RasterRender)
- JPA 系列教程4-单向一对多
- jmeter 前置处理器提取用户cookie信息 比如jsessionid
- nginx 实现所有的子域名301跳转到另外一个域名的对应子域名
- android adb 流程原理代码分析(一)
- .net WCF WF4.5 状态机、书签与持久化
- 使用共同函数,将PNotify弹出提示框公用
- asp.net cookie的操作
- tensorflow显存管理
- css3转盘
- jquery动态创建表格